25th Session of the IRIGC-TEC | 15 Nov 2024
For Prelims: North-South Transport Corridor, Northern Sea Route, European Union, India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, Eurasian Economic Union, Vostro Account, Central Board of Indirect Taxes, Bilateral Investment Treaty
For Mains: Significance of India- Russia Relations, Economic Diplomacy and Strategic Partnerships, India’s Trade Imbalance
Why in News?
Recently, External Affairs Minister of India and Russia's First Deputy Prime Minister co-chaired the 25th session of the India-Russia Intergovernmental Commission on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological, and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC) in New Delhi.
- The discussions highlighted significant progress in trade relations between the two nations and strategic cooperation in various sectors.
Note:
The The Inter-Governmental Commission (IGC) is a mechanism for regularly monitoring bilateral progress across the sectors of trade and economic cooperation between the two countries which was set up by an Agreement on inter-governmental Commission on Trade, Economic, Scientific and Technological Cooperation signed in 1992.
- It comprises 14 Working Groups and 6 Sub-Groups in diverse areas.
What are the Key Highlights of the 25th Session of IRIGC-TEC?
- USD 100 Billion Trade Target: India and Russia aim to achieve a USD 100 billion trade target ahead of the 2030, with both nations optimistic about reaching this goal.
- Progress in Trade and Diversification: India and Russia have made significant strides in overcoming payment and logistics challenges, with nearly 90% of India-Russia trade now being conducted in local or alternative currencies, with the remaining transactions still happening in freely convertible ones(widely used for international transactions).
- Both nations are focusing on diversifying trade beyond crude oil to include agriculture, pharmaceuticals, industrial equipment, and technology.
- Focus on Trade Diversification: Both nations are focused on diversifying the trade basket to reduce the current imbalance, which is largely driven by India’s large crude oil imports from Russia.
- Emphasis on expanding trade in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, industrial equipment, and technology.
- Enhancing Connectivity and Talent Mobility: Significant importance is placed on enhancing connectivity, particularly through the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), the Chennai-Vladivostok Corridor, and the Northern Sea Route to improve trade and logistics.
- The meeting emphasized fostering talent mobility and skills development, tailored to Russia's needs, with a focus on education and workforce collaboration to strengthen bilateral ties.
- Future Steps for Economic Cooperation: Working groups and sub-groups were tasked with accelerating the finalisation of the economic cooperation program for the period leading up to 2030.
- The agenda includes enhancing market access and advancing discussions on services, investments, and technology exchange.
What are the Key Highlights of India- Russia Trade?
- Trade Targets: Initially, India and Russia set targets to elevate bilateral investment to USD 50 billion and bilateral trade to USD 30 billion by 2025.
- However, bilateral trade for FY 2023-24, reached an unprecedented high of USD 65.70 billion, with India’s exports valued at USD 4.26 billion and imports from Russia at USD 61.44 billion.
- Imports and Exports: Imports from Russia include oil and petroleum products, fertilisers, minerals, precious stones and metals, and vegetable oils; exports to Russia include pharmaceuticals, organic chemicals, electrical machinery, mechanical appliances, and iron & steel.
- Major Russian Investments in India: Oil and Gas, Petrochemicals, Banking, Railways, and Steel.
- Major Indian Investments in Russia: Oil and Gas, and Pharmaceuticals.
What are the Key Challenges in India- Russia Trade?
- Trade Imbalance: India faces a trade deficit of nearly USD 57 billion with Russia, primarily due to imports of Russian crude oil, with the trade imbalance skewed in Russia's favour as India's exports to Russia remain comparatively lower.
- Geopolitical Reasons: India's growing ties with the US and the Quad, especially in the context of the Ukraine war, can limit deeper strategic cooperation with Russia.
- Russia's stronger ties with China further reduce its ability to balance the interests of India and China, diminishing India's leverage in multilateral forums.
- Sanctions and Compliance Issues: Sanctions by the European Union(EU) and Western powers on Russia have complicated trade relations with India, with some Indian companies now targeted.
- This puts India in a difficult position, balancing its defence and energy ties with Russia while adhering to international sanctions.
- Diverse Trade Basket: While energy trade, particularly discounted crude oil, has surged, efforts to diversify into sectors like automotive parts, electronics, and renewables have been slow.
- Russia's declining international standing limits its capacity to engage India in new economic areas.
- Additionally, India’s growing economic ties with the United States, the EU, and other advanced economies are restricting opportunities for new strategic collaborations with Russia, particularly in technology and manufacturing.
- Challenges in Connectivity Projects: Projects like the INSTC and the Chennai-Vladivostok Corridor are central to India-Russia trade ambitions.
- However, India’s growing enthusiasm for other connectivity routes, such as the India-Middle East-Europe Corridor, could undermine the INSTC’s strategic importance, leading to potential underperformance of these initiatives that require Russia’s active cooperation.
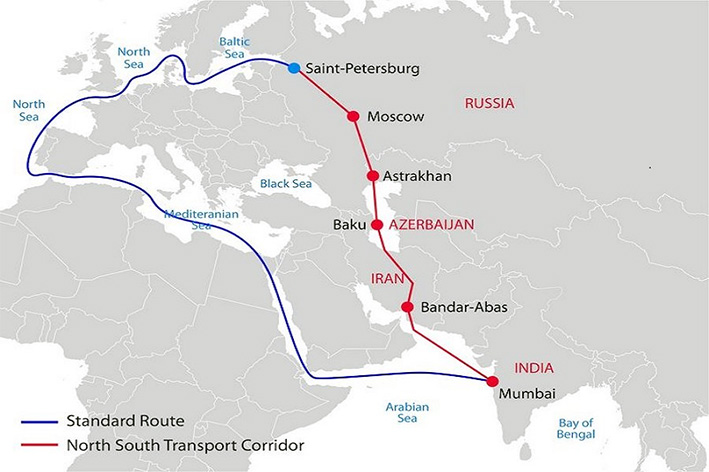
International North-South Transport Corridor
- About: The INSTC is a 7,200 km multimodal transit route linking the Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea, extending to northern Europe via St. Petersburg, Russia.
- It was launched in 2000 through a trilateral agreement by Iran, Russia, and India.
- It connects ship, rail, and road routes between India, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe.
- INSTC can boost India's connectivity with Central Asia and the Eurasian region, leveraging the geo-strategic and economic significance of the involved countries.
- Membership: India, Iran, Russia, Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkey, Ukraine, Belarus, Oman and Syria. Bulgaria has joined as an Observer State.
How are India and Russia Addressing Trade Challenges?
- Special Rupee-Vostro Account Facility: India introduced the Special Rupee-Vostro Account to overcome the challenges posed by international sanctions and facilitate payments in local currencies between Indian and Russian businesses.
- Free Trade Agreement (FTA) and Investment: Both sides are working toward an FTA between India and the Eurasian Economic Union (EEU), which could further streamline trade and reduce barriers.
- The launch of the first bilateral Investment Forum in Moscow in April 2024, and the ongoing negotiations on a Bilateral Investment Treaty, are expected to foster greater economic engagement.
- Facilitating Business Ventures: Russia has shown increasing interest in India’s Make in India program, which could lead to joint ventures and new avenues for economic collaboration.
- Bilateral Agreements: The signing of a bilateral agreement on Authorised Economic Operators(AEO) between the two countries is a significant step toward simplifying trade processes and enhancing business exchanges.
- The Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs and the Federal Customs Service, Russia, have signed the AEO agreement to provide mutual benefits to trusted exporters of both signatories during goods clearance by the customs authorities of the importing country.
- Energy Sector Cooperation: Special focus has been placed on large-scale energy initiatives, including developments in the nuclear sector, solar and wind energy production technology improvements.
- Russian Business Centre: The Russian Business Centre in New Delhi aims to strengthen India-Russia economic ties by facilitating business interactions, regional missions, forums, and offering analytical support.
Conclusion
India and Russia’s complementary economies offer strong collaboration potential, with India’s growth and Russia’s resources paving the way for future partnership. As Russia pivots toward Asia and the world moves to a multipolar order, both nations must strengthen ties for mutual benefit.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Analyze the India-Russia trade relations. Discuss the key sectors driving this partnership and the challenges faced in strengthening it. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
(a) Japan
(b) Russia
(c) The United Kingdom
(d) The United States of America
Ans: B
Mains
Q. What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)