Governance
National Achievement Survey (NAS)-2021
For Prelims: National Achievement Survey (NAS)-2021, Schedule caste, Scheduled Tribe, Part IV of Indian Constitution, Article 45, Article 39 (f), Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP), RTE) Act, 2009, 42nd Amendment, 86th Amendment in 2002, Article 21-A
For Mains: Education, Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Education released the National Achievement Survey (NAS) 2021 report.
- The Triennial Survey was conducted in November 2021.
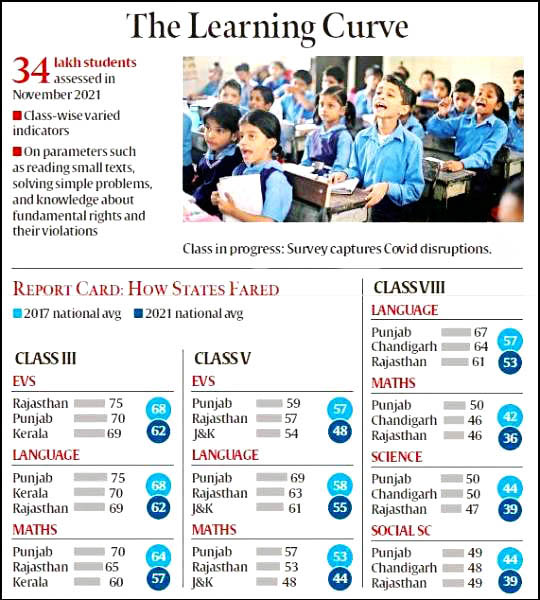
- About 34 lakh students of 1.18 lakh schools in 720 districts from both rural and urban areas have participated in NAS 2021.
What is the National Achievement Survey (NAS)-2021?
- About:
- It is a nationwide survey to assess the learning outcomes and health of the education system.
- It is the largest, nationwide, sample-based education survey conducted across India.
- It is undertaken by the Ministry of Education.
- The Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) conducted NAS 2021.
- The National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT) designed an assessment framework and tools for NAS-2021.
- It provides a system-level reflection on the effectiveness of school education.
- It collects information on relevant background variables such as school environment, teaching processes, and student home and background factors.
- It covers the whole spectrum of schools including Government schools (both State and Central government), Government-aided schools, and Private schools across India.
- It is a nationwide survey to assess the learning outcomes and health of the education system.
- Medium and Grades:
- The NAS 2021 was conducted in 22 mediums of instruction that covered English, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Kannada, Hindi, Malayalam, Marathi, Manipuri, Mizo, Punjabi, Odia, Telugu, Tamil, Bodo, Urdu, Garo, Konkani, Khasi, Bhutia, Nepali, and Lepcha.
- It was conducted in different subjects for different grades. The subject and grades wise break up is below:
- Grade 3 and 5: Language, EVS, and Mathematics
- Grade 8: Language, Science, Mathematics, and Social Science
- Grade 10: Language, Science, Mathematics, Social Science, and English
- Objective:
- To evaluate children's progress and learning competencies as an indicator of the efficiency of the education system, so as to take appropriate steps for remedial actions at different levels.
- Significance:
- It will help to unravel the gaps in learning and will support state/UT governments in developing long term, mid-term and short-term interventions to improve learning levels and orient on differential planning based on NAS 2021 data.
- The findings of NAS 2021 will help in diagnosing a systematic understanding of the consequences that prolonged closure of schools has had on the learning of students in terms of their socio-emotional and cognitive development.
- NAS findings will help in capacity building for teachers, officials involved in the delivery of education.
What are the Key Highlights of the NAS 2021?
- National Average:
- The national average percentage of students for class third was 59%, which declined by 10% to 49% in class fifth.
- It further declined to 41.9% in class eight and then 37.8% in class 10.
- The performance recorded a decline in almost all subjects.
- For instance, the mathematics score nationally was 57% in class third, dropping by almost 10% to 44% in fifth, and to 36% in class eighth, and 32% in class 10th.
- The language score nationally was 62% in class third, and dropped to 52% in class fifth, and to 53% in class eighth.
- For science, the national score declined from 39% in class eighth to 35% in class 10.
- Rural and Urban Areas:
- The average performance of schools in rural areas remained “significantly below” those urban areas in same states and union territories (UTs).
- Social-Group Wise Performance:
- The performance of students from the schedule caste (SC)/ schedule tribe (ST)/ Other Backward Classes (OBC) categories remained lower than that of students from the general category.
- Gender-wise Performance:
- The average performance of girls remained better than the boys in almost all subjects across the classes, both nationally and at state level.
- Perception of Students about Learning:
- The perception of students about learning at home during the pandemic when the schools remained closed, and 78% of students termed it as burdensome with a lot of assignments.
- At least 38% of students faced difficulties in learning at home, while 24% said they did not have digital devices at home.
How did the States Perform?
- The majority of the states performed significantly below the overall national score, some states such as Kerala, Rajasthan, Maharashtra and Punjab performed better than the national average.
- Delhi’s performance in class eighth and class 10 was better when compared with the national average.
- Punjab has scored highest in all subjects for classes 3, 5 and 8.
What is the Status of Education in India?
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Part IV of Indian Constitution, Article 45 and Article 39 (f) of Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP), has a provision for state-funded as well as equitable and accessible education.
- The 42nd Amendment to the Constitution in 1976 moved education from the State to the Concurrent List.
- The 86th Amendment in 2002 made education an enforceable right under Article 21-A.
- Related Laws:
- Right To Education (RTE) Act, 2009 aims to provide primary education to all children aged 6 to 14 years and enforces education as a Fundamental Right.
- It also mandates 25% reservation for disadvantaged sections of the society.
- Right To Education (RTE) Act, 2009 aims to provide primary education to all children aged 6 to 14 years and enforces education as a Fundamental Right.
- Government Initiatives:


Governance
Representation of Women in Armed Forces
For Prelims: Army Aviation Corps, Short-Service Commission
For Mains: Women Representation in Military, Background and Significance, Gender, Issues related to Women
Why in News?
Recently, Captain Abhilasha Barak, created history by becoming the first woman officer to join the Army Aviation Corps as a Combat Aviator (pilot).
- At present women are only given the responsibility of traffic control and ground duty in the Aviation Department but now Abhilasha Barak will take over the responsibility of the pilot.
- Captain Barak has been assigned to the second flight of the 2072 Army Aviation Squadron that operates the Dhruv Advanced Light Helicopter (ALH).
- While women officers in the Indian Air Force and the Indian Navy have been flying helicopters for long, the Indian Army paved the way for women pilots in 2021 by starting the ‘Army Aviation course’.
What is the Army Aviation Corps?
- Army Aviation Corps is the component of the Indian Army which was established on 1st November, 1986.
- The Army Aviation Corps is headed by a director-general at the Army headquarters in New Delhi.
- It was immediately inducted into ‘Operation Pawan’ which was a crucial test for the newly formed corps.
- The Army Aviation Corps of the Indian Army primarily carries out the evacuation of the injured troops during operations or health emergencies in the high-altitude areas.
- The choppers of the Aviation Corps are also used for observation, reconnaissance, casualty evacuation, combat research and rescue, and essential load drops.
What is the State of Women’s Representation in the Military?
- Background:
- The Army, Air Force and Navy began inducting women as short-service commission (SSC) officers in 1992.
- This was the first time when women were allowed to join the military outside the medical stream.
- One of the turning points for women in the military came in 2015 when Indian Air Force (IAF) decided to induct them into the fighter stream.
- In 2020, the Supreme Court (SC) ordered the central government to grant permanent commission (PC) to women officers in the Army's non-combat support units on par with their male counterparts.
- The SC had rejected the government’s stand of women officers’ physiological limitations as being based on "sex stereotypes" and "gender discrimination against women”.
- Women officers have been granted PC in the Indian Army in all the ten branches where women are inducted for SSC.
- Women are now eligible to occupy all the command appointments, at par with male officers, which would open avenues for further promotions to higher ranks for them.
- In early 2021, the Indian Navy deployed four women officers on warships after a gap of almost 25 years.
- India’s only aircraft carrier INS Vikramaditya and fleet tanker INS Shakti are the warships that have been assigned their first women crews since the late 1990s.
- In May 2021, the Army inducted the first batch of women into the Corps of Military Police, the first time that women joined the military in the non-officer cadre.
- However, Women are still not allowed in combat arms like Infantry and Armored Corps.
- The Army, Air Force and Navy began inducting women as short-service commission (SSC) officers in 1992.
- Increment in Numbers:
- It has increased almost three-fold over the last six years, with more avenues being opened to them at a steady pace.
- There are 9,118 women currently serving the army, navy and air force.
- According to 2019 figures, women comprise only 3.8% of the world's second-largest army - compared to 13% of the air force and 6% of the navy.
- Significance:
- Gender is not a Hindrance: As long as an applicant is qualified for a position, one’s gender is arbitrary. In modern high technology battlefield technical expertise and decision-making skills are increasingly more valuable than simple brute strength.
- Military Readiness: Allowing a mixed gender force keeps the military strong. The armed forces are severely troubled by falling retention and recruitment rates. This can be addressed by allowing women in the combat role.
- Effectiveness: The blanket restriction for women limits the ability of commanders in theater to pick the most capable person for the job.
- Tradition: Training will be required to facilitate the integration of women into combat units. Cultures change over time and the masculine subculture can evolve too.
- Global Scenario: When women officially became eligible for combat positions in the American military in 2013, it was widely hailed as another step towards the equality of sexes. In 2018, the UK military lifted a ban on women serving in close combat ground roles, clearing the way for them to serve in elite special forces.
Way Forward
- Women were being kept out of command posts on the reasoning that the largely rank and file will have problems with women as commanding officers. Thus, changes have to take place in the culture, norms, and values of not only the rank and file of the Army but also that of society at large. The responsibility to usher these changes lies with the senior military and political leadership.
- The United States, Israel, North Korea, France, Germany, Netherlands, Australia and Canada are among the global militaries that employ women in front-line combat positions.
- It is the right of every woman to pursue a career of her choice and reach the top since Equality is a constitutional guarantee.


Indian Economy
Annual Survey of Industries (ASI)
For Prelims: Annual Survey of Industries (ASI)
For Mains: Annual Survey of Industries (ASI), Growth & Development
Why in News?
Recently, provisional results of the Annual Survey of Industries (ASI) was released by the Ministry of Statistics and Programme Implementation.
- The survey was conducted during April 2021 to January 2022 through ASI Web Portal.
What is the ASI?
- ASI, the principal source of industrial statistics in India, is the most comprehensive data on organised manufacturing.
- It covers all factories employing 10 or more workers using power and those employing 20 or more workers without using power.
What are the Highlights of the Survey?
- Increase in Factories:
- Factories in the country increased by 1.7% year-on-year to 2.46 lakh in 2019-20, employing a total of 1.3 crore workers.
- Gross Fixed Capital Formation:
- Gross fixed capital formation, an indicator of investment, grew 20.5% to Rs 4.15 lakh crore in the organised manufacturing sector in 2019-20 as against a growth of 10.2% at Rs 3.44 lakh crore in the previous fiscal.
- This compares with a growth of 1.98% in the number of factories to 2.42 lakh in 2018-19 and a 1.2% growth seen in the post-demonetisation year of 2017-18.
- These numbers assume significance as these are the results for the normal year of 2019-20 before the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic, which affected employment growth.
- Fixed capital represents the depreciated value of fixed assets owned by the factory as on the closing day of the accounting year and it includes land including lease- hold land, buildings, plant & machinery, furniture and fixtures, transport equipment, water system and roadways and other fixed assets such as hospitals, schools, etc. used for factory workers.
- Gross fixed capital formation, an indicator of investment, grew 20.5% to Rs 4.15 lakh crore in the organised manufacturing sector in 2019-20 as against a growth of 10.2% at Rs 3.44 lakh crore in the previous fiscal.
- Employment in the Corporate Sector:
- Corporate Sector:
- Employment in the corporate sector, which includes public and private government and non-government companies, increased 5.5% to 97.03 lakh in 2019-20, while that in individual proprietorship declined 3.1% to 11.36 lakh.
- In Partnership:
- Employment in the partnership sector fell by 11.7% to 18.58 lakh in 2019-20 while that for limited liability partnership grew 42% to 1.22 lakh.
- Employment of Workers:
- Among states, Tamil Nadu showed the highest number of employment of workers in 2019-20, followed by Maharashtra and Gujarat.
- Corporate Sector:
- Total Wages Paid:
- Total wages paid to workers grew 6.3% in 2019-20 as against a wage growth of 11.9% in previous fiscal.
- Wages to factory workers in the corporate sector rose by 7.7%in 2019-20.
- Workers figures include all persons employed directly or through any agency whether for wages or not and engaged in any manufacturing process or in cleaning any part of the machinery or premises used for manufacturing process or in any other kind of work connected with the manufacturing process.
International Relations
US-Taiwan Relations
For Prelims: India and its Neighbourhood
For Mains: Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests
Why in News?
Ahead of the Quad summit in Japan, the US President made a controversial statement giving affirmative reply in response to a question with regards to providing military aid to Taiwan in case of China’s invasion.
- This has raised questions about whether the US is shifting from its long-standing policy of strategic ambiguity over Taiwan to that of strategic clarity.
- Quad grouping includes India, the US, Australia and Japan.
What is the Taiwan Issue?
- China-Taiwan Relations:
- Taiwan is an island territory across the Taiwan Strait, located off the coast of mainland China.
- The ruling Kuomintang (Nationalist) government of China fled to Taiwan after being defeated by the communist forces in the Chinese civil war of 1945-1949.
- Following the split of China and Taiwan in the civil war, the Republic of China (ROC) government was relocated to Taiwan. On the other hand, The Communist Party of China (CPC) established the People’s Republic of China (PRC) in the mainland.
- Since then, the PRC observes Taiwan as a traitor province and awaits reintegration with Taiwan, if possible, by peaceful means.
- Simultaneously, the United Nations membership was continued by the ROC maintaining its permanent seat at the UN Security Council (UNSC).
- PRC allied itself with the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) and ROC with the US in the cold war further straining the China-Taiwan relations.
- Consequently, two Taiwan Strait crises of the 1950s happened.
- Reconciliation of the US with China and the Subsequent Events:
- The US and China reconciled in the 1970s due to the Cold War’s shifting geopolitics, so that the growing influence of the USSR could be countered.
- This was followed by the visit of the then US President to the PRC in 1972.
- Subsequently, ROC was displaced by the PRC as the official representative at the UN.
- Then, “One-China Principle” came into picture.
- One-China Principle and its impact:
- This means that the nations who want to have diplomatic relations with the PRC have to recognize the PRC but not the ROC as China, breaking the relations with ROC.
- Simultaneously, China evolved as a multi-party democracy alongside the reformation of its economic system.
- Since then, the two countries became economically entangled and continuously competing.
How has the standpoint of the US on the Taiwan issue unfolded?
- The evolution of the US’s stance:
- The Shanghai Communique (1972), the Normalisation Communique (1979) and the 1982 Communique are the three documents outlining the US-China mutual understanding on the Taiwan question.
- As per the 1979 communique, the US accepts the ‘one China principle’ considering Taiwan, a part of China.
- However, the US started maintaining unofficial relations with Taiwan in the name of people of both the nations.
- In the 1982 communique, China expressed its concerns over the likelihood of continued supply of arms by the US to Taiwan as per the provisions of Taiwan Relations Act (TRA),1979.
- In this way, the US has balanced its recognition of the PRC along with the concerns of Taiwan.
- Impact on Taiwan:
- In Taiwan, Democratic People’s Party (DPP) has become the most powerful political force in Taiwan catering to the pro-independence constituency in Taiwan.
- The DPP wants to expand its economic relations away from China.
- China considers Taiwan as a territory with high geopolitical significance as it is centrally located in the First Island Chain between Japan and the South China Sea.
- Throughout this region, military outposts of the US are scattered. Therefore, it would be a significant breakthrough for China in case it takes Taiwan’s control.
- But, the chances of a peaceful reunification are very slim.
- Also, the tensions are happening in parallel with the Russo-Ukrainian conflict.
Way Forward
- Considering China’s wearing patience and Taiwan’s increasingly pro-independence slant, a strong message to the adversary becomes essential in the backdrop of the Russo-Ukrainian conflict. It may have reached the point where strategic ambiguity may be losing its relevance to strategic clarity.
- However, another plausible interpretation can be that this messaging is aimed by the US for eliciting responses and testing the waters to get a feel of China’s game plan for the Indo-Pacific.


International Relations
Bilateral Security and Defence Cooperation: Indo-Japan
For Prelims: India-Japan Relations, Quad Grouping
For Mains: Bilateral Groupings and Agreements
Why in News?
Recently, India and Japan agreed to further enhance Bilateral Security and Defence Cooperation, including in defence manufacturing.
What are the Highlights of the Meeting?
- Both sides should work jointly towards implementing their decision to have 5 trillion yen in public and private investment and financing from Japan to India in the next five years.
- India highlighted the steps taken by it to improve ease of doing business, logistics through the ‘Gati Shakti’ initiative and urged Japan to support greater investments by Japanese companies in India.
- Such investments would help in creating resilient supply chains and would be mutually beneficial.
- India appreciated that Japanese companies are increasing their investments in India and that 24 Japanese companies had successfully applied under the various Production Linked Incentive schemes.
- Both Countries noted the progress in implementation of Mumbai-Ahmedabad High Speed Rail project and welcomed the signing of exchange of notes of the 3rd tranche of loan for this project.
- Agreed to encourage greater collaboration between private sectors of both sides in the development of next generation communication technologies.
- Also agreed to deepen cooperation in the area of Clean Energy including green hydrogen.
- Took note of the progress in implementation of the Specified Skilled Workers (SSW) programme and agreed to further scale up this programme, boosting people to people linkages.
- Concurred that the India-Japan Act East Forum was useful in prioritising development of India’s North East Region.
What are other Recent Developments between India and Japan?
- In March 2022, the Japanese Prime Minister was on an official visit to India for the 14th India-Japan Annual Summit between the two Countries.
- Earlier, the Indian PM virtually inaugurated a Japanese ‘Zen Garden - Kaizen Academy’ at the Ahmedabad Management Association (AMA) in Gujarat.
- Recently, India, Japan and Australia have formally launched the Supply Chain Resilience Initiative (SCRI) in a move to counter China’s dominance of the supply chain in the Indo-Pacific region.
- In 2020, India and Japan signed a logistics agreement that will allow armed forces of both sides to coordinate closely in services and supplies. The agreement is known as the Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement (ACSA).
- In 2014, India and Japan upgraded their relationship to 'Special Strategic and Global Partnership'.
- The India-Japan Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) that came into force in August 2011 covers trade in goods, services, movement of natural persons, investments, Intellectual Property Rights, custom procedures and other trade related issues.
- Japan is India’s 12th largest trading partner, and trade volumes between the two stand at just a fifth of the value of India-China bilateral trade.
- Defence Exercises: India and Japan defence forces organize a series of bilateral exercises namely, JIMEX (naval), SHINYUU Maitri (Air Force), and Dharma Guardian (Army). Both countries also participate in Malabar exercise (Naval Exercise) with the USA and Australia.
- Both India and Japan are members of Quad, G20 and G-4.
- They are also member countries of the International Thermonuclear Experimental Reactor (ITER).
Way Forward
- More collaboration and cooperation can prove beneficial to both nations, since India needs sophisticated technology from Japan.
- There is a huge potential with respect to Make in India. Joint ventures could be created by merging Japanese digital technology with Indian raw materials and labour.
- Close cooperation is the best measure to combat China’s growing role in Asia and Indo-Pacific, in physical as well as digital space.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Indian Heritage & Culture
Puri Heritage Corridor Project
For Prelims: Jaganath temple, Puri Heritage Corridor Project, ABADHA Scheme, AMSAR Act
For Mains: Preservation of Heritage sites, Controversies in the Excavation Projects, Temple Architecture of India, AMSAR Act
Why in News?
The Odisha government’s ambitious temple corridor project in Puri has become a subject of political controversy.
What is the Puri Heritage Corridor Project?
- It is a redevelopment project of the Odisha government in Puri to create an international heritage site, including the Jagannath temple. Though conceived in 2016, it was unveiled in December 2019.
- Under the umbrella project falls the Shree Jagannatha Heritage Corridor (SJHC) or the Shree Mandira Parikrama Project, for the revamp of the area around the temple.
- The project includes Shree Jagannath Temple Administration (SJTA) building redevelopment, a 600-capacity Srimandir reception centre, Puri Lake, Musa River revival plan, etc.
- The Odisha government has listed three objectives for the revamp of the area around the temple- the security of the temple, the safety of devotees, and the creation of a religious atmosphere for devotees.
- The government allotted funds for the Project from its Augmentation of Basic Amenities and Development of Heritage and Architecture at Puri (ABADHA) scheme.
- The ABADHA scheme includes Land Acquisition Charges/Re-habitation& Resettlement/ Road Improvement for providing better facilities in & around Shree Jagannath Temple.
Why has the Project become a Subject of Controversy?
- Experts and members of civil society objected to the use of heavy machinery for digging, citing the possibility of an adverse impact on the 12th Century temple.
- Questions started being raised about whether the construction around the temple had the due permissions and clearances.
- The Jagannath temple has been designated a monument of national importance by the Archaeological Survey of India and is a centrally protected monument.
- Massive demolition and construction works are taking place within a 100 and 200-meter area of the temple which is prohibited by the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (Amendment and Validation) Act (AMSAR) 2010.
What is the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (Amendment and Validation) Act (AMSAR) 2010?
- As per the AMSAR (Amendment and Validation) Act, construction is prohibited within a 100-meter periphery of a protected area.
- The area extending to 200 meters around the monument in all directions is called a regulated area.
- As per the provisions of the AMSAR Act, the National Monuments Authority (NMA), set up in 2011 under the Ministry of Culture, is charged with protecting and preserving ASI-protected sites by managing the prohibited and regulated area in the periphery of such a site.
- If construction has to be undertaken in a regulated or prohibited area, permission from the NMA is required.
- The term “construction” as defined in the AMSAR Act does not include the construction of public toilets, urinals, and “similar conveniences”.
- It also does not include works for the supply of water, electricity or “provision of similar facilities for publicity”.
- Besides, an impact assessment is also required to be done by the NMA before development around a monument if the built-up area of the monument is beyond 5,000 square meters.
What are the Features of Jagannath Temple?
- The temple is believed to be constructed in the 12th century by King Anatavarman Chodaganga Deva of the Eastern Ganga Dynasty.
- Jagannath Puri temple is called ‘Yamanika Tirtha’ where, according to the Hindu beliefs, the power of ‘Yama’, the god of death has been nullified in Puri due to the presence of Lord Jagannath.
- This temple was called the “White Pagoda” and is a part of Char Dham pilgrimages (Badrinath, Dwaraka, Puri, Rameswaram).
- There are four gates to the temple- Eastern ‘Singhdwara’ which is the main gate with two crouching lions, Southern ‘Ashwadwara’, Western 'Vyaghra Dwara and Northern ‘Hastidwara’. There is a carving of each form at each gate.
- In front of the entrance stands the Aruna stambha or sun pillar, which was originally at the Sun Temple in Konark.
Other Important Monuments of Odisha
- Konark Sun Temple (UNESCO World Heritage Site)
- Lingaraj Temple
- Tara Tarini Temple
- Udaygiri and Khandagiri Caves
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions
Q. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists: (2009)
| List I | List II |
| (Famous Temple) | (State) |
| A. Vidyashankara temple | 1. Andhra Pradesh |
| B. Rajarani temple | 2. Karnataka |
| C. Kandariya Mahadeo | 3. Madhya Pradesh |
| D. Bhimesvara temple | 4. Orissa |
Code: A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 1 4 3 2
(d) 1 3 4 2
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Money Spider, Ant-Mimicking Spider Discovered
Why in News?
Money spiders, commonly found in European meadows, have been reported for the first time in the country from the Muthanga range of the Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary.
- Researchers from Christ College (Kerala) have also discovered ant-mimicking spiders, belonging to the group of jumping spiders, from the Mananthavady range.
Key Points
- About Money Spider:
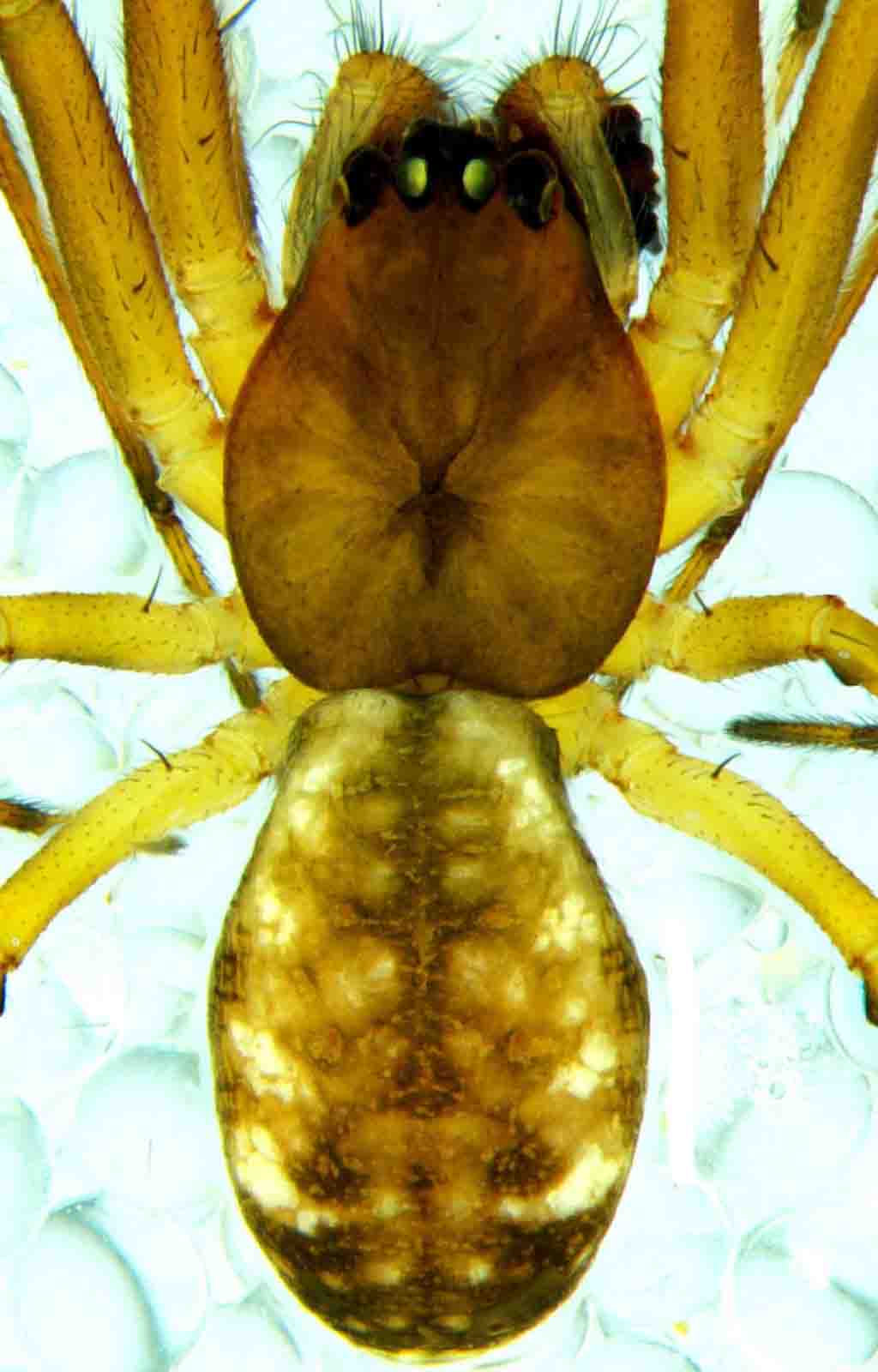

- Money Spider belongs to the family of dwarf spiders ( Linyphiidae) under the genus Prosoponoides.
- Only six species of spiders belonging to this genus have been identified from across the world so far.
- It has been given the name Prosoponoides biflectogynus.
- The male and the female money spiders are typically 3 mm and 4 mm long respectively.
- Both sexes are dark brown and have irregular silver patches and black spots on the elliptical abdomen.
- There are numerous fine black spines on their olive-green legs.
- Eight dark eyes are arranged in two rows.
- Females build triangular webs in between dry tree twigs and feed on small insects, while males prefer to hide beneath dry leaves.
- Two or more male spiders can be found in the web of a single female.
- Money Spider belongs to the family of dwarf spiders ( Linyphiidae) under the genus Prosoponoides.
- About Ant-mimicking Spiders:
- The ant-mimicking spider has been named Toxeus alboclavus.
- They belong to the family of Salticidae.
- The male and the female spiders of this species grow up to 4 mm and 6 mm long respectively.
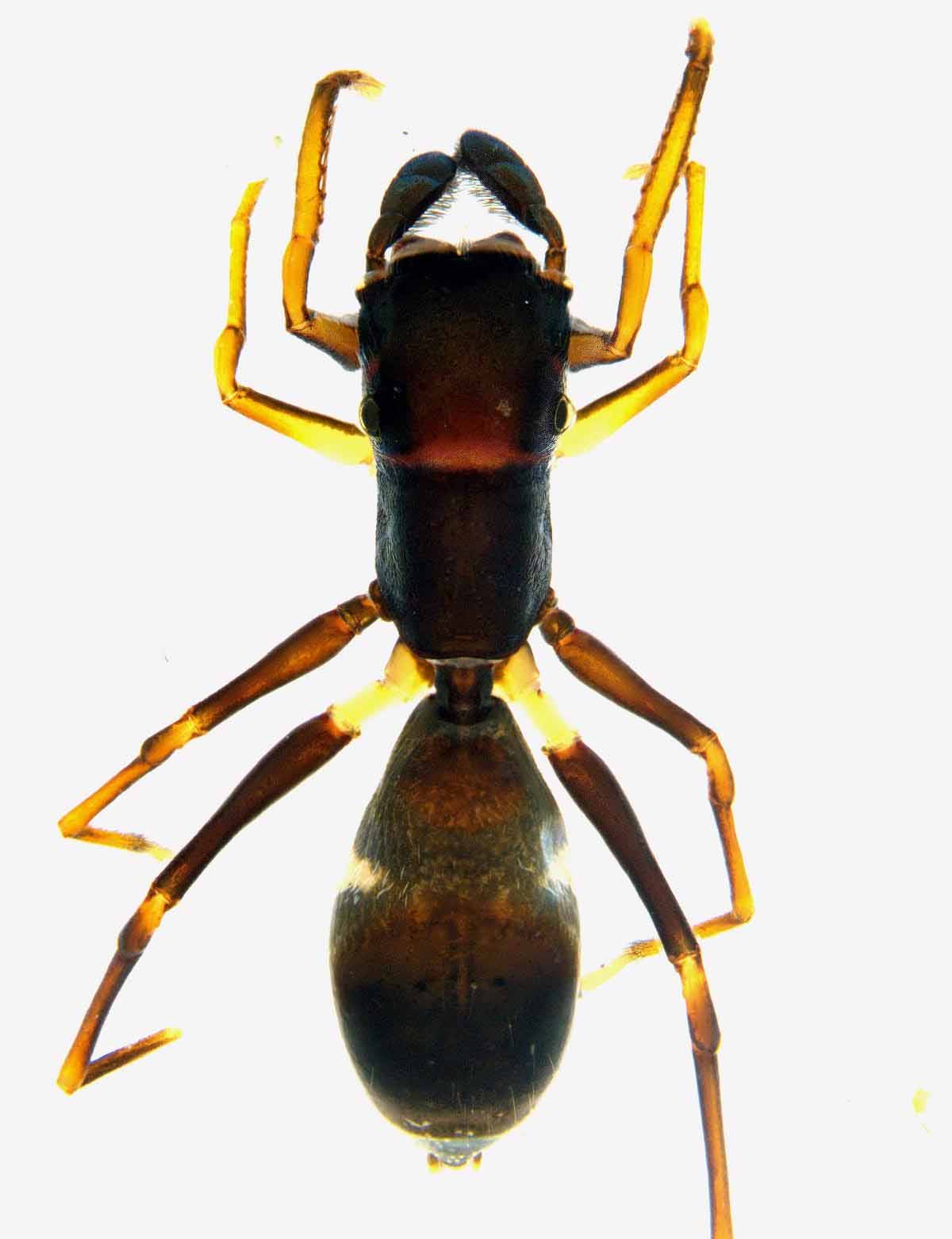

- A pair of white stripes on the dark brown abdomen of females makes them distinct from other spiders of this group (jumping spiders).
- The male of the species is characterized by a brown cephalic region and black thorax with white hairs.
- The forward-projecting fangs have a characteristic shape of an antler.
- Long spines are present on the base of each leg.
Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
- Located in Kerala, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary (WWS) is an integral part of the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve. It was established in 1973.
- Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve was the first from India to be included in the UNESCO designated World Network of Biosphere Reserves (designated in 2012).
- Other wildlife parks within the Reserve are: Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Mukurthi National Park and Silent Valley.
- Spread over 344.44 sq km, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary is contiguous to the tiger reserves of Nagerhole and Bandipur of Karnataka and Mudumalai of Tamil Nadu.
- Kabini river (a tributary of Cauvery river) flows through the sanctuary.
- The forest types include South Indian Moist Deciduous forests, West coast semi-evergreen forests and plantations of teak, eucalyptus and Grewelia.
- Elephant, Gaur, Tiger, Panther,Sambar, Spotted deer, Barking deer, Wild boar, Sloth bear, Nilgiri langur, Bonnet macaque, Common langur, Wild dog, common otter, Malabar giant squirrel etc are the major mammals.
Important Facts For Prelims
‘Tomb of Sand’ won International Booker Prize
Why in News?
“Tomb of Sand’, has become the first book written in an Indian language to be awarded the International Booker Prize.
- Originally published in Hindi as Ret Samadhi, the book is written by Author Geetanjali Shree and translated into English by Daisy Rockwell.
- The book narrates the story of an 80-year-old woman who experiences a deep depression after the death of her husband. Eventually, she overcomes her depression and decides to visit Pakistan to finally confront the past that she left behind during the Partition.
What is the International Booker Prize?
- The International Booker Prize is awarded annually for a single book, translated into English and published in the UK or Ireland.
- The International Booker Prize began life in 2005 as the Man Booker International Prize.
- This prize aims to encourage more reading of quality fiction from all over the world and has already had an impact on those statistics in the UK.
- The vital work of translators is celebrated, with the £50,000 prize money divided equally between the author and translator.
- Each shortlisted author and translator also receive £2,500.
- Novels and collections of short stories are both eligible.