India-Russia Bilateral Meeting
For Prelims: India-Russia Bilateral Meeting, Regional stability, Terrorism, Russian-built nuclear plants, Kudankulam nuclear power plant.
For Mains: India-Russia Bilateral Meeting, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, the External Affairs minister of India has visited Russia for a Bilateral Meeting where both the countries signed agreements on Nuclear Power and in areas of medicines, pharmaceutical substances and medical devices.
What are the Key Highlights of the India-Russia Bilateral Meeting?
- Economic Collaboration:
- Emphasis on strategic collaboration in defense, space exploration, nuclear energy, and technology sharing, reflecting the robustness of the longstanding partnership and exploring avenues for deeper cooperation.
- Both Countries agreed on the expansion of the exports of Russian hydrocarbons to the Indian market as well as the cooperation in the peaceful use of nuclear energy.
- The two sides finalised the programme of cooperation in the Far East and it was decided to hold an early meeting of EaEU-India FTA negotiations.
- Agreement on Nuclear Power Plants:
- India and Russia signed agreements to move forward with future units of the Kudankulam nuclear power project in Tamil Nadu.
- India is already operating two Russian-built nuclear plants while another four are under construction in Kudankulam, Tamil Nadu.
- The Kudankulam nuclear power plant, India's largest, is being built in Tamil Nadu with the technical assistance of Russia. The construction began in March 2002. Since February 2016, the first power unit of the Kudankulam NPP has been steadily operating at its design capacity of 1,000 MW.
- The plant is expected to start operating at full capacity in 2027, according to Russian state media.
- Diplomatic Initiatives:
- Discussion on multilateral forums and international organizations where India and Russia collaborate or hold common interests, including forums like BRICS, SCO (Shanghai Cooperation Organization), and UN affairs.
How has Been the Indo-Russia Relations?
- Historical Background:
- During the Cold War, India and the Soviet Union had a strong strategic, military, economic and diplomatic relationship. After the Dissolution of the Soviet Union, Russia inherited its close relationship with India which resulted in both nations sharing a Special Strategic Relation.
- However, the relations have taken a steep downfall over the past few years, especially in the post-Covid scenario. One of the biggest causes for this is Russia’s close relations with China and Pakistan, which have caused many geopolitical issues in the past few years for India.
- Political Relations:
- Two Inter-Governmental Commissions – one on Trade, Economic, Scientific, Technological and Cultural Cooperation (IRIGC-TEC), and another on Military-Technical Cooperation (IRIGC- MTC), meet annually.
- Bilateral Trade:
- India's total bilateral trade with Russia stood at ~USD 13 Billion in 2021-22 and USD 8.14 Billion in 2020-21.
- Russia is India’s seventh biggest trading partner, up from 25th position in 2021.
- The US, China, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and Indonesia were the six countries that recorded higher volumes of trade with India during the first five months of 2022-23.
- Defence and Security Relations:
- Both countries regularly conduct the Tri-Services exercise ‘INDRA‘.
- The joint military programmes between India and Russia include:
- BrahMos cruise missile programme
- 5th generation fighter jet programme
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI programme
- The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- S-400 Triumf
- Kamov Ka-226 200 to be made in India under the Make in India initiative
- T-90S Bhishma
- INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier programme.
- Science and Technology:
- Science & Technology has played a key role in the bilateral India-Russia (and India-Soviet) partnership, especially in the early days after India’s independence where the erstwhile Soviet Union’s assistance was crucial to the establishment of Bhilai Steel Plant, Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay and India’s space program.
- During the early stages of the Indian space program, the Soviet Union’s assistance played a key role in the launch of the first Indian satellites-Aryabhatta and Bhaskara in 1984.
- Today, India & Russia work together on basic sciences, materials science, mathematics and cutting-edge areas like India’s manned spaceflight program (Gaganyaan), nanotechnologies and quantum computing.
What is the Significance of Russia for India?
- Balancing China:
- The Chinese aggression in the border areas of eastern Ladakh, brought India-China relations to an inflection point, but also demonstrated that Russia can contribute to defusing tensions with China.
- Russia organized a trilateral meeting among the foreign ministers of Russia, India, and China following deadly clashes in the Galwan Valley in the disputed territory of Ladakh.
- Emerging New Sectors of Economic Engagement:
- Apart from traditional areas of cooperation such as weapons, hydrocarbons, nuclear energy, and diamonds, new sectors of economic engagement are likely to emerge — mining, agro-industrial, and high technology, including robotics, nanotech, and biotech.
- India’s footprint in the Russian Far East and in the Arctic is set to expand. Connectivity projects may get a boost too.
- Combating Terrorism:
- India and Russia are working to close the gap on Afghanistan and are calling for early finalization of the Comprehensive Convention on International Terrorism.
- Support At Multilateral Forums:
- Additionally, Russia supports India’s candidacy for permanent membership of a reformed United Nations Security Council and of the Nuclear Suppliers Group.
- Russia’s Military Exports:
- Russia was India’s largest arms supplier in the periods between 2013-17 and 2018-22, but its share of arms imports to India fell from 64% to 45%, according to Stockholm International Peace Research Institute’s (SIPRI) Trends in International Arms Transfers 2022 report.
Way Forward
- Russia will remain a key defense partner for India for decades to come.
- The two countries have been discussing how they can cooperate in using India as a production base for exporting to third countries Russian-origin equipment and services.
- To address this, Russia has made legislative changes allowing its companies to set up joint ventures in India to address it following an Inter-Governmental Agreement signed in 2019.
- This agreement needs to be implemented in a time bound manner.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Recently, India signed a deal known as ‘Action Plan for Prioritization and Implementation of Cooperation Areas in the Nuclear Field’ with which of the following countries? (2019)
(a) Japan
(b) Russia
(c) The United Kingdom
(d) The United States of America
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)
Pesticide Poisoning
For Prelims: Droughts, Crop Failures, pesticide poisoning, Insecticides Act, 1968 and the Insecticides Rules, l971.
For Mains: Importance of pesticides as per agricultural productivity is concerned and associated health and Environmental concern.
Why in News?
Recently, in Maharashtra which is prone to droughts and crop failures, pesticide poisoning has claimed the lives of many farmers and farm workers in recent years.
- 20 farmers have died due to pesticide poisoning in Yavatmal district alone since 2017.
- Many others have suffered from respiratory problems, skin rashes, eye irritation, neurological disorders, reproductive issues, cancer, and even death.
What are Pesticides?
- About:
- Pesticide is any chemical or biological substance intended to prevent, destroy or control damage from pests which has both agricultural and non-agricultural uses.
- They also pose serious risks to human health and the environment, especially when they are misused, overused, or sold illegally.
- Types:
- Insecticides: The chemicals that are used to protect plants from insects and pests are known as Insecticides.
- Fungicides: This class of crop protection chemicals is used to control the spread of fungal diseases in plants.
- Herbicides: Herbicides are chemicals that kill or control the growth of weeds in the cultivation area.
- Bio-Pesticides: They are Pesticides of biological origin, i.e., derivedfrom animals, plants, bacteria etc.
- Others: This includes plant growth regulators, nematicides,rodenticides and fumigants.
- Pesticide Poisoning:
- Pesticide poisoning is a term that refers to the adverse effects of exposure to pesticides on humans or animals.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pesticide poisoning is one of the leading causes of death among agricultural workers worldwide.
- Pesticides can be classified into two types, Acute (short-term) and chronic (long-term).
- Acute poisoning occurs when a person ingests, inhales, or comes into contact with a large amount of pesticide in a short period of time.
- Chronic poisoning occurs when a person is exposed to low doses of pesticide over a long period of time, which can cause damage to various organs and systems in the body.
- Recently Banned Pesticides:
- The government has banned three more insecticides in 2023: Dicofol, Dinocap, and Methomyl, in addition to monocrotophos.
How Pesticides are Regulated in India?
- Pesticides are regulated under the Insecticides Act, 1968 and the Insecticides Rules, l971.
- The Insecticides Act of 1968 covers the registration, manufacture and sale of pesticides in India.
- The Act is administered by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
Note
The Pesticide Management Bill, 2020 was introduced in Rajya Sabha in 2020. It seeks to regulate the manufacture, import, sale, storage, distribution, use, and disposal of pesticides, in order to ensure the availability of safe pesticides and minimize the risk to humans, animals, and environment. The Bill seeks to replace the Insecticides Act, 1968.
What are the Concerns regarding uses of Pesticides?
- Harmful Effects on Farmers:
- Experts believe that chronic low-level pesticide exposure is associated with a broad range of nervous system symptoms such as headache, fatigue, dizziness, tension, anger, depression, and impaired memory, Parkinson's disease, and Alzheimer's disease, among others.
- Harmful Effect on Consumers:
- Pesticides go up the food chain by working their way through the environment and into the soil or the water systems after which they are taken by aquatic animals or plants and ultimately humans. This process is called Biomagnification.
- Harmful Effect on Agriculture:
- Continued use of pesticides for decades has contributed significantly to the current ecological, economic and existential crisis of the Indian agriculture sector.
- Regulatory Issues:
- Although agriculture is a state subject, education, and research related to insecticides are governed by the Insecticides Act, 1968, which is a central act. Therefore, state governments do not have a direct role in amending this act.
- It is due to this that an estimated 104 pesticides that are still produced/ used in India, have been banned in two or more countries in the world.
- In 2021, non-profit Pesticide Action Network (PAN) International released a list of highly hazardous pesticides, of which over 100 pesticides are currently approved for use in India.
- Although agriculture is a state subject, education, and research related to insecticides are governed by the Insecticides Act, 1968, which is a central act. Therefore, state governments do not have a direct role in amending this act.
Way Forward
- Regulatory Reforms:
- Strictly enforce regulations to curb the illegal sale and misuse of pesticides.
- Implement penalties for those found violating pesticide usage guidelines.
- Government Support:
- Provide financial support to farmers to help them adopt safer and more sustainable agricultural practices.
- This could include subsidies for organic farming, integrated pest management, or the purchase of safer pesticides.
- Community Awareness Programs:
- Conduct awareness campaigns at the community level to educate people about the risks associated with pesticide use.
- Involve local communities in monitoring and reporting cases of misuse or poisoning.
- Compensation Mechanism:
- Establish a compensation mechanism for victims of pesticide poisoning.
- Ensure a swift and transparent process for filing claims and receiving compensation for medical expenses and economic losses.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Lead, ingested or inhaled, is a health hazard. After the addition of lead to petrol has been banned, what still are the sources of lead poisoning? (2012)
- Smelting units
- Pens and pencils
- Paints
- Hair oils and cosmetics
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Q. In India, the use of carbofuran, methyl parathion, phorate and triazophos is viewed with apprehension. These chemicals are used as (2019)
(a) pesticides in agriculture
(b) preservatives in processed foods
(c) fruit-ripening agents
(d) moisturizing agents in cosmetics
Ans: (a)
- To promote organic farming, the Department of Agriculture, Kerala, has ordered a ban on the use of around 17 pesticides since 2011.
- The list of banned pesticides are:
- Insecticides: Cabofuran, Methyl Demeton, Methyl Parathion, Monocrotophos, Phorate, Methymol, Profenofos, Triazophos, Endosulfan
- Fungicides: MEMC, Ediphenphos, Tricyclazole, Oxythioquinox
- Weedicides: Anilophos, Paraquat, Thiobencarb, Atrazine
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Artificial Intelligence
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence (AI), Ethical AI, Machine Learning, Large Language Models, Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence, Artificial Intelligence Mission
For Mains: Boosting AI innovation and startups, Artificial Intelligence Technology.
Why in News?
The year 2023 has been a landmark year for Artificial Intelligence (AI) innovation, showcasing incredible advancements in various AI tools. These advancements offer a glimpse into the expanding potential of AI, particularly in creativity, conversation, and visual content generation.
- However, this surge in development emphasizes the critical need for enhanced oversight to ensure ethical AI use and equitable access to its benefits.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
- About:
- AI is defined as the ability of machines and systems to acquire and apply knowledge and to carry out intelligent behaviour.
- The term "Artificial Intelligence" was coined by John McCarthy, an American computer scientist and cognitive scientist. He was one of the founders of the discipline of AI.
- It includes technologies like machine learning, Deep Learning, Big Data, Neural Networks, Computer vision, Large Language Models etc.
- The ideal characteristic of artificial intelligence is its ability to rationalize and take actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific goal.
- AI is defined as the ability of machines and systems to acquire and apply knowledge and to carry out intelligent behaviour.
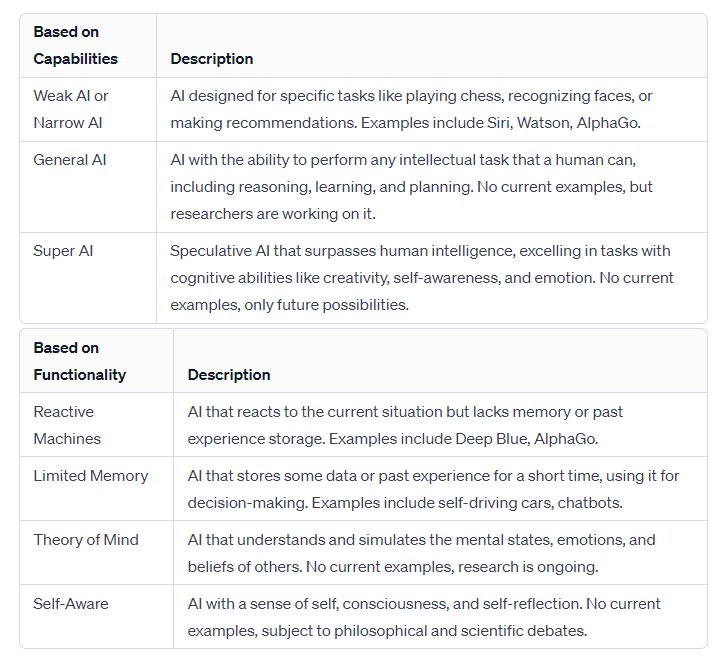
- Types of AI:
- Principles for the Ethical Use of AI:
- AI initiatives should align with established ethical principles, human rights, and societal values to ensure responsible technological advancement.
- Prioritize the positive impact of AI on individuals, communities, and society, emphasizing responsible use for the greater good.
- Design AI systems to be transparent and explainable, allowing users and stakeholders to understand operations and decision-making processes, fostering trust and accountability.
- Mitigate biases in AI algorithms to ensure fair outcomes, preventing discrimination based on race, gender, ethnicity, or socioeconomic status.
- Uphold individuals' privacy rights by responsibly handling personal data, obtaining explicit consent, and complying with relevant privacy laws and regulations.
- Establish clear lines of accountability for developers and organizations deploying AI systems, with mechanisms to address errors or harmful impacts.
- Develop and utilize AI technology to enhance human well-being, address societal challenges, and contribute positively to global progress, economies, and environmental sustainability.
- AI initiatives should align with established ethical principles, human rights, and societal values to ensure responsible technological advancement.
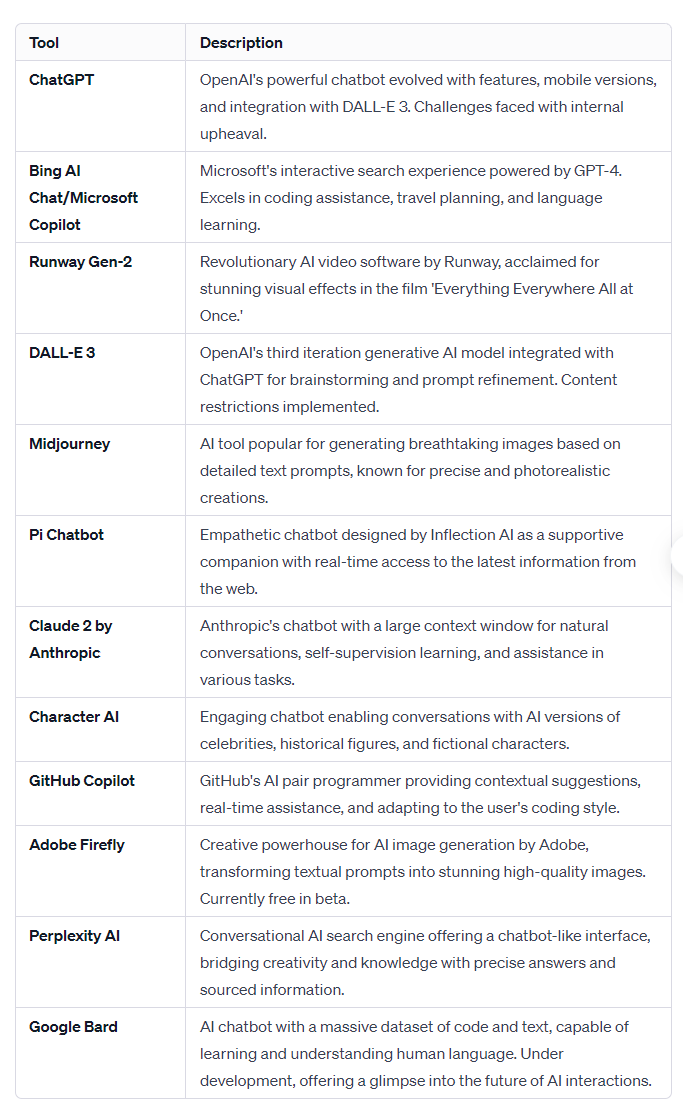
- Major AI Tools:
- India's Initiatives Related to Artificial Intelligence:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Breakthrough Prizes
Why in News?
The 2024 Breakthrough Prizes in the Life Sciences category recognised groundbreaking research set to change the lives of those suffering from three Rare Diseases: Parkinson’s disease, Cystic fibrosis and Cancer.
- Awards were also given in the categories of Fundamental Physics and Mathematics.
What are the 2024 Award-Winning Breakthroughs?
- Life Sciences:
- Cancer Treatment Advances:Carl June and Michel Sadelain genetically engineered T cells with synthetic receptors to recognize individual cancer cells, achieving remarkable success against liquid cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
- Some patients have experienced complete tumor eradication and long-term remission after treatment.
- Cystic Fibrosis Breakthroughs: Sabine Hadida, Paul Negulescu, and Fredrick Van Goor invented the first effective medicines to treat the underlying cause of cystic fibrosis.
- These medicines, including a triple combination medicine, enable a protein to function properly, significantly improving the quality and length of life for people with this disease.
- Parkinson's Disease Discoveries: Thomas Gasser, Ellen Sidransky, and Andrew Singleton discovered the most common genetic causes of Parkinson’s Disease.
- These discoveries offer clues to the mechanisms that cause the disease, pointing to the role of the lysosome in neuronal damage.
- Cancer Treatment Advances:Carl June and Michel Sadelain genetically engineered T cells with synthetic receptors to recognize individual cancer cells, achieving remarkable success against liquid cancers such as leukemia, lymphoma, and myeloma.
- Fundamental Physics:
- Winners John Cardy and Alexander Zamolodchikov have contributed a lifetime of deep insights into quantum field theories,
- Mathematics:
- Awardee Simon Brendle has contributed a series of remarkable leaps in differential geometry, a field that uses the tools of calculus to study curves, surfaces and spaces.
What are the Breakthrough Prizes?
- Establishment:
- Founded in 2012 by prominent Silicon Valley figures including Yuri Milner, Mark Zuckerberg, Priscilla Chan (from Facebook), and Sergey Brin (from Google).
- Recognition of Scientific Excellence:
- The prizes aim to honor outstanding individuals who have made transformative contributions in fundamental sciences, specifically in fields like life sciences, mathematics, and fundamental physics.
- Categories:
- The Breakthrough Prizes are awarded in distinct categories, including life sciences (biology, genetics, medicine), fundamental physics, and mathematics.
- Financial Reward:
- Recipients of the Breakthrough Prizes are awarded a substantial monetary prize. Each recipient receives USD 3 million, surpassing the monetary value associated with Nobel Prizes, which offer USD 1 million per category.
- Oscars of Science:
- Often dubbed as the "Oscars of Science," these awards hold significant prestige within the scientific community, shining a spotlight on groundbreaking discoveries and advancements.
- Recognition Events:
- The awards are presented annually, acknowledging top scientists globally. The inaugural ceremony in 2012 was hosted by actor Morgan Freeman.
- Support for Early-Career Researchers:
- Additionally, there are other prizes associated with the Breakthrough Prizes, such as the New Horizons in Physics and Mathematics and the Maryam Mirzakhani New Frontiers Prize, dedicated to recognizing the work of promising early-career researchers.
What are Rare Diseases?
- About:
- A rare disease is a health condition of low prevalence that affects a small number of people compared with other prevalent diseases in the general population.
- There is no universally accepted definition of rare diseases and the definitions usually vary across different countries.
- Prevalence:
- There are about 7,000 known rare diseases, affecting around 8% of the world’s population” and “75% of rare disease patients are children.
- India has close to 50-100 million people affected by rare diseases or disorders.
- Examples:
- Lysosomal Storage Disorders (LSD)
- Cystic fibrosis
- Haemophilia
- Parkinson’s Disease
T+0 and Instant Settlement Cycle
Why in News?
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) has proposed a new system for settlement of funds and securities on T+0 (same day) and instant settlement cycle on an optional basis, supplementing the existing T+1 (trade plus one day) settlement cycle in the secondary markets for the equity cash segment.
- By embracing popular instant payment methods such as Unified Payment Interface, SEBI aims to adapt equity trading to modern investor preferences for enhanced flexibility.
What is the Settlement Cycle in the Securities Market?
- T in Settlement Cycles: The "T" in settlement cycles within financial markets refers to the day on which a transaction or trade takes place.
- In this context, "T" represents the transaction date. The settlement cycle, denoted as "T+n," specifies the number of days after the transaction date (T) by which the settlement or completion of the trade occurs.
- Evolution of Settlements Cycles : SEBI has shortened the settlement cycle to T+3 from T+5 in 2002 and subsequently to T+2 in 2003.
- Presently, the settlement of funds and securities occurs on the T+1 cycle in India, which was phased in through 2021 and wholly implemented by January 2023.
- SEBI's Proposed Phases for New Settlement Cycles:
- Phase 1: T+0 Settlement Cycle
- An optional T+0 settlement cycle is envisioned for trades until 1:30 PM, aiming to settle funds and securities on the same trading day by 4:30 PM.
- Phase 2: Instant Settlement Cycle
- An optional immediate trade-by-trade settlement, including funds and securities, with trading until 3:30 PM.
- SEBI has proposed the initial rollout of the T+0 settlement for the top 500 listed equity shares in three tranches (200, 200,100) based on market capitalization.
- This initiative corresponds to the changing Indian securities market, marked by surging volumes, values, and participants.
- Phase 1: T+0 Settlement Cycle
- Benefits:
- Clients: Enables faster pay-outs of funds against securities for sellers and vice versa, offering enhanced flexibility.
- Securities Market Ecosystem: Accelerated pay-outs are expected to bolster the market ecosystem's efficiency and liquidity.
Indian Meteorological Department
Why in News?
The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) recently got a new logo ahead of the commencement of its 150th year of providing weather and climate services to the country.
- The new logo, in a mix of orange and green colours, depicts numerical 150 embedded with the present logo showing the Indian monsoon winds crossing over India.
What is the India Meteorological Department?
- About:
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- It works as an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- To take meteorological observations and to provide current and forecast meteorological information for optimum operation of weather-sensitive activities like agriculture, irrigation, shipping, aviation, offshore oil explorations, etc.
- To warn against severe weather phenomena like tropical cyclones, norwesters, dust storms, heavy rains and snow, cold and heat waves, etc., which cause destruction of life and property.
- To provide meteorological statistics required for agriculture, water resource management, industries, oil exploration and other nation-building activities.
- To conduct and promote research in meteorology and allied disciplines.
Note
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere, focusing on understanding and forecasting weather patterns, atmospheric phenomena, and climate.
- It involves analyzing atmospheric conditions, such as temperature, humidity, air pressure, wind, and precipitation, to predict weather and study the processes that drive the Earth's atmospheric system.
What are the Major Initiatives Related to Meteorology in India?
- National Monsoon Mission (NMM): Government of India launched NMM in 2012 with a vision to develop a state-of-the-art dynamical prediction system for monsoon rainfall on different time scales.
- Mausam App: Tool for dissemination of weather information and warnings in an attractive and user friendly manner.
- Doppler Weather Radars: Based on Doppler principle, the radar is designed to improve precision in long-range weather forecasting and surveillance using a parabolic dish antenna and a foam sandwich spherical radome.
- DWR has the equipment to measure rainfall intensity, wind shear and velocity and locate a storm center and the direction of a tornado or gust front.
Angola Exits OPEC
Angola, one of Africa’s two biggest oil producers, has announced it is leaving the oil producers’ organization Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) over a dispute on output quotas.
- OPEC and 10 allied nations decided to further slash oil production in 2024 to prop up volatile global prices, which Angola said goes against its policy of avoiding decline and respecting contracts.
- The OPEC (headquartered in Vienna, Austria) is a permanent, intergovernmental organization, created at the Baghdad Conference in 1960, by Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela.
- Angola joined the group in 2007 and is not the first country to leave the cartel.
- Ecuador, Indonesia and Qatar have all done the same.
- Angola’s departure from OPEC will leave it with 12 members.
Read More: 6th India-OPEC Energy Dialogue
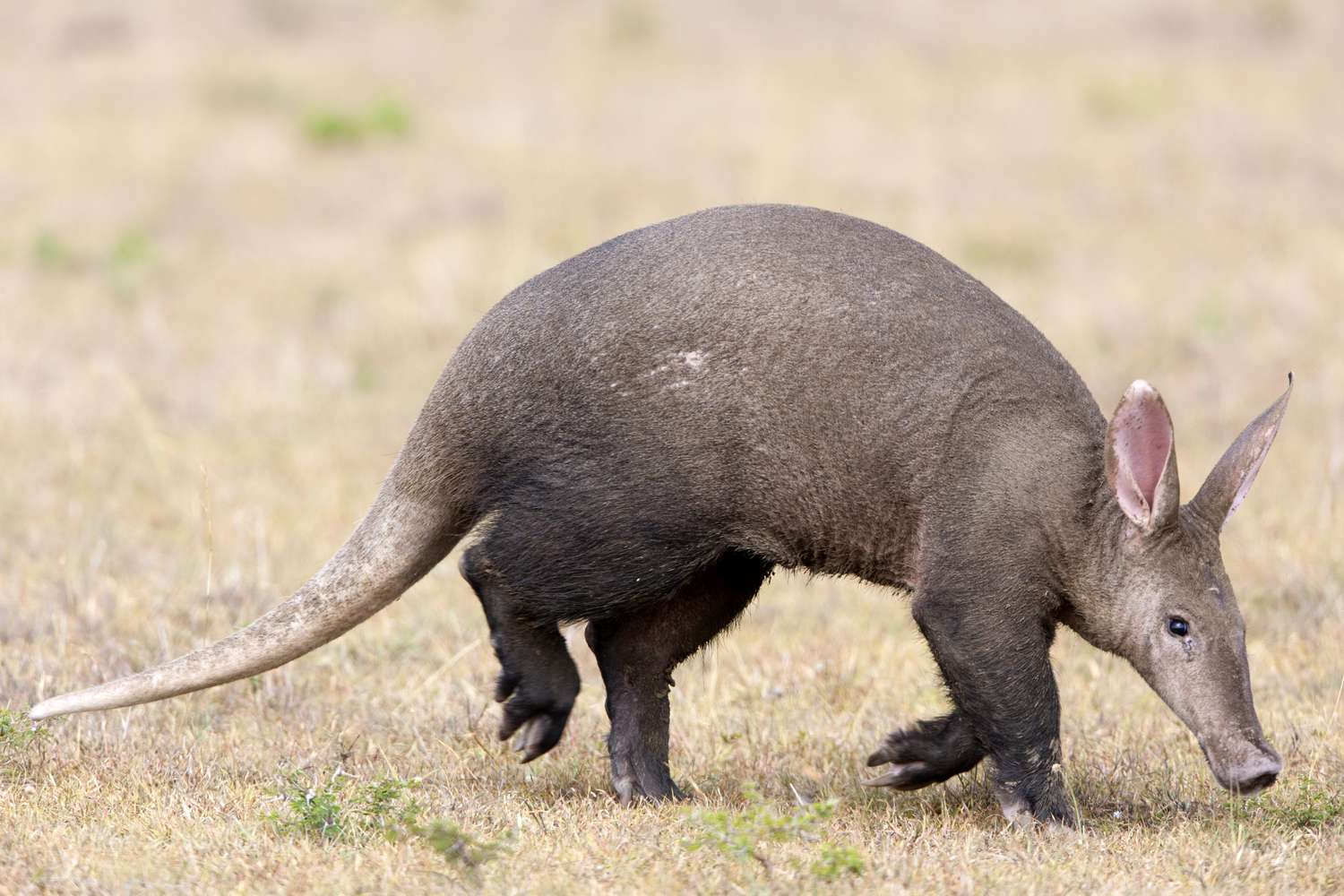
Impact of Climate Change on Aardvarks
A recent study from Oregon State University highlights the vulnerability of Aardvarks (Orycteropus afer) in sub-Saharan Africa (south of the Sahara Desert) to the impacts of climate change.
- Study reveals a concerning trend as increasingly dry landscapes isolate aardvarks, making them susceptible to rapid climate warming.
- Aridification (a gradual process of a region becoming drier) impacts their distribution and movement, with long-term droughts becoming more likely, particularly in the Horn of Africa.
- The Aardvark, a nocturnal mammal native to Africa, belongs to the Tubulidentata order and is the sole living species within this group.
- Aardvarks are burrowing mammals found across the southern two-thirds of Africa, primarily in savannah and semiarid areas.
- They are essential to the ecosystem as they feed on termites, which can damage human-built structures, and their burrows provide crucial habitat for numerous other species.
- The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species: Least Concern.
Read more: Global Climate Crisis and Net Zero
Elevating Copra MSP: Boosting Farmers & Markets
The Cabinet Committee on Economic Affairs (CCEA) recently announced a significant increase in the Minimum Support Price (MSP) for copra, setting it at ₹11,160 per quintal for milling copra and ₹12,000 per quintal for ball copra for the 2024 season.
- These adjustments aim to ensure substantial margins 51.84% for milling copra and 63.26% for ball copra benefiting major producing states like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Karnataka.
- The National Agricultural Cooperative Marketing Federation of India Ltd. (NAFED) and National Cooperative Consumers’ Federation (NCCF) will continue as Central Nodal Agencies (CNAs) for procurement under the Price Support Scheme (PSS), ensuring sustained support for copra and de-husked coconut procurement.
- MSP, set by the government, ensures farmers receive a guaranteed amount for their produce. Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), operating under the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare since 1965, recommends MSP based on production costs, market trends, and demand-supply dynamics.
Read more: Minimum Support Price
Government Declares MLJK-MA as Unlawful Association
The Government of India has officially designated the 'Muslim League Jammu Kashmir (Masarat Alam faction)' (MLJK-MA) as an 'Unlawful Association' under Section 3(1) of the Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act (UAPA) 1967.
- This decision is underscored by the organization's alleged engagement in anti-national and secessionist activities, explicit support for terrorism, and its purported role in inciting efforts to establish Islamic rule in Jammu and Kashmir.
- MLJK-MA is a separatist political organization in Jammu and Kashmir, led by Masarat Alam Bhat, a former militant.
- The UAPA, 1967, initially aimed at addressing secessionist movements and anti-national activities, has undergone multiple amendments.
- The latest amendment in 2019 incorporated provisions concerning terrorist financing, cyber-terrorism, individual designation, and property seizure.
- This legislation grants the National Investigation Agency (NIA) authority to investigate and prosecute cases under UAPA nationwide jurisdiction.
- According to Section 3(1) of the UAPA 1967, if the Central Government is of opinion that any association is, or has become, an unlawful association, it may, by notification in the Official Gazette, declare such association to be unlawful.