6th India-OPEC Energy Dialogue | 16 Nov 2023
For Prelims: Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries, OPEC+, Renewable energy
For Mains: Challenges Related to India’s Energy Sector, Initiatives Shaping India’s Energy Transition
Why in News?
The 6th High-Level Meeting of the India-Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) Energy Dialogue brought together key representatives at the OPEC Secretariat in Vienna, Austria.
- The meeting delved into critical aspects of oil and energy markets.
What are the Key Highlights of India-OPEC Energy Dialogue?
- The Meeting focused on key issues related to oil and energy markets with a specific emphasis on ensuring availability, affordability and sustainability, which are necessary to ensure the stability of energy markets.
- The meeting concluded with both parties underscoring the importance of fostering enhanced cooperation between OPEC and India moving forward.
- World Oil Outlook 2023, which forecasted that India would be the fastest-growing major developing economy, averaging long-term growth of 6.1% between 2022-2045 and accounting for over 28% of incremental global energy demand during the same period.
- Both sides have recognized the importance of India as the third-largest energy consumer, crude oil importer and the fourth-largest global refiner, in global economic growth and energy demand.
- The meeting also acknowledged the achievements and initiatives of India in the fields of renewable energy, energy efficiency, hydrogen economy, and climate change mitigation.
- It was agreed to hold the next High-Level Meeting of the India-OPEC Energy Dialogue in 2024 in India.
What is the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC)?
- About:
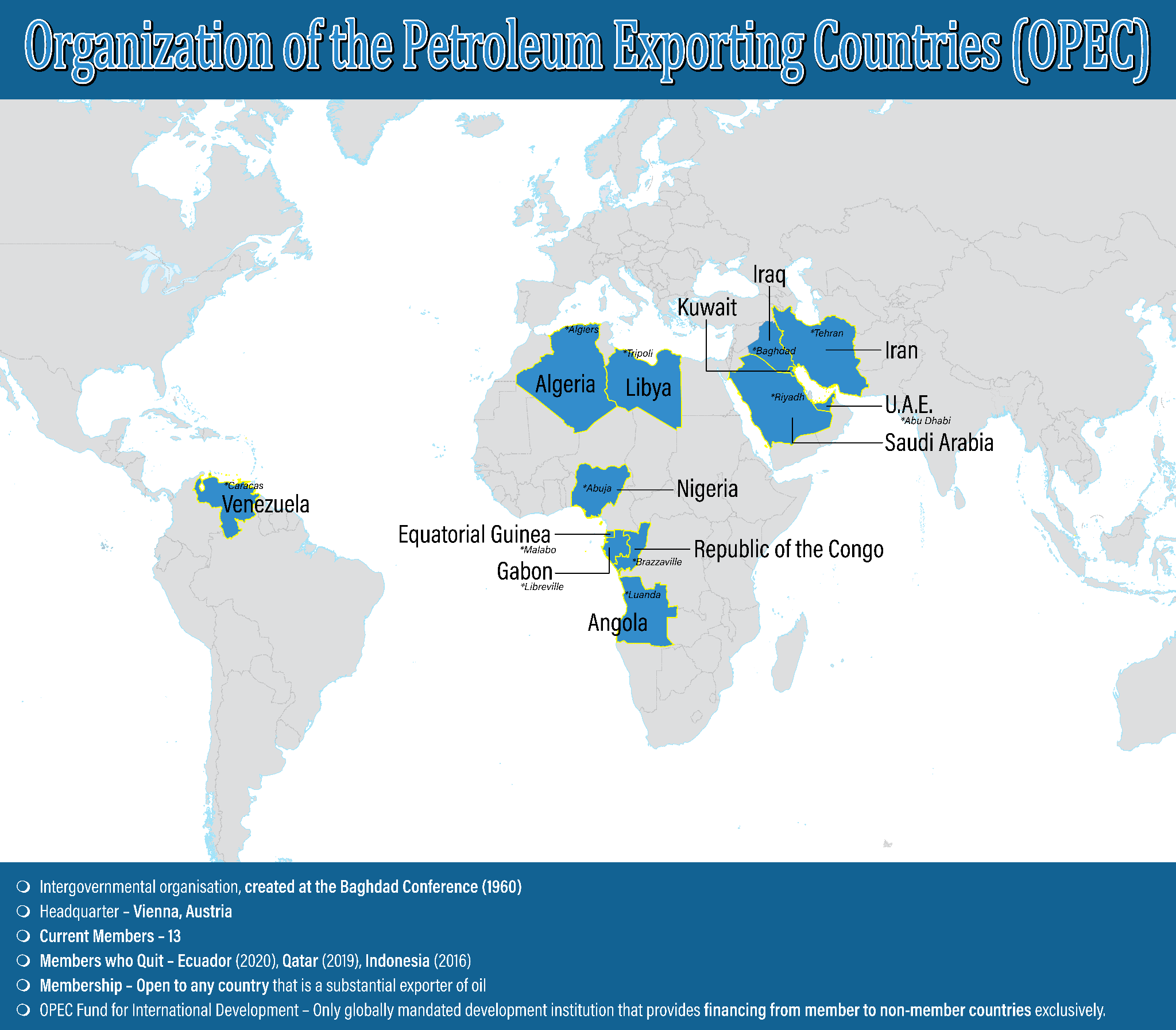
- The OPEC is a permanent, intergovernmental Organization, created at the Baghdad Conference in 1960, by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.
- It is headquartered in Vienna, Austria.
- The OPEC is a permanent, intergovernmental Organization, created at the Baghdad Conference in 1960, by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia and Venezuela.
- Objective:
- OPEC's objective is to coordinate and unify petroleum policies among Member Countries, to secure fair and stable prices for petroleum producers; an efficient, economic and regular supply of petroleum to consuming nations; and a fair return on capital to those investing in the industry.
- Members:
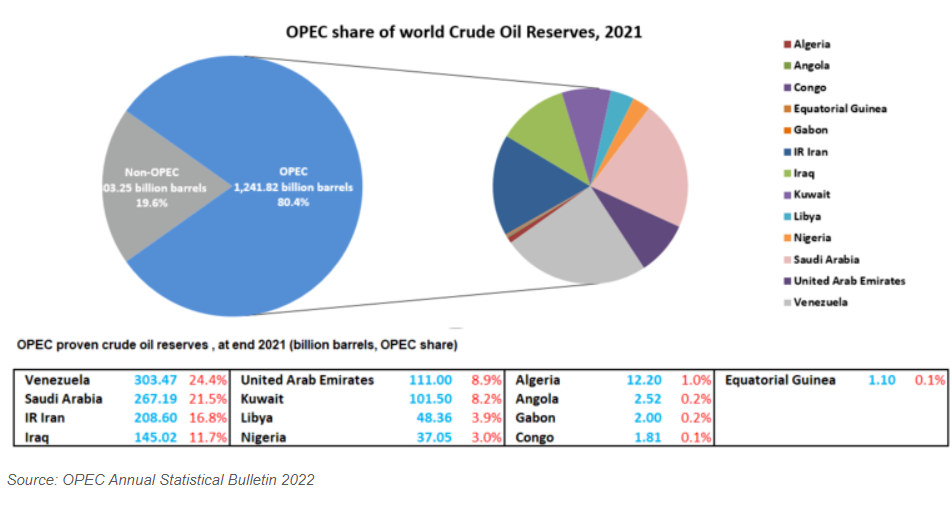
- Algeria, Angola, Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Libya, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates and Venezuela.
- OPEC nations produce about 30% of the world's crude oil.
- Saudi Arabia is the biggest single oil supplier within the group, producing more than 10 million barrels a day.
- Reports and Outlooks:
- Monthly Oil Market Report, Annual Statistical Bulletin and the World Oil Outlook.
- OPEC+:
- In 2016, largely in response to falling oil prices driven by significant increases in U.S. shale oil output, OPEC signed an agreement with 10 other oil-producing countries to create what is now known as OPEC+.
- OPEC+ now includes the 13 OPEC member countries along with Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Brunei, Kazakhstan, Malaysia, Mexico, Oman, Russia, South Sudan, and Sudan.
- OPEC+ countries produce about 40% of all the world's crude oil.
- In 2016, largely in response to falling oil prices driven by significant increases in U.S. shale oil output, OPEC signed an agreement with 10 other oil-producing countries to create what is now known as OPEC+.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”.Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)