Amazon Forest Fire | 01 Jun 2024
For Prelims: Forest fires, El Nino climate, Amazon rainforest , droughts, Climate change
For Mains: Status of the Amazon Forest Fires, Causes of the Amazon Forest Fires
Why in News?
Recently, Brazil's Amazon rainforest has experienced its largest forest fires on record in the first four months of 2024.
- A record drought in the Amazon region, driven by the El Nino climate phenomenon and global warming, has contributed to dry conditions fueling the fires.
What are Key Facts About the Amazon Rainforests?
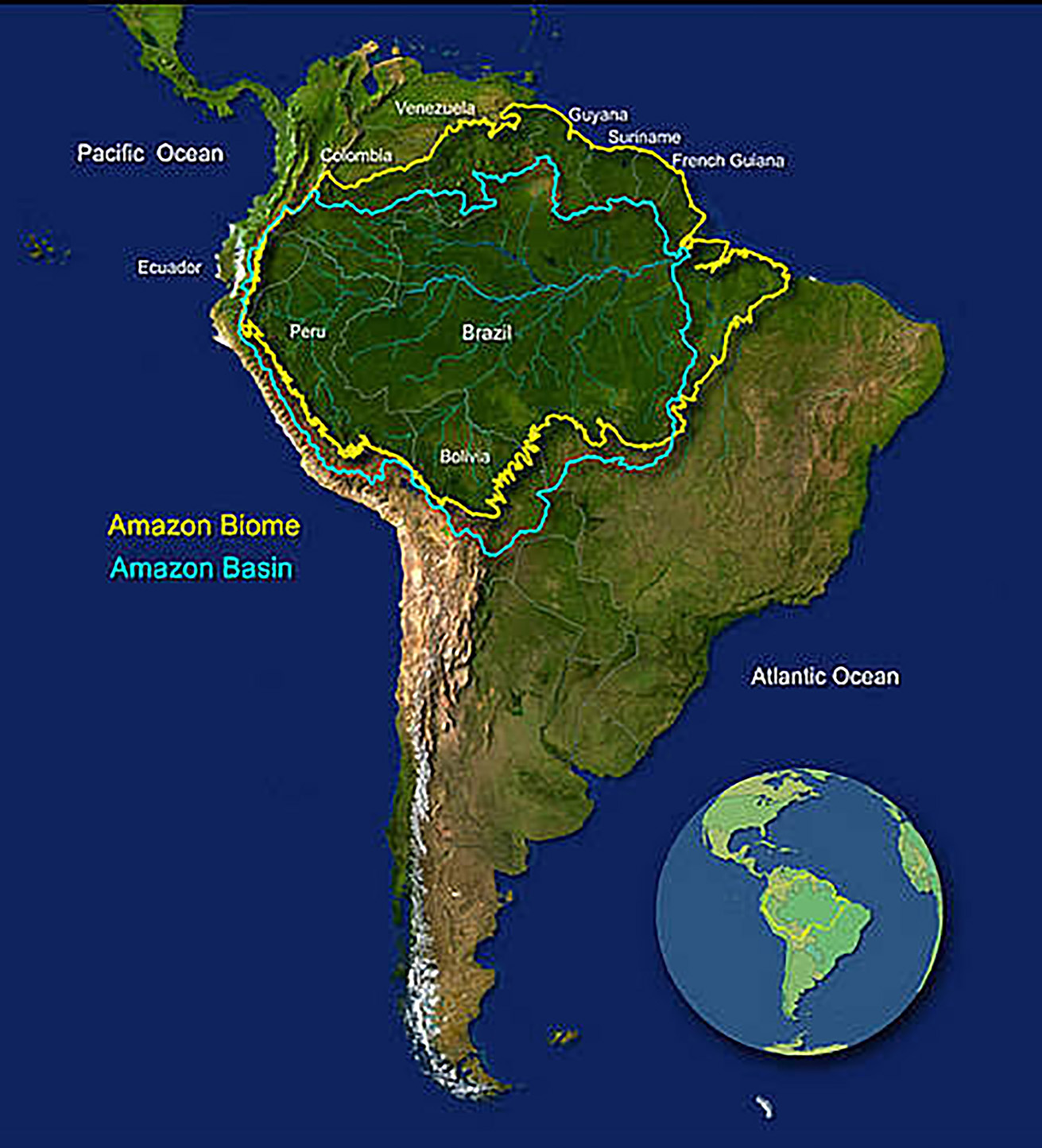
- About:
- These rainforests spans around 8 countries, representing an area twice the size of India.
- Comprising about 40% of Brazil’s total area, the Guiana Highlands bounds it to the north, the Andes Mountains to the west, the Brazilian central plateau to the south, and the Atlantic Ocean to the east.
- Characteristics:
- These are large tropical rainforests occupying the drainage basin of the Amazon River and its tributaries in northern South America and covering an area of 6,000,000 square km.
- They are very wet places, receiving more than 200 cm of rainfall per year, either seasonally or throughout the year.
- The temperatures are uniformly high, ranging between 20°C and 35°C.
- Such forests are found in Asia, Australia, Africa, South America, Central America, Mexico and on many of the Pacific Islands.
- These are large tropical rainforests occupying the drainage basin of the Amazon River and its tributaries in northern South America and covering an area of 6,000,000 square km.
- Significance:
- These rainforests host more than 400 different indigenous groups and around 300 indigenous languages are spoken signifying its cultural and linguistic diversity.
- Despite covering only around 1% of the Earth’s surface, the Amazon rainforest is home to 10% of all the wildlife species found on the Earth.
- The Amazon rainforest is crucial in curbing global warming due to the vast amount of greenhouse gas it absorbs.
What are the Causes of the Amazon Forest Fires?
- Deforestation and Slash-and-Burn Practices:
- Ranchers and farmers often use slash-and-burn techniques to clear land for cattle grazing or agriculture.
- After cutting trees, they intentionally set fires to clear the remaining vegetation and prepare the land. These fires can often spread uncontrollably during dry seasons.
- El Nino and Droughts:
- Research suggests a link between El Nino events (periods of warmer Pacific Ocean temperatures) and increased fire activity in the Amazon.
- The peak fire season in the Amazon often coincides with El Nino events. For instance, the severe fires in 2019 and 2023 coincided with El Nino-related droughts.
- Climate Change and Accidental Ignitions:
- Climate change is causing a rise in global temperatures and altering weather patterns. Studies suggest that climate change can lead to drier conditions in the Amazon, increasing the risk of fires.
- Accidental ignitions from discarded cigarettes sparks from machinery, or lightning strikes can also contribute to fires.
- Industrial Farming:
- Rising global demand for food, especially meat, has led to Brazil becoming the world's biggest beef exporter, and the second-biggest exporter of soya beans, mainly used for livestock feed.This results in further deforestation required to meet the exports needs.
Forest Fire in India
- Recent Status:
- In 2024, according to the Forest Survey of India data, the highest number of forest fires have been reported from Mizoram (3,738), Manipur (1,702), Assam (1,652), Meghalaya (1,252), and Maharashtra (1,215).
- Since early March 2024, satellite data shows numerous fire incidents along the Konkan belt in Maharashtra, south coastal Gujarat, southern Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Jharkhand, and parts of South India.
- Also, in May 2024, a forest fire broke out in the Tuti Kandi area of Shimla (Himachal pradesh), as well as Uttarakhand, threatening the ecologically sensitive Himalayan fauna.
- Causes:
- A majority of forest fires are caused by human activities such as discarded cigarettes, campfires, burning of debris, and other similar processes.
- The exceptionally hot and dry weather conditions experienced in southern India, particularly during the early phase of the summer season, have created a conducive environment for the spread of forest fires.
- The dry vegetation of forests, including the leaves of chir forests, is particularly prone to igniting and spreading fires.
Way Forward
- Enforcing laws and regulations related to forest fire prevention, such as restrictions on burning debris and campfire bans during dry periods, can help reduce the risk of accidental fires.
- Penalties for violating fire safety regulations should be strictly enforced to deter irresponsible behaviour..
- Implementing early detection systems, such as surveillance cameras, satellite monitoring, and lookout towers, can help detect fires in their early stages when they are easier to contain.
- Rapid detection allows for a quicker response, minimizing the size and impact of fires.
- Indigenous communities having a long history of sustainable forest management should be incorporated to play a key role in fire prevention.
- For Example: The Joint Forest Management (JFM) program involves local communities in sustainable forest management practices, including controlled burns and fire line creation.
- Global efforts should be undertaken to reduce greenhouse gas emissions to lessen drought risk in the Amazon.
- For Example: The Amazon Fund uses donations from developed countries to support conservation and sustainable development projects in the Amazon.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Mentioning the status of the Amazon forest fires, discuss the various causes associated with the Amazon Forest Fires. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014)