Economy
Bidenomics
- 27 Oct 2023
- 7 min read
For Prelims: European Union (EU), Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Paris Agreement on Climate Change, Trade Deficit, Reaganomics, Trickle-Down Theory, Reserve Bank of India, Russia-Ukraine War
For Mains: Issues and concerns with respect to Bidenomics on India and the World regarding reviving GDP growth and employment.
Why in News?
The Year 2024 will be highly significant for the global economy due to elections in major influential economies: India, Russia, the UK, the EU, and the US; where in the US, the Bidenomics is supposedly going to be a major electoral plank.
What is Bidenomics?
- About:
- Bidenomics is a term that is used to refer to any and every policy choice made by the Biden administration in the US.
- According to the White House, Biden’s economic vision is centered around three key pillars:
- Making smart public investments in America
- Empowering and educating workers to grow the middle class
- Promoting competition to lower costs and help entrepreneurs and small businesses thrive
- Features:
- Bidenomics involves policies that improve USA's physical and digital infrastructure, reduce its trade dependence on rivals such as China,
- Raise the living standards and opportunities available for the middle 40% and the bottom 50% of the US population and, boost job creation within its borders.
- Implementation:
- Bidenomics aimed to raise revenue via more and higher taxation, while on the other, it decided to make massive spending towards investments in clean energy and in reducing healthcare costs.
What is the Rationale Behind Bidenomics?
- Reagan’s Top Down Model:
- With the failure of Reagan's Top-Down model and trickle down approach, it was envisaged that similar initiatives can not bring results on the ground and groundbreaking initiatives are required to mitigate covid crisis.
- Present Context:
- The US recognized that some of Post-Covid challenges were rooted in a failed trickle-down theory which led to the proposition of a new Economic Model called Bidenomics to alter the trickle-down theory based on Reaganomics.
Why Does Bidenomics Matter?
- Concerns Surrounding Bidenomics:
- Global Influence: Bidenomics is not only influential within the US but is also viewed as a model for change globally, with examples like the UK's Labour Party considering a more interventionist approach.
- Bidenomics: A Double-Edged Sword:
- Potential for a Global Subsidy Race: Critics worry that Bidenomics, with its focus on domestic producer subsidies, could trigger a global race of subsidies among countries, especially post covid crisis.
Did Bidenomics Work?
- Macro-Indicators:
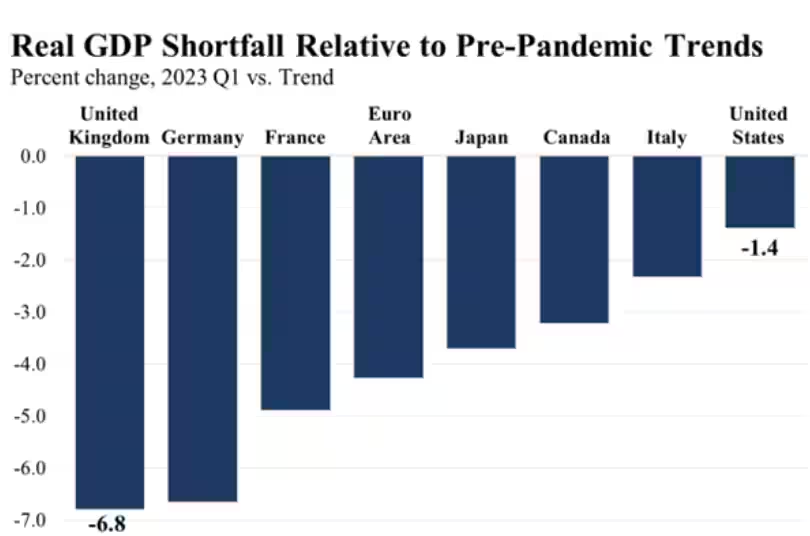
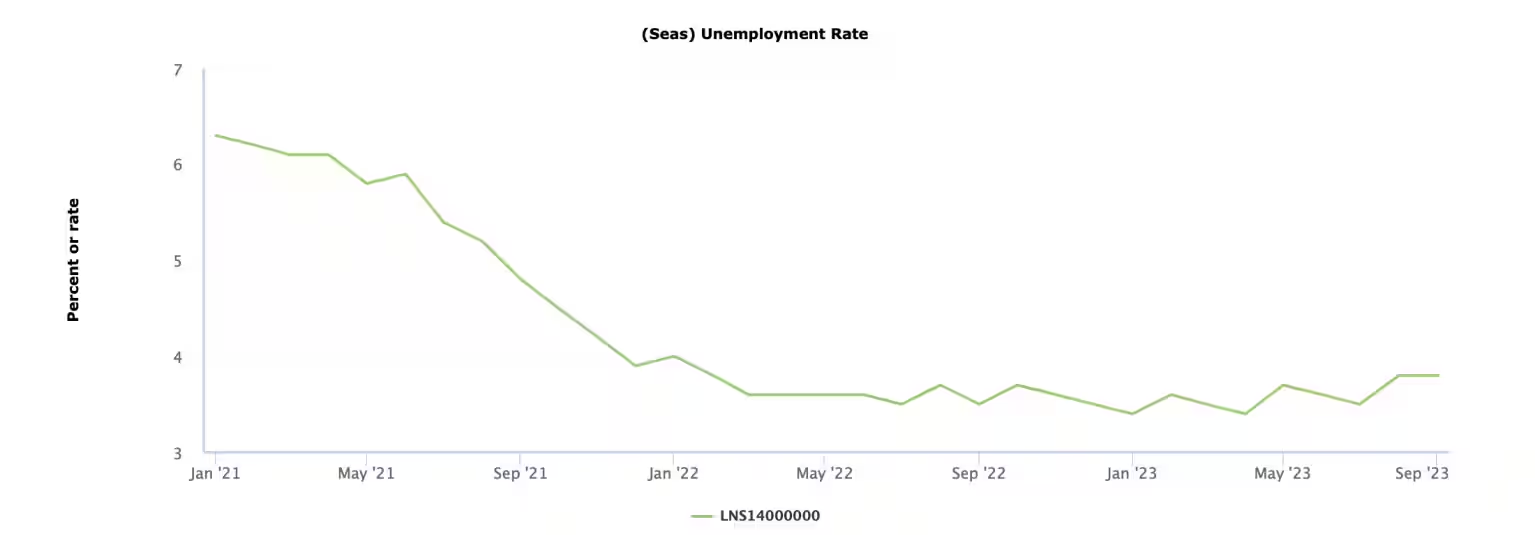
- As things stand, if one looks at the macro indicators — GDP, unemployment and inflation — the Biden administration seems to have done quite well.
- Economic Recovery:
- The US economy continues to create millions of jobs at such a fast pace that there are two vacancies for every unemployed person in the economy.
What are Other Similar Initiatives Adopted by Other Countries?
- Abenomics:
- Abenomics is an economic policy framework that was implemented in Japan by Prime Minister Shinzo Abe. The primary goal of Abenomics was to revitalize the Japanese economy, which had been facing deflation, slow growth, and economic stagnation for many years.
- Monetary Policy: The Bank of Japan, implemented a policy of "quantitative and qualitative monetary easing" (QQE) to combat deflation.
- Fiscal Policy: The second arrow emphasized expansionary fiscal policies, including increased government spending and public investments to stimulate demand and boost economic growth.
- Abenomics is an economic policy framework that was implemented in Japan by Prime Minister Shinzo Abe. The primary goal of Abenomics was to revitalize the Japanese economy, which had been facing deflation, slow growth, and economic stagnation for many years.
What are the Economic Revival Initiatives Undertaken by India?
- Faced with uncertainty in the last two years, the Government of India adopted strategies that combined a bouquet of safety-nets to cushion the impact of Covid Pandemic on vulnerable sections of society/business. Some of the initiatives are:
- New Economic Policy:
- India announced a new economic policy in 2020, in response to the Covid-19 pandemic and its impact on the economy.
- The policy consists of a stimulus package of Rs 20 lakh crore, equivalent to 10% of GDP, to support various sectors and segments of the economy.
- India announced a new economic policy in 2020, in response to the Covid-19 pandemic and its impact on the economy.
- Production-linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme:
- India launched a PLI scheme in 2020, to boost manufacturing and exports in key sectors, such as automobiles, electronics, pharmaceuticals, textiles, and renewable energy.
- The scheme offers financial incentives to eligible manufacturers based on their incremental sales and investment over a period of five years.
- Labour Codes:
- These are four codes that aim to consolidate and simplify central labor laws into four broad categories: wages, industrial relations, social security, and occupational safety and health.
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Mission:
- Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan (or Self-reliant India Mission)’ with an economic stimulus package — worth Rs 20 lakh crores aimed towards achieving the mission was announced.
- New Economic Policy:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which among the following steps is most likely to be taken at the time of an economic recession? (2021)
(a) Cut in tax rates accompanied by increase in interest rate.
(b) Increase in expenditure on public projects.
(c) Increase in tax rates accompanied by reduction of interest rate.
(d) Reduction of expenditure on public projects.
Ans: (b)
Q. With reference to Indian economy, demand-pull inflation can be caused/increased by which of the following? (2021)
- Expansionary policies
- Fiscal stimulus
- Inflation-indexing of wages
- Higher purchasing power
- Rising interest rates
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)