India's Tryst with Antarctica
This editorial is based on “Southern sojourn: On the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting in India” which was published in The Hindu on 25/05/2024. The article brings into picture the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting in Kochi, where delegates focused on regulating rising tourism in Antarctica to protect its environment and address territorial concerns.
For Prelims: Antarctica, 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting, A23a iceberg, IceCube Neutrino Observatory, Penguin, Antarctic Treaty, Maitri and Bharati
For Mains: Significance of Exploring Antarctica For India, Measures for India to Enhance its Role and Contributions in Antarctica
The icy expanse of Antarctica, untouched by human civilization and teeming with unique life forms, has long held a sense of mystery. This remoteness, however, is rapidly changing. Tourism to the continent has seen a phenomenal rise, with visitor numbers jumping from 8,000 in 1993 to over 1,05,000 in 2022. This surge has ignited concerns about the continent's delicate ecosystem, prompting the ongoing 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting (ATCM) held in Kochi, Kerala to debate the very future of tourism in this pristine wilderness.
The debate at the ATCM represents a critical juncture for Antarctica. India, as a rising power with a growing stake in the continent's future, has a unique opportunity to champion responsible tourism and ensure that the pristine beauty of Antarctica remains accessible for generations to come.
Why is Antarctica Becoming Increasingly Significant?
- Climate Change Implications: Antarctica plays a crucial role in Earth's climate system, and the melting of its ice sheets has far-reaching consequences for global sea levels and weather patterns.
- The recent satellite pictures showed that the Antarctic iceberg called A23a was moving beyond the northern tip of the Antarctic Peninsula.
- Resource Potential: Antarctica is believed to hold significant reserves of valuable minerals, including rare earth elements, coal, and potentially untapped oil and gas deposits.
- With the growing global demand for resources and the depletion of traditional sources, the potential for responsible and sustainable resource exploration in Antarctica has gained attention.
- Scientific Research Opportunities: Antarctica's unique and pristine environment offers unparalleled opportunities for scientific research across various disciplines, including glaciology, astronomy, geology, and biology.
- As technological advancements enable more sophisticated research methods, the scientific value of Antarctica continues to increase.
- Example: The IceCube Neutrino Observatory, located at the Amundsen-Scott South Pole Station in Antarctica.
- Rising Geopolitical Interests: As nations seek to establish their presence and influence in strategically important regions, Antarctica has become an area of growing geopolitical interest.
- Countries are vying for a stronger voice in the governance and decision-making processes related to the Antarctic region, driven by potential resource opportunities and a desire for global influence.
- The USA has three stations in Antarctica. China opened its 5th station (Qinling Station) in Antarctica in February, 2024
- Environmental Monitoring and Conservation: Antarctica serves as a critical indicator of global environmental changes, and monitoring its ecosystems and wildlife provides valuable insights into the health of the planet.
- The Antarctic Peninsula is one of the regions experiencing the fastest warming on Earth, leading to significant changes in penguin and krill populations.
- Tourism and Adventure: As adventure tourism continues to grow, Antarctica's unique and untouched landscapes have become an attractive destination for travelers seeking extraordinary experiences.
- According to the International Association of Antarctica Tour Operators (IAATO), a record 105,331 people visited Antarctica over the 2022-23 season.
What is the Antarctic Treaty?
- About: Signed in 1959 by 12 countries active in Antarctic research during the International Geophysical Year (1957-58).
- Currently has 57 member nations including India (joined the treaty in 1983).
- Key Provisions:
- Peaceful Use: Antarctica is dedicated to peaceful purposes only (Article I).
- Scientific Collaboration: Freedom of scientific investigation and cooperation are encouraged (Article II).
- Information Sharing: Scientific observations and results must be exchanged and made readily available (Article III).
- Territorial Claims:
- Seven signatory countries (Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the UK) have overlapping territorial claims.
- Other countries do not recognize these claims.
- The US and Russia maintain a "basis of claim" without asserting it.
- Article IV maintains the status quo by:
- Disallowing any existing activity to be used to support or deny territorial claims.
- Prohibiting new or expanded territorial claims while the Treaty is in force.
- Seven signatory countries (Argentina, Australia, Chile, France, New Zealand, Norway, and the UK) have overlapping territorial claims.
- Inspection Regime:
- To ensure adherence to the Treaty, all areas of Antarctica, including stations and installations, are subject to inspection by any Party at any time (Article VII).
What is the Significance of Exploring Antarctica For India?
- Advancing India's Space Program: Antarctica's unique location and conditions make it an ideal testing ground for India's space technologies, such as landers, rockets and remote sensing systems.
- Conducting environment-friendly experiments and trials in the harsh Antarctic environment could help India refine its space technologies for future missions.
- Securing Energy and Mineral Resources: With India's growing energy demands ( third-largest consumer of energy in the world) and the need for critical minerals, Antarctica's potential for responsible and sustainable resource exploration could help address the country's long-term resource security needs, subject to the Antarctic Treaty System's regulations.
- Advancing Climate Change Research and Adaptation: India's geographical location (Cap of Himalayas to North and Sandal of Seas in South) that increases its vulnerability to climate change impacts make it crucial to understand the changes in Antarctica climate systems.
- Strengthening India's Maritime Capabilities: India's involvement in Antarctic logistics and operations could provide valuable opportunities to enhance its maritime capabilities, including navigation in icy waters, ship-building for polar environments, and developing advanced icebreaker vessels.
- This would bolster India's strategic interests in the Indian Ocean region and beyond.
- Exploring Bioprospecting Opportunities: Antarctica's unique ecosystems have the potential to yield novel microorganisms, enzymes, and bioactive compounds with applications in industries such as pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and agriculture. Indian researchers could explore bioprospecting opportunities in Antarctica, contributing to the country's bioeconomy.
How can India Enhance its Role and Contributions in Antarctica?
- Developing Advanced Autonomous Systems for Polar Exploration: India can be a frontrunner in developing advanced autonomous systems leveraging robotics and artificial intelligence, such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and underwater vehicles (AUVs), specifically designed for polar exploration.
- These systems could be used for mapping, surveying, and monitoring by different countries, enhancing India's scientific diplomacy.
- Collaborate on Rare Earth Element (REE) Exploration: With the growing demand for rare earth elements in high-tech industries, India could collaborate with other nations to conduct geological surveys and assessments of potential REE deposits in Antarctica.
- This could position India as a key player in future responsible and sustainable REE exploration efforts, subject to the Antarctic Treaty System's regulations.
- Invest in Sustainable Infrastructure Development: India could invest in developing sustainable infrastructure in Antarctica, such as renewable energy systems, waste management facilities, and eco-friendly transportation solutions.
- This would not only support India's research and logistical operations but also demonstrate its commitment to minimizing environmental impacts in the region.
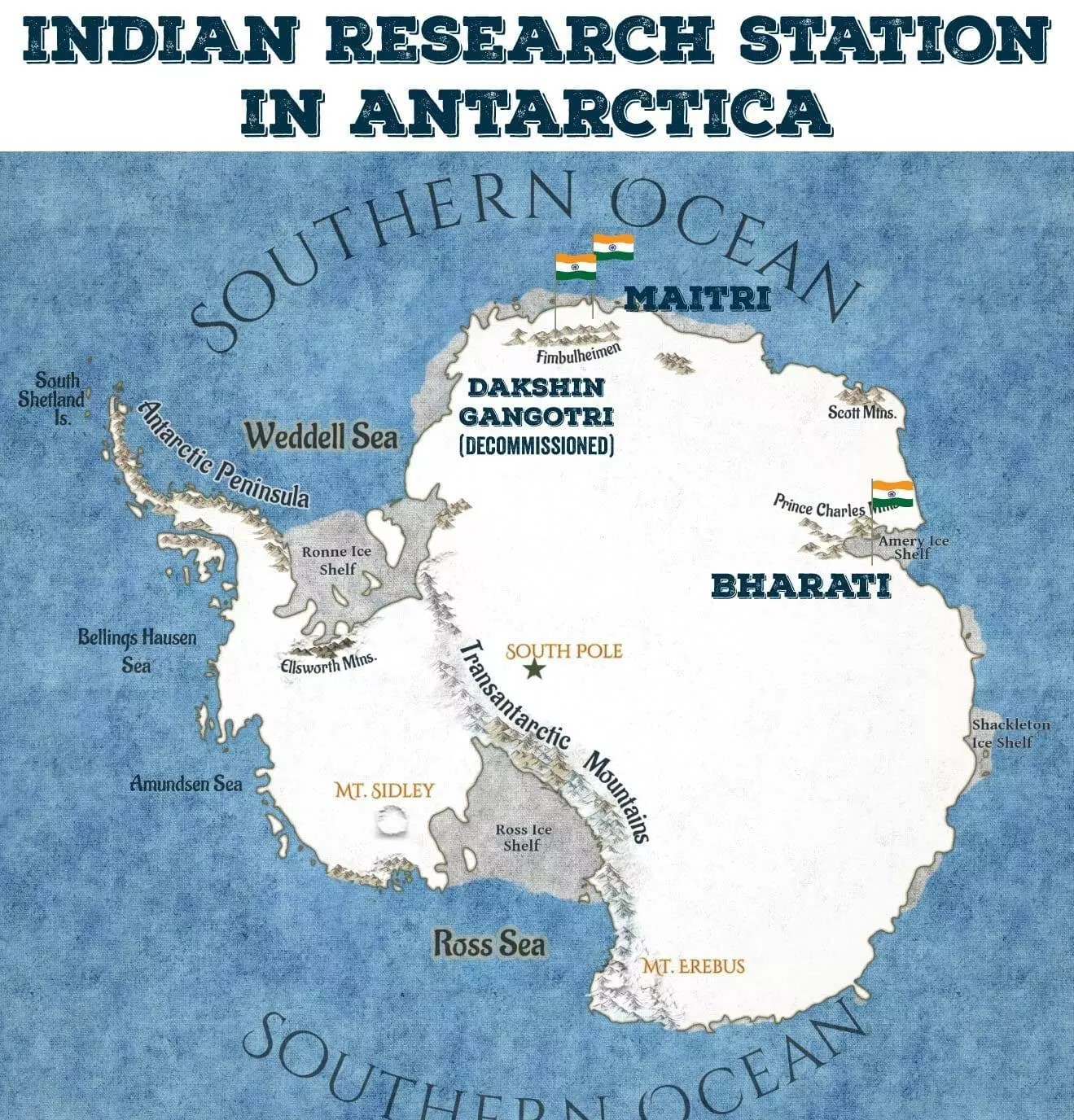
- Currently, Maitri and Bharati are the two active research stations that India operates in Antarctica.
- In April 2024, the Department of Posts opened a second branch of the post office at the Bharati research station in Antarctica after almost four decades.
- Promote Responsible and Sustainable Antarctic Tourism: India could collaborate with international partners to develop guidelines and best practices for responsible and sustainable Antarctic tourism.
- This could involve training Indian tour operators and guides on minimizing environmental impacts, adhering to strict regulations, and offering educational experiences that raise awareness about the region's unique ecosystems and the importance of conservation.
- India, in the 46th Antarctic Treaty Consultative Meeting, pressed for a proposal to introduce a regulatory framework governing tourism in the continent.
Note: In 1984, India established its first post office in Antarctica at Dakshin Gangotri, which was also its first research station. Unfortunately, in 1988-89, Dakshin Gangotri was submerged in ice and subsequently decommissioned.
- National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) is India’s premier R&D institution responsible for the country’s research activities in the Polar and Southern Ocean realms.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the strategic and scientific significance of Antarctica for India and elaborate on how India can enhance its contributions and leadership in the region. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains:
Q. How do the melting of the Arctic ice and glaciers of the Antarctic differently affect the weather patterns and human activities on the Earth? Explain.(2021)
Q. Why is India taking keen interest in resources of Arctic region?(2018)