Infographics
Biodiversity & Environment
Heat Index
For Prelims: India Meteorological Department (IMD), Heat Index, Urban heat Island Effect, National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA).
For Mains: Issues Related to Heat Waves in India.
Why in News?
The India Meteorological Department (IMD) is planning to introduce a ‘heat index’ warning system in Delhi and other parts of the country.
What are Recent Studies of IMD Suggests?
- The IMD has conducted a study on the impact of meteorological factors on heatwaves and the “heat wave hazard zonation” of the country.
- According to "Hot Weather Analysis over India," IMD revealed that the mechanism by which heat impacts humans is complex; it is a result of the interactions between temperature, radiation, wind, and humidity.
- There is strong experimental evidence that physiologic stress from high temperatures is greater if humidity is higher.
What is the Proposed Heat Index?
- About:
- Heat Index will calculate the temperature along with the humidity levels to provide a more accurate measure of what the temperature actually feels like.
- In the US, the heat index is color-coded to provide warnings based on the impact of the heat index.
- The IMD is planning to introduce a similar color-coded warning system in India.
- Significance:
- Heat Index has important considerations for the human body's comfort.
- When the body gets too hot, it begins to perspire or sweat to cool itself off. If the perspiration is not able to evaporate, the body cannot regulate its temperature. Evaporation is a cooling process. When perspiration is evaporated off the body, it effectively reduces the body's temperature.
- When the atmospheric moisture content (i.e., relative humidity) is high, the rate of evaporation from the body decreases. The human body feels warmer in humid conditions. The opposite is true when the relative humidity decreases because the rate of perspiration increases. The body actually feels cooler in arid conditions.
- There is direct relationship between the air temperature and relative humidity and the heat index, meaning as the air temperature and relative humidity increase (decrease), the heat index increases (decreases).
- Heat Index has important considerations for the human body's comfort.
What is a Heatwave?
- A heatwave is a period of abnormally high temperatures, a common phenomenon in India during the months of May-June and in some rare cases even extends till July.
- The Heatwave is considered when the maximum temperature of a station reaches at least 40°C for Plains and at least 30°C for Hilly regions.
- In 2016, the National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) issued comprehensive guidelines to prepare national level key strategies for mitigating the impact of heatwaves.
What are the Factors Responsible for Delhi’s Higher Temperature than its Actual Value?
- Urban Heat Island Effect: Delhi is a highly urbanized area, with large amounts of concrete, buildings, and asphalt. These surfaces absorb and retain heat, creating an urban heat island effect. This can make the temperature feel hotter than it actually is.
- Air Pollution: Delhi experiences high levels of air pollution, because of stubble burning in Punjab and Haryana region, vehicular and industrial emissions, dust from construction activities.
- This pollution can trap heat and create a blanket effect, keeping the city warmer.
- Also, Delhi’s high humidity can also exacerbate air pollution levels.
- Lack of Water Bodies in Close Proximity: Delhi is not located near any large water bodies, such as a sea or a lake. This means that there is no source of cool air coming from the water, which can make the air feel hotter.


Biodiversity & Environment
Critical Assessment of Heat Action Plans
For Prelims: Centre for Policy Research, Heat Action Plans, Climate Change, Heat Waves.
For Mains: Critical Assessment of Heat Action Plans.
Why in News?
Recently, the Centre for Policy Research (CPR), one of India's leading public policy think tanks, has released the first critical assessment, stating that most of the Heat Action Plans (HAPs) may not be suited to the risks faced by local populations.
- CPR analyzed all the 37 HAPs across 18 States, to evaluate how policy action is keeping up with the warming weather in India and found that most HAPs are not built for local contexts.
What are Heat Action Plans?
- HAPs are the primary policy response to economically damaging and life-threatening heat waves. They prescribe a number of activities, disaster responses and post-heatwave response measures to reduce the impact of heat waves.
- HAPs are documents prepared at the state, district and city levels for taking short-term actions to limit the number of human deaths and other adverse impacts of heat waves and further long- term actions to prepare for future heat waves based on the data and analysis of previous heat waves.
- Short term actions can include alerting people to heat waves and coordinating various departments such as healthcare and agriculture.
- Long-term actions can include infrastructural changes such as cool roofs, increase in green cover and water harvesting structures.
What are the Key Findings?
- Unprecedented Challenge:
- Extreme heat poses an unprecedented challenge to health and productivity, heat waves have increased in frequency in recent decades due to Climate Change.
- Landmark heatwaves (1998, 2002, 2010, 2015, 2022) have each led to large death tolls and extensive economic damage by reducing labour productivity and affecting water availability, agriculture, and energy systems.
- Human-induced actions made the chances of extreme heat events 30 times higher in the region.
- Extreme heat poses an unprecedented challenge to health and productivity, heat waves have increased in frequency in recent decades due to Climate Change.
- Increase in Average Heat:
- By 2050, as many as 24 urban centers are projected to breach average summertime highs of at least 35 degrees Celsius, disproportionately impacting economically weaker sections.
- Not Fit for Local Contexts:
- Most HAPs are not built for local contexts. They generally focus on extreme dry heat and ignore the threats posed by humid heat and warm nights.
- Most HAPs adopt national heatwave thresholds that may not be suited to the risks faced by local populations.
- Only 10 out of 37 HAPs seem to have locally specified temperature thresholds.
- HAPs are Underfunded:
- Only three of 37 HAPs identify funding sources. Eight HAPs ask implementing departments to self-allocate resources, indicating a serious funding constraint.
- Weak Legal Foundations:
- HAPs have weak legal foundations. None of the HAPs reviewed indicates the legal sources of their authority. This reduces bureaucratic incentives to prioritize and comply with HAPs instructions.
- Insufficiently Transparent:
- Further, the HAPs are insufficiently transparent. There is no national repository of HAPs, and very few HAPs are listed online. It also needs to be clarified whether these HAPs are being updated periodically and whether this is based on evaluation data.
- India Most Vulnerable:
- India is one of the most exposed and vulnerable countries to heat.
- Between 1951 and 2016, three-day concurrent hot day and hot night events have increased significantly and are projected to increase between two and four-fold by 2050 under the intermediate and high emission pathways of RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5.
What are the Recommendations?
- There is a need for the world to reduce emissions in the next two decades to prevent warm temperatures from reaching 1.5° C.
- There is a need that HAPs to identify sources of financing, either from new funds or by combining actions with existing national and state policies and set up rigorous independent evaluations as a basis for constant improvement.
- Without implementation-oriented HAPs, India's poorest will continue to suffer from extreme heat, paying with both their health and incomes.


Governance
Digital Public Infrastructure
For Prelims: Digital identity (Aadhar), Real-time fast payment (UPI) and Account Aggregator, DEPA.
For Mains: Digital Public Infrastructure.
Why in News?
Public infrastructure has been a cornerstone of human progress, but it has plagued the previous generation, making it imperative for the third type of public infrastructure called Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), with more open and democratic principles built in it.
What is DPI?
- Digital public infrastructure (DPI) refers to blocks or platforms such as digital identification, payment infrastructure and data exchange solutions that help countries deliver essential services to their people, empowering citizens and improving lives by enabling digital inclusion.
- DPIs mediate the flow of people, money and information. First, the flow of people through a digital ID System. Second, the flow of money through a real-time fast payment system. And third, the flow of personal information through a consent-based data sharing system to actualize the benefits of DPIs and to empower the citizen with a real ability to control data.
- These three sets become the foundation for developing an effective DPI ecosystem.
- Each DPI layer fills a clear need and generates considerable value across sectors.
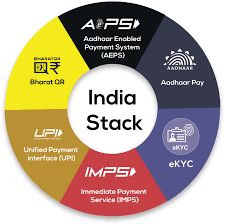
- India, through India Stack, became the first country to develop all three foundational DPIs, Digital identity (Aadhar), Real-time fast payment (UPI) and Account Aggregator built on the Data Empowerment Protection Architecture (DEPA).
- DEPA creates a digital framework that allows users to share their data on their own terms through a third-party entity, who are known as Consent Mangers.
What are the Pillars of India’s DPI Ecosystem?
- Aadhaar:
- Aadhaar is a strategic policy tool for social and financial inclusion, public sector delivery reforms, managing fiscal budgets, increasing convenience and promoting hassle-free people-centric governance.
- Aadhaar holders can voluntarily use their Aadhaar for private sector purposes, and private sector entities need not seek special permission for such usage.
- DigiYatra:
- DigiYatra is a Biometric Enabled Seamless Travel (BEST) experience based on a Facial Recognition System (FRS).
- Air passenger traffic in India was estimated to be over 188 million in airports across India in the financial year 2022, out of whom over 22 million were international passengers.
- DigiYatra is a Biometric Enabled Seamless Travel (BEST) experience based on a Facial Recognition System (FRS).
- DigiLocker:
- DigiLocker has 150 million users, six billion stored documents, and done with a tiny budget of RS 50 crore over seven years.
- The users can store their documents such as insurance, medical reports, PAN card, passport, marriage certificate, school certificate and other documents in the digital format.
- UPI:
- UPI (Unified Payment Interface) has crossed eight billion transactions per month and transacts a value of USD 180 billion a month, or about a staggering 65% of India’s GDP per annum.
- UPI is currently the biggest among the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) operated systems including National Automated Clearing House (NACH), Immediate Payment Service (IMPS), Aadhaar enabled Payment System (AePS), Bharat Bill Payment System (BBPS), RuPay etc.
What is India Stack?
- IndiaStack is a set of APIs (Application programming interface) that allows governments, businesses, startups and developers to utilize a unique digital Infrastructure to solve India’s hard problems towards presence-less, paperless, and cashless service delivery.
- It aims to unlock the economic primitives of identity, data, and payments at population scale.
- The vision of India Stack is not limited to one country; it can be applied to any nation, be it a developed one or an emerging one.
- This project was conceptualized and first implemented in India, where its rapid adoption by billions of individuals and businesses has helped promote financial and social inclusion and positioned the country for the Internet Age.
How can DPI help Boost India’s Digital Infrastructure?
- Independent Steward Institutions:
- A multiparty governance process through independent DPI institutions will be accountable to a broad range of stakeholders rather than be controlled by a single entity or group. This can build trust and confidence in DPI.
- Global Standards:
- There is a need to develop global standards through a multilateral dialogue led by India.
- If standards originating from developed nations were transplanted to an emerging economies’ context smaller countries would simply be captive to dominant technology players.
- Sustainable Financing Models:
- There is a need to develop sustainable financing models for developing DPI for the world.
- Currently backed by philanthropic funding, such models are at risk of becoming a tool of philanthropic competition and positioning.
- New Playbook for Digital Infrastructure:
- The world needs a new playbook for digital infrastructure that mediates the flow of people, money and information.
- This will facilitate countries looking to digitally empower their citizens.
- They can then rapidly build platforms that address the specific needs of people, while ensuring people are able to trust and use the platform – without fear of exclusion or exploitation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The Aadhaar platform helps service providers authenticate identity of residents electronically, in a safe and quick manner, making service delivery more cost effective and efficient. According to the GoI and UIDAI, Aadhaar is not proof of citizenship.
- However, UIDAI has also published a set of contingencies when the Aadhaar issued by it is liable for rejection. An Aadhaar with mixed or anomalous biometric information or multiple names in a single name (like Urf or Alias) can be deactivated. Aadhaar can also get deactivated upon non-usage of the same for three consecutive years.


International Relations
Japan’s Official Development Assistance
For Prelims: India-Japan Relations, Climate Change, Patna Metro, Western Dedicated Freight Corridor.
For Mains: Japan’s Official Development Assistance, India-Japan relations.
Why in News?
Recently, Japan has approved Official Development Assistance (ODA) to India, for a few Key projects.
- India and Japan have had a long and fruitful history of bilateral development cooperation since 1958. In the last few years, the economic cooperation between India and Japan has steadily progressed.
What are the Key Projects under ODA?
- Patna Metro Rail Construction Project:
- Rs. 5,509 crores have been approved for Patna Metro Rail Construction Project (I).
- It aims to cope with the increase of traffic demand in Patna by constructing the new metro corridor, thereby contributing to improvement of the urban environment and development of the economy as well as mitigation of Climate Change.
- Forest and Biodiversity Conservation in West Bengal:
- Rs. 520 crores approx. have been approved for the Project for Forest and Biodiversity Conservation for Climate Change Response in West Bengal.
- It aims to mitigate and adapt to climate change, conserve and restore ecosystems by ecosystem-based climate change measures, biodiversity conservation and restoration, thereby contributing to sustainable socio-economic development in the State.
- Rajasthan Water Sector Livelihood Improvement Project:
- Rs. 1,055.53 crores have been approved for Rajasthan Water Sector Livelihood Improvement Project (II).
- It aims to improve livelihoods of farmers as well as promote gender mainstreaming in agriculture and irrigation sector in the State, by improving water use efficiency and agriculture productivity, through improvement of existing irrigation facilities and agriculture support services.
What are the Other ODAs to India from Japan?
- Delhi Metro is one of the most successful examples of Japanese cooperation through the utilization of ODA.
- India’s Western Dedicated Freight Corridor (DFC) project is funded by a soft loan provided by Japan International Cooperation Agency under Special terms for economic partnership (STEP).
- Besides, Japan and India had committed to build High-Speed Railways in India by introducing Japan’s Shinkansen System.
- India Japan Nuclear Deal 2016 will help India build the six nuclear reactors in southern India, increasing nuclear energy capacity ten-fold by 2032.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘The time has come for India and Japan to build a strong contemporary relationship, one involving global and strategic partnership that will have a great significance for Asia and the world as a whole’. Comment. (2019)


Governance
Overview of Indian Healthcare Sector
For Prelims: Gender Index, Aquaculture, National Health Mission, World Health Organization, non-communicable Diseases.
For Mains: National health Mission, Health sector, eradication of leprosy.
Why in News?
Recently, in the Parliament House, various aspects of India's health and agriculture sectors, as well as their most recent updates, were discussed.
What are the Updates in Indian Health Sector?
- Leprosy:
- India has eliminated Leprosy as a public health problem, according to the World Health Organization criterion, there must be less than one case per 10,000 population at the national level, the criterion set in 2005 stated.
- With several interventions introduced under the National Leprosy Eradication Programme in the last few years, the number of new leprosy cases detected have come down to 75,394 in 2021-22 from 125,785 in 2014-15.
- Menstrual Hygiene Scheme:
- Currently, 26 states and Union Territories implemented the Menstrual Hygiene Scheme with either the National Health Mission (NHM) budget or combined budget of NHM and the state
- In 2021-22, approximately 3.49 million adolescent girls were provided sanitary napkin packs every month as per “Health Management Information System” (HMIS) data.
- The Department of Pharmaceuticals under the Union Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilizers implements the Pradhan Mantri Bharatiya Janausadhi Pariyojna, which is an important step in ensuring the health security for women.
- Under the project, over 8,800 Janaushidhi Kendras have been set up across the country that provide Oxo-biodegradable sanitary napkins named ‘Suvidha’ at Rs 1 per pad.
- Lifestyle Diseases:
- The proportion of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) have increased in India from 30.5 % in 1990 to 55.4 % in 2016.
- The figures were quoted from 2017 Indian Council of Medical Research study report, India: Health of the Nation’s States — The India State-Level Disease Burden Initiative (2017).
- The proportion of Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs) have increased in India from 30.5 % in 1990 to 55.4 % in 2016.
- Gender Gap in India:
- India’s rank has improved on the Global Gender Gap Index in 2022 compared with 2021.
- The Global Gender Gap Report 2022 was released by the World Economic Forum.
- The Global Gender Gap Report 2022 ranks India at 135 out of 146 countries on the Global Gender Gap Index with a score of 0.629 out of 1.
- India’s rank has improved on the Global Gender Gap Index in 2022 compared with 2021.
- High Blood Lead Levels:
- Research by government think tank NITI Aayog and the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, found that 275 million children under 19 years of age in India have blood lead levels that are abnormally high that is, greater than five micrograms per deciliter.
- Cancer due to Arsenic Contamination in Assam and Bihar:
- Assam had an estimated 39,787 cancer cases and Bihar had 109,274 in 2022, according to the ICMR National Cancer Registry Programme.
- Prolonged use of arsenic contaminated water for drinking causes several diseases, predominantly skin pigmentation, thickening, hard patches on the palms and soles of the feet (hyperkeratosis)
- These occur after a minimum exposure of approximately five years and may be a precursor to skin cancer. In addition, long-term exposure to arsenic may also cause cancers of the bladder and lungs.
- Assam had an estimated 39,787 cancer cases and Bihar had 109,274 in 2022, according to the ICMR National Cancer Registry Programme.
What are the Updates in Indian Agriculture Sector?
- The cultivable land area in India has declined 1,79,993 thousand hectares in 2019-20 from 1,80,624 thousand hectares in 2018-19, according to the latest Land Use Statistics-at a Glance 2010-11 to 2019-20.
- The marginal decline in agricultural/cultivable land has been mainly due to the diversion of land for non-agricultural purposes such as urbanization, creation of infrastructure viz roads, airports, housing, etc.,
- While there is shift in agricultural land for non-agricultural purposes, non-agricultural land is also being brought under agricultural uses through various schemes implemented by the government.
What are the Updates in Aquaculture?
- India is the third largest fish-producing country, contributing 8% to global fish production, and ranks second in aquaculture production.
- Fish production in 2021-22 was 16.24 million Tonnes comprising marine fish production of 4.12 million Tonnes and 12.12 million Tonnes from aquaculture.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following are the objectives of ‘National Nutrition Mission’? (2017)
- To create awareness relating to malnutrition among pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- To reduce the incidence of anaemia among young children, adolescent girls and women.
- To promote the consumption of millets, coarse cereals and unpolished rice.
- To promote the consumption of poultry eggs.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 2 and 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 4 only
(d) 3 and 4 only
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- National Nutrition Mission (POSHAN Abhiyaan) is a flagship programme of the Ministry of Women and Child Development, GoI, which ensures convergence with various programmes like Anganwadi services, National Health Mission, Pradhan Mantri Matru Vandana Yojana, Swachh-Bharat Mission, etc.
- The goals of National Nutrition Mission (NNM) are to achieve improvement in nutritional status of children from 0-6 years, adolescent girls, pregnant women and lactating mothers in a time bound manner during the next three years beginning 2017- 18. Hence, 1 is correct.
- NNM targets to reduce stunting, under-nutrition, anaemia (among young children, women and adolescent girls) and reduce low birth weight of babies. Hence, 2 is correct.
- There is no such provision relating to consumption of millets, unpolished rice, coarse cereals and eggs under NNM. Hence, 3 and 4 are not correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. “Besides being a moral imperative of a Welfare State, primary health structure is a necessary precondition for sustainable development.” Analyse. (2021)


Important Facts For Prelims
Hybrid Gamosas
Why in the News?
Recently, the Bangla Sahitya Sabha, Assam (BSSA) felicitated guests at a function with “hybrid gamosas” made up of Assamese Gamocha and Bengali Gamchas cut in half and sewn together. The organization issued an apology after a controversy erupted.
- The BSSA is a newly formed literary and cultural society with the aim of serving as a meeting point for Bengalis of Assam.
What is Assamse Gamocha?
- About:
- Assamese Gamocha is a traditional handwoven cotton towel, which is an integral part of Assamese culture and tradition.
- It is a rectangular piece of cloth. The towel comes in various colors and designs, and the most popular among them are the red and white ones with a Phulam known as the ‘Gamocha design’.
- The word ‘Gamocha’ is derived from the Assamese word ‘Ga’ (body) and ‘Mocha’ (wipe), which means a towel to wipe the body. The weavers use a traditional loom called the ‘Taat Xaal’ to weave the towel.
- Recognition:
- The Assamese Gamocha has gained national and international recognition for its unique design and cultural significance. It was granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, which is a recognition of its origin and unique characteristics.
- The GI tag ensures that the Gamocha is protected from imitations and helps to promote the local weavers and their traditional weaving techniques.
- Cultural Significance:
- The Assamese Gamocha is a symbol of Assamese culture and tradition. The towel is used in various ways in daily life, and each use has a specific cultural significance.
- It is used as a headscarf by women during traditional ceremonies and functions, and it is a sign of respect and honor when it is presented to someone as a gift.
- The Gamocha is also used during the Bihu festival, which is the most important festival of Assam. It is draped around the neck of the Bihu dancers, and it is an essential part of their costume. The towel is also used as a symbol of unity and brotherhood during the Bihu festival.
- The Assamese Gamocha is a symbol of Assamese culture and tradition. The towel is used in various ways in daily life, and each use has a specific cultural significance.
What is Bengali Gamcha?
- Bengali Gamcha traditional handwoven cotton towel, which is an integral part of Assamese culture and tradition. It is a rectangular piece of cloth. It comes in a red-and-white chequered pattern.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 to comply with the obligations to (2018)
(a) ILO
(b) IMF
(c) UNCTAD
(d) WTO
Ans: (d)
- Geographical indications (GIs) are a type of intellectual property (IP).
- The World Trade Organisation (WTO) recognises intellectual property rights under TRIPS (Trade Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights) Agreement.
- Under Article 22(1) of the TRIPS Agreement, the GIs are defined as “indications which identify a good as originating in the territory of a member, or a region or locality in that territory, where a given quality, reputation or other characteristics of the good is essentially attributable to its geographic origin”.
- The GIs act as source identifiers as well as quality indicators. GIs let consumers know that the goods come from an area where a given quality, reputation or other characteristic of the goods is essentially attributable to their geographic origin.
- Further, GIs as intellectual property rights enable relief from the acts of infringement and/or unfair competition. z Following TRIPS Agreement, the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 was passed by the GoI. The Act aims to provide protection by granting GI tags to agricultural goods, natural goods or manufactured goods or any goods of handicraft or goods of industry including food stuff.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q2. Which of the following has/have been accorded ‘Geographical Indication’ status? (2015)
- Banaras Brocades and Sarees
- Rajasthani Daal-Bati-Churma
- Tirupathi Laddu
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
Piezoelectric Effect
Why in News?
Recently, scientists have reported evidence of the Piezoelectric effect in liquids.
- The effect has been known for 143 years and in this time has been observed only in solids.
What is the Piezoelectric Effect?
- The piezoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which certain materials produce an electrical charge in response to mechanical stress or pressure. This effect occurs when the material is subjected to a force that causes its molecules to become polarized, meaning that the positive and negative charges within the material are separated from each other.
- When this polarization occurs, an electric potential is generated across the material, and if the material is connected to a circuit, a current can flow.
- The reverse is also true: if an electric potential is applied to the material, it can cause a mechanical deformation.
- Piezoelectric materials are used in a variety of applications, such as in sensors, actuators, and energy harvesting devices. Some examples of common piezoelectric materials include quartz, ceramics, and certain types of crystals.
- Example: Quartz is the most famous piezoelectric crystal: it is used in this capacity in analog wristwatches and clocks.
- The Piezoelectric effect was discovered in 1880, in quartz, by Jacques and Pierre Curie.
What are the Implications of Discovery?
- The discovery opens the door to applications that have previously not been accessible with solid-state materials and are more readily recyclable and in many instances pose fewer environmental issues than many currently used piezoelectric materials.
- The liquids also displayed the inverse piezoelectric effect: they became distorted when an electric charge was applied, this fact could be used to control how the liquids bent light passing through them by passing different currents through them.
- That is, using this simple control mechanism, vials of these liquids could be lenses with dynamic focusing abilities.
- The new finding challenges the theory that describes this effect as well as opens the door to previously unanticipated applications in electronic and mechanical systems.


Important Facts For Prelims
Ministry of Culture's Initiative to Promote of Art and Culture
Why in News?
The Ministry of Culture has implemented a Scheme to protect all genres of artists, including folk song artists, called the 'Scheme of Scholarship and Fellowship for Promotion of Art and Culture'.
- This scheme has three components that aim to support young artists, outstanding persons in different cultural fields, and those conducting cultural research.
What are the Components of the Scheme?
- Award of Scholarships to Young Artists in Different Cultural Fields (SYA):
- Provides a scholarship for a period of 2 years to selected beneficiaries in the age group of 18-25 years.
- Candidates should have undergone training under any Guru or Institution for a minimum of 5 years.
- Award of Senior/Junior Fellowships:
- Senior Fellowship is provided to selected Fellows in the age group of 40 years and above for 2 years for cultural research.
- Junior Fellowship is provided to selected Fellows in the age group of 25 to 40 for 2 years.
- Up to 400 Senior & Junior Fellowships are awarded in one batch year.
- Award of Tagore National Fellowship for Cultural Research (TNFCR):
- Candidates are selected under two categories, Tagore National Fellowship and Tagore Research Scholarship, to work on cultural research by affiliation under different participating institutions in 4 different groups.
- Selection of Fellows and Scholars is made by the National Selection Committee (NSC).
- Candidates are selected under two categories, Tagore National Fellowship and Tagore Research Scholarship, to work on cultural research by affiliation under different participating institutions in 4 different groups.
- Additional Component:
- Under the scheme of “Project Grants to Individuals for Research in the Performing Arts”, the Sangeet Natak Akademi provides financial assistance to individuals on recommendation of the Advisory Committee.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
NGT Imposes Penalty on Kerala Govt. for Failing to Protect Ramsar Sites
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has imposed a penalty of Rs 10 crore on the Kerala government for failing to protect two wetlands, Vembanad and Ashtamudi lakes, which are included in the Ramsar list of wetlands. The wetlands have become polluted due to the dumping of pharmaceutical waste, plastic waste, household waste, and slaughterhouse waste.
Vembanad, Kerala’s largest wetland ecosystem was designated as a Ramsar site back in 2002. According to a recent study by the Kerala University of Fisheries and Ocean Studies, Vembanad lake’s water retention capacity has decreased by 85% in the last 120 years due to encroachment and devastation of its ecology.
Ashtamudi lake, home to several plant and bird species, was included in the Ramsar list in August 2002. Since then, little has been done to safeguard the site which is currently experiencing a notable build-up of waste.
The Kerala Legislative Assembly’s Environment Committee has listed several proposals, including the formation of the Ashtamudi Wetland Management Authority, to protect the site. It recommended immediate regulations to control unlawful demolition and dumping of boats in the lake and directed the state pollution control board to check the coliform bacteria and oxygen levels in the lake every three months.
Read More: Ramsar Sites.
Saudi Arabia Joins Shanghai Cooperation Organization as a Dialogue Partner
Saudi Arabia has approved to join the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO) as a dialogue partner.
The SCO was formed in 2001 by Russia, China, and former Soviet states in Central Asia, and has since expanded to include India and Pakistan. It aims to play a bigger role as a counterweight to Western influence in the region.
Iran also signed documents for full membership in 2022. The dialogue partner status for Saudi Arabia will be a first step within the organisation before granting the kingdom full membership in the mid-term.
Countries belonging to the organisation plan to hold a joint "counter-terrorism exercise" in Russia's Chelyabinsk region in August 2023.
Indian Coast Guard’s Regional Search and Rescue Exercise
The Indian Coast Guard recently conducted a Regional Search and Rescue exercise in Kakinada, Andhra Pradesh, to simulate a real-time maritime distress scenario and highlight the functioning of the Search and Rescue organization (SAR) for a mass rescue operation.
The exercise involved all stakeholders and effectively used available resources towards Maritime Search and Rescue contingency efficiently.
Sea area off Kakinada was chosen as the venue for the exercise considering the large-scale exploration and production activities in the Krishna Godavari basin which makes the area potential for emergencies necessitating large scale SAR response.
Read More: Indian Coast Guard
Upward Lightning
Researchers in Brazil have captured images of "upward lightning" or "upward flashes".
This phenomenon occurs when a self-initiated lightning streak develops from a tall object and travels upward towards an electrified storm cloud. The phenomenon requires storm electrification and the presence of a cloud charge region.
The vertical elevation of a tall object emphasises the electric field locally on the ground, resulting in conditions favourable for the initiation of an upward streak from a tall object.
The process is also triggered by the development of a stepped leader, which is a channel of negative charge that travels downward in a zigzag pattern from a cloud, leading to an intensification of the positive charge on the ground.
The negatively charged, downward-moving stepped leader makes contact with one of the developing positively charged upward streamers, completing the lightning channel, and causing charges to flow rapidly from the cloud towards the ground.
Read More: Lightning Streak