Important Facts For Prelims
900-Year-Old Chalukyan Inscription
- 01 Apr 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Recently, A 900-year-old Kannada inscription belonging to the Kalyani Chalukya dynasty was discovered in a neglected state in Gangapuram, in Telangana.
- It was issued by Customs Officers under Tailapa-III, son of Emperor 'Bhulokamalla' Someswara-III of the Kalyani Chalukya dynasty.
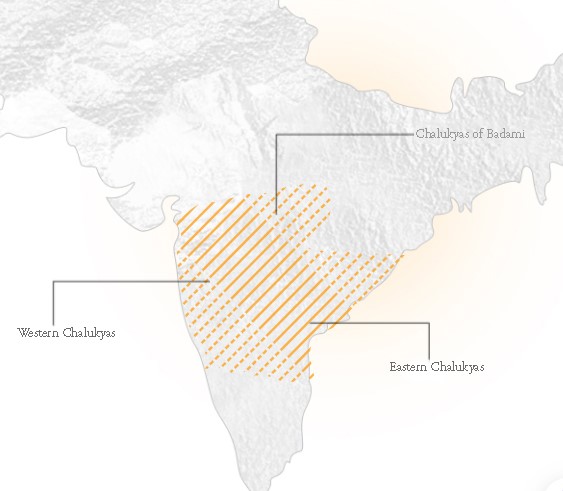
Who were the Chalukyas?
- Overview:
- The Chalukyas ruled parts of Southern and Central India between the 6th century and the 12th century.
- The kingdom of Chalukyas was centred around the Raichur Doab, between the Krishna and Tungabhadra rivers.
- Three distinct but related Chalukya dynasties:
- Badami Chalukyas: They were the earliest Chalukyas with their capital at Badami (Vatapi) in Karnataka.
- Their rule started in the mid-6th century and declined after the death of their greatest king, Pulakesin II in 642 AD.
- Eastern Chalukyas: Emerged after the death of Pulakesin II in Eastern Deccan with the capital at Vengi.
- They ruled till the 11th century.
- Western Chalukyas: They were the descendants of the Badami Chalukyas.
- They emerged in the late 10th century and ruled from Kalyani.
- Badami Chalukyas: They were the earliest Chalukyas with their capital at Badami (Vatapi) in Karnataka.
Note:
Pulakesin II: The Pinnacle of Chalukya Power -
- Conquered various kingdoms including Kadambas, Gangas of Mysore, Mauravas of North Konkan, Latas of Gujarat, Malavas, and Gurjars.
- Secured submissions from Chola, Chera, and Pandya kings.
- Defeated King Harsha of Kannauj and Pallava king Mahendravarman.
- Administration and Cultural Contributions:
- Robust Military: Comprehensive army with infantry, cavalry, elephant unit, and a strong navy.
- Religious Tolerance: Despite being Hindu rulers, they showed tolerance towards Buddhism and Jainism.
- Literary and Numismatic Contributions: Advanced developments in Kannada and Telugu literature.
- Coins featured Nagari and Kannada inscriptions, temple cryptograms, and symbols like lions, boars, and lotuses.
- Architectural Marvels:
- Cave Temples: Built temples with both religious and secular themes adorned with beautiful mural paintings.
- Notable Temples:
- Aihole temples: Lady Khan (Surya), Durga, Huchimalligudi.
- Badami temples.
- Pattadakal Temples: The UNESCO World Heritage site features 10 temples in both Nagar and Dravida styles, including the Virupaksha and Sangameshwara Temples.
- Aihole Inscription of Pulakesin II:
- Situated in the Megudi temple at Aihole, Karnataka, the Aihole inscription provides invaluable insights into Chalukya history and achievements.
- Aihole is considered the “Cradle of Indian temple architecture”.
- Crafted by the renowned poet Ravikriti, the inscription is a lyrical tribute to the Chalukya dynasty, particularly King Pulakesin II, lauded as the embodiment of truth (Sathyasraya).
- The inscription chronicles the Chalukya dynasty's triumphs over adversaries, including the renowned defeat of Harshavardhana.
- Decline:
- After the decline of the Chalukya Kingdom of Kalyani at the end of 12th century, the new kingdoms which arose in South India were Yadavas of Devagiri and Kakatiyas of Warangal and Hoysalas of Dwarasamudra and Pandyas of Madurai.