Startups in Emerging Technology
For Prelims: Startup India Initiative, DPIIT, Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS), National Startup Advisory Council, Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS)
For Mains: Action Plan for Startup, Various Initiatives related to Startups.
Why in News?
Recently, the Government unveiled an Action Plan for Startup India which laid the foundation of Government support, schemes and incentives envisaged to create a vibrant startup ecosystem in the country.
What are Details of Programs to Support Startups?
- Startup India Action Plan:
- The Action Plan comprises of 19 action items spanning across areas such as “Simplification and handholding”, “Funding support and incentives” and “Industry-academia partnership and incubation”.
- Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS) Scheme:
- The Government has established FFS with a corpus of Rs. 10,000 crore, to meet the funding needs of startups.
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) is the monitoring agency and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) is the operating agency for FFS.
- It has not only made capital available for startups at early stage, seed stage and growth stage but also played a catalytic role in facilitating raising of domestic capital, reducing dependence on foreign capital and encouraging home grown and new venture capital funds.
- Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS):
- The Government has established the CGSS for providing credit guarantees to loans extended to DPIIT recognized startups by Scheduled Commercial Banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and Venture Debt Funds (VDFs) under SEBI registered Alternative Investment Funds.
- Ease of Procurement:
- Government e-Marketplace (GeM) Startup Runway has been developed which is a dedicated corner for startups to sell products and services directly to the Government.
- Support for Intellectual Property Protection:
- The Government launched Start-ups Intellectual Property Protection (SIPP) which facilitates the startups to file applications for patents, designs and trademarks through registered facilitators in appropriate IP offices by paying only the statutory fees.
- The Government bears the entire fees of the facilitators for any number of patents, trademarks or designs, and startups only bear the cost of the statutory fees payable.
- Startups are provided with an 80% rebate in filing of patents and 50% rebate in filing of trademark vis-a-vis other companies.
- Self-Certification under Labour and Environmental laws:
- Startups are allowed to self-certify their compliance under 9 Labour and 3 Environment laws for a period of 3 to 5 years from the date of incorporation.
- Income Tax Exemption for 3 years:
- Startups incorporated on or after 1st April 2016 can apply for income tax exemption.
- The recognized startups that are granted an Inter-Ministerial Board Certificate are exempted from income-tax for a period of 3 consecutive years out of 10 years since incorporation.
- International Market Access to Indian Startups:
- This has been done through international Government to Government partnerships, participation in international forums and hosting of global events.
- Startup India has launched bridges with over 15 countries that provides a soft-landing platform for startups from the partner nations and aid in promoting cross collaboration.
- Faster Exit for Startups:
- The Government has notified Startups as ‘fast track firms’ enabling them to wind up operations within 90 days vis-a-vis 180 days for other companies.
- Startup India Hub:
- The Government launched a Startup India Online Hub in 2017 which is one of its kind online platforms for all stakeholders of the entrepreneurial ecosystem in India to discover, connect and engage with each other.
- National Startup Advisory Council:
- The Government in January 2020 notified the constitution of the National Startup Advisory Council to advise the Government on measures needed to build a strong ecosystem for nurturing innovation and startups in the country to drive sustainable economic growth and generate large scale employment opportunities.
- Besides the ex-officio members, the council has a number of non-official members, representing various stakeholders from the startup ecosystem.
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS):
- The Scheme aims to provide financial assistance to startups for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry and commercialization. Rs. 945 crore has been sanctioned under the SISFS Scheme for a period of 4 years starting from 2021-22.
- National Startup Awards (NSA):
- National Startup Awards is an initiative to recognize and reward outstanding startups and ecosystem enablers that are building innovative products or solutions and scalable enterprises, with high potential of employment generation or wealth creation, demonstrating measurable social impact.
- States’ Startup Ranking Framework (SRF):
- States’ Startup Ranking Framework is a unique initiative to harness the strength of competitive federalism and create a flourishing startup ecosystem in the country.
- The major objectives of the ranking exercise are facilitating states to identify, learn and replace good practices, highlighting the policy intervention by states for promoting startup ecosystems and fostering competitiveness among states.
- Startup India Innovation Week:
- The Government organises Startup India Innovation week around the National Startup Day i.e., 16th January.
- TIDE 2.0 Scheme:
- Technology Incubation and Development of Entrepreneurs (TIDE 2.0) Scheme was initiated by Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) in the year 2019 to promote tech entrepreneurship through financial and technical support to incubators engaged in supporting ICT startups using emerging technologies such as IoT, AI, Block-chain, Robotics etc.
- The Scheme is being implemented through 51 incubators through a three-tiered structure with an overarching objective to promote incubation activities at institutes of higher learning and premier R&D organisations.
- Domain specific Centres of Excellence (CoEs):
- MeitY has operationalised 26 CoEs in diverse areas of national interest for driving self-sufficiency and creating capabilities to capture new and emerging technology areas.
- These domain specific CoEs act as enablers and aid in making India an innovation hub in emerging through democratisation of innovation and realisation of prototypes.
- SAMRIDH Scheme:
- MeitY has launched the ‘Start-up Accelerator Programme of MeitY for Product Innovation, Development and Growth (SAMRIDH)’ with an aim to support existing and upcoming Accelerators to further select and accelerate potential software product-based startups to scale.
- Next Generation Incubation Scheme (NGIS):
- NGIS has been approved to support the software product ecosystem and to address a significant portion of National Policy on Software Product (NPSP) 2019.
- Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC):
- An industry-academia interface agency of Department of Biotechnology, Ministry of Science & Technology is supporting biotech startups in all biotech sectors including clean energy and emerging technologies.
- Project based funding is provided to startups and companies for product/technology development under its key Schemes including Biotech Ignition Grant (BIG), Small Business Innovation Research Initiative (SBIRI) and Biotechnology Industry Partnership Programme (BIPP).
- Incubation support to the startups and companies is also provided through Bioincubators Nurturing Entrepreneurship for Scaling Technologies (BioNEST) Scheme.
Falling Long-Term Growth Prospects
For Prelims: World Bank, EMDEs, South Asia Region, GDP.
For Mains: Falling Long-Term Growth Prospects.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Bank (WB) has released a report titled “Falling Long-Term Growth Prospects: Trends, Expectations, and Policies", stating that the current decade (2020-2030) could be a lost decade for the whole world.
- The report uses a comprehensive database of multiple measures of potential growth.
- It examines trends in potential growth and its drivers, global and regional prospects for potential growth and investment over the 2020s, and a range of policy options to lift potential growth.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Overview:
- Today nearly all the economic forces that drove economic progress are in retreat.
- There has been a protracted, broad-based decline in potential growth and its underlying drivers.
- The slowdown in potential growth is expected to persist for the rest of this decade.
- A decline in long-term growth prospects imperils the ability of Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs) to combat poverty, tackle climate change, and meet other key development objectives.
- Reasons for Slowdown:
- The biggest reason for the slowdown is that the EMDEs are in the midst of a prolonged period of weakness.
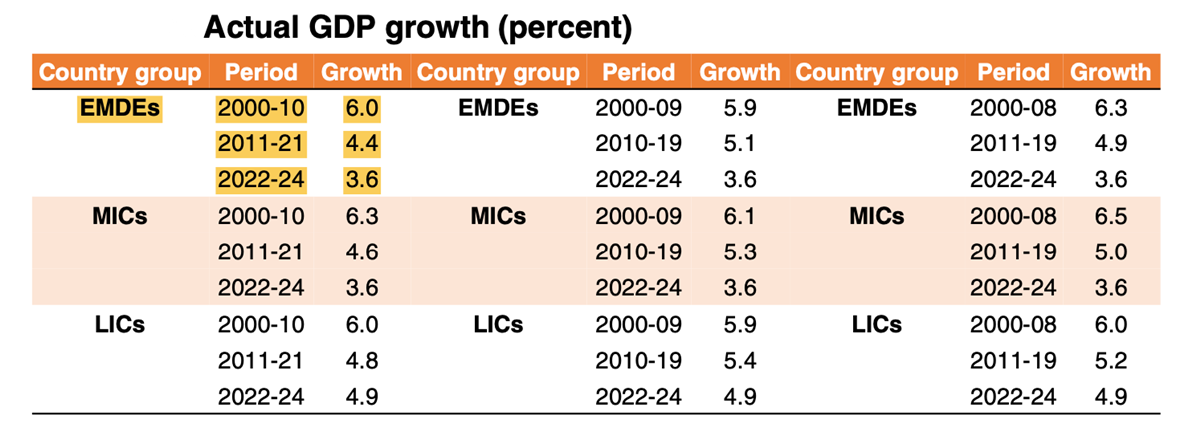
- The World Bank has looked at a whole set of fundamental drivers that determine economic growth and found that all of them have been losing power.
- These fundamental drivers include things like capital accumulation (through investment growth), labor force growth, and the growth of total factor productivity (which is the part of economic growth that results from more efficient use of inputs and which is often the result of technological changes) etc.
- The biggest reason for the slowdown is that the EMDEs are in the midst of a prolonged period of weakness.
- Observations about India:
- Although India has also lost its growth momentum over the past two decades, it is and will likely remain a global leader when it comes to growth rates.
- India falls under the South Asia Region (SAR), which is expected to be fastest growing among emerging market and developing economies for the remainder of this decade.
- SAR includes countries like Afghanistan, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Bangladesh etc.
- Output in the region is on track to grow by about 6.0 % a year between 2022 and 2030, faster than the 2010's annual average of 5.5 %.
What are the Recommendations to boost Potential Global Growth?
- Monetary Fiscal and Financial Frameworks:
- Robust macroeconomic and financial policy frameworks can curb the turmoil in business cycles.
- Policymakers should prioritize taming inflation, ensuring financial-sector stability, reducing debt, and restoring fiscal prudence.
- Scale up Investments:
- Transportation and energy, climate-smart agriculture and manufacturing, and land and water systems.
- In the above-mentioned areas, sound investments aligned with key climate goals could enhance potential growth by up to 0.3 % per year.
- Reduce Trade Costs:
- Trade costs effectively double the cost of internationally traded goods today.
- Countries with the highest shipping and logistics costs could cut their trade costs in half by adopting the trade-facilitation and other practices of countries with the lowest shipping and logistics costs.
- Capitalize on Services:
- The services sector could become the new engine of economic growth.
- Exports of digitally delivered professional services related to information and communications technology climbed to more than 50% of total services exports in 2021, up from 40% in 2019.
- Increase Labor Force:
- About half of the expected slowdown in potential GDP (Gross Domestic Product) growth through 2030 will be attributable to changing demographics.
- This change includes a shrinking working-age population and declining labor force participation as societies age.
- Boosting overall labor force participation rates by the best ten-year increase on record could increase global potential growth rates by as much as 0.2 percentage point a year by 2030.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. India’s ranking in the ‘Ease of Doing Business Index’ is sometimes seen in the news. Which of the following has declared that ranking? (2016)
(a) Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)
(b) World Economic Forum
(c) World Bank
(d) World Trade Organization (WTO)
Ans: (c)
Interchange Charge ON PPI Merchant Transactions
Why in News?
Recently, National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) clarified that there are no charges for bank account - to - bank account based UPI payments.
- NPCI stated that an interchange charge of 1.1% has been introduced on UPI transactions made through PPI instruments above Rs 2,000, and there is no charge to customers.
- Also, NPCI has permitted the PPI wallets to be part of interoperable UPI ecosystem.
What are Prepaid Payment Instruments?
- The RBI defines PPIs as payment instruments that facilitate the buying of goods and services, including the transfer of funds, financial services, and remittances, against the value stored within or on the instrument.
- PPIs are in the form of payment wallets (like Paytm Wallet, Amazon Pay Wallet, PhonePe Wallet, etc.)), smart cards, mobile wallets, magnetic chips, vouchers, etc. As per the regulations, banks and NBFCs can issue PPIs.
What is National Payments Corporation of India?
- About:
- NPCI is an umbrella organisation for all retail payments systems in India. Its primary objective is to provide safe, secure, and efficient retail payment systems in India.
- It aims to promote digital payments and financial inclusion in the country.
- NPCI is an umbrella organisation for all retail payments systems in India. Its primary objective is to provide safe, secure, and efficient retail payment systems in India.
- Establishment:
- NPCI was established in 2008 under the guidance and support of Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Indian Banks' Association (IBA).
- Ownership:
- NPCI is a not-for-profit company, and its ownership is shared by a consortium of major banks in India.
- Products and Services:
- NPCI offers a range of products and services, including Unified Payments Interface (UPI), National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS), RuPay card, and others.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Which one of the following links all the ATMs in India? (2018)
(a) Indian Banks’ Association
(b) National Securities Depository Limited
(c) National Payments Corporation of India
(d) Reserve Bank of India
Ans: (c)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) helps in promoting the financial inclusion in the country.
- NPCI has launched RuPay, a card payment scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
New India Literacy Programme
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of State for Education provided information about the New India Literacy Programme (NILP) in a written reply in the Rajya Sabha.
What is New India Literacy Programme?
- About:
- The Government has launched the Centrally Sponsored Scheme “New India Literacy Programme” (NILP) for implementation during five years from the FYs 2022-23 to 2026-27 with financial outlay of Rs.1037.90 crore.
- Aim:
- The scheme aims to cover a target of 5.00 crore non-literates in the age group of 15 years and above.
- The scheme has five components:
- Foundational Literacy and Numeracy
- Critical Life Skills
- Vocational Skills Development
- Basic Education
- Continuing Education
- Identification of Beneficiaries:
- Door-to-door surveys on a mobile app are conducted by surveyors in the States/UTs to identify beneficiaries.
- Non-literates can also register directly through a mobile app.
- Volunteerism for Teaching and Learning:
- The scheme is mainly based on volunteerism for teaching and learning, and volunteers can register through the mobile app.
- Implementation through Technology:
- The scheme is implemented predominantly through the online mode and is based on technology.
- The teaching and learning material and resources are available on the DIKSHA platform of NCERT and can be accessed through mobile apps.
- Dissemination of Foundational Literacy and Numeracy:
- Modes like TV, Radio, Samajik Chetna Kendra, etc. are also used for dissemination of Foundational Literacy and Numeracy.
- Eligibility:
- All non-literates above 15 years of age are eligible to avail of the benefits of the scheme.
- Need of NILP:
- As per Census 2011, the absolute number of non-literates of the country in 15 years and above age group is 25.76 crore (Male 9.08 crore, Female 16.68 crore).
- In consideration of the progress of persons certified as literates being to the tune of 7.64 crore under the Saakshar Bharat programme implemented during 2009-10 to 2017-18, it is estimated that currently around 18.12 crore adults are still non-literate in India.
Power Generating from Defunct Gold Mines
Why in News?
Recently, an Australian renewable-energy company Green Gravity has proposed a scheme to generate electricity from the defunct Kolar Gold Fields (KGF), in Karnataka, using Low-Tech Gravity Technology.
What is the Mechanism of the Technology?
- The plan is to find defunct mines, which often go hundreds or thousands of meters deep, and haul a Weighted Block, that may be around 40 tonnes, up to the top of the mine shaft using renewable power during the day.
- When backup power is required, the heavy block will fall, under gravity, and the ensuing momentum will power a generator via a connected shaft (or rotor).
- The depth to which the block can slip can be determined via a braking system, thus giving control on the amount of power that can be produced.
- This is similar to the pumped hydropower storage method, where water is pumped uphill electrically into a reservoir, and then released downhill to move a turbine and generate electricity as needed, as in a hydroelectric power plant.
What is the Significance of this Technology?
- A hiccup that makes renewable energy unreliable is that there is no power during nights or windless days. Charging a battery to use as a backup during this downtime hikes power prices.
- Low-tech Gravity Technology can help address this challenge. This technology may use more energy than produced but when accounting for being able to make renewable energy available at off-peak hours, can mean less reliance on coal-produced power and access to reliable power.
- Using weighted blocks instead of water means that decommissioned mines can be put to use and the environmental costs and challenges of moving water up can be avoided.
What are the Key Facts of Kolar Gold Fields?
- Kolar Gold Fields (KGF) is a mining region located in the Kolar district of Karnataka. It is known for its historic gold mines, which were among the deepest in the world.
- Mining in KGF was started by Jhon Taylor & Sons in 1880.
- The mines remained active for 121 years before it experienced an unsystematic closure on February 28, 2001. The mines were closed owing to high operational costs and low revenues.
- Apart from mining Gold, the mines have also been used in particle physics experiments where research teams have discovered elusive, cosmic particles called atmospheric neutrinos.
- Currently, India has three working gold mines in the country -- Hutti and Uti mines in Karnataka and the Hirabuddini mines in Jharkhand.
- India’s gold production is around 1.6 tonnes a year, compared to the 774 tonnes a year of gold that it consumes.
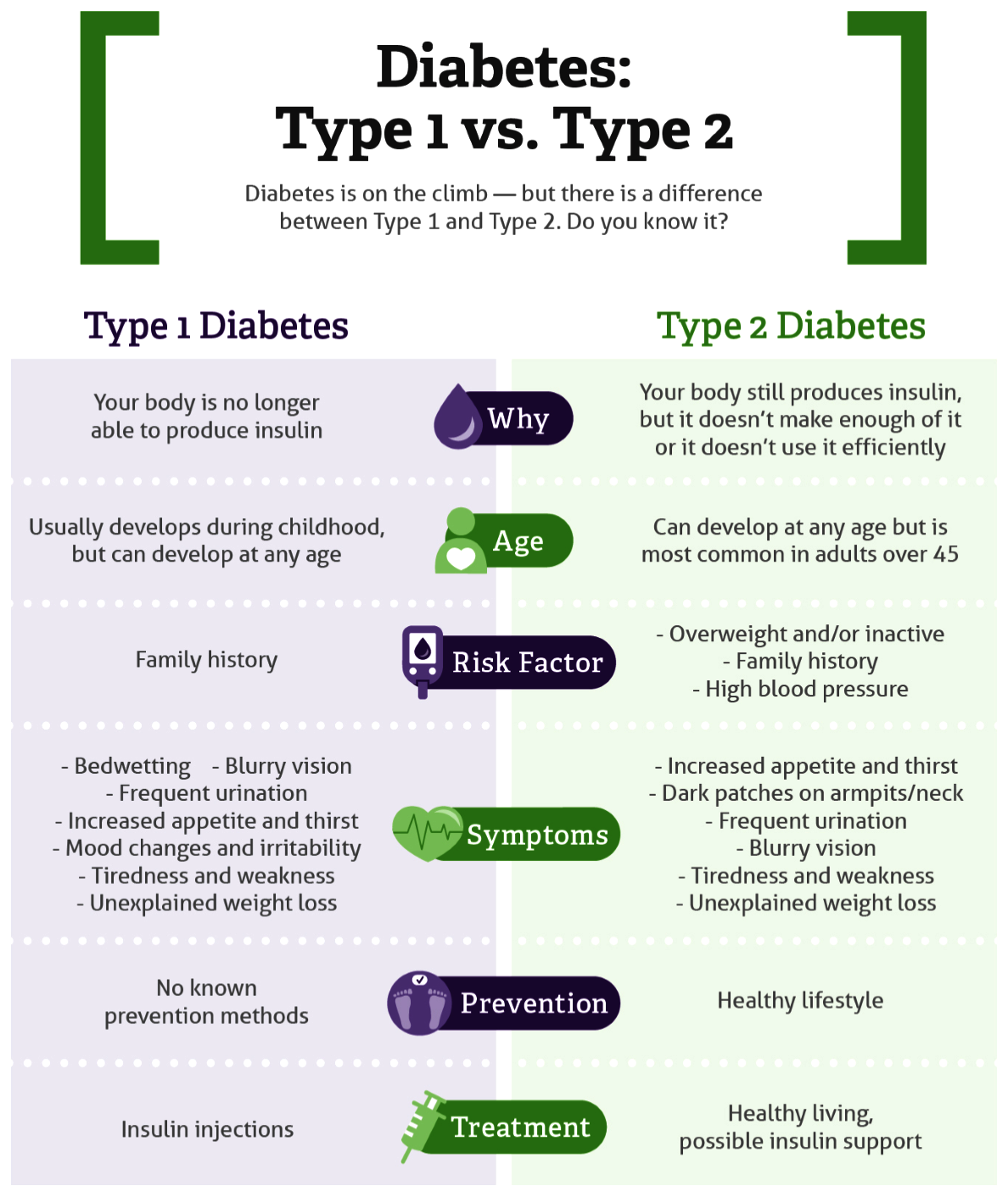
Type 1 Diabetes
Why in News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has written to all States and Union Territories, suggesting that children with Type 1 diabetes (T1D) are provided with proper care and required facilities.
What is T1D?
- About:
- T1D is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, which is a hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes usually occurs in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
- According to data from the International Diabetes Federation Atlas 2021, India has the world’s highest number of children and adolescents living with Type I Diabetes Mellitus (TIDM), at over 2.4 lakh, in the southeast Asia region.
- It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this condition is not known, but genetic and environmental factors are thought to play a role.
- T1D is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, which is a hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes usually occurs in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
- Treatment:
- Type 1 diabetes typically require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage the blood sugar levels.
- Complications in Children:
- Complications of type 1 diabetes in children can include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), ketoacidosis (a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body breaks down fat for energy instead of glucose), and long-term complications such as eye, kidney, nerve, and cardiovascular damage.
What are the other Types of Diabetes?
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- It affects the way the body uses insulin. While the body still makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes can occur at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- This type occurs in women during pregnancy when the body sometimes becomes less sensitive to insulin. Gestational diabetes does not occur in all women and usually resolves after giving birth.
What are Related Initiatives?
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS):
- In order to prevent and control major NCDs, this initiative was launched by India in 2010 with focus on strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, early diagnosis, management and referral.
- World Diabetes Day:
- It is observed on 14th November every year. The 2022 campaign focus on access to diabetes education.
- Global Diabetes Compact:
- WHO launched a Global Diabetes Compact to better fight the disease while marking the centenary of the discovery of insulin.
What is the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights?
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.
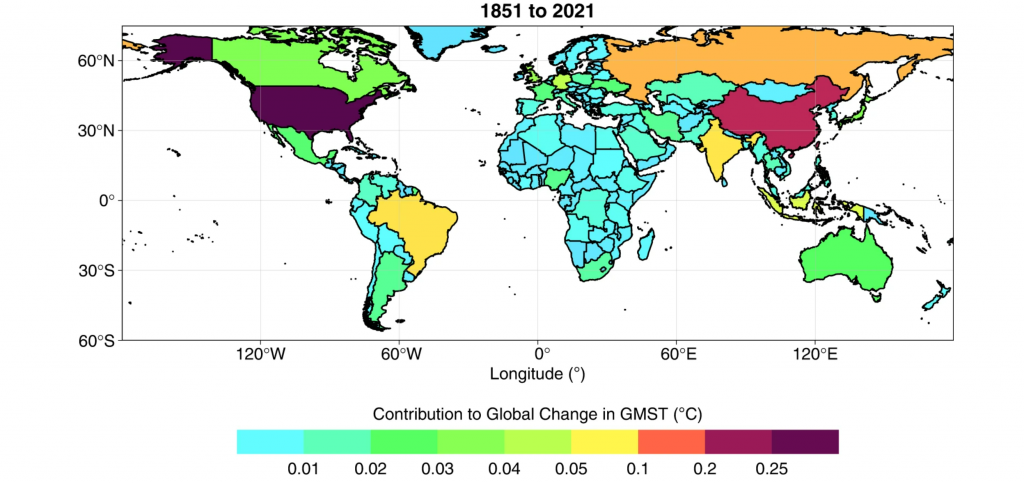
India Ranks Fifth in National Contribution to Warming
Why in News?
Recently, the research published in the journal “Scientific Data’ ranked India fifth among the top 10 contributors to global warming.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Top Contributor:
- The United States topped the list with its emissions causing 0.28°C (17.3%) of rise in temperature.
- China stood second and Russia took third place.
- India's Position:
- Since 2005, India climbed to the fifth spot from the 10th.
- India is responsible for 0.08 degrees Celsius of warming from the 1850s through 2021.
- India’s emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O) from 1851-2021 have resulted in 0.04°C, 0.03°C and 0.006°C of global warming over pre-industrial levels, respectively.
- Cause of Warming:
- The land-use and forestry sector is a significant contributor in half the countries.
- CO2 emissions from land use, land-use change and forestry (LULUCF) in Brazil led to 0.04°C of warming.
- Also, the LULUCF sector accounted for 38% of the total warming from CH4 emissions and 72% from N2O emissions between 1851-2021.
- The report highlighted emissions linked to historical deforestation and agricultural expansion.
- Fossil fuel remains the biggest contributor. Since 1992, the additional warming caused by global fossil fuel emissions has been over four times greater than the additional warming caused by land-use change.
What are Greenhouse Gases?
- A greenhouse gas (GHG) is a gas that absorbs and emits radiant energy at thermal infrared wavelengths, causing the greenhouse effect.
- The primary GHGs in Earth's atmosphere are water vapor (H2O), carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), and ozone (O3).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In the context of which of the following do some scientists suggest the use of cirrus cloud thinning technique and the injection of sulphate aerosol into stratosphere? (2019)
(a) Creating the artificial rains in some regions
(b) Reducing the frequency and intensity of tropical cyclones
(c) Reducing the adverse effects of solar wind on the Earth
(d) Reducing the global warming
Ans: (d)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
India Exempts Import Duty on Rare Disease Drugs and Food
The Indian government has announced an exemption on basic customs duty for all drugs and food used for special medical purposes that are imported for personal use to treat rare diseases.
The exemption will become effective from April 1, 2023. Pembrolizumab (Keytruda), a medication used to treat various cancers, has also been exempted from basic customs duty. Previously, drugs and medicines that were used to treat Spinal Muscular Atrophy or Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy were provided with exemptions.
The individual importer must provide a certificate from the Central or State Director Health Services or District Medical Officer/Civil Surgeon of the district to avail of the exemption. The treatment for rare diseases can be very expensive, and this exemption will result in substantial cost savings for patients.
Read More: Custom Duty, Rare Diseases.
ISRO Releases Global Earth Mosaic Captured by EOS-06 satellite
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has recently released a Global False Colour Composite (FCC) mosaic of images captured by the Ocean Colour Monitor (OCM) payload on board the EOS-06 satellite.
The OCM senses the Earth in 13 distinct wavelengths to provide information about global vegetation cover on land and ocean biota for global oceans.
Launched by ISRO in November 2021, the EOS-06 satellite is the third generation in the Oceansat series and is equipped with four payloads to observe ocean colour data, sea surface temperature, and wind vector data for climatic and meteorological applications, among other things.
Read More: EOS-06 Satellite, Oceansat
Shyamji Krishna Varma
On March 30, 2023 the death anniversary of Shri Shyamji Krishna Varma was commemorated.
Shyamji Krishna Varma was a prominent Indian revolutionary who played a significant role in the country’s freedom struggle against British colonial rule. He was known for his strong nationalist ideals and courage, which inspired many other leaders of the time.
He also established the Indian Home Rule Society in London, which provided a platform for Indian students to voice their opposition to British rule. His contributions to the Indian independence movement are widely recognized and celebrated in India.
Read More: India’s Freedom Struggle
Tiwa Tribes Celebrates Yangli Festival in Assam
Tiwa tribesmen in Assam celebrate the Yangli festival once every three years to mark the beginning of the sowing season.
The Yangli festival, which is related to agriculture, is a significant event for the Tiwas as farming is the main source of income for their community.
During the festival, the Tiwas perform dances and offer prayers for a successful harvest, seeking protection for their crops from pests and natural calamities.
Read More: Tiwa tribe.