Appointment of Governor | 01 Aug 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the President has appointed six new Governors and reshuffled three others.
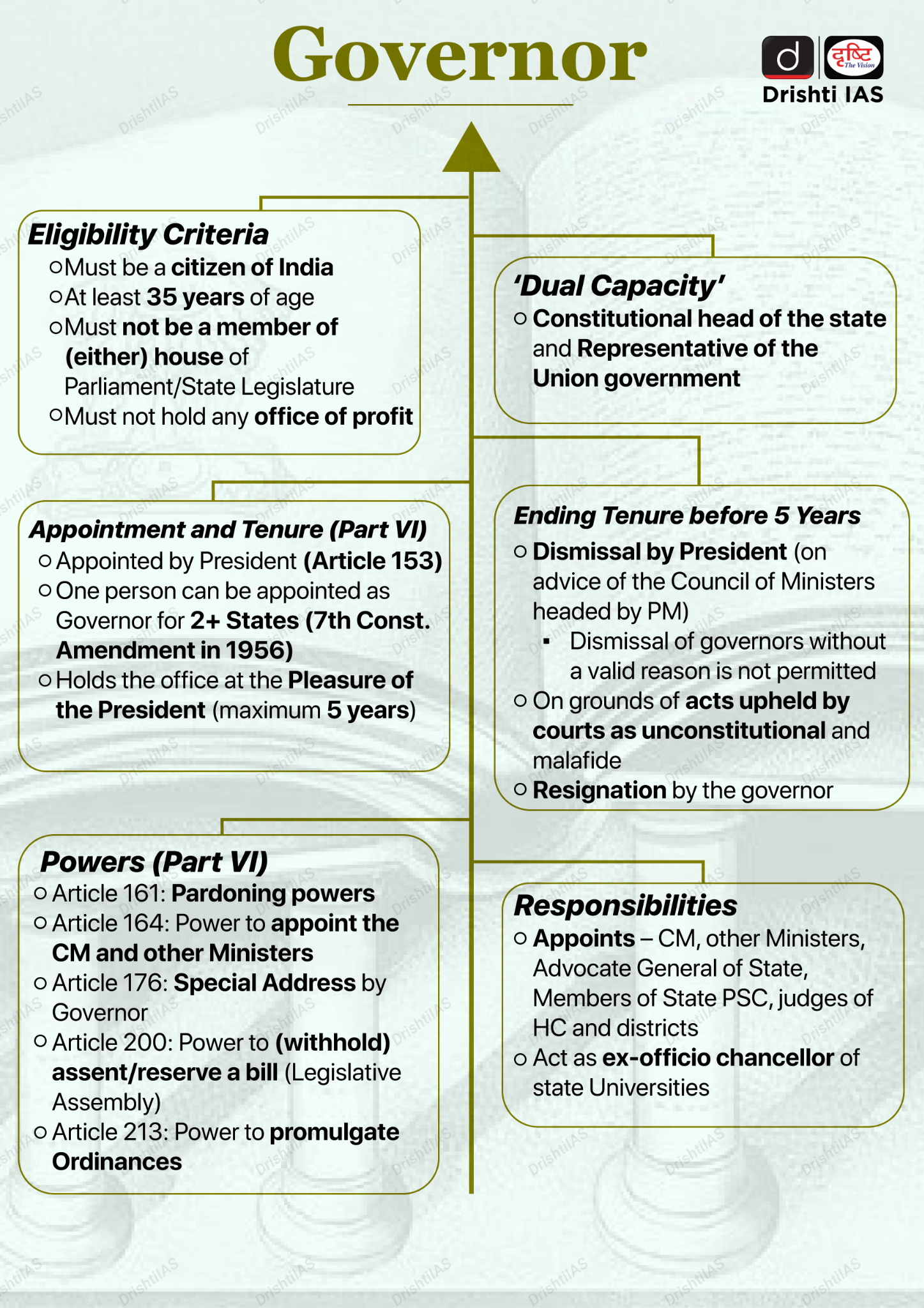
What is the Appointment Process for the Governor?
- About:
- The governor is the chief executive head of the state.
- The office of the Governor is adapted from the Canadian model.
- As per Convention, he should not belong to the state where he is appointed so that he is free from local politics.
- Also, the president is required to consult the chief minister of the state concerned to ensure the smooth functioning of the constitutional machinery of the state.
- The governor is neither directly elected by the people nor indirectly elected by a specially constituted electoral college as is the case with the president.
- He is appointed by the president by warrant under his hand and seal.
- He holds office at the pleasure of the President and may be removed by the President at any time.
- In Surya Narain v Union of India Case, 1982, the Supreme Court held that the pleasure of the President is not justifiable.
- He is a nominee of the Central government.
- However, the Supreme Court in Hargovind Pant Vs. Raghukul Tilak Case held that the office of governor of a state is not an employment under the Central government.
- It is an independent constitutional office.
- Conditions of the Governor’s Office:
- He is entitled without payment of rent to the use of his official residence (the Raj Bhavan).
- He is entitled to such emoluments, allowances, and privileges as may be determined by Parliament.
- When the same person is appointed as the governor of two or more states, the emoluments and allowances payable to him are shared by the states in such proportion as determined by the president.
- His emoluments and allowances cannot be diminished during his term of office.
- Privileges:
- Under Article 361, he enjoys personal immunity from legal liability for his official acts.
- During his term of office, he is immune from any criminal proceedings, even in respect of his personal acts.
- He cannot be arrested or imprisoned.
- However, after giving two months’ notice, civil proceedings can be instituted against him during his term of office in respect of his personal acts.
- Oath:
- Before entering his office, the governor has to make and subscribe to an oath or affirmation.
- In his oath, the governor swears
- to faithfully execute the office
- to preserve, protect, and defend the Constitution and the law
- to devote himself to the service and well-being of the people of the state.
- The oath of office to the governor is administered by the chief justice of the concerned state high court and in his absence, the senior-most judge of that court available.
Constitutional Provisions Related to the Governor
- Article 153: There shall be a Governor for each state.
- A single person can be appointed as the Governor for two or more states (recommended by the Sarkaria Commission).
- The Governor is appointed by the President and is a nominee of the Central Government.
- Articles 157 and 158: Specify the eligibility requirements for the post of Governor.
- Article 163: There is a Council of Ministers with the Chief Minister at the head to aid and advise the Governor in the exercise of his functions, except in some conditions where discretion is allowed.
Read more: Governor, The Governor's Role: Challenges and Reform Proposals, Governors in the Limelight: Calls for Reform in India, Governor’s Role in State Legislature
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- No criminal proceedings shall be instituted against the Governor of a State in any court during his term of office.
- The emoluments and allowances of the Governor of a State shall not be diminished during his term of office.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Q. Which of the following are the discretionary powers given to the Governor of a State? (2014)
- Sending a report to the President of India for imposing the President’s rule
- Appointing the Ministers
- Reserving certain bills passed by the State Legislature for consideration of the President of India
- Making the rules to conduct the business of the State Government
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. Which one of the following statements is correct? (2013)
(a) In India, the same person cannot be appointed as Governor for two or more States at the same time
(b) The Judges of the High Court of the States in India are appointed by the Governor of the State just as the Judges of the Supreme Court are appointed by the President
(c) No procedure has been laid down in the Constitution of India for the removal of a Governor from his/her post
(d) In the case of a Union Territory having a legislative setup, the Chief Minister is appointed by the Lt. Governor on the basis of majority support
Ans: (c)