International Relations
G-20 Foreign Ministers Meeting
- 12 Jul 2022
- 14 min read
For Prelims: G20, International Organisation, India and International Groupings
For Mains: India’s foreign policy, Significance of G20 in India’s Foreign Policy, Challenges of global happenings on international groupings
Why in News?
Recently, the External Affairs Minister of India met with the US Secretary of State and Russian Foreign Minister and other counter parts in Bali (Indonesia) on the sidelines of the G20 Foreign Ministers Meeting.
- The meeting was held under the theme of “Building a more peaceful, stable, and prosperous world together.”
What do we know about the recent G20 Meeting?
- India & China:
- The External Affairs Minister of India met the State Councilor and Foreign Minister of China.
- India called for an early resolution of all the outstanding issues along the LAC in Eastern Ladakh.
- Recalling the disengagement achieved in some friction areas, India reiterated the need to sustain the momentum to complete disengagement from all the remaining areas to restore peace and tranquility in the border areas.
- Both sides affirmed that the military and diplomatic officials of the two sides should continue maintaining regular contact and looked forward to the next round of Senior Commanders’ meeting at an early date.
- China appreciated India’s support during its BRICS Chairmanship this year and assured China’s support for India’s upcoming G20 and SCO Presidency.
- India called for an early resolution of all the outstanding issues along the LAC in Eastern Ladakh.
- The External Affairs Minister of India met the State Councilor and Foreign Minister of China.
- Other Areas of Discussion:
- The meetings indicated the emerging differences within the G20 grouping as Russia accused the United States of forcing Europe and the rest of the world to abandon cheap energy sources while the US blamed Russia for “global food insecurity”.
- The G20 that includes 20 of the world’s biggest economic powers has a mandate to discuss global economic matters but the Foreign Ministers Meeting in Bali was dominated by criticism of Russia by the western members.
- The Ukraine war and its economic fallouts are hinting at a division within the ranks of the global grouping, with the US, EU, Japan, Canada, Australia, France forming one anti-Russia block while the rest of the countries prefer a cautious approach asking for peaceful resolution of the war in Ukraine.
What do we need to know about G20?
- About:
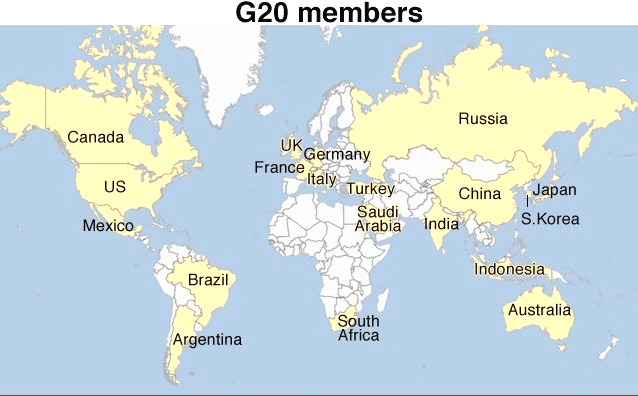
- It is an informal group of 19 countries and the European Union (EU), founded in 1999, with representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- Its members are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the EU.
- Nigeria was meant to be the “20th” member and was dropped at the last minute due to political troubles at the time.
- The membership comprises a mix of the world’s largest advanced and emerging economies, representing about two-thirds of the world’s population.
- It is an informal group of 19 countries and the European Union (EU), founded in 1999, with representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- Functioning of G20:
- The G-20 has no fixed headquarters, and the secretariat moves by rotation between the countries hosting or assuming Presidency of the grouping each year.
- The members are divided into five groups (India is in Group 2, along with Russia, South Africa and Turkey).
- The G-20 agenda that still depends heavily on the guidance of Finance Ministers and central Governors is finalised by a unique system of ‘Sherpas’, who are special envoys of G-20 leaders.
- Another feature of the G-20 is ‘Troika’ meetings, comprising the countries presiding over the G-20 in the past year, present year, and next year. At present, the Troika is made up of Italy, Indonesia and India.
How has the G20 Evolved over the years?
- The Global Financial Crisis (2007-08) cemented G20’s reputation as the premier crisis management and coordination body.
- The US, which held the G20 Presidency in 2008, elevated the meeting of the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to Heads of State, resulting in the first G20 Summit.
- The Summits in Washington DC, London, and Pittsburgh set the scene for some of the most durable global reforms:
- Blacklisting states in an effort to tackle tax evasion and avoidance, provisioning stricter controls on hedge funds and rating agencies, making the Financial Stability Board an effective supervisory and watchdog body for the global financial system, proposing stricter regulations for too-big-to fail banks, refraining members from imposing new barriers to trade etc.
- By the time Covid-19 struck, the G20 had wandered off from its original mission and G20 lost its focus.
- G20 reinvented itself by widening its agenda to include issues such as climate change, jobs and social security issues, inequality, agriculture, migration, corruption, terror financing, drug trafficking, food security and nutrition, disruptive technologies, and meeting the sustainable development goals.
- In recent times, G20 members have made all the right commitments after the pandemic, but there is little to show in action.
- At the Riyadh Summit in October 2020, they prioritised four things: fighting the pandemic, safeguarding the global economy, addressing international trade disruptions, and enhancing global cooperation.
- The Italian Presidency in 2021 had focused on three broad, interconnected pillars of action — People, Planet, Prosperity — vowing to take the lead in ensuring a swift international response to the pandemic.
What is India’s Potential for the G20 Presidency?
- As a founding member of the G20, India has used the platform to raise issues of vital importance and those that impact on the most vulnerable around the world.
- But due to the rising toll of unemployment rates and poverty in the domestic portion, it’s hard to take the lead effectively.
- Concurrently, India’s leadership role in delineating the success of India-France led International Solar Alliance is globally well acclaimed as a turning point intervention in mobilising resources towards promoting research and development in renewable energy.
- Also, the vision of ‘Self Reliant India (Atmanirbhar Bharat)’ initiative is expected to play a transformational role for “New India” in the global paradigm as an important and reliable pillar of world economy and global supply chains in the aftermath of Covid -19 crisis.
- India’s endeavour of establishing the Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure, comprising nine of the G20 nations amongst others provides new dimensions of leadership in the global growth process.
What are the Challenges G20 Facing?
- Global:
- Polarisation of Interests:
- Russian and Ukrainian Presidents are invited to the G20 Summit to be held in November, 2022.
- The U.S. has already demanded to not invite Russian President, or U.S. and European countries would boycott his address.
- China’s strategic rise, NATO’s expansion and Russia’s territorial aggression in Georgia and Crimea and now Russia Ukraine Conflict in 2022 changed global priorities.
- Globalisation is no longer a cool word, and multilateral organisations have a credibility crisis as countries around the world pick being ‘G-zero’ (a term coined by political commentator Ian Bremmer to denote ‘Every Nation for Itself’) over the G-7, G-20, BRICS, P-5 (UNSC Permanent Members) and others.
- Russian and Ukrainian Presidents are invited to the G20 Summit to be held in November, 2022.
- Other Challenges:
- International Finance:
- According to the recent IMF World Economic Outlook, the debt-to-GDP ratio in the median emerging market and the middle-income country was about 60% in 2021.
- Macroeconomic Policy:
- The war-induced supply shortages have amplified the inflationary pressure, especially in the energy and agriculture sectors.
- Proving Global Public Health Goods:
- The recovery from the pandemic has been largely uneven due to inadequate access to essential healthcare.
- Digital Economy:
- The Russia–Ukraine war has led to resurfacing of concerns regarding the illicit use of crypto-assets and its impact on the global financial stability.
- International Finance:
- Polarisation of Interests:
- Challenges for India:
- For India, the G-20’s challenges come with the hosting of Summit next November efficiently with member countries of polarised international interests.
- Former NITI Ayog CEO Amitabh Kant has been appointed the PM’s G-20 Sherpa, and former Foreign Secretary Harsh Shringla will be the G-20 Coordinator.
- The government plans to hold 100 preparatory meetings in different parts of the country, which led to a controversy over whether the G-20 summit or Ministerial level meetings would be held in Jammu Kashmir, considering India’s conflict with neighbouring countries.
- The bigger challenges, however, will remain for India to assist Indonesia in protecting the idea of the G-20, and keeping it from fragmentation in the face of geopolitical fissures, where leaders are loath to hear each other speak, or even sit in the same room together.
- For India, the G-20’s challenges come with the hosting of Summit next November efficiently with member countries of polarised international interests.
Way Forward
- The G20 must strengthen the partnership with international organisations such as the IMF, the OECD, the WHO, the World Bank and the WTO, and delegate them the task of monitoring progress.
- Global Cooperation should be given priority over individual interest for the benefit of all the member countries.
- Use of Dialogue and Diplomacy should be carried out to resolve issues like Ukraine - Russia conflict and differences between Russia and the west.
- India should focus upon utilizing the G20 2023 summit as a platform to raise discussions on issues such as aggressive trade barriers/ sanctions, inter country conflicts and advocate for global peace and cooperation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20?
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Explanation:
- The G20 is an informal group of 19 countries and the European Union, with representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- In order to achieve a robust global economic growth, the member countries which represent and contribute more than 80% of the global GDP came at the premier forum for international economic cooperation, which was agreed by leaders at the Pittsburgh Summit in Pennsylvania (USA) in September 2009.
- The G20 members include Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Republic of Korea , Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the European Union (EU).
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.





-min.jpg)