Biodiversity & Environment
Arctic Region and Melting Aspirations
This editorial is based on “Fast-melting Arctic ice is turning the ocean acidic, threatening life” which was published in The Indian Express on 03/10/2022. It talks about the impact of Climate Change on the Arctic Region and related issues.
For Prelims: Arctic Region, Climate Change, Himadri Research Base, Greenland, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), Permafrost, Global Warming, State of Global Climate in 2021, Polar bears, National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR).
For Mains: Significance of the Arctic Region for India, Recent Challenges Related to the Arctic Region, India’s Arctic Policy.
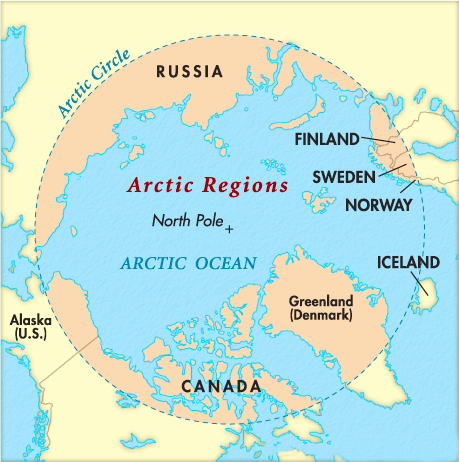
Arctic region, the enormous area around the North Pole spreading over one-sixth of the earth’s landmass. It is increasingly being affected by external global forces: environmental, commercial and strategic and in turn is poised to play an increasingly greater role in shaping the course of world affairs.
By far, Climate Change and the rapid melting of the Arctic Ice cap is the most important phenomenon that is redefining the global perspective on the Arctic.
The impact of rapid changes in the Arctic region goes beyond the littoral states. There is a need for global cooperation to respond to the current challenges regarding conservation, governance and the exploration of Arctic.
What is the Significance of the Arctic Region?
- Economic Significance:
- Mineral Resources and Hydrocarbons: Arctic region has rich deposits of coal, gypsum and diamonds and also substantial reserves of zinc, lead, placer gold and quartz. Greenland alone possesses about a quarter of the world's rare earth reserves.
- The Arctic also contains a wealth of unexplored hydrocarbon resources.amounting to 30% of the world’s undiscovered natural gas.
- India is the 3rd largest energy-consuming country in the world, the 3rd-largest oil importer. Increasing ice-melt makes these resources more accessible and feasible for extraction.
- The Arctic can therefore potentially address India’s energy security needs and deficiency of strategic and rare earth minerals.
- Mineral Resources and Hydrocarbons: Arctic region has rich deposits of coal, gypsum and diamonds and also substantial reserves of zinc, lead, placer gold and quartz. Greenland alone possesses about a quarter of the world's rare earth reserves.
- Geographical Significance: The Arctic helps circulate the world's ocean currents, moving cold and warm water around the globe.
- Also, Arctic sea ice acts as a huge white reflector at the top of the planet, bouncing some of the sun's rays back into space, helping keep the Earth at an even temperature.
- Geopolitical Significance:
- Countering China From Arctic: The melting Arctic ice is also raising the geopolitical temperatures to levels not seen since the Cold War. China referred to trans-Arctic shipping routes as the Polar Silk Road, identifying it as a third transportation corridor for the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and is the only country apart from Russia, to be constructing nuclear ice-breakers.
- As a result, it is crucial to counter China's soft power manoeuvres in the Arctic, in line India is also taking a keen interest in the Arctic states through its Arctic policy.
- Countering China From Arctic: The melting Arctic ice is also raising the geopolitical temperatures to levels not seen since the Cold War. China referred to trans-Arctic shipping routes as the Polar Silk Road, identifying it as a third transportation corridor for the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and is the only country apart from Russia, to be constructing nuclear ice-breakers.
- Environmental Significance:
- Arctic-Himalaya Link: The Arctic and the Himalayas, though geographically distant, are interconnected and share similar concerns.
- The Arctic meltdown is helping the scientific community to better understand the glacial melt in the Himalayas, which has often been referred to as the ‘third pole’ and has the largest freshwater reserves after the North and South poles.
- Therefore, the study of the Arctic is critical to Indian scientists. In line, India launched its first scientific expedition to the Arctic Ocean in 2007 and opened the Himadri research base in the Svalbard archipelago (Norway) and has been actively engaging in research there ever since.
- Arctic-Himalaya Link: The Arctic and the Himalayas, though geographically distant, are interconnected and share similar concerns.
What are the Recent Challenges Related to the Arctic Region?
- Arctic Amplification: In recent decades, the warming in the Arctic has been much faster than in the rest of the world.
- The permafrost in the Arctic is thawing and in turn releasing carbon and methane which are among the major greenhouse gases responsible for global warming amplifying the melting of ice, thereby driving the arctic amplification.
- Rising Sea Level Concern: Melting Arctic ice adds to rising sea levels, which in turn increases coastal erosion and elevates storm surge as warming air and ocean temperatures create more frequent and intense coastal storms likeb
- It can significantly impact India which has a 7,516.6 km of coastline and important port cities.
- According to the World Meteorological Organisation’s report, ‘State of Global Climate in 2021’, sea level along the Indian coast is rising faster than the global average rate.
- It can significantly impact India which has a 7,516.6 km of coastline and important port cities.
- Emerging Race Course: The opening of the shipping routes and possibilities in the arctic is giving thrust to the race of resource extraction leading to the geopolitical poles: US, China and Russia, jockeying for position and influence in this region.
- Tundra Degradation: Tundra is returning to swampy state because sudden storms are ravaging coastlines especially interior Canada and Russia, and wildfires are damaging permafrost in tundra areas.
- Threat to Biodiversity: The absence of year-long ice and higher temperatures are making the survival of Arctic animal life, plants and birds difficult.
- Polar bears need sea ice to hunt seals as well as to move across the large home ranges. Due to shrinking ice, life of polar bears along with other Arctic species are under threat.
- Also, warming seas have triggered a poleward shift in fish species reshuffling the food web.
What Should be the Way Forward?
- Opportunity for India:
- Whole-of-Government Focus: Presently, the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) deals with polar and Southern Ocean realms. includes the Arctic. The Ministry of External Affairs provides the external interface to the Arctic Council.
- There is a need to devise a single nodal body to explicitly deal with Arctic Research and Development and coordinate all the activities of the Government of India relating to the Arctic
- Beyond Scientific Approach: India needs to go beyond the purely scientific approach in the Arctic.
- In keeping with its growing stature and consequent say in world affairs, it should be well positioned to understand the dynamics of the Arctic demography and governance, and become the voice of arctic tribes and raising their issues in global forums.
- Whole-of-Government Focus: Presently, the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR) deals with polar and Southern Ocean realms. includes the Arctic. The Ministry of External Affairs provides the external interface to the Arctic Council.
- Towards Global Ocean Treaty: It is important to place global ocean governance under scrutiny and make progress towards a collaborative global ocean treaty with special attention to polar regions and associated sea level rise challenges.
- Safe and Sustainable Exploration: There is a need to promote safe and sustainable resource exploration and development in the arctic region, with efficient multilateral actions taking into account cumulative environmental impacts.
|
Drishti Mains Question The impact of rapid changes in the Arctic region goes beyond the littoral states. Comment. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The term ‘IndARC’, sometimes seen in the news, is the name of (2015)
(a) an indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence
(b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim
(c) a scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region
(d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.1 Why is India taking keen in resources of Arctic region? (2018)
Q.2 What are the economic significances of discovery of oil in Arctic Sea and its possible environmental consequences? (2015)