Indian Economy
Rise of the Gig Economy in India
This article is based on “Making the ‘gig’ work” which was published in Hindu Business Line on 10/01/2023. It talks about the Gig economy in India and related challenges.
For Prelims: Gig Economy in India, Gig Worker, Open Market system, High-speed Internet, Economic Liberalisation, E-commerce, Social security, Labour Rights.
For Mains: Growth Drivers of the Gig Economy in India, Issues Associated with the Gig Economy in India, Social Security Blanket for Gig Workers.
The Gig Economy in India refers to the trend of individuals working temporary or flexible jobs, often through online platforms such as Uber, Ola, Swiggy, and Zomato. This type of work has grown in popularity in recent years as it offers more flexibility and independence for workers, and can be a cost-effective solution for businesses.
However, there are also concerns about the lack of job security and benefits for gig economy workers. The gig economy in India is expected to continue to grow in the future, but it should also be backed by government regulations and policies to protect workers' rights and ensure fair treatment.
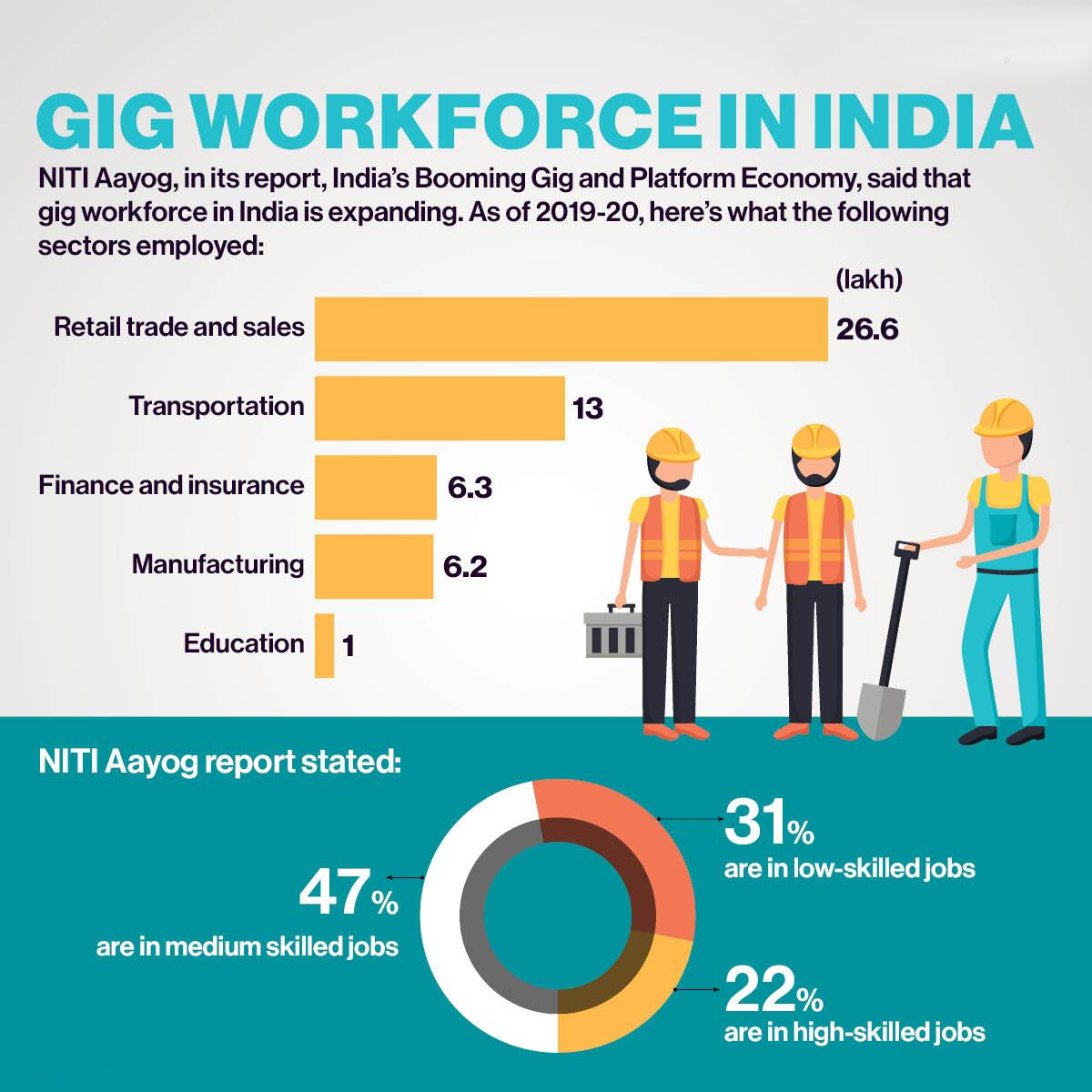
What is the Gig Economy?
- A Gig economy is a free market system in which temporary positions are common and organisations contract with independent workers for short-term engagements.
- Gig Worker: A person who performs work or participates in a gig work arrangement and earns from such activities outside of traditional employer-employee relationship.
- According to a report by Boston Consulting Group, India’s gig workforce comprises 15 million workers employed across industries such as software, shared services and professional services.
What are the Growth Drivers of the Gig Economy in India?
- Rise of the Internet and Mobile Technology: The widespread adoption of smartphones and the availability of high-speed internet has made it easier for workers and businesses to connect through online platforms, facilitating the growth of the gig economy.
- Economic Liberalisation: The Indian government's economic liberalisation policies have led to increased competition and a more open market, which has encouraged the growth of the gig economy.
- Increasing Demand for Flexible Work: The gig economy is particularly attractive for Indian workers who are looking for flexible work arrangements that allow them to balance their personal and professional lives.
- Demographic factors: The gig economy is also driven by the large and growing number of young, educated and ambitious Indians who are seeking to improve their livelihoods with side income generation.
- Growth of E-commerce: The rapid growth of e-commerce in India has led to a significant increase in demand for delivery and logistics services, which has in turn led to the growth of the gig economy in these sectors.
What are the Issues Associated with the Gig Economy in India?
- Lack of Job and Social Security: Many gig workers in India are not covered by labour codes and do not have access to benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans.
- Additionally, gig workers often do not receive the same level of protection as traditional employees in the event of injury or illness.
- Digital Divide: The gig economy heavily relies on technology and internet access, this creates a barrier for those who lack access to these resources, and further exacerbates income inequality.
- Lack of Data: There is a lack of data and research on the gig economy in India which makes it difficult for policy makers to understand its size, scope, and impact on the economy and workforce.
- Exploitation by Companies: Gig workers in India are often paid less than traditional employees and may not have the same legal protections.
- Some companies may also exploit gig workers by misclassifying them as independent contractors to avoid liability and avoid paying taxes.
- Social Isolation: Gig workers may not have the same social connections and support systems as traditional employees, as they often work independently and may not have a physical workplace.
What Should be the Way Forward?
- Clear Regulations: The Indian government should establish clear regulations and policies for the gig economy to ensure that gig workers are protected and that companies are held accountable.
- Social Security Blanket: The government should ensure that gig workers have access to social security programs such as pension schemes and health insurance to ensure financial security for older workers.
- Also, gig workers should be granted the same labour rights as traditional employees, including the right to organise and form unions.
- Education and Training: The government should invest in education and training programs for gig workers to improve their skills and increase their earning potential.
- Encourage Fair Competition and Innovation: Government can encourage fair competition by having regulations that prevent companies from misclassifying workers as independent contractors and by enforcing fair trade practices.
- Also, the government can encourage innovation in the gig economy by providing tax incentives, funding and other support to companies that are creating new business models and technologies.
- Linking Women Empowerment with Gig Economy: There is a need to build the right physical and social infrastructure that supports the engagement of women in the gig workforce.
|
Drishti Mains Question Analyse the impact of the gig economy on the traditional labour market and discuss the challenges faced by gig workers in India. |