Aurorae in Ladakh | 18 Oct 2024
Why in News?
Recently, auroras were sighted in lower-latitude regions (below 66.5 degrees north and south latitudes) like India (Hanle and Merak in Ladakh), Mexico and Germany.
- Their occurrence in lower-latitude regions is an indication of heightened solar activity.
What are the Key Highlights About Aurora Sightings?
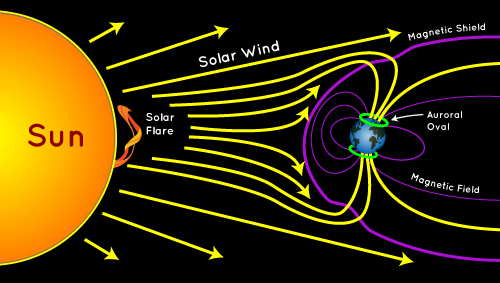
- Aurora and Peak Solar Cycle: Auroras occur when coronal mass ejections (CMEs) interact with Earth’s Magnetosphere.
- Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are part of the solar activity cycle, which lasts around 11 years.
- The current solar cycle called Solar Cycle 25 is at its peak in 2024.
- Lower Latitude Aurora: A severe solar storm, initially classified as a level 4 on a scale from 1 to 5, is the reason for aurora sightings in lower-latitude regions.
- It typically appears in northern regions like Canada, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Alaska, Russia, Iceland, and Greenland.
- Severe solar storms can trigger auroras and accelerate satellite decay, while extreme storms may destroy satellites, disrupt power grids, and cause widespread communication blackouts.
- It typically appears in northern regions like Canada, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Alaska, Russia, Iceland, and Greenland.
What are Key Facts About Auroras?
- About Aurora: An aurora is a mesmerising natural light display visible in the night sky, often characterised by shifting colours such as blue, red, yellow, green, and orange.
- The more common green-yellow auroras result from ions striking oxygen atoms at lower altitudes.
- Reddish and bluish lights, seen in the lower edges of auroras, are caused by ions interacting with nitrogen atoms.
- Collisions with hydrogen and helium atoms can produce blue and purple auroras, but these colours are rarely visible to the naked eye.
- Geographical Occurrence: Auroras are most commonly seen near the Arctic and Antarctic Circles, approximately 66.5 degrees north and south of the Equator.
- The northern aurora is called the aurora borealis (northern lights), while the southern counterpart is known as aurora australis (southern lights).
- Cause of Auroras: Auroras are caused when charged particles from solar storms interact with the Earth’s magnetosphere, which acts as a shield against harmful solar and cosmic rays.
- Solar storms occur when the Sun's magnetic field intensifies and weakens, allowing charged particles to penetrate the Earth's magnetic field.
- Role of Solar Wind and Earth's Magnetosphere: Auroras form when charged ions from the solar wind collide with oxygen and nitrogen atoms in the Earth's ionosphere, usually at altitudes between 97 and 1,000 kilometers.
- The Earth's magnetosphere deflects most of the solar wind, but some ions get trapped near the geomagnetic poles, creating these stunning light displays.
- Scientific Study of Auroras: NASA’s IMAGE satellite, which operated until 2005, was designed specifically to study auroras.
- Using ultraviolet and radio waves, IMAGE gathered important data on how auroras form and behave.
- Aurora on Other Planets: Planets with an atmosphere and magnetic field likely experience auroras.
- E.g., Stunning auroras have been observed on Jupiter and Saturn.
What are Key Facts About Hanle Observatory?
- Location: It is located on Mt. Saraswati in the Nilamkhul Plain, Hanle Valley, Ladakh. at a height of approximately 4,500 metres above sea level.
- It is also known as the Indian Astronomical Observatory managed by Indian Institute of Astrophysics.
- Recognition: It is recognised for its exceptionally dark and cloudless skies ideal for stargazing and astronomical observations.
- Observational Capabilities: It is home to a 2-metre optical infrared telescope for space observation.
- Dark Sky Reserve: Hanle is designated as a Dark Sky Reserve by the International Dark-Sky Association (IDA) to protect the quality of night skies by minimising light pollution.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth? (2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
(b) 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
(c) 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Ans: (c)