Governance
Tackling Disparities in Human Development
This editorial is based on “The wide disparities in human development” which was published in the Hindu on 21/03/2023. It discusses the issues of rising disparities in human development and ways to address the same.
For Prelims: United Nations Development Programme, Gross Domestic Product, NFHS-5, Anaemia, World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report 2022, Human Development Index
For Mains: Obstacles that India Faces in Attaining Human Development, Government Policies & Interventions
Human development is not solely focused on the pursuit of economic growth and maximizing wealth in the economy. Instead, it is centered around the idea of humanity, which involves expanding freedom, improving capabilities, promoting equal opportunities, and ensuring a prosperous, healthy, and lengthy life.
India is now one of the fastest-growing economies globally. However, this growth has not resulted in a corresponding increase in its Human Development Index (HDI). According to the Human Development Report of 2021-22, India ranks 132 out of 191 countries, behind Bangladesh and Sri Lanka.
Given India’s size and large population, it is critical to address the subnational or State-wise disparities in human development, which will help India realises its demographic dividend.
What is HDI?
- The HDI is a composite statistical measure created by the United Nations Development Programme to evaluate and compare the level of human development in different regions around the world.
- It was introduced in 1990 as an alternative to conventional economic measures such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which do not consider the broader aspects of human development.
- The HDI assesses a country’s average accomplishment in three aspects: a long and healthy life, knowledge, and a decent standard of living.
- The subnational HDI shows that while some States have made considerable progress, others continue to struggle.
- Delhi occupies the top spot and Bihar occupies the bottom spot.
- Nonetheless, it is worth noting that Bihar, unlike the previous HDI reports, is no longer considered a low human development State.
What are the Obstacles that India Faces in Attaining Human Development?
- Unevenly Distribution of Economic Growth:
- One of the main reasons in achieving human development is that economic growth has been unevenly distributed.
- The top 10% of the Indian population holds over 77% of the wealth.
- This has resulted in significant disparities in access to basic amenities, healthcare and education.
- One of the main reasons in achieving human development is that economic growth has been unevenly distributed.
- Low Quality of Services:
- While India has made significant progress in reducing poverty and increasing access to healthcare and education, the quality of such services remains a concern.
- For example, while the country has achieved near-universal enrolment in primary education, the quality of education remains low.
- While India has made significant progress in reducing poverty and increasing access to healthcare and education, the quality of such services remains a concern.
- Lack of Effective Educational Infrastructure:
- India also faces challenges in providing quality education to its citizens. Many schools lack basic facilities such as adequate classrooms, clean water, and trained teachers.
- Lack of Proper Nutrition:
- Malnutrition and undernourishment are major problems in India, particularly among children. This can have long-term impacts on health, cognitive development, and overall well-being.
- Lack of Social Security:
- India also struggles with providing social security to its citizens, particularly those in the informal sector. Many workers lack access to basic benefits such as health care, retirement pensions, and job security.
- Gender Inequality:
- Despite progress in recent years, gender inequality remains a significant obstacle to human development in India. Women and girls face discrimination in areas such as education, employment, and access to health care, and are often subject to violence and abuse.
- Male-female ratio for Expected Years of Schooling (EYS) declined from 1.43 in 1990 to 0.989 in 2021 and for Mean Years of Schooling (MYS), it declined from 1.26 to 1.06.
- As per the World Economic Forum’s Global Gender Gap Report 2022, women make up only 22% of the AI workforce.
- Despite progress in recent years, gender inequality remains a significant obstacle to human development in India. Women and girls face discrimination in areas such as education, employment, and access to health care, and are often subject to violence and abuse.
What should be the Way Forward?
- Addressing Income Inequality and gender inequality:
- Addressing income inequality and gender inequality requires a multifaceted approach that involves both policy changes and cultural shifts. Here are some potential ways forward:
- Equal Pay, Education and Skill Development, Affordable Childcare, Empowerment programmes for women etc can be helpful.
- Government can focus on promoting these schemes: Beti Bachao Beti Padhao, National Skill Development Mission, Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), Mahila E-Haat.
- Addressing income inequality and gender inequality requires a multifaceted approach that involves both policy changes and cultural shifts. Here are some potential ways forward:
- Invest in Education:
- Education is a fundamental aspect of human development. Governments can invest in education by building schools, hiring teachers, providing scholarships and improving access to education for disadvantaged communities.
- Providing Healthcare:
- Access to healthcare is another critical component of human development. Governments can ensure that all citizens have access to affordable healthcare services, including preventative care, treatment for illnesses, and mental health support.
- Government needs to focus on these schemes: Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), Pradhan Mantri Swasthya Suraksha Yojana (PMSSY), National Urban Health Mission (NUHM), Mission Indradhanush.
- Addressing Poverty:
- Poverty is a significant barrier to human development. Governments can address poverty by implementing social welfare programs, such as unemployment benefits, food assistance, and housing subsidies.
- Promoting Gender Equality:
- Gender equality is essential for human development. Governments can promote gender equality by implementing policies that ensure equal opportunities for women and girls, such as laws against gender discrimination in employment and education.
- Protecting Human Rights:
- Human rights are fundamental to human development. Governments can protect human rights by ensuring that citizens have the right to free speech, freedom of religion, and freedom from discrimination.
- Building Infrastructure:
- Infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, and electricity, is crucial for economic development and human development. Governments can invest in infrastructure projects that improve access to basic services, such as clean water and electricity, and create job opportunities.
- Fostering Innovation and Entrepreneurship:
- Innovation and entrepreneurship can drive economic growth and improve human development. Governments can create policies that support innovation and entrepreneurship, such as tax incentives for small businesses and research grants for scientists and inventors.
|
Drishti Mains Question What are the key obstacles hindering India's progress towards achieving human development, and how can these obstacles be overcome? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
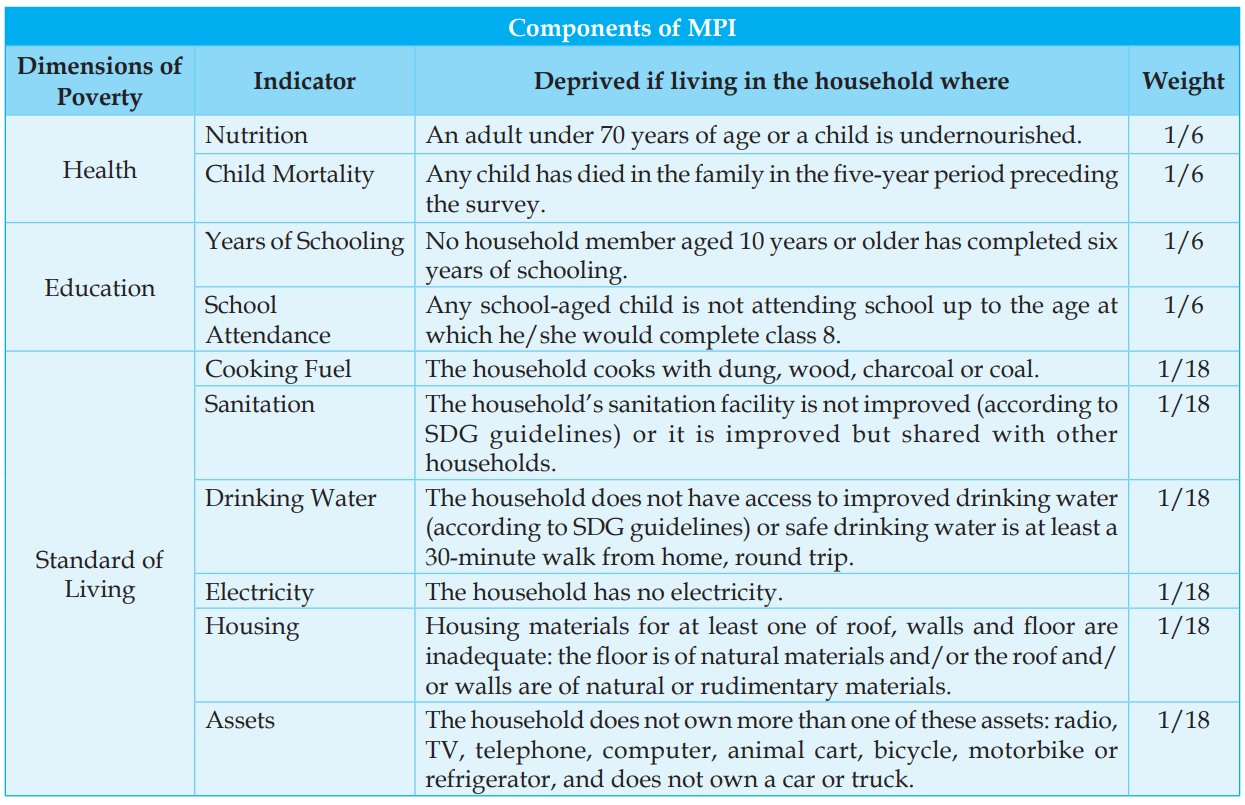
Q. The Multi-Dimensional Poverty Index developed by Oxford Poverty and Human Development Initiative with UNDP support covers which of the following? (2012)
- Deprivation of education, health, assets and services at household level
- Purchasing power parity at national level
- Extent of budget deficit and GDP growth rate at national level
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Multidimensional Poverty Index (MPI) reflects the deprivations that a poor person faces simultaneously with respect to education, health and living standards, as reflected in the following table. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Despite Consistent experience of high growth, India still goes with the lowest indicators of human development. Examine the issues that make balanced and inclusive development elusive. (2016)