International Relations
3rd ASEAN Digital Ministers Meeting
- 13 Feb 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, India-ASEAN Digital Work Plan 2023, ASEAN Declaration, Look East Policy, ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA), Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement, ASEAN India Friendship Year, ASEAN-India Green Fund.
For Mains: India-ASEAN Relations, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement.
Why in News?
The 3rd ASEAN Digital Ministers (ADGMIN) meeting was held recently .
- The theme of the meeting was "Synergy Towards a Sustainable Digital Future”.
What are the Major Highlights of the Meeting?
- The meeting focused on enhancing the relationship between India and ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) in the area of Information and Communication Technologies (ICTs) .
- India emphasised its reforms to promote fair competition, and increase broadband and telecom connectivity.
- The significance of digital transformation was also highlighted as a means of creating an inclusive and equitable society, promoting sustainable development, and empowering citizens through digital means.
- India-ASEAN Digital Work Plan 2023 was approved, which includes initiatives for capacity building and knowledge sharing in areas such as Artificial Intelligence in Cybersecurity, IoT and AI in Next Generation Smart Cities, and the role of ICTs in implementing digital health and security.
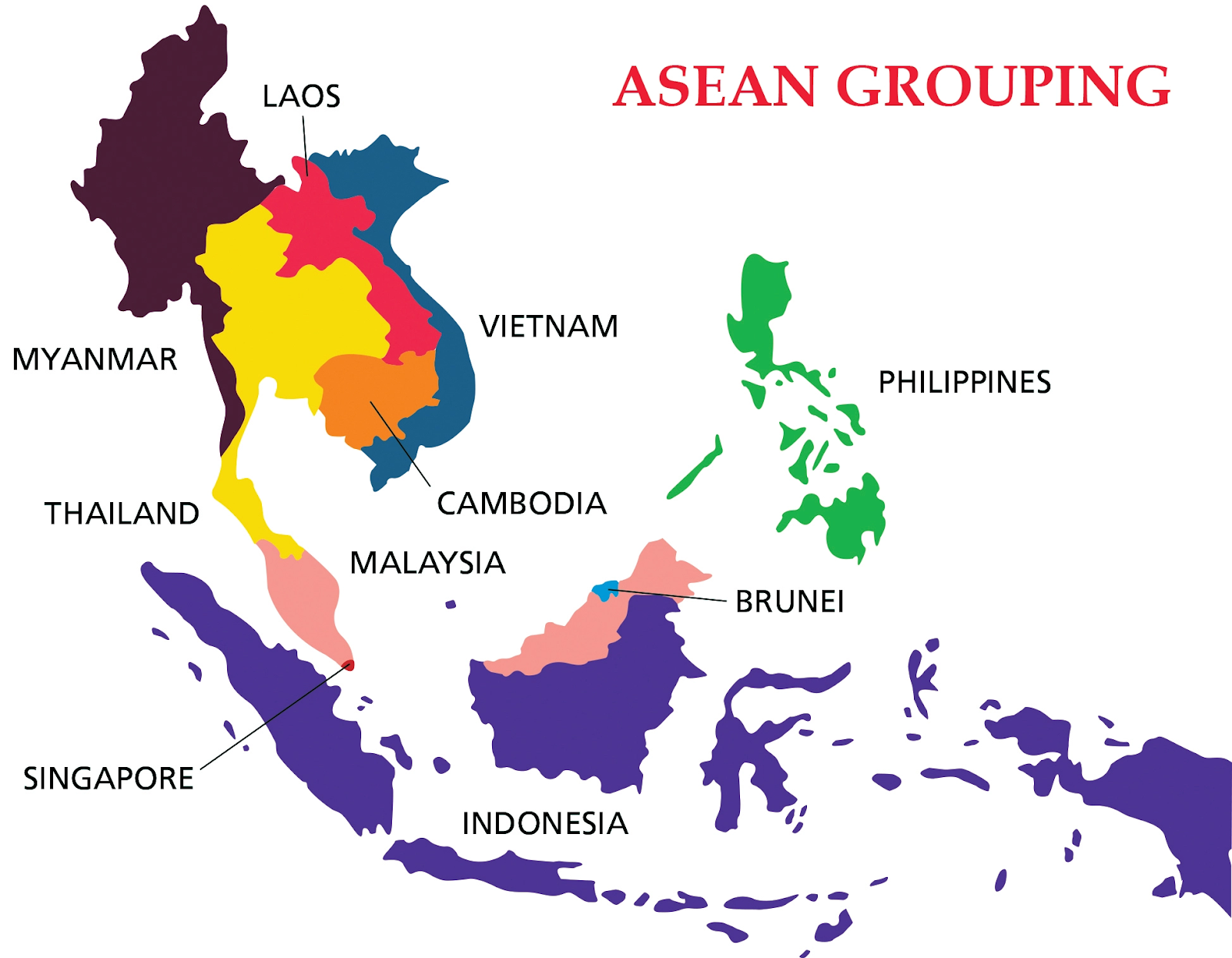
What is ASEAN Grouping?
- About:
- It is a regional grouping that promotes economic, political, and security cooperation.
- It was established in August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the founding fathers of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Its chairmanship rotates annually, based on the alphabetical order of the English names of Member States.
- Members:
How is India’s Relations with ASEAN?
- About:
- India and ASEAN have a long-standing and multi-faceted relationship that encompasses political, economic, cultural, and security dimensions.
- Evolution of Bilateral Relations:
- India-ASEAN bilateral relationship started evolving since India introduced 'Look East Policy' in 1990s.
- This initiative was further transformed to ‘Act East Policy’ in 2014 mainly to develop economic and strategic relations with the nations of Southeast Asian countries.
- In 1992, India emerged as a Sectoral Partner of ASEAN followed by Dialogue Partner in 1996 and a Summit-level Partner in 2002.
- In 2009, The ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA) was signed and entered into force on 1 January 2010.
- Also, India has a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) with various countries of the ASEAN region (Singapore, Malaysia and Thailand) which has resulted in concessional trade and a rise in investments.
- In 2015, India also set up a separate Mission to ASEAN and the East Asia Summit in Jakarta in 2015 to strengthen engagement with ASEAN countries.
- In 2022, the ASEAN India Friendship Year was observed to commemorate the 30-year milestone of the establishment of dialogue relations between ASEAN and India, leading to the elevation of their Strategic Partnership to a Comprehensive Strategic Partnership (CSP).
- India-ASEAN bilateral relationship started evolving since India introduced 'Look East Policy' in 1990s.
- Other Areas of Engagement:
- Financial Assistance:
- India offers financial support to ASEAN countries through various channels such as the ASEAN-India Cooperation Fund, the ASEAN-India Science and Technology Development Fund, and the ASEAN-India Green Fund.
- Connectivity:
- India has been implementing several connectivity initiatives, such as the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway and the Kaladan Multimodal Project.
- Additionally, India is working towards establishing a Maritime Transportation Agreement with ASEAN and has plans for a railway connection between New Delhi, India and Hanoi, Vietnam.
- Financial Assistance:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q2. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Q3. In the Mekong-Ganga Cooperation, an initiative of six countries, which of the following is/are not a participant/ participants? (2015)
- Bangladesh
- Cambodia
- China
- Myanmar
- Thailand
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 1, 2 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)