Navigating the Ethical Frontier of Artificial Intelligence
This editorial is based on “ AI needs cultural policies, not just regulation” which was published in The Hindu on 01/08/2024. The article highlights that to advance AI responsibly, we must balance regulation with promoting high-quality, ethical data, including digitizing and sharing cultural heritage. This approach will ensure more inclusive and effective AI systems by enhancing transparency and access.
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence (AI),Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), Generative AI, World Economic Forum, Autonomous Weapons, The European Union, UK AI Safety Summit, Information Technology Rules 2021, Large Language Models (LLMs), IndiaAI Mission ,Responsible Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Youth, NITI Aayog.
For Mains: Significance of Technology for Indian Society and Ethical Concerns Associated with them.
Artificial Intelligence (AI), which is the ability of machines to mimic human intelligence, promises to transform industries and enhance human capabilities through its advanced data processing and predictive abilities. However, as AI becomes more integral to daily life, its ethical implications demand urgent attention. The technology's potential to perpetuate biases, infringe on privacy, and cause job displacement raises significant concerns. Additionally, the rapid pace of AI development often outstrips existing regulatory frameworks, complicating issues of accountability and responsible use.
The ethical debate around AI encompasses various applications, from automated decision-making in critical sectors to its role in creative fields. Addressing these concerns requires a collaborative approach involving policymakers, technologists, and ethicists. Developing robust ethical guidelines, ensuring transparency, and safeguarding privacy are essential steps. As AI continues to evolve, navigating its ethical frontier is crucial to maximise its benefits while minimising risks and aligning its use with societal values.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- About:
- AI refers to the capability of a computer or robot controlled by a computer to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence and judgment.
- While no AI can handle the full range of tasks an average human can, some AI systems excel at specific tasks.
- AI refers to the capability of a computer or robot controlled by a computer to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence and judgment.
- Characteristics & Components:
- The key feature of AI is its ability to reason and take actions that maximise the likelihood of achieving a particular goal.
- Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI, and Deep Learning (DL) techniques facilitate automatic learning by processing large volumes of unstructured data, such as text, images, or video.
What is Ethical AI?
- About:
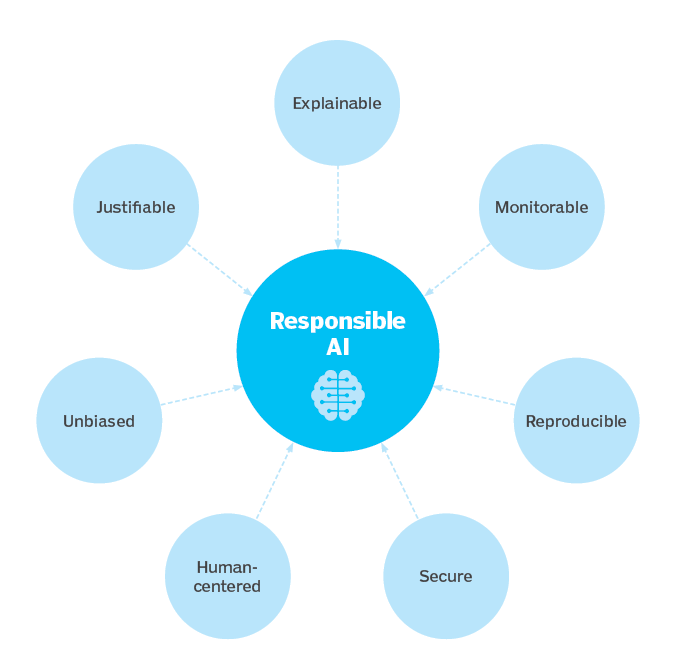
- Ethical AI, also known as Moral or Responsible AI, refers to the development and deployment of AI systems in a manner that aligns with ethical principles, societal values, and human rights.
- It emphasizes the responsible use of AI technology to ensure that it benefits individuals, communities, and society as a whole, while minimizing potential harms and biases.
- Key Aspects of Ethical AI:
| Principle | Description |
| Transparency and Explainability |
|
| Fairness and Bias Mitigation |
|
| Privacy and Data Protection |
|
| Accountability and Responsibility |
|
| Robustness and Reliability |
|
| Benefit to Humanity |
|
What are the Ethical Concerns Associated with AI?
- Deepfakes and Misinformation Concern: The increasing sophistication of AI-generated deepfakes poses a significant threat to the spread of misinformation and disinformation.
- For instance, the creator of the viral deep fake video featuring an actor admitted to the police that the video was made to boost the number of followers on an Instagram channel. This demonstrates a lack of ethics in the use of such technologies.
- Algorithmic Bias: AI systems can perpetuate or amplify existing societal biases if trained on biased data leading to discriminatory outcomes.
- For example, when researchers asked Stable Diffusion (a generative AI model) to generate images of a poor person, the people depicted often appeared to be Black.
- Also, a United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) study found that Large Language Models (LLMs) exhibit significant gender bias, homophobia, and racial stereotyping.
- For instance, women were disproportionately associated with domestic roles and terms like “home” and “family,” whereas men were more often linked to “business” and “career.”
- Challenges of Primary Source Representation: AI systems often rely on secondary sources, predominantly in English, and miss out on primary sources like archival documents and oral traditions.
- Neglecting primary sources can result in the underrepresentation or misrepresentation of certain societies and cultures. This oversight often leads to biases being embedded in the data used to train AI models.
- Accessing and digitizing the primary literacy sources could enhance AI's understanding of diverse cultures and histories but remains largely untapped.
- Data Privacy: The collection and use of personal data for AI development raises concerns about privacy infringement and misuse. Also, the increasing reliance on AI for surveillance purposes can lead to mass surveillance and erosion of civil liberties.
- For instance, generative AI tools that are trained on data scraped from the internet might retain personal details about individuals, including information about their family and friends leading to potential identity theft or fraud.
- Black Box Problem: Many AI models are complex and difficult to understand, making it challenging to explain their decision-making processes. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability.
- For instance, self-driving cars face complex ethical dilemmas, such as deciding who to prioritise in an accident scenario.
- Liability Issue: Determining who is responsible when an AI system causes harm is a complex legal and ethical challenge.
- For example, Air Canada was held liable for a negligent misrepresentation made to a customer by one of its chatbots in a case that highlights broader risks businesses must consider when adopting AI tools.
- Automation and Unemployment: The potential for AI to automate jobs raises concerns about job displacement and economic inequality. The rapid pace of AI development can lead to economic disruption and challenges for industries and workers.
- For instance, according to the World Economic Forum, around 85 million jobs may be lost to AI by 2025. Such a scenario may lead to an increase in economic inequality.
- Data Ownership: The ownership of data generated by individuals is a complex legal and ethical issue. As AI systems increasingly rely on user-generated content, questions arise about who owns the data and how it can be used. It also raises concerns on copyright and intellectual property rights.
- For instance, the creation of art using AI raises questions about copyright ownership and the potential for plagiarism and copyright infringement.
- Autonomous Weapons: The development of autonomous weapons raises questions about the role of humans in decision-making and the potential for unintended consequences. The use of lethal force by autonomous systems presents complex ethical and security dilemmas.
- Digital Divide: Unequal access to AI technology can exacerbate existing social inequalities.
- For instance, with internet penetration at around 52% of the total population in India, discriminate use of AI could further lead to widening of the digital divide and benefits of AI.
- Environmental Ethics: The development and deployment of AI technologies have environmental impacts, raising questions about sustainability and ethical responsibility.
- In its latest annual environment report, Google noted a 17% rise in electricity use by data centers in 2023, a trend expected to persist as AI tools become more widely deployed and used.
What Steps Have Been Taken to Address Ethical Concerns of AI?
- At International Level:
- Global Alliance for Social Entrepreneurship: At the World Economic Forum 2024 in Davos, the Schwab Foundation’s Global Alliance for Social Entrepreneurship launched a new initiative on AI for Social Innovation, co-initiated by Microsoft.
- This initiative, involving major tech and ecosystem leaders, aims to promote the use of AI for positive social impact, showcase successful applications, and develop responsible implementation guidelines.
- EU AI Act: The European Union has come up with the first comprehensive AI regulation (EU AI Act) that aims to govern the risks of AI systems and protect fundamental rights of EU citizens.
- Countries like China, Canada, and Singapore have introduced their own AI regulations or guidelines.
- Example of California: Lawmakers of California have advanced a bill requiring AI companies to test their systems and implement safety measures to prevent misuse, such as attacks on the electric grid or aiding in chemical weapon creation.
- Effects by Tech Gaints: Microsoft, Meta, Google, Amazon and Twitter are among the companies that have formed responsible AI teams, who advise on the safety of consumer products that use artificial intelligence and oversee their alignment with ethical standards, and foster accountability.
- UK AI Safety Summit: The 2023 UK AI Safety Summit focused on addressing the safety and security aspects of AI, emphasizing the need for international cooperation.
- Global Alliance for Social Entrepreneurship: At the World Economic Forum 2024 in Davos, the Schwab Foundation’s Global Alliance for Social Entrepreneurship launched a new initiative on AI for Social Innovation, co-initiated by Microsoft.
- At National Level:
- Advisory on AI Models: The Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeiTY) issued an advisory on AI models and deepfakes in 2024, under Information Technology Rules 2021.
- IndiaAI Mission: The IndiaAI mission aims to foster AI innovation by creating a robust ecosystem through strategic public-private partnerships.
- It will enhance computing access, data quality, and indigenous AI capabilities, attract top talent, support startups, and promote ethical, impactful AI for responsible, inclusive growth in India's AI sector.
- Responsible AI for Youth: The government has launched a National Program for the youth namely, ‘Responsible Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Youth’.
- National Strategy on AI: In 2018, NITI Aayog released the National Strategy on Artificial Intelligence (NSAI), which outlined a roadmap for safe and inclusive AI adoption across five public sectors in India.
- The strategy introduced the "AI for All" mantra as a benchmark for future AI development and emphasised ensuring the responsible use of AI.
Other Initiatives Related to AI
What Should be the Road Ahead?
Addressing the ethical challenges of AI requires a multidisciplinary approach involving policymakers, technologists, ethicists, and civil society. Key steps include:
- Develop and Implement Ethical Frameworks: Create comprehensive ethical guidelines and regulations at national and international levels to govern AI development and deployment.
- Enhance Diversity and Inclusivity: Ensure that AI development teams are diverse to reduce biases and foster inclusive design. For example, accessing and digitizing the primary literary sources could enhance AI's understanding of diverse cultures and histories but remains largely untapped.
- Digitising Cultural Heritage. It can provide AI with a rich and diverse dataset, transforming our understanding of history and safeguarding cultural artifacts. This effort could benefit smaller companies and the open-source AI community by democratizing access to data and fostering global innovation.
- Adopt Best Practices: Follow established best practices for transparency, fairness, and accountability in AI systems.
- Promote Transparency and Explainability: Design AI systems that provide clear and understandable explanations for their decisions and actions.
- Implement Algorithmic Audits: Regularly assess AI systems for fairness and bias through audits to maintain accountability.
- Strengthen Privacy and Data Protection: Adopt strong data privacy measures and ensure secure handling of personal and sensitive information. Also, obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting or utilizing their data.
- Invest in AI Ethics Education and Training: Integrate ethics courses into AI and computer science curricula and offer ongoing ethics training for AI professionals.
- Raise Public Awareness: Educate the public about AI technologies, their benefits, risks, and ethical implications.
- Establish Accountability and Oversight Mechanisms: Develop regulatory bodies to monitor AI systems and ensure compliance with ethical standards.
- Implement Accountability Measures: Define clear lines of responsibility for AI decisions and outcomes, and address violations through legal and regulatory frameworks.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Discuss the ethical challenges associated with the use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in decision-making processes within public sector institutions. How can these challenges be effectively managed to ensure transparency and accountability? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
1. Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
2. Create meaningful short stories and songs
3. Disease diagnosis
4. Text-to-Speech Conversion
5. Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Impact of digital technology as a reliable source of input for rational decision making is an issue. Critically evaluate with suitable examples. (2021)