International Relations
West Asia: A Heavily Militarised Region
This editorial is based on “Tensions grows in west asia, a heavily militiarised region” which was published in The Hindu on 25/04/2024. The article talks about the report of Stockholm International Peace Research Institute that West Asia is among the most heavily militarized regions globally, with four of the top 10 arms importers located there.
For Prelims: Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, Iran, Israel, Middle East,1979 Islamic Revolution, Stuxnet, Gaza Strip, Red Sea Crisis, Israeli air defense system, Two State Solution, Gulf Cooperation Council, European Union, United Nations, Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA)
For Mains: Impact of recent conflict in West Asia in other regions of the world.
Tensions are escalating in West Asia, a region heavily reliant on militarization and accounting for 30% of global arms imports. Despite being a major supplier of extractive resources for global energy consumption, West Asia faces increasing instability due to various conflicts.
The Israel-Gaza conflict, hostilities between Iran and Israel, and ongoing attacks involving Iran-backed militias from Lebanon and Yemen are exacerbating tensions.
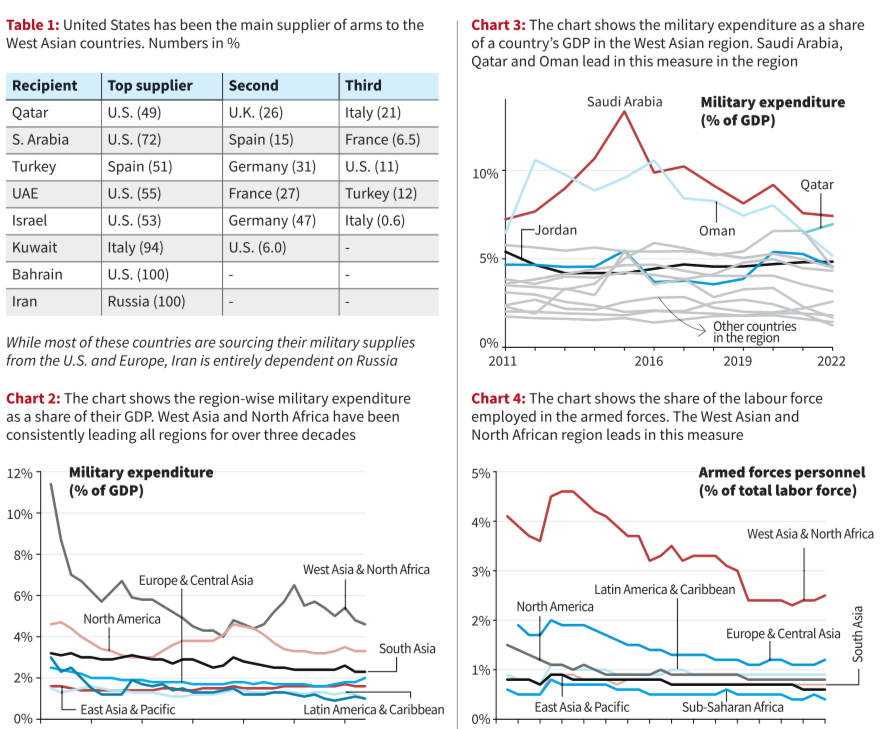
According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, West Asia is among the most heavily militarized regions globally, with four of the top 10 arms importers located there. The United States is the primary arms supplier to the region. This militarization has turned West Asia into a potential powder keg.
What are the Reasons behind Recent West Asia Turmoil?
- Israel launched its war on Gaza, Hezbollah (the Lebanese Shia group) that Iran backs, fired rockets at Israeli forces in the Shebaa Farms, an Israeli-controlled territory that Lebanon claims as its own, in solidarity with the Palestinians.
- Arab countries, too, were upset with Israel’s indiscriminate bombing and stuck to the path of diplomacy to put pressure on the Jewish state.
- Iran-backed militias also opened new fronts against Israel.
- Houthis, the Shia militias of Yemen, started attacking commercial vessels in the Red Sea in mid-November in “solidarity with the Palestinians.”
- They forced several shipping giants to suspend operations in the Red Sea, which connects the Mediterranean Sea with the Arabian Sea (and the Indian Ocean) through the Suez Canal and the Bab el-Mandeb Strait.
- Israel has carried out multiple strikes inside Syria and Lebanon, killing Hamas, Hezbollah and Iranian commanders.
- Iran carried out strikes on January 16 in Iraq’s Kurdistan, Syria and Pakistan, claiming to have hit a Mossad operational centre and Sunni Islamist militants.
- West Asia's military expenditure as a share of GDP remains high, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Jordan, Oman, Kuwait, and Israel consistently allocating significant portions of their GDP to defense.
- Additionally, the region has the highest proportion of its labor force employed in the military compared to other regions.
What is the Historical background behind West Asian Conflict?
- Ottoman Empire’s Influence: Western Asia was largely under the control of the Ottoman Empire from the 14th century AD until the early 20th century.
- The empire managed a diverse population with varying races, religions, and cultures through a successful administrative system.
- Post-World War I Developments: After World War I and the defeat of the Ottoman Empire, the region underwent significant changes. The victorious Allied powers, mainly Britain and France, divided the former Ottoman territories among themselves, often disregarding the wishes of the local Arab population.
- This led to feelings of betrayal and resentment, particularly due to broken promises made in exchange for Arab support during the war.
- Sykes-Picot Agreement:The Sykes-Picot Agreement was a 1916 unofficial treaty between the United Kingdom and France, with assent from the Russian Empire and Italy, to define their mutually agreed spheres of influence and control in an eventual partition of the Ottoman Empire.
- The agreement effectively divided the Ottoman provinces outside the Arabian Peninsula into areas of British and French control and influence.
- Balfour Declaration: The Balfour Declaration was a public statement issued by the British government in 1917 during the First World War announcing support for the establishment of a “national home for the Jewish people” in Palestine, then an Ottoman region with a small minority Jewish population. The declaration had many long-lasting consequences.
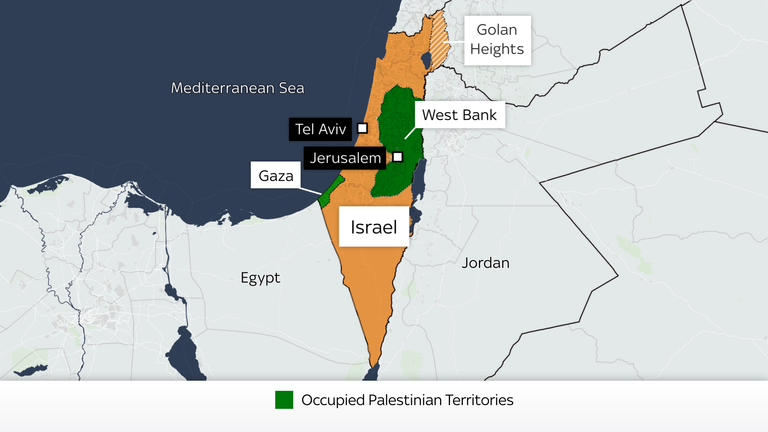
- Creation of Israel :
- In 1917, during world war I The British government issued the Balfour Declaration, expressing support for the establishment of a "national home for the Jewish people" in Palestine.
- After World War II, In 1947, the United Nations proposed a partition plan that would divide Palestine into separate Jewish and Arab states, with Jerusalem as an international city.
- In 1948, Israel declared its independence, leading to a war with neighboring Arab states..
- Arab Israel War (1948):
- In 1948, the Jewish declaration of Israel's independence prompted surrounding Arab states to attack.
- At the end of the war, Israel controlled about 50 % more territory than originally envisioned by the UN partition plan.
- The 1979 Revolution:
- A religious state was established in Iran after the Shah was overthrown in the 1979 Islamic Revolution. The regime’s view of Israel changed, and it was seen as an occupier of Palestinian land.
- Israel’s Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khomeini termed Israel “Little Satan” and the United States the “Great Satan”, seeing the two as parties interfering in the region.
- A Shadow War after 1979:
- As a result, the ties between the countries worsened. While Israel and Iran have never engaged in direct military confrontation, both have attempted to inflict damage on the other through proxies and limited strategic attacks.
- In the early 2010s, Israel targeted several facilities and nuclear scientists in a bit to prevent it from developing nuclear weapons.
- In 2010, the US and Israel are believed to have developed Stuxnet, a malicious computer virus. It was aimed at attacking a uranium enrichment facility at Iran’s Natanz nuclear site and was the “first publicly known cyberattack on industrial machinery”.
- Iran, meanwhile, is seen as responsible for funding and supporting several militant groups in the region that are anti-Israel and anti-US, such as Hezbollah in Lebanon and Hamas in the Gaza Strip.
- Recent Developments:
- Iran's full-scale military attack on Israel and Israel's continued actions in Gaza, further contribute to the region's volatility.
- The persistence of conflicts, including the Yemeni civil war, the Lebanese political crisis, the Syrian civil war, and the Turkey-Cyprus conflict, adds to the concerns of the international community.
Who are the Key Players and Their Divergent Objectives?
- Israel: Aims to dismantle Hamas, release hostages, and neutralize threats to its security.
- Its military actions in Gaza and strikes in other regions reflect this objective.
- Hamas: Seeks to challenge Israeli policies and actions in Gaza and the West Bank.
- As a Palestinian Islamist political organization and militant group, it has been involved in long-standing conflict with Israel.
- Iran: Backs various anti-Israel non-state actors in West Asia (Hamas, the Islamic Jihad, Hezbollah, Houthis or the Shia militias of Iraq and Syria)
- Iran aims to extend its influence in the region, often opposing U.S. and Israeli interests.
- Hezbollah and Other Militias: These groups, often backed by Iran, have engaged in the conflict, primarily in opposition to Israel and in support of Palestinian causes.
- United States: Supports Israel and seeks to maintain regional stability and protect its interests.
- The U.S., which has a widespread military presence in the region and a diplomatic foothold, has three objectives —
- To ensure the security of Israel
- The security of America’s troops and assets deployed in the region
- The perseverance of the U.S.-led order in the region
- Other Regional Actors: Countries like Pakistan have their own strategic interests in the conflict, often influenced by religious, political, and regional dynamics.
What are the Geopolitical Impact of the Conflicts in West?
- Humanitarian Crisis: Continued military actions risk significant civilian casualties and worsening humanitarian conditions, particularly in Gaza.
- Regional Instability: Prolonged conflict can destabilize the already volatile West Asian region, affecting neighboring countries, as the conflict persists, Israel's offensive in Gaza shows little sign of winding down, prompting continued attacks from Hezbollah and the Houthis.
- Global Economic Impact: Disruptions in major shipping routes (like the Red Sea) and oil supply can have global economic repercussions.
- Spread of Extremism: Ongoing conflict can fuel radicalization and give rise to extremist groups, further destabilizing the region.
- International Relations: The conflict strains diplomatic relations among global powers and regional states, complicating international efforts for peace and stability.
- Security Breakdown: Unlike past conflicts in West Asia, which often involved nation-states or state and non-state actors, the current crisis is marked by a widespread security breakdown.
What are the Possible Impacts on India?
- Impact on Energy Security: India’s dependence on imported oil from West Asia makes it vulnerable to price volatility and supply disruptions.
- The increasing competition for energy resources in West Asia can lead to higher prices and greater competition for supplies, making it more difficult for India to secure the energy it needs.
- India is the world's third-largest consumer and importer of oil. More than 40% of India's oil comes from West Asia.
- Indian Diaspora: Indians are residing there in very large numbers and this turmoil can have impact on their wages and incomes.
- Remittances: The non-resident Indians (NRIs) annually send home about USD40 billion, and account for more than 55% of the country’s total remittance inflows.
- As per the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), 82% of the total remittances received by India originated from seven West Asia countries: the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the United States (US), Saudi Arabia, Qatar, Kuwait, the United Kingdom, and Oman.
- Remittances: The non-resident Indians (NRIs) annually send home about USD40 billion, and account for more than 55% of the country’s total remittance inflows.
- Trade and investment: According to the UN Comtrade database, Iran and the GCC member states accounted for a 15.3% share of India’s cumulative two-way merchandise trade from 2017 through 2021.
What is the India’s Approach toward West Asia?
- The Middle East Quad (I2U2) Initiative: The idea behind I2U2 (India, Israel, the U.S. and the UAE) is to connect South Asia, the Middle East, and the United States for economic, technological, and diplomatic collaboration.
- Medical Diplomacy: Vaccine Maitri is a humanitarian initiative undertaken by the Indian government to provide COVID-19 vaccines to West Asia countries.
- For Example: Saudi Arabia , were Bahrain beneficiaries of this initiative.
- Downstream Projects: India invited West Asia countries to invest in downstream projects in India’s hydrocarbon sector.
- The agreement on oil storage and management between Abu Dhabi National Oil Company and the Indian Strategic Petroleum Reserves Limited was signed in January 2017.
- It underscores that crude oil supply from UAE for the Mangalore cavern would be a significant transformational step in building a strategic partnership in the energy sector.
- Strategic Partnership in Energy Sector: Abu Dhabi awarded a major oil concession to an ONGC-led consortium from India in Lower Zakum.
- A High-Level Ministerial Taskforce has been created in order to keep track of various high-level promises and agreements.
- Tech Diplomacy: India is taking the technological route in strengthening its relations with West Asian countries.
- For example, The RuPay card, a key initiative by India in the digital payment system, was launched in Abu Dhabi.
- Cultural Diplomacy: India inaugurated the first Hindu temple in Dubai as a special gift to the Indian community by the UAE. Yoga, Bollywood, and Music are other dimensions of Soft Power.
What are the Approaches proposed to address the conflict?
- Negotiations and Two-State Solution: Many international actors have advocated for a negotiated two-state solution, where Israel and Palestine would coexist as independent states.
- Negotiations would aim to establish clear borders, address issues like the status of Jerusalem, and provide security guarantees for both sides.
- The Oslo Accords: Previous negotiations between Israel and the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) aimed at achieving a two-state solution.
- Various peace plans proposed by international actors, such as the United States, the United Nations, and the Arab League.
- Ceasefire and Humanitarian Assistance: Immediate ceasefire agreements and humanitarian assistance to the people affected by the conflict can help alleviate suffering and create an environment for diplomatic solutions.
- Temporary ceasefires brokered by Egypt, Qatar, and other regional actors to halt hostilities during periods of intense conflict.
- International humanitarian organizations provide aid and support to affected populations in Gaza and the West Bank.
- International Mediation: Involvement of neutral international mediators or organizations, such as the United Nations, to facilitate negotiations and peace talks.
- Addressing Core Issues: Addressing the root causes of the conflict, such as land disputes, access to resources, and the rights of refugees, can contribute to long-term stability.
- People-to-People Initiatives: Encouraging dialogue and cooperation between Israelis and Palestinians at the grassroots level to build trust and understanding.
- Organizations like Seeds of Peace and OneVoice that promote dialogue and cooperation between Israeli and Palestinian youth.
- Joint Israeli-Palestinian ventures in business, education, and culture that foster cooperation.
- Human Rights and International Law: Ensuring that both parties respect international humanitarian law and human rights standards, and holding violators accountable.
- International Criminal Court (ICC) investigations into alleged war crimes and human rights abuses in the region.
- United Nations resolutions condemning illegal settlements and calling for respect of international law.
- Regional Cooperation: Involving regional actors and neighboring countries in peace efforts to create a more stable environment.
- The Arab Peace Initiative, which offers normalization of relations between Israel and Arab states in exchange for a comprehensive peace agreement with the Palestinians.
- Regional summits and initiatives aimed at promoting peace and stability in the Middle East.
- Economic Development: Supporting economic development in the region to improve living conditions and create opportunities for both Israelis and Palestinians.
- The Palestinian Investment Promotion Agency (PIPA) and other organizations working to stimulate economic growth in the West Bank and Gaza.
- International donor conferences to raise funds for infrastructure and economic development projects.
- Security Measures: Implementing measures to ensure the security of both Israelis and Palestinians, which may involve international peacekeeping forces.
- United Nations peacekeeping missions, such as the United Nations Truce Supervision Organization (UNTSO), deployed in the region to monitor ceasefires.
- Border security arrangements and confidence-building measures to reduce violence.
- Educational Initiatives: Promoting education and awareness about the history and culture of both sides to foster understanding and tolerance.
- Educational programs that promote understanding and tolerance, such as the Hand in Hand bilingual schools in Israel.
- Cultural exchange initiatives and joint artistic projects.
Conclusion
It is highly unlikely that the conflicts raging now in Syria, Yemen and other parts of the Middle East will come to an end. It will take too much diligent political manoeuvring to bring all the parties to the negotiation table. Even initiatives such as the West Asia Peace Plan are self-serving at best as they only benefit one party by completely neglecting the other.
|
Drishti Mains Question Discuss the Historical Background behind the West Asian conflict and what are the approaches through which it can be tackled. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following countries of South-West Asia does not open out to the Mediterranean Sea? (2015)
(a) Syria
(b) Jordan
(c) Lebanon
(d) Israel
Ans: B
Q. The term “two-state solution” is sometimes mentioned in the news in the context of the affairs of (2018)
(a) China
(b) Israel
(c) Iraq
(d) Yemen
Ans: B
Mains
Q. “India’s relations with Israel have, of late, acquired a depth and diversity, which cannot be rolled back.” Discuss. (2018)