ONDC and its Potential
This editorial is based on ONDC has potential to dilute market concentration which was published in The Economic Times on 11/05/2023. It discusses India's government-backed e-commerce platform, the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), and explores its potential and challenges.
For Prelims: Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), UPI
For Mains: Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC): Potential, Challenges and Way Forward
The government’s efforts to use technology to make e-commerce more competitive are beginning to show up in food delivery services. Customers are reporting noticeable price differences in orders placed on online apps using the Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC), which creates a network of interconnected e-marketplaces that makes it easier for small store-owners to tap demand online.
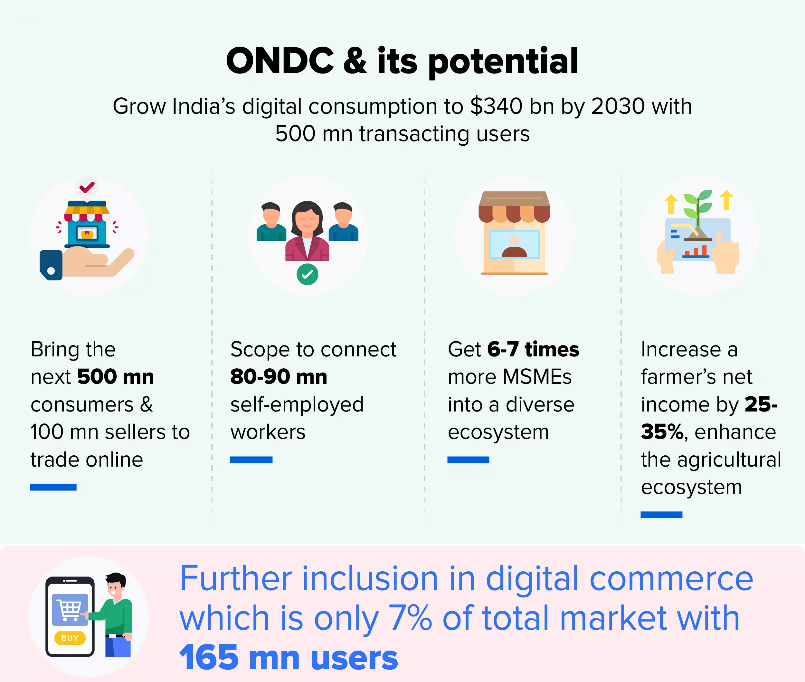
It could be a game-changer on the lines of the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), the infrastructure on which digital transactions are growing in this country exponentially.
What is ONDC?
- About:
- It was launched in late 2021 under the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) by the Ministry of Commerce as part of the Digital India push.
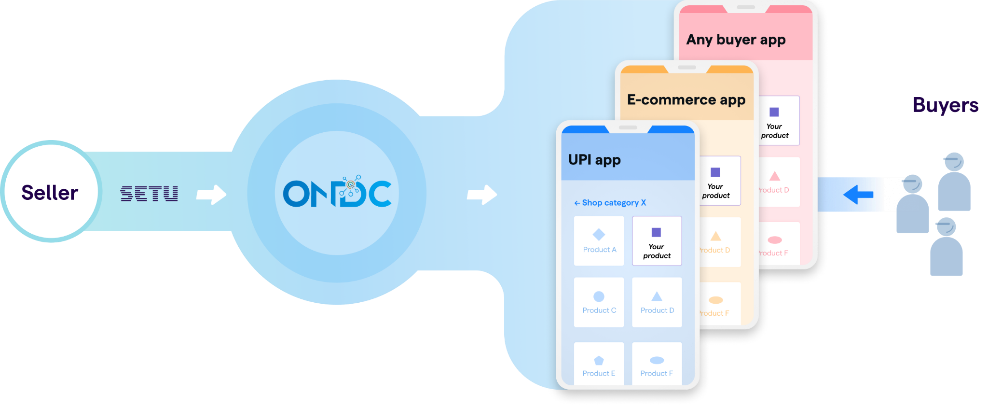
- ONDC works as a network of interconnected e-marketplaces through which sellers, including brands, can list and sell their products directly to customers bypassing any middlemen or intermediaries.
- Along with food delivery, ONDC also offers delivery services for groceries, home decor, cleaning essentials, and other products.
- Objectives:
- Democratisation and decentralization of e-Commerce
- Inclusivity and access for sellers, especially small and medium enterprises as well as local businesses
- Increased choices and independency for consumers
- Making goods and services cheaper
- Working Mechanism: ONDC functions on the basis of an open network where it will not be a single platform similar to Amazon or Flipkart but rather in the form of a gateway where buyers and sellers across different platforms will be able to connect.
What are the Potential Advantages of ONDC?
- Increased Transparency: ONDC can provide greater transparency by making government data more accessible to the public. This can help increase trust and accountability.
- Increased Customer Choice: ONDC has the potential to dilute market concentration by increased consumer choice and lower entry barriers.
- Innovation: ONDC can spur innovation by providing entrepreneurs and researchers with access to government data. This can lead to the development of new products and services that benefit society.
- Cost Savings: ONDC can save money by reducing duplication of effort and enabling more efficient use of resources.
- Platform fees for food delivery using ONDC are being reported at a fifth of those charged by the market leaders. This is a considerable reduction in the cost of intermediation.
- Protecting the Consumers’ Interest: By breaking the hegemony of existing e-commerce, ONDC can bring huge benefits to consumers.
- Level Playing Field: ONDC is keen to level the playing field for e-commerce operators and widen the digital market access for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) and small traders in the country.
- Neutral and Regulated Platform: ONDC aims at fostering open networks developed on open-sourced methodology, using open specifications and network protocols, and independent of any specific platform.
What are the challenges ahead?
- Complexity: ONDC is a complex mechanism as compared to other systems like UPI. People found UPI's convenience appealing, which made them adopt it. The same may not be true for ONDC.
- People have already become accustomed to the user interface of existing companies.
- Increase in Disputes: In ONDC, only the buying and selling process happens online, while the delivery and use of the product happens offline. This can lead to more disputes as ONDC is not an intermediary platform.
- Lack of a Robust Grievance Addressal Mechanism: The lack of clarity on responsibility for customer service and handling complaints may deter people from joining the platform.
- Not an Easy-Peasy Task: The existing e-Commerce companies have deepened up ties with the consumers through their lucrative and interoperable services. Like Amazon provides its streaming platform along with its prime membership.
- So, it’ll not be easy for the ONDC to attract the customers.
- Goods & Services may not be Really Cheaper: Since ONDC is a facilitator of trade among buyers and sellers, it may not be able to provide offers the products like existing players. For Example, Amazon has tied up ICICI bank to provide 5% cashback on goods purchases through Amazon ICICI Credit Card.
What should be the Way Forward?
- A better digital space for e-commerce must be built by the government in order to compete with the dominant e-commerce platforms.
- Along with this, it's important to create a proper digital education policy that takes into account various languages and user-friendly interface for the benefit of the consumers as well as sellers.
- A massive, well-funded adoption campaign will be needed to bring over small sellers like kirana stores to the platform.
- The demand and supply sides should be able to access a secured single window to resolve issues such as information asymmetry, opaque pricing, quality concerns, and buyer-seller disputes.
- Proper Grievance Redressal Mechanism: There should be a secured single window to navigate both the demand and supply-side problems like information asymmetry, opaque pricing, quality and product concerns and buyer-seller conflict.
| Drishti Mains Question
The Open Network for Digital Commerce which has been launched recently by Ministry of Commerce & Industry has a huge potential to revolutionise the e-Commerce sector in India. In this light discuss the challenges in promoting the platform and suggest some way forward also. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following: (2022)
- Aarogya Setu
- CoWIN
- DigiLocker
- DIKSHA
Which of the above are built on top of open-source digital platforms?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)