Internal Security
India’s National Security Strategy
This editorial is based on “India to bring in a National Security Strategy: what is it, why is it important?” which was published in The Indian Express on 06/11/2023. It talks about how a National Security Strategy document outlines the security goals of a nation and the strategies to attain them.
For Prelims : National Security Strategy, National Security Council, National Security Advisory Board, Naresh Chandra Task Force on Security, Gen. D.S. Hooda's Document on NSS, Cold War, Left-wing Extremism, National Security Adviser (NSA), Defence Planning Committee (DPC),Indo- Pacific Region.
For Mains: About National Security Strategy, Significance of National Security Strategy,Challenges for Developing a National Security Strategy, Strategy for Better Formulation of NSS.
After years of deliberations in the military and strategic community, India has started the process of bringing in a National Security Strategy(NSS). The National Security Council Secretariat (NSCS) is in the process of collating inputs from several Central ministries and departments to stitch together the draft of the strategy before seeking the final cabinet approval for it. This is the first time that India will come out with a National Security Strategy.
What is a National Security Strategy?
- About:
- A National Security Strategy document outlines the country’s security objectives and the ways to be adopted to achieve these.
- An NSS should consider traditional (affect only the state) and non-traditional threats(affect the state, individual and the entirety of humanity). Also, It must work within the framework of India's Constitution and democratic principles.
- The strategy often includes assessments of potential threats, resource allocation, diplomatic and military actions, and policies related to intelligence, defense, and other security-related areas.
- Countries with a National Security Strategy:
- Developed nations with advanced military and security structures, such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and Russia, have National Security Strategies.
- China also has a Comprehensive National Security strategy, and Pakistan has released a National Security Policy 2022-2026.
- India’s Previous Attempts to Formulate a National Security Strategy (NSS) :
- Kargil Review Committee Report (2000): The Kargil Review Committee, formed in the aftermath of the Kargil conflict in 1999, submitted a comprehensive report that included recommendations on national security. While the report itself was made public, it did not lead to the immediate formulation of a formal NSS.
- Report of the Naresh Chandra Task Force on Security (2012): In 2012, the Naresh Chandra Task Force on Security submitted a report that discussed various aspects of national security, including defense and intelligence reforms. However, the report did not result in the immediate release of a formal NSS.
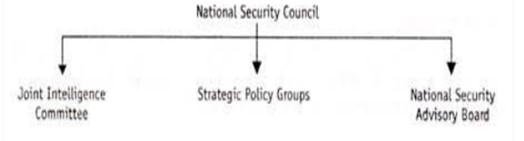
- National Security Advisory Board (NSAB): The NSAB, which comprises experts and advisers on national security matters, has reportedly formulated draft national security strategy documents on multiple occasions. These drafts were presented to successive governments, but a formal NSS did not materialize.
- Gen. D.S. Hooda's Document (2019): In 2019, Lt. Gen. (retd) D.S. Hooda, a former Army Commander, prepared a national security strategy document which marked a significant step toward the development of an NSS for India.
- Suggested Outline of a National Security Strategy Document:
A National Security Strategy document should have the following elements:- a working definition of national security and national security objectives;
- an appreciation of the emerging security environment taking into account the geopolitical changes in the world;
- an assessment of the national strengths and weaknesses of the country in dealing with the challenges;
- identification of the military, economic, diplomatic resources needed to meet the challenges.
What is the Need of the National Security Strategy in India?
- Era of Strategic Uncertainty:
- The end of the Cold War has created a complex and unpredictable global landscape, with a growing number of potential adversaries and expanding missions for armed forces.
- While some regional groupings are assuming state functions, non-state actors like warlords, ethnic chieftains, multinational corporations, and international NGOs are influencing global politics.
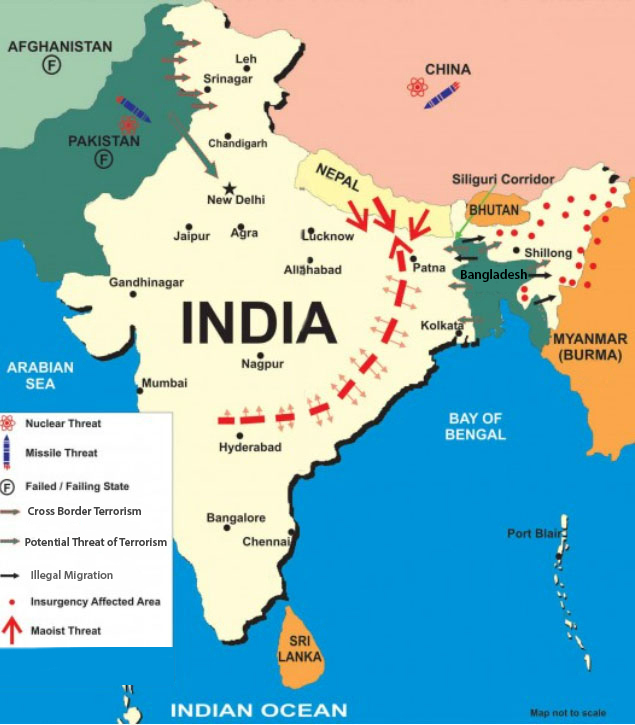
- Key challenges include terrorism, ethnic diversity, small arms proliferation, narcotics trafficking, and religious extremism, which require vigilant attention.
- Nuclear Security and Geopolitical Shifts:
- The future of nuclear deterrence is a vital aspect of India's security. India has long been concerned about the nuclear capabilities of China and Pakistan in its neighborhood.
- India has also expressed concerns about the presence of US nuclear weapons at Diego Garcia, an island in the Indian Ocean.India's nuclear deterrent needs to adapt to technological change and geopolitical shifts.
- Emerging Indo-Pacific Security Framework:
- The balance of power is shifting from North America and Europe to the Indo-Pacific region, which is becoming the new strategic center of gravity.
- An emerging security framework envisions "competitive cooperation" within a matrix of "cooperative security" in the Indo- Pacific Region.
- Challenges Beyond Conventional Threats:
- Domestic stability can be threatened by economic and social issues, such as left-wing extremism in tribal areas.
- Technological Advancements and Cybersecurity:
- Technology impacts national security, by both enhancing capabilities and creating vulnerabilities.
- Cybersecurity is a major concern, requiring advanced technological capabilities.
- Ecological Degradation and Climate Change:
- Environmental changes have security implications, such as glacier melting and sea-level rise.
- Need to Strengthen National Security Architecture:
- The National Security Council (NSC) has been underutilized in its advisory role.
- There is a pressing need to empower the authority of the National Security Adviser (NSA).
What can be the Potential Benefits of the National Security Strategy in India?
- Comprehensive Approach: An NSS provides a comprehensive framework for addressing various security challenges, both internal and external, in a holistic manner.
- Clear Objectives: It outlines clear security objectives, helping to define the assets and interests that need protection and the identification of potential threats.
- Policy Guidance: An NSS offers policy guidance, helping the government formulate and implement strategies and policies to safeguard national security.
- Prioritization: It helps prioritize security concerns, enabling the allocation of resources and efforts to the most critical issues..
- Resource Allocation: It assists in resource allocation, enabling efficient use of financial and human resources to enhance security.
- Deterrence: The strategy can help deter potential adversaries by demonstrating a clear and well-thought-out approach to national security
- Whole-of-Government Approach: NSS promotes a "whole-of-government" approach by involving multiple government departments and agencies, ensuring coordination and cooperation in security-related matters.
- Public Awareness: Elements of the NSS can be shared with the public, raising awareness about national security concerns and garnering public support.
- International Engagement: An NSS can guide India's engagement with other countries and international organizations on security matters.
What are the Challenges for Developing a National Security Strategy?
- Political Hesitation: Governments have been reluctant to put their security strategies in writing, possibly due to concerns about commitment traps, potential criticism, or rigidity in decision-making.
- Achieving a political consensus on the content and priorities of the NSS can be challenging, as different political parties may have varying perspectives on national security.
- Legal Framework: Ensuring that the NSS complies with existing legal frameworks, including international agreements and domestic laws, is essential but can be complex.
- Resource Allocation: Allocating the necessary resources, both financial and human, to implement the NSS effectively can be a challenge, especially when there are competing demands on the budget.
- Divergence between the military and political leadership: The bureaucratic setup within the Ministry of Defence and other government agencies may have diverging opinions on a formal NSS.
- Changing Threat Landscape: Adapting the NSS to address evolving security threats, such as cyber threats, terrorism, and non-traditional security challenges, is a continuous challenge.
- Reactive Approach: India has often adopted a reactive approach to national security, addressing security challenges as they arise rather than having a proactive and overarching strategy in place.
- National Security Culture: Building a national security culture that emphasizes the importance of a NSS and systematic thinking about security has been a gradual process.
What are the Recommendations of the Hooda Committee?
The Hooda Committee(2019), under the leadership of Lieutenant General (Retd) D.S. Hooda, crafted the following suggestions to enhance India's National Security Strategy framework :
- Assuming the Rightful Place in Global Affairs:
- India is encouraged to support international cooperation, prioritize equitable and inclusive digital development, and provide an intellectual dimension to global cooperation.
- Engage confidently with major powers, including the US, Russia, and China, based on its own national interests
- India's engagement with the Middle East is emphasized, focusing on shared interests in energy, trade, and security.
- Achieving a Secure Neighborhood:
- India must strengthen relations with neighboring countries through soft power, improved connectivity, and regional trade.
- India-Pakistan relations are strained, with a need for a sustained strategy to pressure Pakistan to end support for terror. Diplomacy, economic isolation, and even limited military actions may be necessary. Nuclear issues must also be addressed through dialogue.
- Future rivalry between China and India is certain, and it must be managed carefully. India desires a peaceful relationship but cannot compromise on core interests, such as border integrity and counterterrorism efforts.
- Resolution of Internal Conflicts:
- In Jammu & Kashmir, countering radicalization and eliminating terrorists must go hand in hand, supported by a clearly defined political objective to mainstream the region with a campaign to replace fear with hope.
- In the North East, there should be a greater focus on development and integration, with a simultaneous effort to resolve the Naga insurgency.
- Tackling LWE requires addressing the root causes like tribal deprivation and exploitation.
- Combating transnational terrorism requires restructuring and cooperation among agencies.
- Protect People from Global and Domestic Risks:
- Effective national security strategy should prioritize the protection of common citizens.
- Risks can arise from global phenomena like climate change and cyber threats and internal changes driven by demographics, urbanization, and inequalities.
- Strengthening Capabilities:
- India needs to enhance capabilities for protecting its citizens and deterring adversaries by securing our Land and Maritime Borders.
- The government must support Research and development for indigenous defense platforms.
- India needs to create a dedicated Cyber Command.
Conclusion
In an ever-evolving world, an anticipatory and flexible National Security Strategy serves asthe cornerstone of India's well-being and success. Through the adoption of a watchful and adaptable National Security Strategy, India can more effectively steer through the dynamic landscape of global security and protect its interests and principles in the 21st century.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the key elements and priorities that India should consider in the National Security Strategy to effectively address current and future security challenges of the country. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.With reference to the ‘Trans-Pacific Partnership’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- It is an agreement among all the Pacific Rim countries except China and Russia.
- It is a strategic alliance for the purpose of maritime security only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: D
Mains :
Q.“The diverse nature of India as a multi-religious and multi-ethnic society is not immune to the impact of radicalism which is seen in her neighborhood.” Discuss along with strategies to be adopted to counter this environment. (200 words) [2014]