6th Session of India-Ethiopia Joint Trade Committee | 13 Nov 2023
For Prelims: India-Ethiopia Joint Trade Committee (JTC), Unified Payment Interface
For Mains: India-Ethiopia Relations, Policies & Politics of Countries Fon India's Interests
Why in News?
The 6th Session of the India-Ethiopia Joint Trade Committee (JTC) recently concluded in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, bringing together officials from both countries to strengthen economic ties.
What is the India-Ethiopia JTC?
- The India-Ethiopia JTC is a bilateral forum that meets periodically to review and enhance trade and investment relations between the two countries.
- The JTC is co-chaired by senior officials from the Ministry of Commerce and Industry of India and the Ministry of Trade and Regional Integration of Ethiopia.
- The JTC discusses various issues and opportunities related to trade, investment, cooperation, and policy matters.
What are the Key Highlights of the JTC meeting?
- India invited Ethiopia to collaborate on integrating the Unified Payment Interface (UPI) with Ethiopia's Ethswitch.
- Ethswitch is a payment platform infrastructure in Ethiopia.
- India urged Ethiopia to explore settling trade transactions in the local currency for enhanced bilateral trade and conservation of foreign exchange.
- Health and pharmaceuticals, automobiles, textiles, infrastructure projects, food, and agro-processing are identified as key sectors for mutual investments.
- Both sides also reviewed the progress of ongoing discussions for Memorandum of Understanding (MoUs) in the field of Standardization and quality assurance and Customs procedure and agreed to conclude them expeditiously.
How have been the India-EthiopiaTrade Trade Relations?
- India is one of the largest sources of long-term concessional credit to Ethiopia, with over USD 1 billion for sectors such as rural electrification, sugar industry and railways
- Bilateral trade between India and Ethiopia reached USD 642.59 million in 2022-23.
- Ethiopia's economy grew by an estimated 6.4% in 2021-22.
- India is the second-largest exporter to Ethiopia.
- Indian companies rank among the top three foreign investors in Ethiopia with existing investments totalling USD 5 billion.
- India and Ethiopia have exchanged several high-level visits, including those of presidents, prime ministers and ministers.
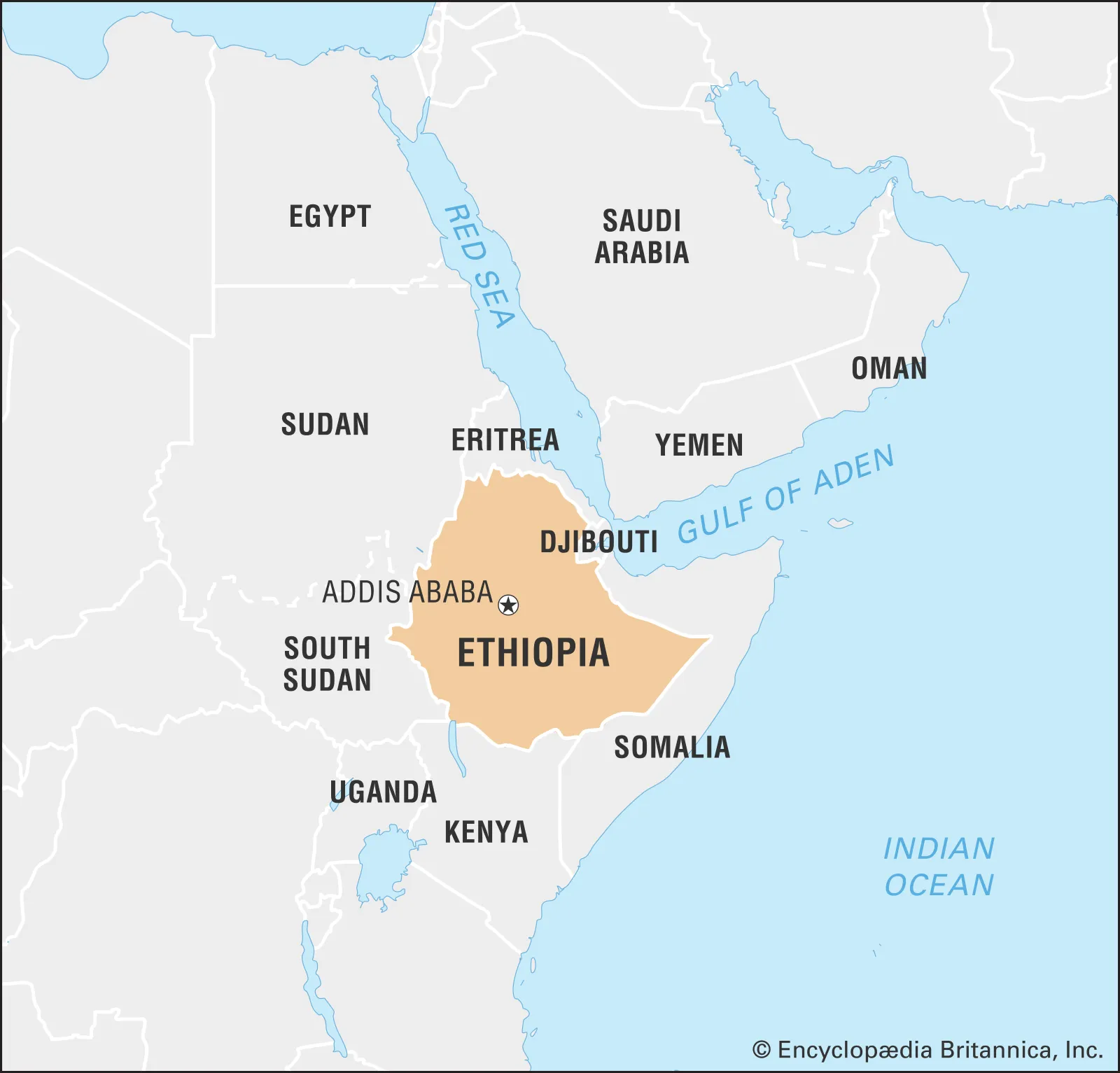
Key Facts About Ethiopia
- It is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa, officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia.
- The capital is Addis Ababa.
- Ethiopia is located from Sudan to the southeast, Eritrea to the south, Djibouti and Somalia to the west, Kenya to the north, and South Sudan to the east.
- Ethiopia is one of the oldest countries in the world that managed to remain uncolonized by European powers even though 90% of Africa was colonized by European nations.
- The Ethiopian Calendar has 12 months of 30 days each, plus five or six additional days (sometimes known as the 13th month).
- Ras Dejen (or Dashen), the highest peak in Ethiopia.
- The largest lake in Ethiopia is Lake Tana, and is the source of the Blue Nile river.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following pairs is correctly matched? (2013)
| Geographical Feature | Region |
| (a) Abyssinian Plateau | Arabia |
| (b) Atlas Mountains | North-Western Africa |
| (c) Guiana Highlands | South-Western Africa |
| (d) Okavango Basin | Patagonia |
Ans: (b)
- Abyssinian Plateau is a plateau in Ethiopia (Africa) located at an elevation of 1388 metres above sea level.
- Atlas Mountains are a series of mountain ranges in northwestern Africa, running generally southwest to northeast. It forms the geologic backbone of the countries of the Maghreb (the western region of the Arab world) – Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia.
- Guiana Highlands is the region in northern South America where Brazil, Guyana, and Venezuela meet at Mount Roraima. It is bounded by the Orinoco and Amazon river basins, and by the coastal lowlands of the Guianas.
- The Okavango river basin is the fourth-longest river system in southern Africa. It is an endorheic basin (watershed which does not drain to the sea) found in southwestern Africa.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.