Government Securities
For Prelims: Government Securities, Reserve Bank of India (RBI), Fiscal Deficit, Treasury Bills (T-bills), Open Market Operations.
For Mains: Government Securities, Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilisation of resources, growth, development and employment.
Why in News?
The government has completed Government Securities (G-Sec) borrowing for the current fiscal 2023-24 and it expects a dividend from the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in Financial Year 25 (FR 25), similar to FY 24.
- The government's approach to borrowing remains cautious, focusing on prudent fiscal management and ensuring borrowing aligns with the actual needs.
- The completion of G-Sec borrowing, coupled with expectations for dividend income from the RBI, reflects efforts to maintain fiscal stability and meet expenditure targets.
What are the Rules Under Which RBI Transfers its Surplus to the Government?
- The RBI transfers its surplus to the government in accordance with Section 47 (Allocation of Surplus Profits) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- A technical committee of the RBI Board headed by Y H Malegam (2013), which reviewed the adequacy of reserves and surplus distribution policy, recommended a higher transfer to the government.
- According to this section, after making provisions for reserves and retained earnings, the RBI transfers the surplus to the government.
- The amount transferred is determined based on various factors, including the RBI's income from sources such as interest on holdings of domestic and foreign securities, fees and commissions from its services, profits from foreign exchange transactions, and returns from subsidiaries and associates.
- On the expenditure side, the RBI incurs costs such as printing of currency notes, payment of interest on deposits and borrowings, salaries and pensions of staff, operational expenses of offices and branches, as well as provisions for contingencies and depreciation.
What are Government Securities (G-Sec)?
- About:
- A G-Sec is a tradable instrument issued by the Central Government or the State Governments.
- A G-Sec is a type of debt instrument issued by the government to borrow money from the public to finance its Fiscal Deficit.
- A debt instrument is a financial instrument that represents a contractual obligation by the issuer to pay the holder a fixed amount of money, known as principal or face value, on a specified date.
- It acknowledges the Government’s debt obligation.
- Such securities are short-term (usually called treasury bills, with original maturities of less than one year- presently issued in three tenors, namely, 91-day, 182 days and 364 days) or long-term (usually called Government bonds or dated securities with original maturity of one year or more).
- In India, the Central Government issues both, treasury bills and bonds or dated securities while the State Governments issue only bonds or dated securities, which are called the State Development Loans (SDLs).
- G-Secs carry practically no risk of default and, hence, are called risk-free gilt-edged instruments.
- Gilt-edged securities are high-grade investment bonds offered by governments and large corporations as a means of borrowing funds.
- Types of G-Sec:
- Treasury Bills (T-bills):
- Treasury bills are zero coupon securities and pay no interest. Instead, they are issued at a discount and redeemed at the face value at maturity.
- Cash Management Bills (CMBs):
- In 2010, the Government of India, in consultation with RBI introduced a new short-term instrument, known as CMBs, to meet the temporary mismatches in the cash flow of the Government of India.
- The CMBs have the generic character of T-bills but are issued for maturities of less than 91 days.
- In 2010, the Government of India, in consultation with RBI introduced a new short-term instrument, known as CMBs, to meet the temporary mismatches in the cash flow of the Government of India.
- Dated G-Secs:
- Dated G-Secs are securities that carry a fixed or floating coupon rate (interest rate) which is paid on the face value, on a half-yearly basis. Generally, the tenor of dated securities ranges from 5 years to 40 years.
- State Development Loans (SDLs):
- State Governments also raise loans from the market which are called SDLs. SDLs are dated securities issued through normal auctions similar to the auctions conducted for dated securities issued by the Central Government.
- Treasury Bills (T-bills):
- Issue Mechanism:
- The RBI conducts Open Market Operations (OMOs) for sale or purchase of G-secs to adjust money supply conditions.
- The RBI sells g-secs to remove liquidity from the market and buys back g-secs to infuse liquidity into the market.
- These operations are often conducted on a day-to-day basis in a manner that balances inflation while helping banks continue to lend.
- RBI carries out the OMO through commercial banks and does not directly deal with the public.
- The RBI uses OMO along with other monetary policy tools such as repo rate, cash reserve ratio and statutory liquidity ratio to adjust the quantum and price of money in the system.
- The RBI conducts Open Market Operations (OMOs) for sale or purchase of G-secs to adjust money supply conditions.
Retail Sale and Purchase of T Bills
- Method of Purchase: Retail investors can open an online Retail Direct Gilt (RDG) Account with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to directly purchase T-bills. Additionally, they can place bids via select banks and registered primary agents.
- Portal for Purchase: The Retail Direct Gilt (RDG) platform provided by RBI facilitates the purchase of T-bills for retail investors.
- Rules Regarding Purchase and Sale: Retail investors must adhere to certain rules and regulations when buying and selling T-bills. This includes meeting the minimum investment amount requirement (INR 10,000 per lot for various durations) and ensuring compliance with RBI guidelines.
- Participation in Primary Market: Retail investors can participate in the primary market by placing bids for T-bills through the designated channels mentioned earlier. This allows them to directly purchase newly issued T-bills from the RBI on behalf of the Government of India.
- Participation in Secondary Market: Retail investors can also participate in the secondary market for T-bills through their demat accounts. In the secondary market, investors can buy and sell T-bills before their maturity dates, providing liquidity and opportunities for trading.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of Indian economy, ‘Open Market Operations’ refers to (2013)
(a) borrowing by scheduled banks from the RBI
(b) lending by commercial banks to industry and trade
(c) purchase and sale of government securities by the RBI
(d) None of the above
Ans: (c)
Q.2 In the context of the Indian economy, non-financial debt includes which of the following? (2020)
- Housing loans owed by households
- Amounts outstanding on credit cards
- Treasury bills
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- Debts are contractual obligations to repay monetary loans, often with related interest expenses.
- Non-financial Debt
- It consists of credit instruments issued by governmental entities, households and businesses that are not included in the financial sector.
- It includes industrial or commercial loans, Treasury bills and credit card balances.
- They share most of the same characteristics with financial debt, except the issuers are non-financial. Hence, statements 1, 2 and 3 are correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Q.3 Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Reserve Bank of India manages and services Government of India Securities but not any State Government Securities.
- Treasury bills are issued by the Government of India and there are no treasury bills issued by the State Governments.
- Treasury bills offer are issued at a discount from the par value.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Uyghur Forced Labor
For Prelims: Uyghur Forced Labour Prevention Act (UFLPA), Uyghurs, Uyghur Autonomous Region, Commissioner of U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP), European Union (EU), World Trade Organization (WTO), International Labour Organization (ILO)
For Mains: Human Right Violation and its impact on Society.
Why in News?
Recently, A German vehicle brand (Volkswagen (VW)) based in China has been seized in the US due to Uyghur Forced Labour Prevention Act (UFLPA) violations.
- Allegations have been made against several notable companies from the US and European Union including Apple and Zara (Spain) regarding their involvement in forced labour in Xinjiang province of China.
- The U.S. State Department and UN Human Rights Commissioner’s reports highlight Uyghur repression as genocide and potential crimes against humanity.
Who are Uyghurs?
- About:
- The Uyghurs are a predominantly Muslim minority Turkic ethnic group, whose origins can be traced to Central and East Asia.
- The Uyghurs speak their own language, similar to Turkish, and see themselves as culturally and ethnically closer to Central Asian nations than Han ethnic Chinese.
- The Uyghurs are considered to be one of the 55 officially recognized ethnic minority communities in China.
- However, China recognizes the community only as a regional minority and rejects that they are an indigenous group.
- Currently, the largest population of the Uyghur ethnic community lives in the Xinjiang region of China.
- A significant population of Uyghurs also lives in the neighbouring Central Asian countries such as Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.
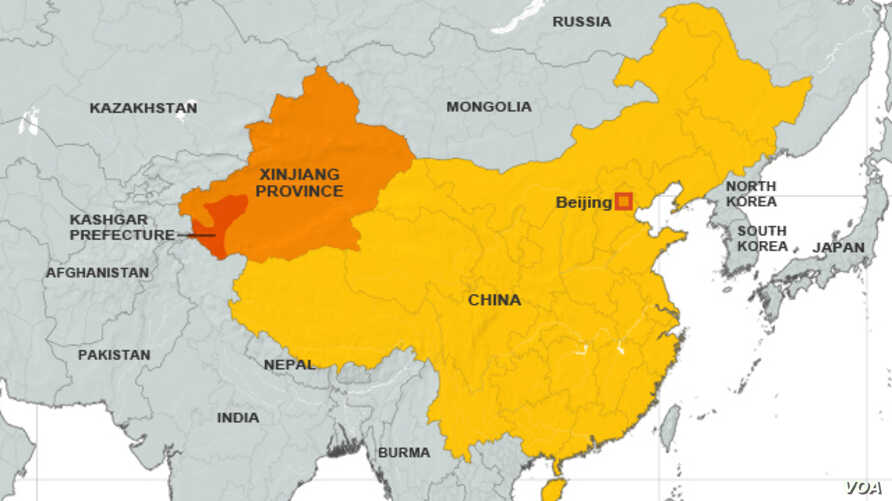
- Xinjiang is technically an autonomous region within China — its largest region, rich in minerals, and sharing borders with eight countries, including India (Union Territory of Ladakh), Pakistan, Russia and Afghanistan.
- A significant population of Uyghurs also lives in the neighbouring Central Asian countries such as Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.
- The Uyghurs are a predominantly Muslim minority Turkic ethnic group, whose origins can be traced to Central and East Asia.
- China’s Move Against Human Rights of Uyghurs:
- UN Report: A report by the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) concluded that “serious human rights violations” against the Uyghur and other predominantly Muslim communities have occurred in Xinjiang.
- These violations include allegations of torture, ill-treatment, forced medical treatment, and sexual and gender-based violence.
- Arbitrary Detentions: The extent of arbitrary detentions against Uyghurs and others, coupled with restrictions on fundamental rights, may constitute crimes against humanity.
- The Chinese government’s counter-extremism strategy involves the use of so-called Vocational Educational and Training Centers (VETCs) or re-education camps.
- Interlocking Patterns of Restrictions: China’s policies in Xinjiang have led to severe and undue restrictions on a wide range of human rights. Even if the VETC system has been reduced, the underlying laws and policies remain, resulting in increased imprisonment and abuse since 2017.
- Discrimination: The violations occur against the backdrop of broader discrimination targeting Uyghurs and other minorities.
- The Chinese government’s assertion of targeting terrorists through its counter-extremism measures has raised serious concerns.
- International Condemnation: Fifty-one UN member countries issued a joint declaration condemning China’s crimes against humanity committed against Uyghurs and other communities.
- UN Report: A report by the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) concluded that “serious human rights violations” against the Uyghur and other predominantly Muslim communities have occurred in Xinjiang.
- China's Response to the Allegations of Uyghers’ Human Rights Violation:
- Beijing either denied the existence of the internment camps or dismissed such claims as outright falsehoods.
- The government has described them as vocational training centres aimed at providing employment opportunities and addressing religious and separatist extremism among the Uyghur Muslim population.
- In reaction to the global allegations, the Chinese government has relocated detainees to different regions within the country and redirected exports away from Xinjiang.
How are Different Nations Addressing Human Rights Violations Against the Uyghurs?
- United States:
- The Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA), directs the Forced Labor Enforcement Task Force to develop a strategy for supporting the enforcement of the prohibition on the importation of goods into the United States manufactured wholly or in part with forced labour in the People's Republic of China, especially from the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region.
- The law creates a presumption that importing goods from China, or made by certain entities in this region, is banned under Section 307 of the Tariff Act of 1930.
- Such goods, wares, articles, and merchandise are not entitled to entry to the United States.
- The presumption applies unless the Commissioner of U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP) determines, through clear and convincing evidence, that the goods, wares, articles, or merchandise were not produced using forced labour.
- The Act seeks to penalize domestic companies for human rights abuses, such as torture, arbitrary detentions, and forced labour, affecting approximately one million Uyghur Muslims who have been held in the internment camps in the China’s north-western region.
- The law seeks to utilise the definition of forced labour provided by the International Labour Organization (ILO) and focus on large corporations.
- European Union:
- In contrast to the U.S. ban, which primarily targets imports from Xinjiang, the European Union (EU) has put forward a broader law that addresses all products dependent on forced labour, including those manufactured within the 27-member bloc.
- There is worry that bans targeting specific countries could be seen as discriminatory actions according to the regulations of the World Trade Organization (WTO).
- EU-wide Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive, addressing social, environmental, and human rights abuses in supply chains, has been at a standstill since 2022.
International Labour Organization
- About:
- International Labour Organization (ILO) is the only tripartite U.N. agency, since 1919. It brings together governments, employers and workers of 187 member States, to set labour standards, develop policies and devise programmes promoting decent work for all women and men.
- Established:
- 1919, by the Treaty of Versailles as an affiliated agency of the League of Nations.
- Became the first affiliated specialized agency of the United Nations in 1946.
- Headquarters: Geneva, Switzerland
- Founding Mission: Social justice is essential to universal and lasting peace.
- Promotes internationally recognized human and labour rights.
- Nobel Peace Prize:
- Received in 1969.
- For improving peace among classes
- Pursuing decent work and justice for workers
- Providing technical assistance to other developing nations
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2016)
Community sometimes in the affairs of mentioned in the news
- Kurd — Bangladesh
- Madhesi — Nepal
- Rohingya — Myanmar
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (c)
- Kurd: They are one of the indigenous peoples of the Mesopotamian plains and the highlands in what are now South-eastern Turkey, North-eastern Syria, northern Iraq, North-western Iran and South-western Armenia. They also adhere to a number of different religions and creeds, although the majority is Sunni Muslims. Hence, pair 1 is not correctly matched.
- Madhesi: It is an ethnic group living mainly in the southern plains of Nepal, close to the border with India. Madhesis are predominantly Hindus with some Muslims and Christians. Hence, pair 2 is correctly matched.
- Rohingya: They are an ethnic group, largely comprising Muslims, who predominantly live in the Western Myanmar province of Rakhine. They speak a dialect of Bengali, as opposed to the commonly spoken Burmese language. According to Myanmar authorities, they are not the authorised citizens of the country. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.
Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Google DeepMind’s Genie
For Prelims: Google DeepMind’s Genie, ChatGPT and deep fakes, Generative Artificial Intelligence, Machine learning.
For Mains: Google DeepMind’s Genie, Issues Associated with Generative AI, AI and Ethics.
Why in News?
Recently, Google DeepMind has introduced Genie AI (Artificial Intelligence), a new model that can generate interactive video games from just a text or image prompt.
- Google DeepMind is a British-American AI research laboratory that is a subsidiary of Google. DeepMind is based in London and has research centres in Canada, France, Germany, and the US.
What is Genie?
- About:
- Generative Interactive Environments (Genie) is a foundation world model that is trained on videos sourced from the Internet.
- The model can “generate an endless variety of playable (action-controllable) worlds from synthetic images, photographs, and even sketches”.
- It is the first generative interactive environment that has been trained in an unsupervised manner from unlabelled internet videos.
- Generative Interactive Environments (Genie) is a foundation world model that is trained on videos sourced from the Internet.
- Significance:
- Genie can be prompted to generate a diverse set of interactive and controllable environments although it is trained on video-only data.
- Genie learns not only which parts of an observation are generally controllable, but also infers diverse latent actions that are consistent across the generated environments.
- Genie is a breakthrough as it makes playable environments from a single image prompt. Genie can be prompted with images it has never seen. The same can be done with sketches.
- This includes real world photographs, sketches, allowing people to interact with their imagined virtual worlds.
- This opens up many possibilities, especially new ways to create and step into virtual worlds.
- The model’s ability to learn and develop new world models signals a significant leap towards general AI agents (an independent programme or entity that interacts with its environments by perceiving its surroundings via sensors).
- Genie can be prompted to generate a diverse set of interactive and controllable environments although it is trained on video-only data.
What is Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI)?
- About:
- GAI is a rapidly growing branch of AI that focuses on generating new content (such as images, audio, text, etc.) based on patterns and rules learned from data.
- The rise of GAI can be attributed to the development of advanced generative models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs).
- These models are trained on large amounts of data and are able to generate new outputs that are similar to the training data. For example, a GAN trained on images of faces can generate new, synthetic images of faces that look realistic.
- While GAI is often associated with ChatGPT and deep fakes, the technology was initially used to automate the repetitive processes used in digital image correction and digital audio correction.
- Arguably, because machine learning and deep learning are inherently focused on generative processes, they can be considered types of GAI, too.
- Applications:
- Art and Creativity: It can be used to generate new works of art that are unique and innovative, helping artists and creatives explore new ideas and push the boundaries of traditional art forms.
- DeepDream Generator - An open-source platform that uses deep learning algorithms to create surrealistic, dream-like images.
- DALL·E2 - This AI model from OpenAI generates new images from text descriptions.
- Music: It can help musicians and music producers explore new sounds and styles, leading to more diverse and interesting music.
- Amper Music - creates musical tracks from pre-recorded samples.
- AIVA - uses AI algorithms to compose original music in various genres and styles.
- Computer Graphics: It can generate new 3D models, animations, and special effects, helping movie studios and game developers create more realistic and engaging experiences.
- Healthcare: By generating new medical images and simulations, improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatments.
- Manufacturing and Robotics: It can help optimise manufacturing processes, improving the efficiency and quality of these processes.
- Art and Creativity: It can be used to generate new works of art that are unique and innovative, helping artists and creatives explore new ideas and push the boundaries of traditional art forms.
- Significance for India:
- As per NASSCOM data, the overall AI employment in India is estimated at about 416,000 professionals.
- The growth rate for the sector is estimated at about 20-25%. Further, AI is expected to contribute an additional USD 957 billion to India’s economy, by 2035.
What are the Concerns Related to GAI?
- Accuracy: One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that the outputs generated by GAI are of high quality and accurate.
- This requires the development of advanced generative models that can accurately capture the patterns and rules learned from data.
- Partisan GAI Models: GAI models are trained on large amounts of data, and if that data is biassed, the outputs generated by GAI may also be biassed.
- This can lead to discrimination and reinforce existing societal biases.
- Privacy: Training GAI models requires access to large amounts of data, which could include personal and sensitive information.
- There is a risk that this data could be used for unethical purposes, such as for targeted advertising or for political manipulation.
- Accountability for Misinformation: Since GAI models can generate new content, such as images, audio, or text it may be used to generate fake news or other malicious content, without knowing who is responsible for the output.
- This could lead to ethical dilemmas over responsibility.
- Automation and Lowering Job: GAI has the potential to automate many processes, which could lead to job displacement for people who are skilled in those areas.
- This raises questions about the ethics of using AI for job displacement and the potential impact on workers and society.
What are India's Initiatives for Generative AI?
- Generative AI Report: INDIAai, the Government of India's National AI Portal, conducted numerous studies and hosted three roundtable discussions with some of the most prominent voices in Generative AI, AI Policy, AI Governance and Ethics, and academia to examine the impact, ethical and regulatory questions, and opportunities it brings to India.
- Co-Founding Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI): In 2020, India joined forces with 15 other countries to form the GPAI. The purpose of this alliance is to establish frameworks for the responsible utilisation of emerging technologies.
- Fostering an AI Ecosystem: The Indian government has been dedicated to fostering an AI ecosystem within the country by investing in R&D, supporting startups and innovation hubs, creating AI policies and strategies, and promoting AI education and skilling.
- National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence: The Government has published the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence with the objective of developing an ecosystem for the research and adoption of Artificial Intelligence.
- National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems: Under this Mission, Technology Innovation Hubs (TIH) has been established on AI & ML at IIT - Kharagpur, which aims to provide the state-of-the-art training and capacity building for the creation of next-generation scientists, engineers, technicians, and technocrats in the field of Artificial Intelligence.
- Artificial Intelligence Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation Platform: It is a Cloud computing platform, aiming to make India a pioneer amongst emerging economies with regards to AI and transform sectors like education, health, agriculture, urbanisation and mobility.
Conclusion
- Generative AI is a powerful and promising technology that can bring many benefits. However, it also poses many challenges and risks that need to be addressed by effective and responsible regulation.
- India should adopt a proactive and balanced approach to generative AI implementation that ensures its safety, security, and ethical use.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q2. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
| Terms sometimes seen in news | Context/Topic | |
| 1. | Belle II experiment | Artificial Intelligence |
| 2. | Blockchain technology | Digital/Cryptocurrency |
| 3. | CRISPR–Cas9 | Particle Physics |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Used Heavy Duty Vehicles and the Environment
For Prelims: Used Heavy Duty Vehicles and the Environment, United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), United Nations Environment Assembly.
For Mains: Used Heavy Duty Vehicles and the Environment, Environmental pollution and degradation.
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and Climate and Clean Air Coalition have released a report titled- Used Heavy Duty Vehicles and the Environment-A Global Overview of Used Heavy-Duty Vehicles: Flow, Scale and Regulation ahead of the 6th session of the United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA-6).
- UNEA-6 will be held in Nairobi from 26th February to 1st March 2024 under the theme of “effective, inclusive and sustainable multilateral actions to tackle the triple planetary crisis: climate change, nature and biodiversity loss, and pollution and waste.”
What is the United Nations Environment Assembly?
- It is the governing body of the UN Environment Programme (UNEP).
- It is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on the environment.
- The Assembly is made up of the 193 UN Member States and convenes every two years to advance global environmental governance.
- It was created in June 2012, during the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, also referred to as RIO+20.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Pollution Escalation:
- There is a significant increase in pollution levels attributed to the rising use of Heavy-Duty Vehicles (HDVs), particularly since 2000.
- Carbon dioxide emissions associated with HDVs have surged by more than 30%.
- HDVs, weighing above 3.5 tonnes, contribute substantially to global emissions, with trucks being the major contributors.
- HDV are vehicles that are designed for heavy-duty tasks such as transporting goods, materials, or large numbers of people over long distances.
- They account for over 40% of on-road nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions, over 60% of on-road particulate matter (PM 2.5), and over 20% of black carbon emissions.
- Growth Projection:
- The report projects a significant increase in the number of HDVs on roads due to economic activities and the need for transportation. Past trends indicate a doubling of worldwide truck and bus sales between 2000-2015.
- Global Trade:
- The analysis of global used HDVs highlights their flow and scale, particularly noting their import dependence in developing countries.
- Japan, the European Union, and the Republic of Korea constitute nearly 60% of the global export market share of both new and used HDVs.
- In 2015, a total of 6.3 million new and used HDVs were sold worldwide.
- Among these, 3.4 million units were found to be newly manufactured. This figure makes the number of used HDVs comprise about half of the sales in total.
- Regulation and Enforcement:
- Several developing countries depend on imports of used HDVs in order to grow their fleet, there is a lack of regulation and enforcement regarding the quality of imported used HDVs, exacerbating environmental and health impacts.
- Many importing countries have weak or non-existent regulations, leading to inadequate enforcement.
- Netherlands removed catalytic converters in many vehicles before shipment to Africa. Because of their old age, they were also found to lack diesel particulate filters.
What are the Key Recommendations of the Report?
- Ensure Cleaner and Safer Used Vehicles:
- The report stressed the importance of sharing the responsibility of importing and exporting countries to ensure cleaner and safer used vehicles on the roads in developing countries.
- It raised the growing need for regional cooperation in introducing and enforcing minimum standards.
- Emission Standards and Age Limits:
- The report suggested emission standards and age limits, raising public awareness and further research needs for the environment and road safety benefits.
- It exemplified that with steps like adopting Euro VI equivalent vehicle emission standards and cleaner fuels, as many as 700 thousand premature deaths can be avoided by 2030.
- At present, 97% of all newly registered trucks and 73% of buses in the EU run on diesel.
- Better Regulations on Used HDVs:
- The report recommended better regulations on used HDVs to promote greater uptake of advanced technologies, such as electric buses and trucks, in developing countries.
- International Collaborations for Super Pollutants:
- There is a need for international collaboration to phase out short-lived climate pollutants, or “super pollutants”, such as Methane, Black Carbon and hydrofluorocarbons.
- Super pollutants are termed "super" because they have a much higher global warming potential (GWP) per unit mass than carbon dioxide (CO2), the most well-known greenhouse gas.
- Long-term pollutants are those that persist in the atmosphere for extended periods, contributing to ongoing environmental issues over time.
- By addressing short-lived climate pollutants, the world can deliver climate action, and improve air quality and human health.
- There is a need for international collaboration to phase out short-lived climate pollutants, or “super pollutants”, such as Methane, Black Carbon and hydrofluorocarbons.
What is the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC)?
- The UNEP-CCAC is a partnership of over 160 governments, intergovernmental organizations, and non-governmental organizations.
- It works to reduce powerful but short-lived climate pollutants (SLCPs) – methane, black carbon, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), and tropospheric ozone – that drive both climate change and air pollution.
- It aims to connect ambitious agenda-setting with targeted mitigation action within countries and sectors.
- Robust science and analysis underpin its efforts and bolstered by its Trust Fund, it has given rise to a high level of political commitment, in-country support, and a range of tools that help make the case for action and support implementation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? (2021)
Bitcoin Halving
Why in News?
In April 2024, the anticipated Bitcoin (BTC) halving is poised to take place, with potentially profound implications for the cryptocurrency's market value.
What is Bitcoin Halving?
- About:
- A bitcoin halving is an event where the reward for mining new blocks is halved, meaning miners receive 50% fewer bitcoins for verifying transactions.
- Bitcoin halvings are scheduled to occur once every 210,000 blocks – roughly every four years – until the maximum supply of 21 million bitcoins has been generated by the network.
- Bitcoin halvings are important events for traders because they reduce the number of new bitcoins being generated by the network. This limits the supply of new coins, so prices could rise if demand remains strong.
- Impact:
- The BTC halving reduces the rate at which new bitcoins are created, decreasing the available supply. This scarcity tends to drive up prices over time due to increased demand.
- Bitcoin mining becomes less profitable immediately after the halving since miners receive half the reward for validating transactions. This could lead to consolidation in the mining industry and potentially push out less efficient miners.
What is Bitcoin?
- About:
- Bitcoin is a type of digital currency that enables instant payments to anyone. Bitcoin was introduced in 2009. Bitcoin is based on an open-source protocol and is not issued by any central authority.
- History:
- The origin of Bitcoin is unclear, as is who founded it. A person, or a group of people, who went by the identity of Satoshi Nakamoto are said to have conceptualised an accounting system in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis.
- Use:
- Originally, Bitcoin was intended to provide an alternative to fiat money and become a universally accepted medium of exchange directly between two involved parties.
- Record of Bitcoins:
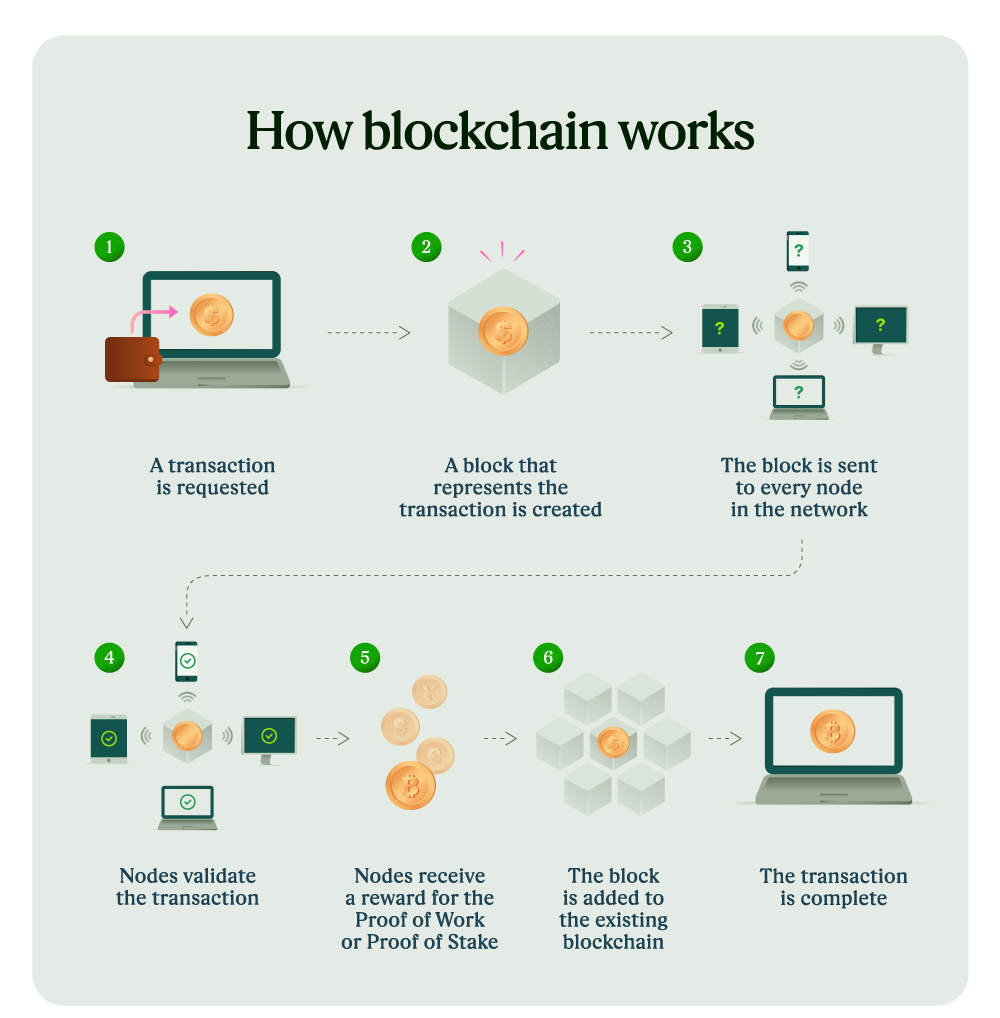
- All the transactions ever made are contained in a publicly available, open ledger, although in an anonymous and an encrypted form called a blockchain.
- Transactions can be denominated in sub-units of Bitcoin.
- Satoshi is the smallest fraction of a Bitcoin.
- Transactions can be denominated in sub-units of Bitcoin.
- Blockchain Technology:
- Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network.
- An asset can be tangible (a house, car, cash, land) or intangible (intellectual property, patents, copyrights, branding).
- A simple analogy for understanding blockchain technology is a Google Doc.
- When one creates a document and shares it with a group of people, the document is distributed instead of copied or transferred.
- This creates a decentralized distribution chain that gives everyone access to the document at the same time.
- Blockchain is a shared, immutable ledger that facilitates the process of recording transactions and tracking assets in a business network.
- All the transactions ever made are contained in a publicly available, open ledger, although in an anonymous and an encrypted form called a blockchain.
India and Cryptocurrency
- Cryptocurrencies in India fall under the virtual digital assets (VDAs) category and are subject to taxation.
- The profits generated from cryptocurrency trading are taxed at a rate of 30%, with an additional 4% cess (Union budget 2022-23).
- In 2022, the RBI launched its own Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) known as e-Rupee which is based on blockchain technology.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 With reference to “Blockchain Technology”, consider the following statements: (2020)
- It is a public ledger that everyone can inspect, but which no single user controls.
- The structure and design of blockchain is such that all the data in it are about cryptocurrency only.
- Applications that depend on basic features of blockchain can be developed without anybody’s permission.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (d)
Large Language Models
Why in News?
In the era of advanced artificial intelligence (AI), the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs) has revolutionized the way computers interact with humans and process language. From enhancing virtual conversations to powering creative tasks, LLMs have paved the way for a new frontier in the realm of AI technology.
What are Large Language Models (LLMs)?
- Definition:
- LLMs are large general-purpose language models capable of solving common language problems such as text classification, question answering, and text generation.
- These models are trained on massive datasets to understand patterns, structures, and relationships within human language.
- Types of Large Language Models (LLMs)
- Based on Architecture:
- Autoregressive Models: Predict the next word in a sequence based on previous words. Example: GPT-3.
- Transformer-based Models: Utilise a specific artificial neural network architecture for language processing. Examples: LaMDA, Gemini (formerly Bard).
- Encoder-decoder Models: Encode input text into a representation and then decode it into another language or format.
- Based on Training Data:
- Pretrained and Fine-tuned Models: Adapt to specific tasks through fine-tuning on particular datasets.
- Multilingual Models: Capable of understanding and generating text in multiple languages.
- Domain-specific Models: Trained on data related to specific domains like legal, finance, or healthcare.
- Based on Size and Availability:
- Size: Large models require more computational resources but offer better performance.
- Availability: Open-source models are freely available, while closed-source models are proprietary.
- Examples of open-source LLMs: LLaMA2, BlOOM, Google BERT, Falcon 180B, OPT-175 B.
- Examples of closed-source LLMs: GPT 3.5 by OpenAI, Gemini by Google.
- Based on Architecture:
- Operational Mechanisms of LLMs:
- At their core, LLMs utilize deep learning techniques, to predict the probability of words or sequences given preceding text.
- LLMs analyze patterns and relationships in data to predict the next word or sequence based on input prompts, akin to how humans comprehend language.
- LLMs typically rely on transformer models, such as the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT), with attention mechanisms for contextual understanding.
- At their core, LLMs utilize deep learning techniques, to predict the probability of words or sequences given preceding text.
- Applications of LLMs:
- LLMs generate human-like content, from stories to songs, and act as virtual assistants, excelling in sentiment analysis, translation, and text summarization, crucial for marketing strategies.
- Advantages of LLMs:
- LLMs can adapt to various tasks and domains, leveraging their extensive training data to generalise patterns.
- They can perform well even with limited domain-specific data, thanks to their ability to learn from general language training datasets.
- As more data and parameters are added, LLMs continuously enhance their performance, making them valuable assets in evolving AI landscapes.
What are Large Action Models (LAMs)?
- LAMs are specialized AI models built to perform specific tasks or sequences of actions, often beyond just understanding and generating text.
- LAMs can understand human intention and predict actions. LAMs are designed to help with repetitive tasks.
- They are designed to execute actions based on inputs, which may include text, images, or other forms of data.
- LAMs can be used in various applications such as virtual assistants, robotic systems, automated customer service, and more.
- Example of LAM: Rabbit r1.
- These models are trained on datasets that include both linguistic information and action-oriented data to learn how to perform tasks based on given contexts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q 2. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
SWAYAM Plus Platform
Recently SWAYAM Plus Platform was inaugurated by the Union Minister of Education and Skill Development & Entrepreneurship in New Delhi.
- SWAYAM, the Massive Open Online Course (MOOC) platform providing educational opportunities for a vast number of learners, was launched by the Ministry of Education in 2017.
- Aligned with NEP 2020, SWAYAM Plus now offers industry-relevant courses to boost employability, with features like multilingual content, AI guidance, credit recognition, and pathways to employment, developed in collaboration with companies like L&T, Microsoft, CISCO, and others.
- SWAYAM Plus primarily focuses on achieving the following:
- Creating an ecosystem that supports professional and career development for learners, course providers, industry, academia, and strategic partners.
- Implementing a system that acknowledges high-quality certifications and courses from top industry and academic partners.
- Reaching a broad learner base nationwide, especially in tier 2 and 3 towns and rural areas, by providing employment-focused courses in various disciplines with vernacular language resources.
- SWAYAM Plus primarily focuses on achieving the following:
Read more: SWAYAM and SWAYAM Prabha
Ultra-high Net Worth Individuals in India
In India, the number of Ultra-high Net Worth Individuals (UHNWIs) has been steadily increasing, reaching 13,263 individuals in 2023 and projected to grow to nearly 20,000 by 2028, as per Knight Frank's 'The Wealth Report 2024'.
- UHNWIs are individuals with a net worth of USD 30 million and above.
- The UHNWI population in India saw a 6.1% growth in 2023 it is projected to rise 50% by 2028, reflecting a positive trend in wealth accumulation.
- Globally, the number of wealthy individuals is expected to rise by 28.1% to 8,02,891 by 2028.
- Turkey leads in UHNWI growth with a 9.7% Yearly expansion, followed by the US, South Korea, and Switzerland.
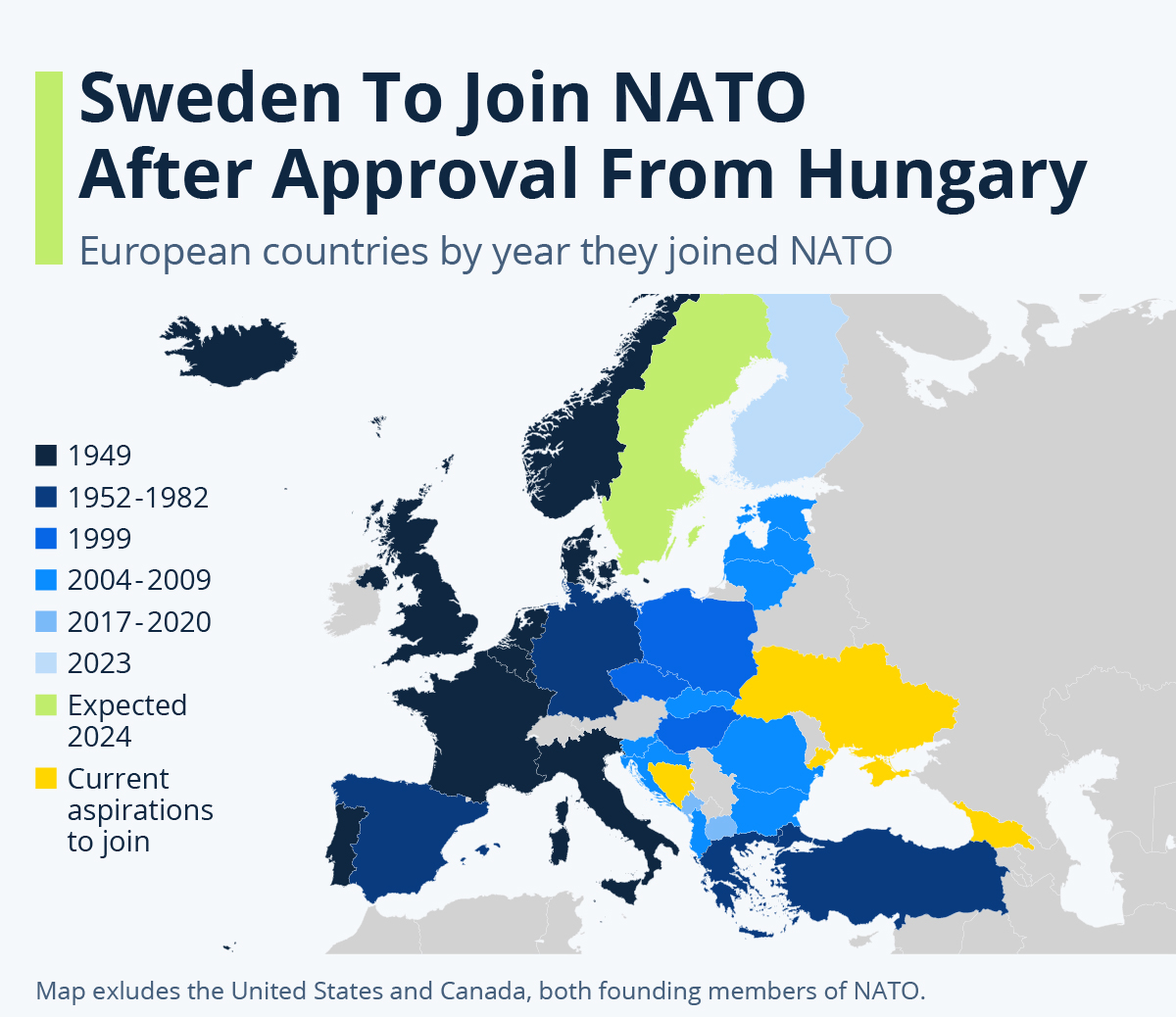
Hungary Ratifies Sweden's NATO Membership
Hungary's parliament voted to approve Sweden's bid to join the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), making it the 32nd nation to join the alliance.
- NATO, a vital transatlantic military and political alliance, ensures collective security for its member countries. Established in 1949 by 12 founding nations, with a majority from Europe and North America, it remains a cornerstone of international stability.
- NATO is headquartered at Boulevard Leopold III in Brussels, Belgium.
- Alliances of NATO:
- Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council (EAPC)
- Mediterranean Dialogue fosters security and stability in the Mediterranean by enhancing relations between participating countries and NATO Allies.
- Istanbul Cooperation Initiative (ICI) offers non-NATO countries in the broader Middle East region the opportunity to cooperate with NATO, aiming to enhance regional security.
- “NATO plus” refers to a security arrangement of NATO and the five treaty allies of the U.S. — Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Israel, and South Korea as members — to enhance “global defence cooperation” and win the “strategic competition with the Chinese Communist Party”.
- NATO Plus is not an officially recognised or established concept within NATO.
Read more: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
Homosep Atom
Homosep Atom, developed by the startup named Solinas, is India's first septic tank/manhole cleaning robot, is revolutionising sanitation efforts nationwide, replacing manual scavenging with a comprehensive robotic solution, bolstering the Swachh Bharat Campaign.
- It streamlines sewer cleaning with multifunctional capabilities, curbing costs and fostering robotic sanitation while mitigating blockages in congested areas.
- Extending its reach to large complexes and individual residences, it has enhanced municipal waste management, prioritising worker safety and efficiency.
- Solinas, a deep-tech startup from IIT Madras, pioneers miniature robots for water-sewer pipelines, aided by the Department of Science and Technology -Technology Business Incubator (DST-TBI), addressing contamination challenges, climate tech solutions, and AI-based pipeline diagnostics for sustainable water management.
- DST's Technology Business Incubators (TBIs) in academic, technical, and R&D institutions under the NIDHI program support innovative startups, encouraging youth to create knowledge-based enterprises, solve societal challenges, and contribute to national growth.
Read more: Manual Scavenging