Abortion | 14 Mar 2024
For Prelims: Abortion, Article 34 of the French Constitution, Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971, Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
For Mains: Abortion Law in India, Legal Provisions Related to Abortion in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the French lawmakers have overwhelmingly approved a bill to enshrine abortion rights in France's constitution, making it the only country to explicitly guarantee a woman’s right to voluntarily terminate a pregnancy.
- The approved bill amends Article 34 of the French Constitution, explicitly stating that “the law determines the conditions by which the freedom of women to have recourse to an abortion, which is guaranteed.”
Note
The bill was brought forth in response to concerns about the erosion of abortion rights globally, particularly highlighted by the US Supreme Court's decision in Roe v Wade case to overturn long standing abortion rights in 2022.
What is Abortion?
- About:
- Abortion is the deliberate termination of a pregnancy, typically performed during the first 28 weeks of gestation. It can be achieved through various medical procedures or medications, depending on the stage of pregnancy and the preferences of the individual seeking abortion.
- Abortion can be a highly contentious and debated topic, often involving ethical, moral, religious, and legal considerations.
- Proponents:
- Proponents of abortion rights argue that it is a fundamental reproductive right that allows individuals to make choices about their own bodies, health, and future.
- They emphasise the importance of access to safe and legal abortion services in preventing unwanted pregnancies, protecting women's health, and supporting reproductive autonomy.
- Opponents:
- Opponents of abortion, often referred to as "pro-life," believe that abortion is morally wrong and should be restricted or prohibited entirely.
- They typically argue that life begins at conception and that terminating a pregnancy is equivalent to taking a human life, thus violating the rights of the unborn foetus.
- Legal Provisions Related to Abortion in India:
- Until the 1960s, abortion was prohibited in India, and violating this led to imprisonment or fines under Section 312 of the Indian Penal Code.
- The Shantilal Shah Committee was set up in the mid-1960s to investigate the need for abortion regulations.
- Based on its findings, the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971 was enacted, allowing safe and legal abortions, safeguarding women's health, and reducing maternal mortality.
- The Supreme Court recognized martial rape as a ground for abortion, even though marital rape itself is not recognized, in a progressive move for women's reproductive rights.
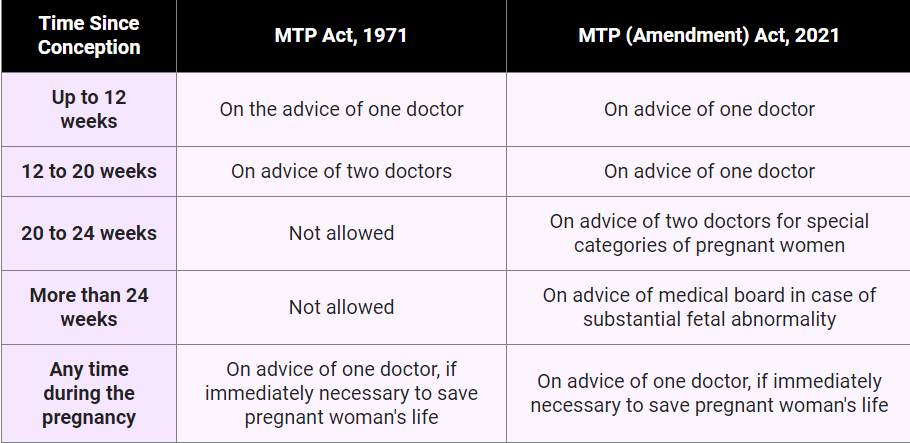
- The MTP Act, 1971, allows abortion up to 20 weeks of gestation, with the consent of the woman and on the advice of one registered medical practitioner (RMP). However, the law was updated in 2002 and 2021.
- The MTP Amendment Act, 2021 permits abortion from 20 to 24 weeks of gestation for specific cases like rape survivors, with approval from two doctors.
- It sets up state level Medical Boards to decide if a pregnancy may be terminated after 24 weeks in cases of substantial fetal abnormalities.
- It extends the failure of contraceptive clauses to unmarried women (initially only married women), allowing them to seek abortion services on grounds of their choice, irrespective of their marital status.
- Consent requirements vary based on age and mental state, ensuring medical practitioner oversight.
- Until the 1960s, abortion was prohibited in India, and violating this led to imprisonment or fines under Section 312 of the Indian Penal Code.
- The Constitution of India, which guarantees the right to life and personal liberty to all citizens under Article 21. This right has been interpreted by the Supreme Court of India to include the right to reproductive choice and autonomy for women.
Note
- In Justice K.S. Puttaswamy (Retd.) vs. the Union Of India Case, 2017, the Supreme court recognized the constitutional right of women to make reproductive choices, as a part of personal liberty under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution.
What are the Concerns Related to Abortion?
- Cases of Unsafe Abortions:
- Unsafe abortions are the third leading cause of maternal mortality in India, and close to 8 women die from causes related to unsafe abortions each day, according to the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA)'s State of the World Population Report 2022.
- The women outside marriages and in poor families are left with no choice but to use unsafe or illegal ways to abort unwanted pregnancies.
- Preference for a Male Child:
- The selective abortion of female foetuses is most common where male children are valued over female children, especially in parts of East Asia and South Asia (particularly in countries such as China, India and Pakistan).
- Shortage of Medical Expert in Rural India:
- According to a 2018 study in the Lancet, 15.6 million abortions were accessed every year in India as of 2015.
- The MTP Act requires abortion to be performed only by doctors with specialisation in gynaecology or obstetrics.
- However, the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare’s 2019-20 report on Rural Health Statistics indicates that there is a 70% shortage of obstetrician-gynaecologists in rural India.
Way Forward
- Efforts should be made to ensure that women have access to safe and legal abortion services without facing unnecessary barriers or stigma.
- This may involve expanding the availability of abortion services in both urban and rural areas, training healthcare providers to offer comprehensive reproductive health services, and raising awareness about women's rights under the MTP Act.
- Medical practitioners play a vital role in ensuring women's access to safe abortion services.
- Policies should be designed to support healthcare providers in delivering high-quality, non-judgmental care to women seeking abortion services, while also addressing any ethical or legal concerns they may have.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Mains
Q. What are the continued challenges for Women in India against time and space? (2019)