Free Foodgrains Scheme
For Prelims: National Food and Security Act, 2013, Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana
For Mains: National Food and Security Act, 2013, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food and Public Distribution issued a notification to provide free foodgrains (rice, wheat and coarse grains) to all eligible households under the National Food Security Act, 2013, for one year from January 1, 2023.
- The government, however, discontinued the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana.
What are Coarse Cereals?
- Coarse cereals are traditionally grown in resource-poor agro-climatic regions of the country.
- Agro-climatic zone is a land unit in terms of major climates suitable for a certain range of crops and cultivars.
- Sorghum, pearl millet, maize, barley, finger millet and several small millets such as kodo millet, little millet, foxtail millet, proso millet and barnyard millet together called coarse cereals.
- Sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet, maize and small millet (barnyard millet, proso millet, kodo millet and foxtail millet) are also called nutri-cereals.
- Coarse cereals are known for their nutri-rich content and having characteristics like drought tolerance, photo-insensitivity and resilient to climate change etc.
What is NFSA?
- Notified On:
- 10th September, 2013.
- Objective:
- To provide for food and nutritional security in the human life cycle approach, by ensuring access to adequate quantities of quality food at affordable prices to people to live a life with dignity.
- Coverage:
- 75% of the rural population and upto 50% of the urban population for receiving subsidised foodgrains under the Targeted Public Distribution System (TPDS).
- Overall, NFSA covers about 81.35 crore citizens.
- Eligibility:
- Priority Households are to be covered under TPDS, according to guidelines by the State government.
- Households are covered under the Antyodaya Anna Yojana.
- Provisions:
- 5 Kgs of foodgrains per person per month at Rs. 3/2/1 per Kg for rice/wheat/coarse grains.
- The existing AAY household will continue to receive 35 Kgs of foodgrains per household per month.
- Meal and maternity benefits of not less than Rs. 6,000 to pregnant women and lactating mothers during pregnancy and six months after child birth.
- Meals for children upto 14 years of age.
- Food security allowance to beneficiaries in case of non-supply of entitled foodgrains or meals.
- Setting up grievance redressal mechanisms at the district and state level.
What are Government Initiatives in this Regard?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the provisions made under the National Food Security Act, 2013, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The families coming under the category of ‘below poverty line (BPL)’ only are eligible to receive subsidised food grains
- The eldest woman in a household, of age 18 years or above, shall be the head of the household for the purpose of issuance of a ration card.
- Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a ‘take-home ration’ of 1600 calories per day during pregnancy and for six months thereafter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Hunger and Poverty are the biggest challenges for good governance in India still today. Evaluate how far successive governments have progressed in dealing with these humongous problems. Suggest measures for improvement. (2017)
Q. What are the reformative steps taken by the Government to make the food grain distribution system more effective? (2019)
Q. What are the major challenges of Public Distribution System (PDS) in India? How can it be made effective and transparent? (2022)
Vokkaligas, Lingayats share in Reservation
Prelims: Socio-cultural Reform Movements, Vokkaligas, Lingayats, OBC.
Mains: Vokkaligas and Lingayats Communities.
Why in News?
Recently, Karnataka has categorized the two dominant communities, Vokkaligas and Lingayats, as “moderately backward” from the “backward” category in a move that could increase their share in reservation for Other Backward Classes (OBC).
What are the Key Points of the Move?
- Karnataka currently has 32% quota for OBC, and 17% and 7% quota for Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes, respectively, taking the total to 56%.
- The Panchamasali sub-sect of Veerashaiva Lingayats has demanded inclusion in the 2A category which has 15% quota from their current 3B category which has 5% quota.
- The Cabinet’s decision is based on the recommendations of the Karnataka State Commission for Backward Classes.
- The Vokkaliga community, which is currently in the 3A category, will be moved to a newly-created 2C category with 4% reservation. And the Lingayat community, which is in the 3B category, will now be in a new 2D category with 5% reservation.
- The Cabinet decision ensures that there is no sub-categorisation of the Lingayat community.
- The Lingayats are a dominant community who make up nearly 17% of Karnataka’s six crore population- followed by Vokkaligas. The new categories will not affect the existing reservation provided to other communities.
- The reservation will be applicable only in education and jobs, and “not political reservation.
Who are Lingayats?
- About:
- The term Lingayat denotes a person who wears a personal linga, an iconic form of god Shiva, on the body which is received during the initiation ceremony.
- Lingayats are the followers of the 12th-century social reformer-philosopher poet, Basaveshwara.
- Basaveshwara was against the caste system and Vedic rituals.
- The Lingayats are strict monotheists. They enjoin the worship of only one God, namely, Linga (Shiva).
- Lingayats had been classified as a Hindu subcaste called “Veerashaiva Lingayats” and they are considered to be Shaivites.
- Separate Religion for Lingayats:
- Lingayats had distanced themselves from Hindu Veerashaivas because the latter followed the Vedas and supported the caste system, to which Basaveshwara was against.
- Veerashaivas are the followers of the five peethas (religious centers), called Pancha Peethas. These peethas are set up on similar lines to the four peethas set up by Adi Shankara.
Who are Vokkaligas?
- It is even believed that the Rashtrakutas and Western Gangas were of Vokkaliga origin.
- Vokkaliga is a category defined in terms of occupation, and to that extent could be an ethnic category; these are largely farmers by origin.
- The Vokkaliga caste originates in the Indian state of Karnataka. In the former princely state of Mysore, the Vokkaligas were the largest community.
- As a community of warriors and cultivators, they have historically wielded tremendous demographic, political, and economic dominance in Old Mysore.
How has the Status of OBC Reservation Emerged Over Time?
- The Kalelkar Commission, set up in 1953, was the first to identify backward classes other than the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and Scheduled Tribes (STs) at the national level.
- The Mandal Commission Report, 1980 estimated the OBC population at 52% and classified 1,257 communities as backward.
- It recommended increasing the existing quotas, which were only for SC/ST, from 22.5% to 49.5% to include the OBCs.
- The central government reserved 27% of seats in union civil posts and services for OBCs [Article 16(4)]. The quotas were subsequently enforced in central government educational institutions [Article 15 (4)].
- In 2008, the Supreme Court directed the central government to exclude the creamy layer (advanced sections) among the OBCs.
- The 102nd Constitution Amendment Act, 2018 provided constitutional status to the National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC), which was previously a statutory body under the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Do government’s schemes for up-lifting vulnerable and backward communities by protecting required social resources for them, lead to their exclusion in establishing businesses in urban economies? (2014)
Q. Discuss the role of the National Commission for Backward Classes in the wake of its transformation from a statutory body to a constitutional body. (2022)
India's Startup Boom
For Prelims: Startup India Seed Fund Scheme, National Startup Awards, SCO Startup Forum, Prarambh
For Mains: Startup Ecosystem and its Significance
Why in News?
According to figures presented in Parliament in December 2022, over the last five years, the number of registered startups in India have grown from 452 in 2016 to 84,012.
- Many of them are located in the cloud, which refers to the servers and data storage that are accessible through the internet, and storage companies are offering a variety of incentives to lure and retain them.
What is the Role of AWS Cloud Services in India's Start-up Boom?
- About:
- AWS, or Amazon Web Services, one of India’s largest providers of cloud-based services, has provided start up credits that allow aspirant startups to use a suite of services from computing, storage and hosting for free.
- AWS has helped “compress” the lifecycle of a startup, allowing them to become more innovative.
- Cloud services mean that they can simulate experiments on the cloud, run tests, fail, and learn from it.
- India has the world’s third-largest startup ecosystem after United States (US) and China and therefore, one of the biggest markets for such cloud services.
- Some of the companies supported by AWS included: HealthifyME, which developed an app called ‘Vaccinate Me,’ which allowed feature phones to book close to 50 million vaccination-appointments.
- AWS also powered the Ayushman Bharat Digital mission as well as the Cowin system for Covid-19 vaccinations.
- India’s Cloud Computing Market:
- India’s cloud computing market was expected to grow at 28.1% during the forecast period until 2027.
- The high concentration and increasing number of small and medium-sized businesses in India that are rapidly shifting towards cloud computing is emerging as the major driving factor for the market.
- Furthermore, growing investment towards the construction of cloud data centres is expected to boost the India cloud computing market.
What is the State of Start-ups in India?
- About:
- 49% of start-ups are from tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
- As of September 2022, India is home to 107 unicorns with a total valuation of USD 340.79 Billion.
- According to the India Venture Capital Report 2021 published by Bain and Company, the number of cumulative start-ups has grown at a CAGR of 17% since 2012 and crossed 1,12,000.
- Major Challenges Related to Start-ups in India:
- Lack of Forward Thrust to Innovation: India’s education system lacks vocational training and industry exposure that keeps students deprived of pursuing innovation. As a result, this makes the Indian higher education system lags behind in terms of research and development.
- Lack of Recognition: Since nearly 70% of the Indian population lives in rural areas that are still deprived from reliable internet access. Consequently, many village-based start-up go unrecognised and are deprived of government funding initiatives.
- Bootstrapped Nature: For running a start-up, a significant amount of working capital is required. Many start-ups in India, especially at early stages, are bootstrapped, i.e., self-funded through the founders’ own savings, since domestic financing is limited.
- Scalability Concern: Small start-ups in India have limited understanding of customers and are confined to only certain regions, where they know the local language and local people.
- Marginal Penetration in Space Sector: Indian startups in fintech and e-commerce are doing exceptionally well, but space startups remain outliers.
- Globally, the space economy is valued at USD 440 billion, with India holding less than 2% of the market.
What are the Government’s Initiatives for Startups?
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS): It aims to provide financial assistance to startups for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry and commercialization.
- National Startup Awards: It seeks to recognize and reward outstanding startups and ecosystem enablers that are contributing to economic dynamism by spurring innovation and injecting competition.
- SCO Startup Forum: The first-ever Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum was launched in October 2020 to develop and improve startup ecosystems collectively.
- Prarambh: The ‘Prarambh’ Summit aims to provide a platform to startups and young minds from around the world to come up with new ideas, innovation and invention.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What does venture capital mean? (2014)
(a) A short-term capital provided to industries
(b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
(c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
(d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- Venture capital is a form of fund for a new or growing business. It usually comes from venture capital firms that specialize in building high risk financial portfolios.
- With venture capital, the venture capital firm gives funding to the startup company in exchange for equity in the startup.
- The people who invest this money are called venture capitalists (VCs). Venture capital investment is also referred as risk capital or patient risk capital, as it includes the risk of losing the money if the venture does not succeed and takes a medium to long term period for the investments to fructify.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
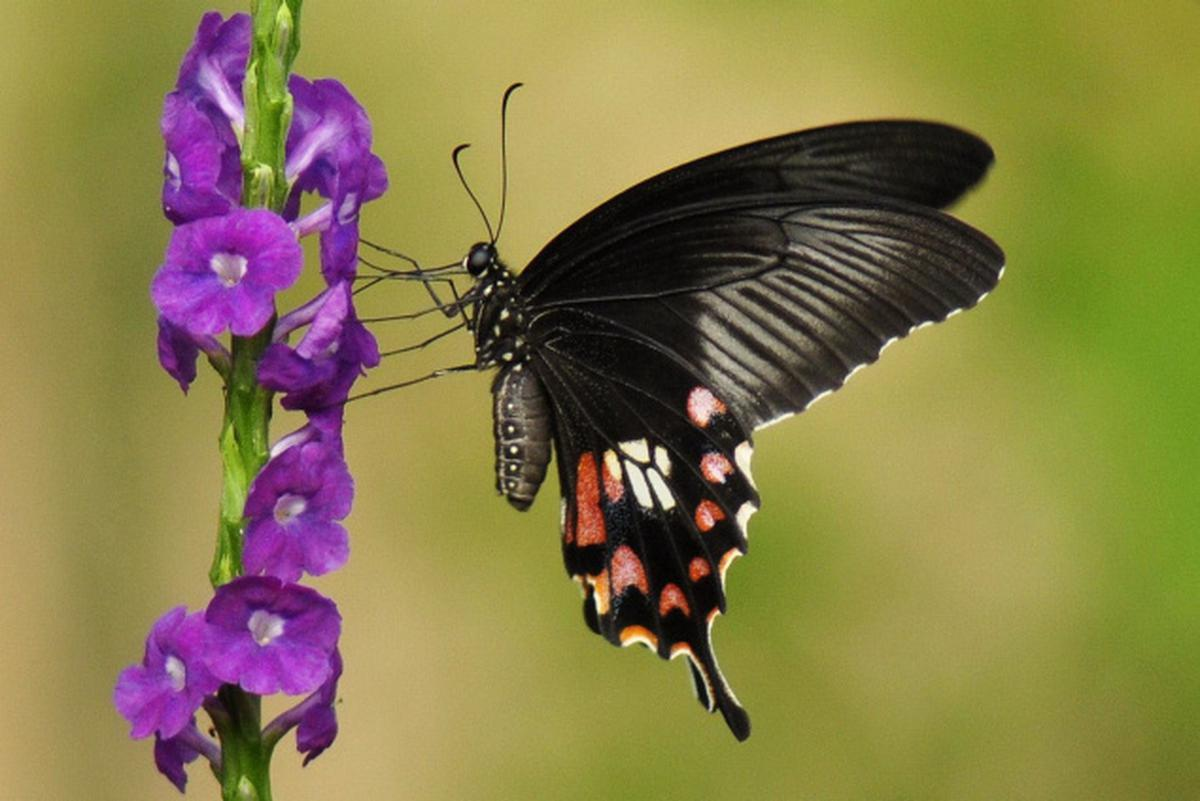
Butterflies Adaptation and Evolution Processes
Why in News?
A new study has thrown light on many interesting aspects of butterflies’ adaptation and evolution processes.
- The study was conducted on several species of butterflies and their imitative traits in the Western Ghats in Karnataka.
What are the Highlights of the Study?
- The findings were categorised into three:
- Model Species: Those that are toxic to predators.
- Batesian Mimicry Species: Those that evolved traits of unpalatable species (poisonous) to avoid predators.
- Non-mimetic Species: Those that are closely related to Batesian mimics but did not evolve mimicry trait.
- The unpalatable one is called models and the palatable one is called mimics.
- Butterflies that have evolved to make use of mimicry evolve faster than the species that don’t make use of mimicry.
- Batesian mimics adapt to avoiding predators by evolving similar wing colour patterns and flight behaviours.
- Analyses revealed that not only had colour patterns evolved at a much faster rate, but that members of mimetic communities had evolved at a faster rate than their close relatives.
- Butterflies exhibit a wide range of colours and colour patterns, suggesting that the genetic architecture underlying wing patterns and colour pigments are relatively malleable and susceptible to change.
What is the Significance of Western Ghats?
- About:
- Western Ghats consist of a chain of mountains running parallel to India’s Western Coast and passing from the states of Kerala, Maharashtra, Goa, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- Significance:
- The Ghats influence the Indian monsoon weather patterns that mediate the warm tropical climate of the region.
- They act as a barrier to rain-laden monsoon winds that sweep in from the south-west.
- Western Ghats are home to tropical evergreen forests, as well as to 325 globally threatened species.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Recently, for the first time in our country, which of the following States has declared a particular butterfly as State Butterfly? (2016)
(a) Arunachal Pradesh
(b) Himachal Pradesh
(c) Karnataka
(d) Maharashtra
Ans: (d)
- Maharashtra became the first State in the country to have a ‘State Butterfly’. It declared the Blue Mormon (Papilio polymnestor) as the State Butterfly.
- It is the second largest butterfly in India after the Troides minos commonly known as the Southern Birdwing.
- It is found only in Sri Lanka, Western Ghats of Maharashtra, South India and coastal belts of the country.
- It has velvet and black wings with bright blue spots. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q. In which of the following regions of India are you most likely to come across the ‘Great Indian Hornbill’ in its natural habitat? (2016)
(a) Sand deserts of northwest India
(b) Higher Himalayas of Jammu and Kashmir
(c) Salt marshes of western Gujarat
(d) Western Ghats
Ans: (d)
- Great Indian Hornbills are large and wide-ranging birds and most species are dependent on tropical forest habitats that contain large and tall trees.
- India has nine Hornbill species, of which four are found in the Western Ghats – Indian Grey Hornbill (endemic to India), Malabar Grey Hornbill (endemic to the Western Ghats), Malabar Pied Hornbill (endemic to India and Sri Lanka) and endangered Great Indian Hornbill. India also has one species that has one of the smallest ranges of any Hornbill – the Narcondam Hornbill, found only on the island of Narcondam in Andaman Sea. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
Prahari App
Why in News?
Recently the Union Home minister launched ‘Prahari’ app for Border Security Force (BSF) Jawans.
- The Ministry also revised 13 BSF manuals to increase the understanding of the administration, training and operations of the border guarding organization.
- These manuals will help speed up the tasks of the BSF jawans. They will ease the work of all ranks of BSF jawans and officers.
What are the Key Features of the App?
- Through the ‘Prahari’ app, jawans can get personal and service-related information, housing, Ayushman- Central Armed Police Forces (CAPF) and leave related information on their mobile.
- Other Features of the App Include:
- Availability of Bio Data
- Grievance redressal on “Centralized Public Grievance Redress and Monitoring System” (CP-GRAMS)”
- Information on various welfare schemes
- The app will also connect the Jawans with the portal of the Ministry of Home Affairs.
What is BSF?
- The BSF was raised in 1965, after the India-Pakistan war.
- It is one of the seven Central Armed Police Forces of the Union of India under the administrative control of the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA).
- Other Central Armed Police Forces are: Assam Rifles (AR), Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP), Central Industrial Security Force (CISF), Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), National Security Guards (NSG) and Sashastra Seema Bal (SSB).
- It is deployed on Indo-Pakistan International Border, Indo-Bangladesh International Border, Line of Control (LoC) along with Indian Army and in Anti-Naxal Operations.
- It has an air wing, marine wing, an artillery regiment, and commando units.
- BSF has been defending Sir Creek in Arabian Sea and Sundarban delta in the Bay of Bengal with its state of art fleet of Water Crafts.
- BSF has an instrumental role in helping state administration in maintaining Law and Order and conducting peaceful elections.
- BSF has been crusading against natural calamity to save precious human lives as and when warranted.
- It contributes dedicated services to the UN peacekeeping Mission by sending a large contingent of its trained manpower every year.
- It has been termed as the First Line of Defence of Indian Territories.
- The Border Security Force has been awarded numerous gallantry awards including one Mahavir Chakra, 4 Kirti Chakras, 13 Vir Chakras and 13 Shaurya Chakras.
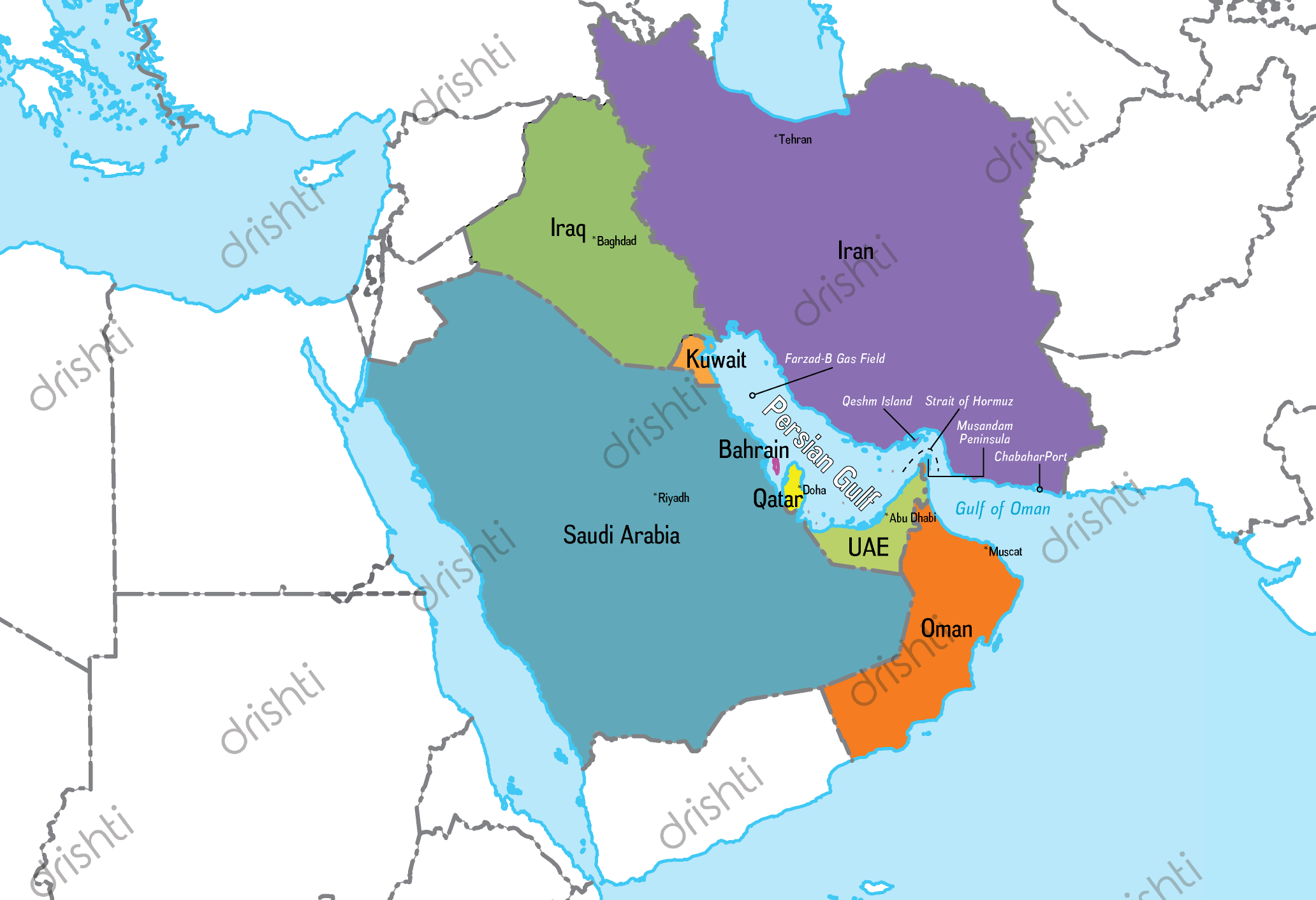
Strait of Hormuz
Why in News?
Recently, the United Arab Emirates and Iran’s military have started their annual Drill in the coastal area of the Gulf of Oman and near the strategic Strait of Hormuz.
- The maneuvers are aimed at improving readiness in confronting foreign threats and any possible invasion.
What is the Strait of Hormuz?
- The strait is located at the mouth of the Persian Gulf and is crucial to global energy supplies, with about a fifth of all oil traded at sea passing through it.
- The waterway separates Iran and Oman, linking the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman and the Arabian Sea.
- The Strait is 33 km wide at its narrowest point, but the shipping lane is just three km wide in either direction.
- Most crude exported from Saudi Arabia, Iran, the UAE, Kuwait and Iraq – all members of the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) – is shipped through this waterway.
- It is also the route used for nearly all the Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) produced by the world’s biggest LNG exporter, Qatar.
- The UAE and Saudi Arabia have sought to find other routes to bypass the Strait, including building more oil pipelines.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which one of the following straits is nearest to the International Date Line? (2008)
(a) Malacca Strait
(b) Bering Strait
(c) Strait of Florida
(d) Strait of Gibraltar
Ans: (b)
- The International Date Line (IDL) is an imaginary line on the Earth‘s surface which functions as a “line of demarcation” separating two consecutive calendar dates.
- The IDL is located halfway around the world from the prime meridian (0° longitude) or about 180° east (or west) of Greenwich (London, UK), the reference point of time zones.
- The date line runs from the North Pole to the South Pole and marks the divide between the Western and Eastern Hemisphere.
- Despite its name, the IDL has no legal international status and countries are free to choose the dates that they observe.
- In the north, the date line swings to the east through the Bering strait and then west past the Aleutian Islands.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
No-Confidence Motion
The Opposition party in Maharashtra moved a no-confidence motion against the Speaker of the State’s Legislative Assembly (SLA).
A no-confidence motion means that one or more members of the Parliament/State Legislature have lost confidence in the appointed government. It can be moved only in LS/SLA by an LS/SLA member. It needs to be supported by at least 50 MPs to be accepted by the Speaker.
If the motion is accepted, then the party in power has to prove its majority in the House (Floor Test). If the government fails to prove its majority in the House, then it has to resign.
Read More - No Confidence Motion, Floor Test
India-Saudi MLAT
India and Saudi Arabia are in talks to sign a Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT) to obtain formal assistance from each other in investigations related to criminal cases.
MLAT is a mechanism whereby countries cooperate with one another in order to provide/obtain formal assistance in prevention/investigation/prosecution of crime to ensure that the criminals don’t escape/sabotage the due process of law.
So far, India has signed MLATs with 45 countries, but Saudi is one of the many other countries with whom India does not have an MLAT. The countries that do not share such a mechanism serve summons, notices and judicial processes on the basis of an "assurance of reciprocity".
Read More - India Saudi Arabia Relations, Mutual Legal Assistance Treaty (MLAT)
RBI Macro Stress Test
The RBI in its latest Financial Stability Report (FSR) conducted macro-stress tests indicating marginal improvement in the Gross NPA ratio of all Scheduled Commercial Banks by Sept 2023.
Marco-stress testing on the banking sector is undertaken to assess the resilience of the banking system to exceptional but plausible stress events. These tests cover credit risk, interest rate risk, liquidity risk and the resilience of commercial banks in response to these shocks.
Generally, RBI considers three scenarios for stress tests: baseline and two adverse - medium and severe scenarios. The baseline is derived from the steady state forecast values of key macroeconomic variables (GDP growth, combined fiscal deficit-to-GDP ratio, CPI inflation, weighted average lending rate, export-to-GDP ratio and current account balance-to-GDP ratio).
Read More - Financial Stability Report: RBI
Increase in Core Sector Output
Production of 8 core sectors increased by 5.4% in November 2022 against a 3.2% (Nov 2021). The 8 core sectors include - Coal, Crude Oil, Natural Gas, Refinery Products, Fertiliser, Steel, Cement, Electricity. These sectors have 40.27% share in the overall Index of Industrial Production (IIP) (decreasing order - Refinery Products> Electricity> Steel> Coal> Crude Oil> Natural Gas> Cement> Fertilisers).
Read More - Eight Core Sectors