ASI Discovers 1,300-yr-old Buddhist Stupa | 28 Feb 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) discovered a 1,300-year-old stupa right in the middle of a mining site in Odisha’s Jajpur district at a Khondalite mining site.
- It is the place from where Khondalite stones were supplied for the beautification project around the 12th Century Shree Jagannath Temple in Puri.
What are the Findings of the ASI?
- The stupa could be 4.5-metre tall and initial assessment showed it may belong to the 7th or 8th century.
- It was found at Parabhadi which is situated near Lalitagiri, a major Buddhist complex, having a large number of stupas and monasteries.
- Lalitgiri Buddhist site is believed to be the most sacred among the three sites (Lalitagiri, Ratnagiri and Udayagiri) as it unearthed a massive stupa where a relic of Buddha was discovered inside a stone casket.
What are the Khondalite Stones?
- Khondalite is a type of metamorphic rock that is found in the Eastern Ghats region of India, particularly in the state of Odisha. It is named after the Khondalite Group of rocks, which is believed to have formed around 1.6 billion years ago during the Proterozoic era.
- Khondalite is primarily composed of feldspar, quartz, and mica, and has a distinct pinkish-grey coloration. It is commonly used as a decorative stone in construction and is particularly prized for its durability and resistance to weathering.
- Khondalite stones were widely used in ancient temple complexes. They are proposed to be used widely to maintain aesthetic value of some projects such as heritage security zone, Jagannath Ballav pilgrim centre, etc.
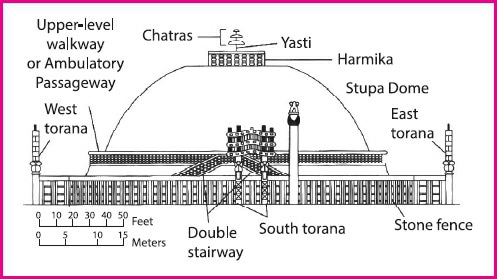
What is Stupa?
- About: Stupas were burial mounds prevalent in India from the vedic period.
- Architecture: Stupas consist of a cylindrical drum with a circular anda and a harmika and a chhatra on the top.
- Anda: Hemispherical mound symbolic of the mound of dirt used to cover Buddha’s remains (in many stupas actual relics were used).
- Harmika: Square railing on top of the mound.
- Chhatra: Central pillar supporting a triple umbrella form.
- Material Used: The core of the stupa was made of unburnt brick while the outer surface was made by using burnt bricks, which were then covered with a thick layer of plaster and medhi and the toran were decorated with wooden sculptures.
- Examples:
- Sanchi Stupa in Madhya Pradesh is the most famous of the Ashokan stupas.
- Piprahwa Stupa in Uttar Pradesh is the oldest one.
- Stupas built after the death of Buddha: Rajagriha, Vaishali, Kapilavastu, Allakappa, Ramagrama, Vethapida, Pava, Kushinagar and Pippalivana.
- Stupa at Bairat, Rajasthan: Grand stupa with a circular mound and a circumambulatory path.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
(a) Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of Waghora river.
(b) Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of Chambal river.
(c) Pandu-lena Cave Shrines lie in the gorge of Narmada river.
(d) Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of Godavari river.
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Ajanta is a series of rock-cut caves in the Sahyadri ranges (Western Ghats) on Waghora river near Aurangabad in Maharashtra. There are a total of 29 caves (all Buddhist) of which 25 were used as Viharas or residential caves while 4 were used as Chaitya or prayer halls. This UNESCO World Heritage Site is a collection of paintings, sculptures and temples of Buddhist art, constructed from 200 BC to 500 AD.
- Sanchi Stupa is located in west-central Madhya Pradesh. It lies in an upland plateau region, just west of the Betwa River and about 5 miles (8 km) southwest of Vidisha. It was designated a UNESCO World Heritage site in 1989.
- The Buddhist monument Pandavleni Caves, also known by the name Pandu Lena caves and Trirashmi caves are a group of 24 rock-cut caves. They are located on the north face of Trivashmi hill of Nasik city. Nasik city is situated on the banks of river Godavari.
- Amravati Stupa illustrates Lord Buddha in a human form, subduing an elephant. The stupa is taller than the Sanchi stupa and has high platforms, extending in the four cardinal directions, along with a huge circular dome. Amravati Stupa is situated near river Krishna.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Early Buddhist Stupa-art, while depicting folk motifs and narratives successfully expounds Buddhist ideals. Elucidate. (2016)