Aravali Green Wall Project | 28 Mar 2023
For Prelims: International Day of Forests, Aravalli Green Wall Project, Africa’s Great Green Wall, Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas.
For Mains: Causes of Land Degradation and initiatives to curb it.
Why in News?
Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change inaugurated the Aravali Green Wall Project on the occasion of International day of Forests and unveiled the National Action Plan to Combat Desertification and Land Degradation Through Forestry Interventions.
What is Aravali Green Wall Project?
- About:
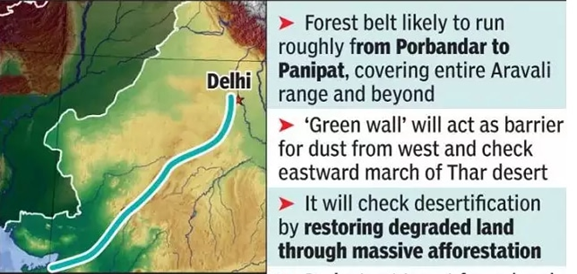
- It is an ambitious plan to create a 1,400km long and 5km wide green belt buffer around the Aravali Mountain range covering states of Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat and Delhi.
- In the initial phase, 75 water bodies will be rejuvenated, starting with five waterbodies each in every district of Aravalli landscape.
- It will cover degraded land in Gurgaon, Faridabad, Bhiwani, Mahendergarh and in Rewari districts of Haryana.
- The plan is inspired by Africa’s ‘Great Green Wall’ project, running from Senegal (West) to Djibouti (East), which came into effect in 2007.
- Objectives:
- The overarching objective of India’s Green Wall will be to address the rising rates of land degradation and the eastward expansion of the Thar desert.
- The green belt being planned from Porbandar to Panipat will help in restoring degraded land through afforestation along the Aravali hill range. It will also act as a barrier for dust coming from the deserts in western India and Pakistan.
- It aims to enhance the biodiversity and ecosystem services of the Aravalli range by planting native trees, which will help in carbon sequestration, provide habitat for wildlife, and improve water quality and quantity.
- The involvement of local communities in afforestation, agro-forestry, and water conservation activities can promote sustainable development.
- Further, it will help generate income and employment opportunities, improve food security, and provide social benefits.
- Background:
- According to Desertification and Land Degradation Atlas by Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), some 97.85 million hectares (29.7%) of India’s total geographical area (TGA) of 328.72 mha underwent land degradation during 2018-19.
- The Aravali has been identified as one of the key degraded zones to be taken up for greening under India’s target to restore 26 million hectares (mha) of its land.
- A 2016 report from the ISRO had also indicated that Delhi, Gujarat and Rajasthan had already degraded over 50% of their land.
What is Aravali Mountain Range?
- About:
- The Aravallis, is the oldest fold mountains on Earth.
- It spans over 800km from Gujarat to Delhi (through Rajasthan and Haryana).
- The highest peak in the Aravalli Range is Guru Peak on Mount Abu.
- Impact on Climate:
- The Aravallis have an impact upon the climate of northwest India and beyond.
- During monsoons, the mountain range gently guides the monsoon clouds eastwards towards Shimla and Nainital, thus helping nurture the sub-Himalayan rivers and feeding the north Indian plains.
- In the winter months, it protects the fertile alluvial river valleys (the para-Indus and Gangetic) from the assault of cold westerly winds from Central Asia.
What is Great Green Wall of Africa (GGW)?
- About:
- GGW is a project launched by African union to restore the continent’s degraded landscapes and transform millions of lives in the Sahel.
- The project plans 8km wide band of trees stretching 8,000km across Africa.
- Objectives:
- It aims to restore 100 million hectares of currently degraded land.
- Also, the project envisages to sequester 250 million tons of carbon and create 10 million green jobs by 2030.
- Participating countries:
- Eleven countries in the Sahel-Sahara region—Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Sudan, Chad, Niger, Nigeria, Mali, Burkina Faso, Mauritania, and Senegal have joined to combat land degradation and restore native plant life to the landscape.