China's Geopolitical Initiatives in Nepal
For Prelims: China's Geopolitical Initiatives in Nepal, China-Nepal Relations, India-Nepal Relations, Six-Month Economic Blockade of Nepal, China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
For Mains: China's Geopolitical Initiatives in Nepal, its implications for India.
Why in News?
Recently, China and Nepal have signed 12 agreements to enhance Bilateral Cooperation in sectors including trade, road connectivity, and information technology.
What are the Agreements Signed between Nepal and China?
- The agreements include MoUs for:
- Cooperation between The National Planning Commission of Nepal and China’s National Development and Reform Commission
- Enhancing digital economy corporation,
- Cooperation on green and low-carbon development
- Cooperation in the fields of agriculture, livestock and fisheries,
- Cooperation in the field of science, technology and innovation; and in the field of Human Resources Development.
- Mechanism to review the Nepal-China trade and payment agreement.
- They also signed a protocol of phytosanitary requirements for the export of plant-derived medicinal materials for Chinese medicine from Nepal to China.
- Nepal declined China’s invitation to join China’s Global Security Initiative (GSI), advocating that joint security is not in the interest of Nepal to maintain a strategic balance between India, China and the US.
How Have Been China Nepal Relations So Far?
- Geopolitical Relations:
- Nepal has increasingly sought to balance its relations with its two giant neighbours, India and China, as part of its foreign policy strategy.
- China's influence in Nepal has grown significantly in recent years, the almost Six-Month Economic Blockade of Nepal by India from September 2015 onward gave China a fast track into the country.
- China intervened aggressively in Nepal’s politics and played a role in bringing the two communist parties, Maoist Centre and Unified Marxist-Leninist together.
- China has historical ties with the communist movement in Nepal, particularly with the Communist Party of Nepal (Maoist Centre), which was involved in a decade-long armed insurgency against the Nepalese state. During this period, the Maoist movement received ideological, logistical, and even military support from China.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Economic cooperation between China and Nepal has intensified, focusing on trade, investment, and infrastructure development.
- Key projects like cross-Himalayan railways, ports, and hydroelectric power plants are enhancing connectivity and contributing to Nepal's economic growth.
- Nepal has expressed interest in China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), aiming to improve infrastructure connectivity and trade facilitation.
- Security and Defense Cooperation:
- China and Nepal have engaged in joint military exercises and increased defense cooperation, focusing on capacity building and military training.
- China has provided military aid to Nepal, further strengthening their defense ties.
- Issue Between China and Nepal:
- In its new map, China refused to recognize a portion of land in Nepal's northwestern region—an area that Nepal had claimed and depicted in its own map in 2020.
What are the Implications of China’s Growing Presence in Nepal for India?
- Security Concerns:
- China's enhanced influence in Nepal could potentially lead to strategic encirclement for India, as it strengthens its presence in a country that shares a long border with India.
- This raises security concerns for India.
- Access to Resources:
- China's infrastructure projects and economic engagement in Nepal may compete with Indian investments and economic interests, affecting India's access to resources and markets in the region.
- Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) and Connectivity:
- Nepal's participation in China's BRI Initiative can result in a significant increase in Chinese-backed infrastructure projects and connectivity, which will increase Nepal's dependence on China for trade and consequently harm the interest of India.
- Challenges in Regional Coordination:
- Nepal's closer ties with China provide strategic depth to China in South Asia, potentially allowing China to project power and influence beyond its borders.
- China's deepening involvement in Nepal might make it more challenging for India to coordinate regional responses and initiatives effectively.
What is the Significance of Nepal for India?
- Nepal's Strategic Importance:
- Nepal shares border with 5 Indian states- Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Sikkim and Bihar. Hence an important point of cultural and economic exchange.
- Nepal is right in the middle of India’s ‘Himalayan frontiers’, and along with Bhutan, it acts as a northern ‘borderland’ flank and acts as buffer states against any possible aggression from China.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India has been assisting the Nepal Army (NA) in its modernisation by supplying equipment and providing training.
- The ‘Indo-Nepal Battalion-level Joint Military Exercise Surya Kiran’ is conducted alternately in India and in Nepal.
- Also, Currently, about 32,000 Gorkha Soldiers from Nepal are serving in the Indian Army.
- Economic Cooperation:
- India is the largest trading partner of Nepal. Nepal is also India’s 11th largest export destination.
- Indian firms are among the largest investors in Nepal, accounting for more than 30% of the total approved foreign direct investments.
- Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1950:
- The treaty talks about the reciprocal treatment of Indian and Nepali citizens in the two countries, in residence, property, business and movement.
- Power Sector Cooperation:
- In June 20023 India and Nepal signed a long-term Power Trade Agreement, targeting the import of 10,000 MW of electricity from Nepal in the coming years.
- Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed between National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC), India and Vidyut Utpadan Company Ltd, Nepal for the development of the Phukot Karnali Hydroelectric Project and the Lower Arun Hydroelectric Project.
Way Forward
- To mitigate the challenges, India needs to engage proactively with Nepal, enhance development assistance, strengthen economic ties, and foster people-to-people relations.
- Additionally, India must work on multilateral initiatives and regional cooperation to counterbalance the expanding Chinese influence in Nepal and ensure stability and prosperity in the region.
- Diplomacy, dialogue, and collaboration will be crucial in managing these challenges effectively.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2016)
Community sometimes In the affairs of mentioned in the news
- Kurd — Bangladesh
- Madhesi — Nepal
- Rohingya — Myanmar
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (c)
Delimitation Concerns in Women's Reservation Bill, 2023
For Prelims: Women's Reservation Bill,2023, Delimitation Commission, Article 82, Article 170
For Mains: Indian Constitution, Elections, Statutory Bodies, Delimitation Process
Why in News?
The recent passage of the Women's Reservation Bill,2023 in the Indian Parliament has been hailed as a historic milestone towards gender equality in the country's political landscape.
- However, the fate of this landmark legislation is currently intertwined with the issue of delimitation, a move criticized by opposition parties.
What is Delimitation?
- About:
- Delimitation is the process of redrawing parliamentary or assembly seat borders to ensure an equal number of voters in each constituency.
- It is done every few years after each census to ensure each constituency has one representative in both the Lok Sabha and state assembly across the nation.
- Delimitation links population increase to the number of elected legislators in a state, ensuring that no delegates are overrepresented or underrepresented.
- Constitutional Provisions Related to Delimitation:
- Article 82:
- The Parliament enacts a Delimitation Act after every census. This act allows the Parliament to readjust the allocation of seats in the Lok Sabha and the Legislative Assemblies of States.
- Article 170:
- This article deals with the composition of state Legislative Assemblies, specifying a minimum of 60 members and a maximum of 500.
- The size of the population, as determined by the most recent census, forms the basis for delimitation and seat distribution.
- Article 82:
- Delimitation Commission:
- The Delimitation Commission Act was enacted in 1952.
- Once the Act is in force, the Union government sets up a Delimitation Commission.
- Delimitation Commissions have been set up four times 1952, 1963, 1973 and 2002 under the Acts of 1952, 1962, 1972 and 2002.
- The Delimitation Commission is appointed by the President of India and works in collaboration with the Election Commission of India.
- The commission's main task is to redraw the boundaries based on a recent census.
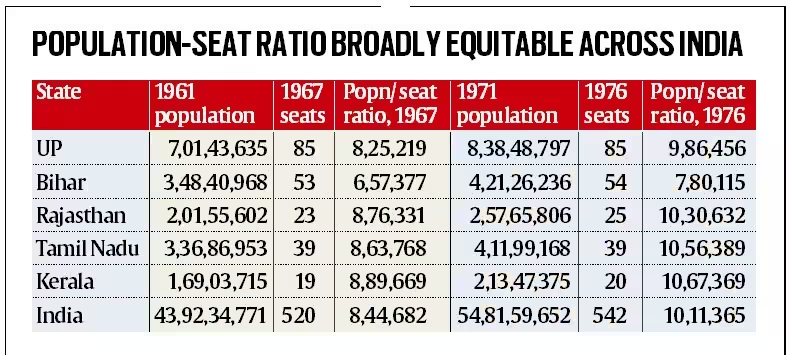
- The current boundaries of the Lok Sabha and State Assembly constituencies were drawn on the basis of the 2001 Census by the Delimitation Commission of 2002.
- However, the number of seats allocated to each state in the Lok Sabha and the total number of seats in a Legislative Assembly were frozen on the basis of the 1971 Census by the 42nd Amendment Act of 1976.
- This freeze was extended until the first census after 2026 by the 84th Amendment Act of 2001.
- The Delimitation Commission Act was enacted in 1952.
How is Women's Reservation Bill,2023 Linked to Delimitation?
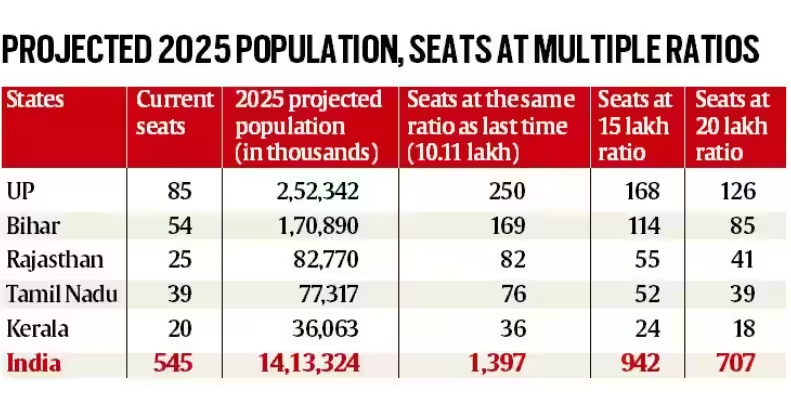
- The Indian government has stated that the Women's Reservation Bill, 2023 will come into effect only after the delimitation exercise is undertaken based on the census data, which has been delayed due to the Covid-19 pandemic and several other reasons has been further pushed to 2024-25 until further orders.
- The government has argued that linking the reservation with delimitation will ensure a transparent and fair allocation of seats for women, and will also increase the total number of seats for both men and women, as the delimitation exercise is expected to raise the strength of the Lok Sabha and the state assemblies seats.
What are the Concerns Regarding the Delimitation?
- Potential Underrepresentation:
- One of the primary concerns is that if delimitation is carried out based on population parameters, southern states like Telangana and others that have successfully implemented population control measures may face underrepresentation in Parliament.
- This fear arises from the possibility that northern states with higher population growth, such as Bihar and Uttar Pradesh, could gain more seats in Parliament at the expense of the south.
- Despite having only 18% of the country's population, the southern states contribute 35% to the country's GDP.
- Leaders argue that their economic strength should be reflected in political representation to ensure that their interests are adequately represented.
- Southern political leaders worry that a shift in the number of Lok Sabha seats towards northern states could result in a reduced political voice for the South at the national level.
- One of the primary concerns is that if delimitation is carried out based on population parameters, southern states like Telangana and others that have successfully implemented population control measures may face underrepresentation in Parliament.
- Linkage with Women's Reservation Bill:
- The government's decision to link the implementation of the Women's Reservation Bill with delimitation is a major concern for opposition parties.
- Opposition argues that there is no apparent reason or requirement to connect the two issues, as there was no such linkage in previous discussions of the women's reservation Bill.
- They suggest that the government could have chosen to delink the women's quota from the census and delimitation. A simpler bill could have allowed all parties to ensure 33% reservation for women within the current architecture of the Lok Sabha.
 |
 |
Legal Insights
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the Delimitation Commission consider the following statements: (2012)
- The orders of the Delimitation Commission cannot be challenged in a Court of Law.
- When the orders of the Delimitation Commission are laid before the Lok Sabha or State Legislative Assembly, they cannot effect any modification in the orders.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Geospatial Intelligence
For Prelims: Geospatial Intelligence, Global positioning Systems (GPS), Satellites, Mobile Sensors, Aerial Images
For Mains: Importance and Significance of Geospatial Technologies in Management of Disasters
Why in News?
The summer of 2023 has witnessed a series of unprecedented natural disasters across the United States, including record-breaking temperatures, Canadian wildfires, historic flooding, and a powerful hurricane where usage of geospatial intelligence can mitigate such crises.
What is Geospatial Intelligence?
- Geospatial technology uses tools like GIS (Geographic Information System), GPS (Global Positioning System) and Remote Sensing for geographic mapping and analysis.
- These tools capture spatial information about objects, events and phenomena (indexed to their geographical location on earth, geotag). The location data may be Static or Dynamic.
- Static location data include position of a road, an earthquake event or malnutrition among children in a particular region while dynamic location data include data related to a moving vehicle or pedestrian, the spread of an infectious disease etc.
- The technology may be used to create intelligent maps to help identify spatial patterns in large volumes of data.
- The technology facilitates decision making based on the importance and priority of scarce resources.
What is the Significance of Geospatial Intelligence?
- Monitoring Tropical Cyclones:
- The National Hurricane Center relies on geospatial intelligence to monitor cyclone location, its formation, and trajectory.
- This information aids in resource allocation, issuing warnings, and managing evacuations.
- Search-and-Rescue Effort:
- After the 7.8 magnitude earthquake in Turkey and Syria (February 2023), geospatial intelligence identified damage and helped locate survivors.
- It facilitated the establishment of aid stations and emergency supply distribution.
- Environmental Monitoring:
- Predicting Climate-Related Events
- Temperature, precipitation, snowpack, and polar ice monitoring help anticipate and prepare for disturbances.
- This is crucial in addressing the increasing threats posed by climate change-induced extreme weather events.
- Predicting Climate-Related Events
- Military and Civilian Applications:
- Geospatial Intelligence in Border Management
- Satellite images play a vital role in reporting critical information, such as Russian ground forces' movements in the Ukrainian conflict and infiltration into India from Pakistan.
- Transportation and Logistics
- GPS technology and geospatial data enable efficient management of global supply chains.
- It provides governments and businesses with essential information on cargo movement.
- Geospatial Intelligence in Border Management
- Urban Planning and Autonomous Vehicles:
- Enhancing Urban Development
- High-resolution imagery aids city planners in designing safer and more efficient communities.
- Features like bicycle lanes and traffic directions are easily detectable.
- Role in Autonomous Vehicles
- Geospatial intelligence supports the development of autonomous vehicles by providing ground-level details.
- Safer and smarter transportation systems are being built.
- Enhancing Urban Development
- Digital Twins for Decision Making:
- Concept and Applications
- Digital twins are virtual replicas of real systems, used for modeling and predicting outcomes.
- They have proven effective in conflict settings for simulating weather and terrain.
- Concept and Applications
Why is there a Growing Need for Geospatial Intelligence?
- Addressing Future Challenges:
- Rising temperatures and urbanization increase the demand for geospatial intelligence.
- It aids in safeguarding communities and adapting to evolving conditions.
- Industry Growth
- The geospatial intelligence industry is projected to grow from $61 billion in 2020 to over $209 billion by 2030.
- It plays an essential role in shaping a safe and informed future.
- Precision Agriculture:
- Agriculture is becoming increasingly data-driven. Geospatial Intelligence helps farmers make informed decisions about crop management, soil quality, irrigation, and pest control.
- This becomes important for India, given around 18% of GDP is contributed by agriculture and 48% of the workforce is employed in it.
What are Government’s Initiatives to Promote Geospatial Technology in India?
- Government introduced the "Geospatial Information Regulation Bill, 2021." This bill aimed to regulate the acquisition, dissemination, and use of geospatial information in India.
- It proposed to set guidelines for mapping and geospatial data collection, with a focus on national security concerns.
- National Geospatial Policy, 2022 was launched to streamline the utilization of geospatial intelligence.
What are the Challenges in Geospatial Intelligence?
- There is no demand for geospatial services and products on a scale linked to India’s potential and size.
- This is mainly due to the lack of awareness among potential users in government and private.
- The other hurdle has been the lack of skilled manpower across the entire pyramid.
- The unavailability of foundation data, especially at high-resolution, is also a constraint.
- Essentially, foundation data can be seen as common data tables which are shared between multiple applications or processes which are supposed to create a sturdy foundation for good service automation and management.
- The lack of clarity on data sharing and collaboration prevents co-creation and asset maximization.
- There are still no ready-to-use solutions especially built to solve the problems of India.
Way Forward
- Establishing a Geo-Portal and Data Cloud: There is a need to establish a geo-portal to make all public-funded data accessible through data as a service model.
- It is important to inculcate the culture of data sharing, collaboration and co-creation.
- Generation of Foundation Data: This should include the data aggregation, data layers for cities, and data of natural resources.
- Bachelor’s Programme in Geospatial: India should start a bachelor’s programme in geospatial in India's premier institutions.
- These programmes will propel research and development efforts which are crucial for the development of technologies and solutions locally.
- Regulation: National organizations like Survey of India (SoI) and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) should be entrusted with the responsibility of regulation and the projects related to the nation’s security and scientific significance.
- These organizations should not compete with entrepreneurs for government business as the latter remains in a disadvantageous position.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: C
Mains
Q.1 What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q.2 Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
Policy Initiatives for Pharma Med Tech Sector
For Prelims: Pharmaceutical sectors, National Policy on Research and Development and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector in India, Research and Innovation in Pharma MedTech Sector (PRIP)
For Mains: Policies and Initiatives of Medical and Pharmaceutical sectors
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers has launched initiatives to nurture Innovation, research, and development in the Medical and Pharmaceutical sectors.
- These Initiatives are National Policy on Research and Development and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector in India and Scheme for Promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma MedTech Sector (PRIP).
Note
Indian pharmaceutical industry is the 3rd largest pharmaceutical industry in the world by volume with current market size of around USD 50 Billions.
What are the Initiatives Launched?
- National Policy on Research and Development and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector:
- The policy aims to encourage R&D in pharmaceuticals, including traditional medicines & phytopharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- It can potentially help in growing the sector to USD 120-130 Billion over the next decade, increasing its contribution to the GDP by about 100 basis points.
- Objectives:
- To create a regulatory environment that facilitates innovation and research in product development, expanding the traditional regulatory objectives of safety and quality.
- To incentivize private and public investment in Innovation through a mix of fiscal and non-fiscal measures.
- To build an enabling ecosystem designed to support innovation and cross-sectoral research as a strong institutional foundation for sustainable growth in the sector.
- The policy aims to encourage R&D in pharmaceuticals, including traditional medicines & phytopharmaceuticals and medical devices.
- Scheme for Promotion of Research and Innovation in Pharma-MedTech Sector (PRIP):
- The PRIP scheme focuses on fostering innovation and transforming the MedTech sector into an innovation-driven powerhouse.
- It emphasizes high-quality research and innovation, aiming to shift the sector towards value and innovation-based approaches.
- Components:
- Component A: Strengthening the research infrastructure by establishment of 7 Centres of Excellence’ at National Institutes of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER).
- Component B: Promoting research in pharmaceutical sector by encouraging research in six priority areas like New Chemical Entities, Complex generics including biosimilars, medical devices, stem cell therapy, orphan drugs, Anti-microbial resistance etc., wherein financial assistance will be provided for the Industries, MSME, SME, Startups working with government institutes and for both in- house and academic research.
What are the Initiatives Related to the Pharmaceutical Sector?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ):
Mains:
Q. How is the Government of India protecting traditional knowledge of medicine from patenting by pharmaceutical companies? (2019)
Women, Power and Cancer: Lancet
For Prelims: Women, Power and Cancer: Lancet, Cancer, Gender Inequity, Human Development Index, Years of Life Lost (YLLs), Lancet Global Health, Hepatitis B and C infections.
For Mains: Women, Power and Cancer: Lancet, Cancer Prevention.
Why in News?
Recently, The Lancet Global Health has released a report titled-“Women, Power and Cancer”, which highlights how societal apathy towards women’s health has delayed their access to Cancer prevention.
What is the Methodology of the Study?
- This study estimated premature deaths at ages 30–69 years and distinguished these as deaths that are preventable or treatable in 185 countries worldwide.
- For this population-based study, estimated Cancer deaths by country, cancer, sex, and age groups were retrieved from the International Agency for Research on Cancer's GLOBOCAN 2020 database.
- Crude and age-adjusted cancer-specific Years of Life Lost (YLLs) were calculated for 36 cancer types.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Cancer-Related Mortality and Burden:
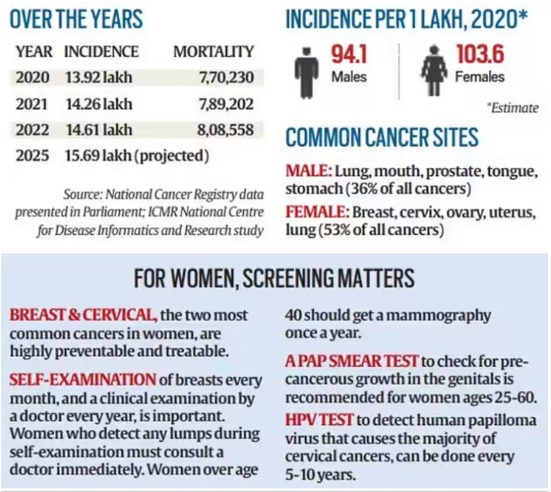
- In 2020, there were 5.28 million premature cancer-related deaths worldwide, occurring between the ages of 30 and 69.
- These premature deaths resulted in a significant burden of 182.8 million years of life lost (YLLs), accounting for 68.8% of the total YLLs from cancer across all age groups.
- Preventable and Treatable Deaths:
- Among the premature YLLs, 68% were deemed preventable, achievable through primary prevention or early detection efforts.
- The remaining 32.0% YLLs were considered treatable, where effective evidence-based treatment with curative intent could reduce mortality.
- Gender Disparities:
- Men experienced a higher proportion of preventable premature YLLs compared to women (70.3% for men vs. 65.2% for women).
- However, the proportion of treatable premature YLLs was higher for women than for men (34.8% for women vs. 29.7% for men).
- Human Development Index (HDI) and Mortality:
- Countries with lower HDI levels had greater proportions of YLLs at premature ages compared to very high HDI countries.
- Lung cancer was a major contributor to preventable premature YLLs in medium to very high HDI countries, while cervical cancer led in low HDI countries.
- Colorectal and breast cancers were major treatable cancers across all tiers of HDI.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study Pertaining to India?
- Cancer Deaths Among Women in India:
- Nearly 63% of cancer deaths among women in India could have been prevented by reducing risk factors, screening, or early diagnosis.
- 37% of deaths could have been averted with appropriate and timely treatment.
- Challenges and Factors Affecting Cancer Care for Women:
- Societal apathy towards women’s health, lack of awareness, and absence of quality expertise at the primary care level delayed access to cancer prevention, detection, and care for women.
- Gender Gap and Discrimination in Healthcare:
- Because of Gender Inequity in cancer care, a woman's health concerns were dismissed or ignored.
- Women are less likely to be in a position of power and may face difficulty in determining their care due to gender bias and discrimination.
- Leading Risk Factors Among Women in India:
- The top three cancers among women in India are Breast, Cervical, and Ovarian Cancers.
- One woman dies from cervical cancer every eight minutes.
- Infection continues to be the biggest risk factor for cancer in Indian women, contributing to 23% of deaths.
- Infections that increase the risk of cancers include the HPV virus, which causes cervical cancer, and Hepatitis B and C infections that increase the risk of liver cancer.
- Tobacco is the second important risk factor, contributing to 6% of the cancer deaths.
- Alcohol and obesity each contributed to 1% cancer mortality in India.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa) nations lost out on USD 46.3 billion because of productivity loss as a result of premature cancer deaths.
- The value of unpaid cancer care-giving by women is about 3.66 of India’s national health expenditure.
What are the Recommendations of the Report?
- There is a need to call for a new feminist and inclusive agenda for cancer care, aiming to address the gender disparities and challenges women face in accessing appropriate cancer prevention, detection, and treatment.
- There is a need for more sex- and gender-inclusive policies and guidelines, addressing long-standing discriminatory practices undermining women’s interaction with the health system.
- There should be tailored programs for early diagnosis, screening, comprehensive treatment, risk factor reduction, and vaccination to address premature cancer inequalities.
- Screening is crucial for early detection and prevention of breast and cervical cancers.
- Self-examination of breasts every month and clinical examination by a doctor every year is advised.
- Women over the age of 40 should get a mammography once a year to check for breast cancer.
- Women between the ages of 25 and 65 years should get a pap smear test to check for pre-cancerous growth on their cervix.
Why are Women More Precarious to Dying of Cancer?
- Many women in India face barriers in accessing healthcare. Their headaches, stemming from a developing brain cancer, are ignored generally in many cases.
- There is a need of addressing societal apathy towards women's health, lack of awareness, and absence of quality healthcare at the primary level.
- The challenges faced by dispossessed women, including early marriage, lack of education, and financial dependence, hinder their ability to seek medical attention and sustain treatment.
- Lack of knowledge and delayed diagnosis by local healthcare providers can severely impact a patient's prognosis and quality of life.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Cancer Treatment?
Surety Bonds
Why in News?
Recently, some of the leading general insurers like New India Assurance, SBI General Insurance etc. have announced their plans to issue Surety Bonds, but nobody has been able to do so due to lack of supporting elements.
- The Ministry of Finance and the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways are putting pressure on the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) to push the insurance industry to launch surety Bond Products.
What is Surety Bond?
- About:
- A surety bond can be defined in its simplest form as a written agreement to guarantee compliance, payment, or performance of an act.
- It is a unique type of insurance because it involves a three-party agreement. The three parties in a surety agreement are:
- Principal – The party that purchases the bond and undertakes an obligation to perform an act as promised.
- Surety – The insurance company or surety company that guarantees the obligation will be performed. If the principal fails to perform the act as promised, the surety is contractually liable for losses sustained.
- Obligee - The party who requires, and often receives the benefit of the surety bond. For most surety bonds, the obligee is a local, state or federal government organization.
- Surety bond is provided by the insurance company on behalf of the contractor to the entity that is awarding the project.
- It will help contractors to have financial closure of their projects without depending upon only bank guarantees.
- Aim:
- Surety bonds are mainly aimed at infrastructure development, mainly to reduce indirect cost for suppliers and work contractors thereby diversifying their options and acting as a substitute for bank guarantee.
- Benefits:
- Surety bonds protect the beneficiary against acts or events that impair the underlying obligations of the principal.
- They guarantee the performance of a variety of obligations, from construction or service contracts to licensing and commercial undertakings.
How can it Boost the Infra Project?
- The move to frame rules for surety contracts will help address the large liquidity and funding requirements of the infrastructure sector.
- It will create a level-playing field for large, mid and small contractors.
- The Surety insurance business will assist in developing an alternative to bank guarantees for construction projects.
- This shall enable the efficient use of working capital and reduce the requirement of collateral to be provided by construction companies.
- Insurers shall work together with financial institutions to share risk information.
- Hence, this shall assist in releasing liquidity in infrastructure space without compromising on risk aspects.
What are the Issues with the Surety Bonds?
- Surety bonds, a new concept, are risky and insurance companies in India are yet to achieve expertise in risk assessment in such business.
- Also, there’s no clarity on pricing, the recourse available against defaulting contractors and reinsurance options.
- These are critical and may impede the creation of surety-related expertise and capacities and eventually deter insurers from writing this class of businesses.
- Surety Bonds need extensive reinsurance support and no primary insurers can issue any policy without proper reinsurance backup.
- The issuer of Surety Bonds in India should be in a position to legally enforce tripartite contracts that guarantee compliance, payment and/or performance.
- Indian Contract Act and Insolvency and Bankruptcy code does not recognize rights of Insurers at par with financial creditors yet and thus insurance companies do not have recourse to recovery like banks in case of any default.
UPSC Civil Services,Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. With reference to ‘IFC Masala Bonds’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the statements given below is/ are correct? (2016)
- The International Finance Corporation, which offers these bonds, is an arm of the World Bank.
- They are the rupee-denominated bonds and are a source of debt financing for the public and private sector.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans:(c)
Mains:
Q. The product diversification of financial institutions and insurance companies, resulting in overlapping of products and services strengthens the case for the merger of the two regulatory agencies, namely SEBI and IRDA. Justify. (2013)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Green Ammonia Import through VOC Port
Recently, V.O. Chidambaranar Port inTamil Nadu imported Green Ammonia for the first time,as part of its 'Go Green' initiative.
- Green Ammonia will be used to produce green soda ash on a trial basis, moving away from conventional Grey Ammonia usage.
- The port has been a leader in 'Green Port' initiatives, promoting eco-friendly practices.
- Green ammonia production is where the process of making ammonia is 100% renewable and carbon-free.
- Green Ammonia is produced by using hydrogen from water electrolysis and nitrogen separated from the air. These are then fed into the Haber process (Also known as Haber-Bosch), all powered by sustainable electricity.
- The V. O. Chidambaranar Port Trust, formerly known as the Tuticorin Port Trust, is one of the major ports in India. It is located in Thoothukudi, Tamil Nadu. The port was declared a major port in 1974.
- It is the second-largest port in Tamil Nadu and the fourth-largest container terminal in India. The port offers various facilities such as berthing, navigation, storage, and port security.
Read More: Green Hydrogen, Draft Indian Ports Bill,2022
Sarna Code
Recently, Jharkhand Chief Minister wrote a letter to Prime Minister, requesting the recognition of the Sarna religious code for tribals.
- Concerns have been raised regarding the neglect of Sarna Code, which could adversely affect tribal development policies under Fifth Schedule and Sixth Schedule of the Constitution.
- Sarna religion, followed by a significant tribal population in Jharkhand, is unique, based on nature worship, and distinct from mainstream religions.
- There is need to protect the cultural and religious identity of tribals who worship nature.
- Fifth Schedule lays out provisions for the Administration and Control of Scheduled Areas and STs in states other than 6th Schedule States.
- Sixth Schedule deals with the administration of the tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
Read More: Tribes in India, National Commission for Scheduled Tribes
Monoclonal Antibodies
In recent times, Monoclonal antibodies being considered for compassionate use in India amidst the Nipah virus outbreak in Kerala's Kozhikode district.
- This option is being explored due to the absence of effective treatments for Nipah, a virus with a high mortality rate and also far more severe than Covid-19.
- The antibody binds to a part of the viral envelope, neutralizing the Nipah virus.
- The monoclonal antibody has also been used against the Hendra virus, a related virus from the same family.
- Antibodies are proteins produced naturally by the immune system that target a specific foreign object (antigen). They are called monoclonal Antibodies (mAbs) when they are produced by clones derived from a single parent cell.
- Monoclonal Antibodies are man-made proteins that act like a human antibody in the immune system. They are made by cloning a unique white blood cell.
Read More: ELISA Antibody kits, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR)
FSSAI Prohibits Use of Newspapers for Food Storing
Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) has notified the Food Safety and Standards (Packaging) Regulations, 2018 which strictly prohibits the use of newspapers or similar materials for storing and wrapping food.
- The ink used in newspapers contains various bioactive materials with known negative health effects, which can contaminate food and lead to health issues when ingested.
- Additionally, printing inks may contain chemicals including lead and heavy metal that can leach into the food, posing serious health risks over time.
- FSSAI is an autonomous statutory body established under the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 (FSS Act) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
Read More: State Food Safety Index, Eat Right Station