Bamboo-Dwelling Bat | 20 Jun 2022
Why in News?
Recently, Scientists have discovered a new species of bamboo-dwelling bat near the Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary.
What do we Need to Know about Newly Discovered Species?
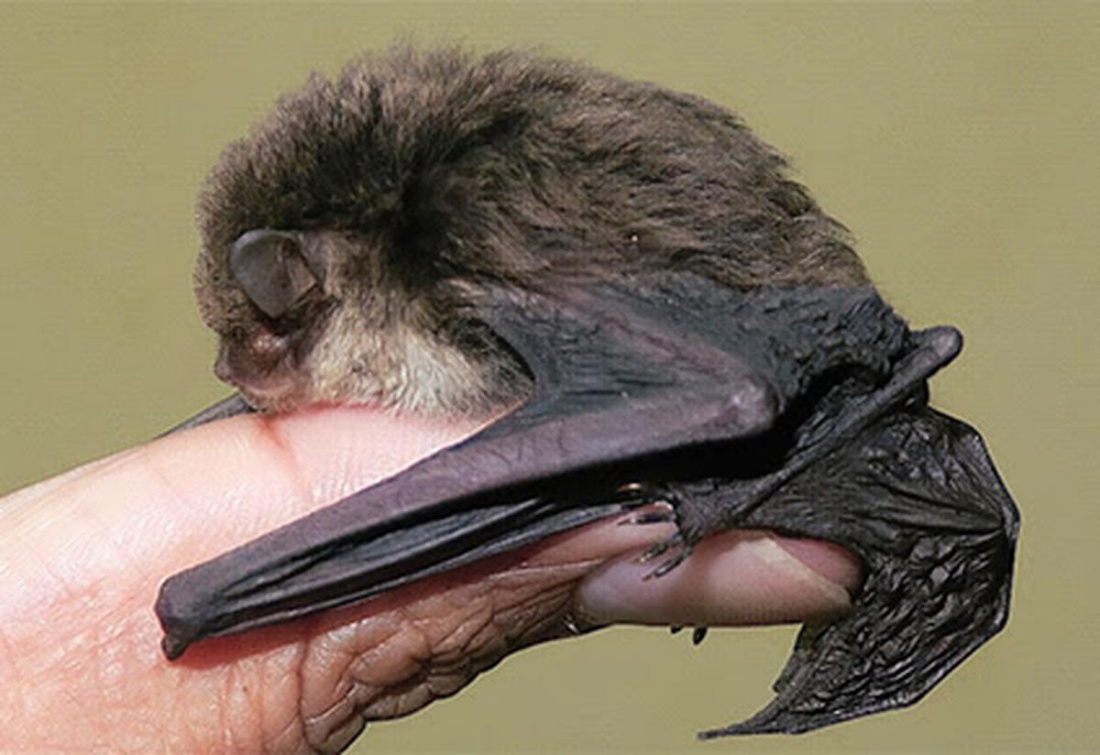
- The new species of bamboo-dwelling bat has been named Glischropus meghalayanus.
- Bamboo-dwelling bats are a particular kind of bat living in the internodes of bamboo with specialised morphological characters that help them to adapt to the life inside a bamboo plant.
- It is small in size and has a dark brown colour with sulphur yellow belly.
- The present discovery is the first report of a thick-thumbed bat not only from India but also from South Asia.
What are Thick-Thumbed Bats?
- This bat has typical fleshy pads on the thumb and soles of feet which aid them to crawl over smooth surfaces of bamboo internodes.
- Thick-thumbed bats of the genus Glischropus are currently composed of four recognized species from Southeast Asia.
- G. aquilus is endemic to Sumatra, G. javanus is restricted to western Java, whereas G. bucephalus is widely distributed north to the Isthmus of Kra and G. tylopus is widespread south to this zoogeographic boundary.
- Earlier, a new species of thick-thumbed bat (Chiroptera: Vespertilionidae: Glischropus) from Meghalaya, north-eastern India was discovered.
What are the Recent Discoveries of Bats from Meghalaya?
- From the same forested patches outside Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary, another species of disk-footed bat Eudiscopus denticulus was found which was a new record in India.
- In the past few years, three bamboo-dwelling bats have been reported from the area which highlights the ecological significance of the region.
- Since the bamboo forest around the wildlife sanctuary has a rich bio-diversity there should be attempts to conserve it.
What is the Number of Bat Species in India?
- Total Number:
- With this new discovery, the total number of bat species known from India stands at 131.
- Highest Bat Diversity:
- Meghalaya harbors the highest bat diversity in the country with 67 species, which is about 51% of total bat species in the country.
- Meghalaya, because of its unique terrain, vegetation and climate condition, was a haven for both flora and fauna.
- The unique caves in the northeastern State provided roosting opportunities for a large number of bats.
- There were a number of cave-dwelling bats species from Meghalaya, the most common being Horseshoe bat and Leaf-nosed bats.
Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary
- Situated in the Ri-Bhoi district near Lailad village and spread over an area of 29 sq. kms, Nongkhyllem Wildlife Sanctuary is one of the famous attractions of Meghalaya.
- The Sanctuary falls in the Eastern Himalayan Global biodiversity hotspot.
- The sanctuary supports different species of fauna such as Royal Bengal Tiger, Clouded Leopard, Indian Bison, and Himalayan Black Bear etc.
- Among the birds, the rare species which can be spotted here are Manipur Bush Quail, Rufous Necked Hornbill and Brown Hornbill.
- Other Wildlife Sanctuary in Meghalaya:
- Siju Wildlife Sanctuary
- Narpuh Wildlife Sanctuary
- Baghmara Pitcher Plant Sanctuary
- Nokrek National Park
UPSC Civil Services,Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. Recently, our scientists have discovered a new and distinct species of banana plant which attains a height of about 11 meters and has orange coloured fruit pulp. In which part of India has it been discovered? (2016)
(a) Andaman Islands
(b) Anaimalai Forests
(c) Maikala Hills
(d) Tropical rain forests of northeast
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- A new species of banana, Musa idandamanensis was discovered by a team of scientists from the Botanical Survey of India (BSI) from a remote Krishna Nalah tropical rain forest on the Little Andaman Islands.
- Its flowers are cylindrical in shape compared to the conical shape of regular banana species.
- It is about 11 metres high, whereas the usual banana species is about three to four metres high.
- The species is edible and very sweet. The fruit pulp is orange in colour, distinctive from the white and yellow colour of regular bananas.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.