Important Facts For Prelims
BharatNet Project
- 22 Apr 2025
- 5 min read
Why in News?
The BharatNet project is making significant progress in connecting rural India with high-speed internet, fostering inclusive growth and bridging the urban-rural divide.
What is BharatNet?
- About: The National Optical Fibre Network (NOFN) was launched in 2011 and later renamed the BharatNet Project in 2015 under the Ministry of Communications.
- It aimed at providing high-speed broadband connectivity to every Gram Panchayat (GP) across the country.
- It is one of the largest rural telecom projects in the world, designed to offer affordable broadband access and enable the delivery of e-health, e-education, and e-governance services in rural India.
- The project initially aimed to connect approximately 2.5 lakh GPs across the country.
- Phases of Implementation:
- Phase I: Connected 1 lakh GPs using optical fiber (OF) cables and existing infrastructure, completed in 2017.
- Phase II (ongoing): Expands coverage to 1.5 lakh GPs using optical fiber, radio, and satellite technologies, with collaboration from state governments and private entities.
- Phase III (ongoing): Focuses on integrating 5G technologies, increasing bandwidth, and enhancing last-mile connectivity.
- The Amended BharatNet Program (ABP), approved in 2023, is part of this phase.
- Amended BharatNet Program: It aims to provide optical fiber connectivity to 2.64 lakh GPs in ring topology (a network design where connected devices form a circular data channel) and OF connectivity to non-GP villages on demand.
- It includes features such as an Internet Protocol Multi-Protocol Label Switching network (a method for efficiently routing data across networks) with routers at Blocks and GPs and Remote Fibre Monitoring System (a system for monitoring the status of OF connections remotely).
- Funding and Execution: BharatNet is primarily funded through the Digital Bharat Nidhi (DBN), a fund that replaced the Universal Service Obligation Fund.
- The project is executed by the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV), Bharat Broadband Network Limited (BBNL), incorporated under the Indian Companies Act 1956.
- Under the ABP, Bharat Sanchar Nigam Limited (BSNL) serves as the Project Management Agency for the operation and maintenance of the network.
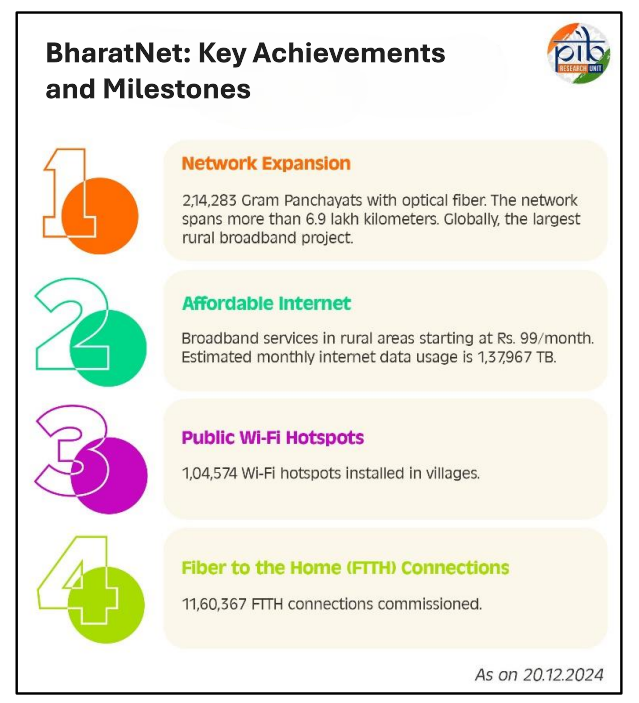
- Current Status: As of 2025, approximately 2.18 lakh GPs have been made service-ready under the BharatNet project.
- The total Optical Fiber Cable (OFC) length has surpassed 42 lakh route kilometers.
- Additionally, more than 12 lakh Fibre-To-The-Home (FTTH) connections have been commissioned, and over 1 lakh Wi-Fi hotspots have been installed.
- The total Optical Fiber Cable (OFC) length has surpassed 42 lakh route kilometers.
Other Initiatives Supporting Digital Empowerment in Rural India
- Pradhan Mantri Gramin Digital Saksharta Abhiyan (PMGDISHA): Aims to ensure digital literacy in rural households, trained over 6.39 crore individuals by March 2024.
- National Broadband Mission (NBM): Launched to accelerate digital infrastructure, it includes NBM 2.0 (launched in January 2025).
- Key initiatives under NBM include the Centralized Right of Way (RoW) Portal GatiShakti Sanchar.
- CSC e-Governance Services India Limited (CSC SPV): A SPV, set up by the Ministry of Electronics & IT under the Companies Act, 1956, provides a collaborative framework for service delivery through CSCs.
- As of September 2024, it has installed 1.04 lakh Wi-Fi access points and 11.42 lakh FTTH connections in GPs, and also piloted overhead optical fiber deployment under BharatNet.
- Mobile Connectivity: By December 2024, around 6.25 lakh villages were mobile-connected, with 6.18 lakh having 4G coverage. This complements BharatNet in bridging the digital divide.
- India has achieved the world’s fastest 5G rollout, with over 4 lakh 5G Base Transceiver Stations (BTSs) deployed across 779 districts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2022)
- Aarogya Setu
- CoWIN
- DigiLocker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)





-min.jpg)