Bangla for Classical Language, GangaSagar Mela for National Status | 20 Jan 2024
For Prelims: Classical language, Gangasagar Mela, Makar Sankrati, Kumbh Mela, Kapil Muni temple, Hemis Gompa Fair, University Grants Commission
For Mains: Benefits of Classical Language Status, Major Melas in India.
Why in News?
Recently, West Bengal’s Chief Minister made headlines with two distinct pursuits: advocating for classical language status for Bangla, which is the world's 7th most spoken language and seeking national fair status for the Gangasagar Mela.
What is Gangasagar Mela?
- About:
- Gangasagar Mela, which takes place during Makar Sankrati (mid-January), is said to be India's second largest pilgrimage gathering after the Kumbh Mela.
- This annual pilgrimage draws millions to Sagar Island at the confluence of the Ganges and Bay of Bengal and commemorates the legendary King Bhagirath's descent of the Ganges to Earth.
- Benefits of National Status:
- Elevating the Mela to national status would bring increased central funding and infrastructure development, potentially boosting tourism and economic activity in West Bengal.
- Other Major Melas in India:
- Kumbh Mela: It is celebrated four times every 12 years, the site of the observation rotating between four pilgrimages on the four sacred rivers at Allahabad, Haridwar, Ujjain and Nashik.
- Ardha (half) Kumbh Mela is held at only two places, Haridwar and Allahabad, every sixth year.
- And a Maha Kumbh is held after every 144 years.
- Pushkar Mela: Pushkar Mela is an annual five day camel and livestock fair held in the town of Pushkar, Rajasthan.
- It is one of the world's largest cattle fairs.
- Hemis Gompa Fair : In the northernmost corner of India, the chilly deserts of Ladakh celebrate a 300-year-old annual fair known as the Hemis Gompa Fair.
- The Hemis Monastery commemorates the fair on the birth anniversary of Guru Padmasambhava.
- Kumbh Mela: It is celebrated four times every 12 years, the site of the observation rotating between four pilgrimages on the four sacred rivers at Allahabad, Haridwar, Ujjain and Nashik.
Note
Ganga Sagar Mela has recently faced challenges due to rising sea levels and beach erosion near the Kapil Muni temple on Sagar Island. Despite dredging and tetrapods to counter erosion, the situation remains uncertain.
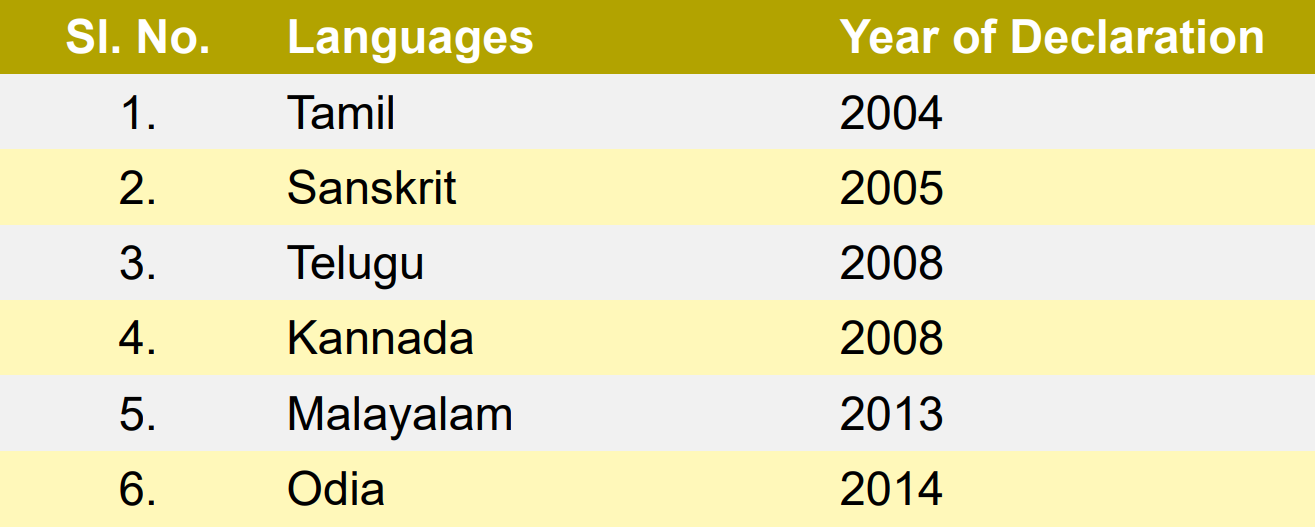
What are Classical Languages?
- About:
- In 2004, the Government of India decided to create a new category of languages called “classical languages”.
- In 2006, it laid down the criteria for conferring classical language status. So far, the 6 languages are granted classical language status.
- Criteria:
- High antiquity of early texts/recorded history spanning 1,500–2,000 years.
- Possession of a body of ancient literature/texts considered valuable heritage by generations.
- Presence of an original literary tradition not borrowed from another speech community.
- The classical language and literature being distinct from modern, there may also be a discontinuity between the classical language and its later forms or its offshoots.
- Benefits:
- Once a language is declared classical, it gets financial assistance for setting up a center of excellence for the study of that language and also opens up an avenue for two major awards for scholars of eminence.
- Besides, the University Grants Commission can be requested to create - to begin with at least in Central Universities, a certain number of professional chairs for classical languages for scholars of eminence in the language.
Note
8th Schedule of Indian Constitution lists the official languages of the Republic of India that currently includes 22 languages namely: Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi,Sanskrit, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Bodo, Santhali, Maithili and Dogri.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which one of the following was given classical language status recently? (2015)
(a) Odia
(b) Konkani
(c) Bhojpuri
(d) Assamese
Ans: (a)
Q. Under which one of the following Constitution Amendment Acts, four languages were added to the languages under the Eighth Schedule of the Constitution of India, thereby raising their number to 22? (2008)
(a) Constitution (Ninetieth Amendment) Act
(b) Constitution (Ninety-first Amendment) Act
(c) Constitution (Ninety-second Amendment) Act
(d) Constitution (Ninety-third Amendment) Act
Ans: (c)