91st Amendment & Ceiling on Cabinet
For Prelims: Public interest Litigation (PIL), Cabinet minister, 91st Amendment) Act, 2003
For Mains: Public Interest Litigation, Parliament
Why in News?
Recently, the High Court of Bombay noted that arguable issues have been raised in a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) challenging the “lifetime status of the rank of Cabinet minister” according to Pratap Singh Rane, a six-time Chief Minister of Goa and a legislator for a full 50 years.
- The PIL has contended that Goa has a 12-member Cabinet, and the conferment of Cabinet status on Rane results in the number of Cabinet ranks rising to 13, which exceeds the ceiling mandated by the Constitution.
- This limit was set by 91st Amendment) Act, 2003 to the Indian Constitution.
What is the 91st Amendment Act?
- The Constitution (91st Amendment) Act, 2003 inserted clause 1A in Article 164, which says “the total number of Ministers, including the Chief Minister, in the Council of Ministers in a State shall not exceed 15% of the total number of members of the Legislative Assembly of that State.
- It also provided that the number of Ministers, including the Chief Minister in a State shall not be less than twelve”.
- Similar amendments were also made under Article 75.
- According to it, the PM shall be appointed by the President and the other Ministers shall be appointed by the President on the advice of the PM.
- The total number of ministers, including the Prime Minister, in the COM shall not exceed 15% of the total strength of the Lok Sabha.
- The purpose of the 91st Amendment was to prevent jumbo Cabinets and the resultant drain on the public exchequer.
What is the Council of Ministers?
- Article 74 of the Constitution deals with the status of the council of ministers while Article 75 deals with the appointment, tenure, responsibility, qualification, oath and salaries and allowances of the ministers.
- The COM consists of three categories of ministers, namely, cabinet ministers, ministers of state, and deputy ministers. At the top of all these ministers stands the Prime Minister.
- Cabinet Ministers: These head the important ministries of the Central government like home, defense, finance, external affairs and so forth.
- The Cabinet is the chief policy formulating body of the Central government.
- Ministers of State: These can either be given independent charge of ministries/ departments or can be attached to cabinet ministers.
- Deputy Ministers: They are attached to the cabinet ministers or ministers of state and assist them in their administrative, political, and parliamentary duties.
- Cabinet Ministers: These head the important ministries of the Central government like home, defense, finance, external affairs and so forth.
What is Public Interest Litigation?
- Public interest Litigation (PIL) means litigation filed in a court of law, for the protection of “Public Interest”, such as Pollution, Terrorism, Road safety, Constructional hazards etc.
- Any matter where the interest of the public at large is affected can be redressed by filing a Public Interest Litigation in a court of law.
- Public interest litigation is not defined in any statute or in any act. It has been interpreted by judges to consider the intent of the public at large.
- Public interest litigation is the power given to the public by courts through judicial activism.
- However, the person filing the petition must prove to the satisfaction of the court that the petition is being filed for a public interest and not just as frivolous litigation by a busy body.
- The court can itself take cognizance of the matter and proceed suo motu or cases can commence on the petition of any public spirited individual.
- Some of the matters which are entertained under PIL are:
- Bonded Labour matters
- Neglected Children
- Non-payment of minimum wages to workers and exploitation of casual workers
- Atrocities on women
- Environmental pollution and disturbance of ecological balance
- Food adulteration
- Maintenance of heritage and culture
- The era of the PIL movement was heralded by Justice P.N. Bhagawati in the case of S.P. Gupta vs. Union of India 1981.
- In this case it was held that “any member of the public or social action group acting Bonafide” can invoke the Writ Jurisdiction of the High Courts (under article 226) or the Supreme Court (under Article 32).
- Through PIL any person can seek redressal against violation of legal or constitutional rights of persons who due to social or economic or any other disability cannot approach the Court.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions
Q. Out of the following statements, choose the one that brings out the principle underlying the Cabinet form of Government: (2017)
(a) An arrangement for minimizing the criticism against the Government whose responsibilities are complex and hard to carry out to the satisfaction of all.
(b) A mechanism for speeding up the activities of the Government whose responsibilities are increasing day by day.
(c) A mechanism of parliamentary democracy for ensuring collective responsibility of the Government to the people.
(d) A device for strengthening the hands of the head of the Government whose hold over the people is in a state of decline.
Ans: (c)
MHA on Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA), 2019
For Prelims: Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) 2019, Assam Accord of 1985, National Register of Citizens (NRC)
For Mains: Government Policies & Interventions, Secularism, Sixth Schedule of the Constitution
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) in its latest annual report for 2020-21, has said that the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA) 2019 is a compassionate and ameliorative legislation and does not deprive any Indian of citizenship.
- The CAA, which aims to give citizenship to migrants belonging to Hindu, Sikh, Buddhist, Jain, Parsi or Christian communities from Afghanistan, Bangladesh or Pakistan, was notified on 12th December 2019, and came into force on 10th January 2020.
- The legislation evoked widespread protests across the country.
What are Associated Concerns with CAA?
- Targeting a Particular Community: There are apprehensions that the CAA, followed by a country-wide compilation of the National Register of Citizens (NRC), will benefit non-Muslims excluded from the proposed citizens’ register, while excluded Muslims will have to prove their citizenship.
- Issues in the North-East: It contradicts the Assam Accord of 1985, which states that illegal migrants, irrespective of religion, heading in from Bangladesh after 25th March, 1971, would be deported.
- There are an estimated 20 million illegal Bangladeshi migrants in Assam and they have inalienably altered the demography of the state, besides putting a severe strain on the state’s resources and economy.
- Against Fundamental Rights: Critics argue that it is violative of Article 14 of the Constitution (which guarantees the right to equality and is applicable to both the citizens and foreigners) and the principle of secularism enshrined in the preamble of the constitution.
- Discriminatory in Nature: India has several other refugees that include Tamils from Sri Lanka and Hindu Rohingya from Myanmar. They are not covered under the Act.
- Difficulty in Administration: It will be difficult for the government to differentiate between illegal migrants and those persecuted.
- Hampering Bilateral Ties: The Act throws light on the religious oppression that has happened and is happening in these three countries and thus may worsen our bilateral ties with them
What does MHA Clarified?
- Not Applicable on Indian Citizens: The CAA does not apply to Indian citizens. Therefore, it does not in any way take away or abridge the rights of any Indian citizen.
- Legal Process of Acquiring Indian Citizenship Remain Unchanged: Further, the present legal process of acquiring Indian citizenship by any foreigner of any category as provided in the Citizenship Act,1955 is very much operational and the CAA does not amend or alter this legal position in any manner whatsoever.
- Hence, legal migrants of any religion from any country will continue to get Indian citizenship once they fulfil the eligibility conditions already provided in the law for registration or naturalization.
- Dealing With Issues of North-east India: The annual report has attempted to once again allay fears in the Northeast over the legislation saying that exclusion of areas under the Sixth Schedule of the Constitution and those covered under the Inner Line Permit regime would ensure the protection of indigenous and tribal populations of the region.
Way Forward
- The notification of its rules, without which the law cannot be implemented, continues to be pending with no commitment from the government as to when it will happen.
- Thus, MHA should notify the CAA rules with utmost transparency and clear the apprehensions associated with CAA.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. The provisions in Fifth Schedule and Sixth Schedule in the Constitution of India are made in order to (2015)
(a) protect the interests of Scheduled Tribes
(b) determine the boundaries between States
(c) determine the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats
(d) protect the interests of all the border States
Ans: (a)
- The Fifth Schedule lays out provision for Administration and Control of Scheduled Areas and Scheduled Tribes in states other than Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- The Sixth Schedule deals with the administration of the tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
Tamil Nadu Bill on Vice Chancellor in Universities
For Prelims: Tamil Nadu Bill on Vice Chancellor in Universities, Role of Governor in appointment of Governor in State Universitates
For Mains: Role of Governor in Center-State Relations
Why in News?
Recently, the Tamil Nadu Assembly passed two Bills that seek to transfer the Governor’s power in appointing Vice-Chancellors (VC) of 13 state universities to the state government.
- Earlier, the Maharashtra and West Bengal Governments have made similar provisions vis-a-vis the governor appointing Vice-Chancellor of the Universities.
- In Karnataka, Jharkhand and Rajasthan, state laws underline the need for concurrence between the state and the Governor.
- The terms “concurrence” or “consultation” are absent from state legislation in most cases.
What are the Highlights of the two Bills?
- The Bills passed in Tamil Nadu stress that “every appointment of the Vice-Chancellor shall be made by the Government from out of a panel of three names” recommended by a search-cum-selection committee.
- Currently, the Governor, in his capacity as the Chancellor of state universities, has the power to pick a VC from the shortlisted names.
- The Bills also seek to empower the state government to have the final word on the removal of VCs, if needed.
- Removal will be carried out based on inquiries by a retired High Court judge or a bureaucrat who has served at least as a Chief Secretary.
What is the UGC’s role in this?
- Education comes under the Concurrent List, but entry 66 of the Union List — “coordination and determination of standards in institutions for higher education or research and scientific and technical institutions” — gives the Centre substantial authority over higher education.
- The University Grants Commission plays that standard-setting role, even in the case of appointments in universities and colleges.
- Recently, the University Grants Commission has released Academic Collaboration between Indian and Foreign Higher Education Institutions to offer Joint Degree, Dual Degree, and Twinning Programmes Regulations, 2022.
- Under these regulations collaborating institutes will be allowed to offer three kinds of programmes — twinning, joint degrees and dual degrees.
- According to the UGC (Minimum Qualifications for Appointment of Teachers and other Academic Staff in Universities and Colleges and other Measures for the Maintenance of Standards in Higher Education) Regulations, 2018, the “Visitor/Chancellor” — mostly the Governor in states — shall appoint the VC out of the panel of names recommended by search-cum-selection committees.
- Higher educational institutions, particularly those that get UGC funds, are mandated to follow its regulations.
- These are usually followed without friction in the case of central universities but are sometimes resisted by the states in the case of state universities.
What is the view of Judiciary in this matter?
- The Supreme Court in various judgment held that any appointment as a Vice Chancellor contrary to the provisions of the UGC Regulations can be said to be in violation of the statutory provisions, warranting a writ of quo warranto”.
- In case of any conflict between state legislation and central legislation, central legislation shall prevail, as the education’ is in the Concurrent List of the Seventh Schedule of the Constitution.
What is the Role of Governors in State Universities?
- In most cases, the Governor of the state is the ex-officio chancellor of the universities in that state.
- While as Governor he functions with the aid and advice of the Council of Ministers, as Chancellor he acts independently of the Council of Ministers and takes his own decisions on all University matters.
- Case of Central Universities:
- Under the Central Universities Act, 2009, and other statutes, the President of India shall be the Visitor of a central university.
- With their role limited to presiding over convocations, Chancellors in central universities are titular heads, who are appointed by the President in his capacity as Visitor.
- The Vice Chancellor too is appointed by the Visitor from panels of names picked by search and selection committees formed by the Union government.
- The Act adds that the President, as Visitor, shall have the right to authorize inspections of academic and non-academic aspects of the universities and to institute inquiries.
Harnessing India’s Tech Strength
For Prelims: Initiatives for Start-ups
For Mains: Startups in India and challenges in achieving the true potential of start-ups, Steps taken to promote Start-ups
Why in News?
Recently, an agreement has been signed between CSIR (Council of Scientific and Industrial Research) and iCreate to harness the country's technological strength.
What is iCreate?
- iCreate is an autonomous centre of excellence of the Gujarat government and is India's largest institution for transforming start-ups based on tech innovation into businesses.
What is CSIR?
- CSIR is known for its cutting-edge Research & Development and Industrial knowledge base in diverse S&T areas.
- It is a contemporary R&D organization.
- CSIR has a dynamic network of 37 national laboratories, 39 outreach centres, one Innovation Complex, and three units with a pan-India presence.
- CSIR has a patent portfolio of 8366 Indian patents and 7806 foreign patents.
- CSIR covers a wide spectrum of science and technology – from oceanography, geophysics, chemicals, drugs, genomics, biotechnology and nanotechnology to mining, aeronautics, instrumentation, environmental engineering and information technology.
- It provides significant technological intervention in many areas concerning societal efforts.
- Societal efforts include environment, health, drinking water, food, housing, energy, farm and non-farm sectors.
- Further, CSIR’s role in Science & Technology human resource development is noteworthy.
What are the Highlights of MoU?
- Under the MoU, CSIR and iCreate intend to establish a collaborative support system for promising tech start-ups by making combined resources available for entrepreneurs and innovators in the country.
- The partnership will also catalyse scientific innovation and the marketability of high-tech start-ups.
- Fintech, neobanks, and e-commerce players make the most of the digital environment and their enterprise can leverage it to the fullest as well and ride the digital boom.
- Further, iCreate will help set up new incubators at identified CSIR labs.
- Such start-ups will access CSIR's equipment, facilities, and scientific manpower.
- CSIR will provide intellectual property support and explore methods of financially supporting innovative start-ups from India to boost emerging entrepreneurs.
- iCreate will also leverage its deep industry connections and market linkages to identify real needs that can be addressed through scientific innovation by CSIR scientists.
- It will thus lead to faster commercialisation of the innovations coming out of CSIR.
What is the State of Start-ups in India?
- About:
- Today, India is the third largest start-up ecosystem globally (by number of start-ups) with more than 15,000 start-ups established in 2020, up from 5000 in 2010.
- The underlying enablers of this startup ecosystem include smartphone and internet penetration, cloud computing, application programming interfaces (APIs), and a national payments stack in place.
- Additionally, amid the Covid-19 pandemic, India has witnessed more number of Unicorn startups (startups having valuation of over USD1 billion) in just 2021 than it did in the period 2011-20.
- However, still there are many challenges (Building and Scaling an Indian Startup, Diversity and the Digital Divide, Complex Regulatory Environment) that act as a hindrance in realizing the true potential of startups in India.
- Other Related Initiatives:
- Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems: It is an evolved evaluation tool aimed to strengthen the support of States and UTs to holistically build their startup ecosystems.
- SCO Startup Forum: The first-ever Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum was launched in October 2020 to develop and improve startup ecosystems collectively.
- Prarambh: The ‘Prarambh’ Summit aims to provide a platform to the startups and young minds from around the world to come up with new ideas, innovation and invention.
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme: It aims to provide financial assistance to startups for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry, and commercialization.
- Fisheries Startup Grand Challenge: The Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying In association with Startup India, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry inaugurated the Fisheries Startup Grand Challenge.
Perseverance Rover Captures Eclipse on Mars
For Prelims: Solar Eclipse, Perseverance Rover, Mars Missions, Planet Mars, NASA
For Mains: Space Technology, Perseverance Rover, Phobos, Mars
Why in News?
Recently, NASA’s (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) Perseverance Rover has captured a solar eclipse on Mars.
- Perseverance Mars rover captured an eclipse featuring Phobos, one of Mars' two moons. Phobos is moving very slowly towards Mars, and millions of years from now, they will collide.
- These observations can help scientists better understand the moon’s orbit and how its gravity pulls on the Martian surface, ultimately shaping the Red Planet’s crust and mantle.
What is Solar Eclipse?
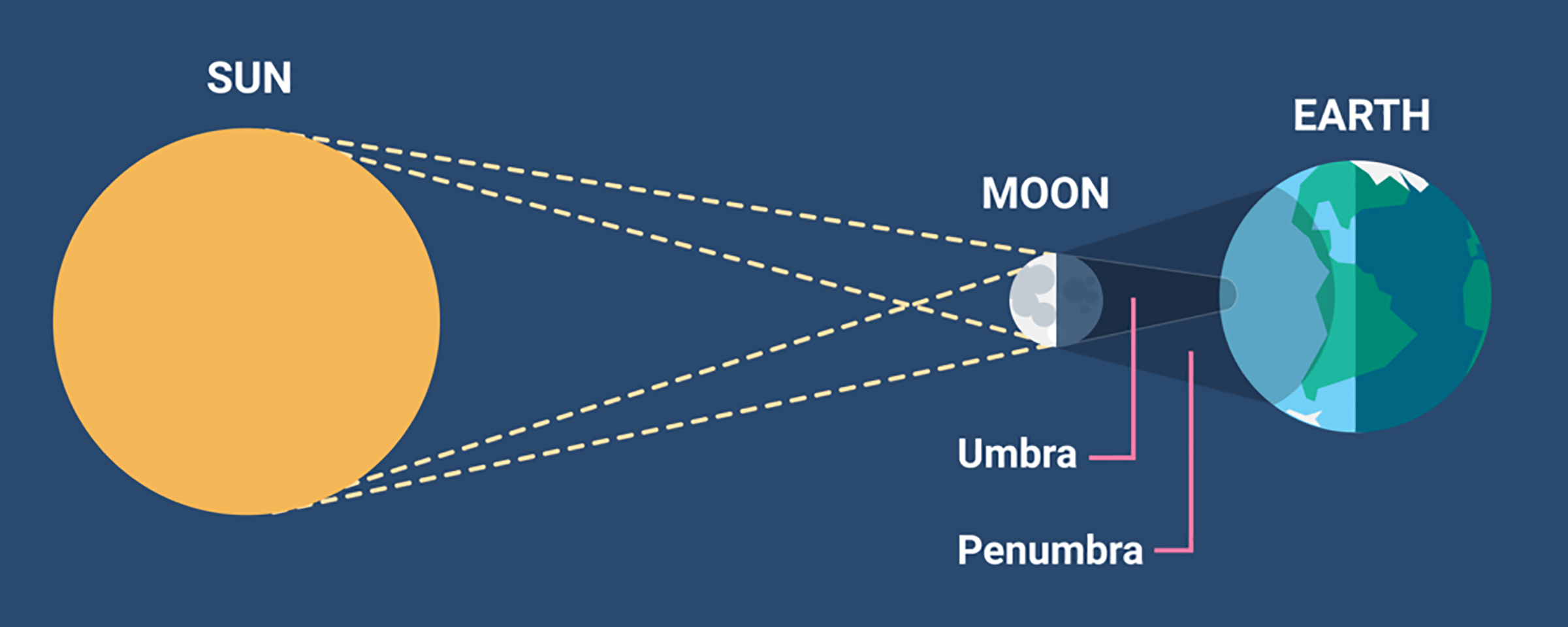
- A solar eclipse is a phenomenon that occurs when the moon comes in the way of the sun’s light. The moon's shadow casts itself on Earth, blocking out the sun's light (as seen from Earth).
- The moon's shadow has two parts: a central region (umbra) and an outer region (penumbra). Depending upon which part of the shadow passes over the Earth, one of three types of solar eclipses could be observed:
- Total Solar Eclipse- The entire central portion of the sun is blocked out by the moon.
- Partial Solar Eclipse- Only part of the sun's surface is blocked out.
- Annular Solar Eclipse- The sun is covered in such a way that only a small ring-like sliver of light is seen from the sun's disc. This ring is known as the ring of fire.
- An annular eclipse happens when the moon is farthest from Earth. As the moon is farther away from Earth, it seems smaller and is unable to block the entire view of the sun, because of which the ring-like structure could be observed.
What is Perseverance Rover?
- About:
- Perseverance is the most advanced, most expensive and most sophisticated mobile laboratory sent to Mars.
- It is different from previous missions because it is capable of drilling and collecting core samples of the most promising rocks and soils and setting them aside in a "cache" on the surface of Mars.
- It is the centerpiece of NASA's Mars 2020 mission which also included the small robotic and coaxial helicopter Ingenuity.
- Launch: 30th July 2020
- Landing: 18th February 2021
- Power Source:
- A Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator (MMRTG) which converts heat from the natural radioactive decay of plutonium (Plutonium Dioxide) into electricity.
- Objectives:
- Perseverance’s primary objective is looking for signs of ancient microbial life.
- The rover is studying and analyzing the Red Planet's regolith, rock and dust, and is the first rover to collect and cache samples.
What is Mars?
- Size and Distance:
- It is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System.
- Mars is about half the size of Earth.
- Similarity to the Earth (Orbit and Rotation):
- As Mars orbits the Sun, it completes one rotation every 24.6 hours, which is very similar to one day on Earth (23.9 hours).
- Mars' axis of rotation is tilted 25 degrees with respect to the plane of its orbit around the Sun. This is similar with Earth, which has an axial tilt of 23.4 degrees.
- Like Earth, Mars has distinct seasons, but they last longer than seasons on Earth since Mars takes longer to orbit the Sun (because it's farther away).
- Martian days are called sols—short for ‘solar day’.
- Surface:
- It has colors such as brown, gold and tan. The reason Mars looks reddish is due to oxidation or rusting of iron in the rocks, and dust of Mars. Hence it is also called Red Planet.
- Mars has the largest volcano in the solar system i.e. Olympus Mons. It's three times taller than Earth's Mt. Everest with a base the size of the state of New Mexico.
- Atmosphere:
- Mars has a thin atmosphere made up mostly of carbon dioxide, nitrogen and argon gases.
- Magnetosphere:
- Mars has no magnetic field till date, but areas of the Martian crust in the southern hemisphere are highly magnetized, indicating traces of a magnetic field.
- Moons:
- Mars has two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, that may be captured asteroids.
What are the other Mars Missions?
- ExoMars rover (2021):
- The European Space Agency and Russian space agency planned to send a joint mission to Mars in September 2022.
- It has since been suspended after Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
- The European Space Agency and Russian space agency planned to send a joint mission to Mars in September 2022.
- Tianwen-1: China's Mars Mission (2021):
- China’s first Mars mission will search for pockets of water beneath the surface that could host life.
- UAE’s Hope Mars Mission (UAE’s first-ever interplanetary mission) (2021):
- The UAE Hope Mars Mission is building a complete picture of Mars' climate.
- India’s Mars Orbiter Mission (MOM) or Mangalyaan (2013):
- Mangalyaan is India’s Mars orbiter that has been observing the planet since September 2014.
- Mars 2 and Mars 3 (1971):
- The identical Soviet Mars 2 and Mars 3 spacecraft, launched in 1971, each released descent craft 4.5 hours prior to their arrivals at Mars. But the landers had the misfortune of arriving at Mars during one of the greatest dust storms in recorded history.
Forest Fires Reducing Solar Power Production
For Prelims: Forest Fires, Solar Energy
For Mains: Conservation, Renewable Energy
Why in News?
A new study by Aryabhatta Research Institute of Observational Sciences (ARIES) and National Observatory of Athens (NOA), Greece has found that Forest Fires can reduce solar power production in India.
- The scientists used remote sensing data for the research and studied the impact of aerosols and clouds on the solar energy potential over the Indian region with extensive analysis and model simulations.
- Large-scale development of a solar energy system requires proper planning, and there is a need to estimate the solar potential.
- ARIES is an autonomous institute under the Department of Science & Technology and is located in Nainital (Uttarakhand).
What are the Forest Fires?
- Also called bush or vegetation fire or wildfire, it can be described as any uncontrolled and non-prescribed combustion or burning of plants in a natural setting such as a forest, grassland, brush land or tundra, which consumes the natural fuels and spreads based on environmental conditions (e.g., wind, topography).
- Forest Fires can be incited by human actions, such as land clearing, extreme drought or in rare cases by lightning.
- There are three conditions that need to be present in order for a wildfire to burn: fuel, oxygen, and a heat source.
What are the Findings?
- Several factors like clouds, aerosols, and pollution generated from various sources limit the solar irradiance causing performance issues in the photovoltaic and concentrated solar power plant installations.
- Apart from clouds and aerosols, forest fires play a very crucial role in reducing solar energy production.
- The findings of the present study will drastically increase the awareness among decision-makers about the effect of forest fires on energy management and planning at a country level.
- In addition, this research can support the mitigation processes and policies for climate change and its direct and indirect impacts on sustainable development.
- Such analysis of the energy and financial losses due to the direct and indirect effects of forest fires on the production of solar plants can help grid operators to plan and schedule power generation, as also the distribution, supply, security, and overall stability of power production.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to solar power production in India, consider the following statements: (2018)
- India is the third largest in the world in the manufacture of silicon wafers used in photovoltaic units.
- The solar power tariffs are determined by the Solar Energy Corporation of India.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
- Silicon wafers are thin slices of semiconductor, such as a crystalline Silicon (c-Si), used for the fabrication of integrated circuits and, in photovoltaics, to manufacture solar cells. China is by far the world’s largest producer of Silicon, followed by Russia, the United States, and Brazil. India does not figure among the top five producers of Silicon and Silicon wafers. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Solar tariffs are determined by the Central Electricity Regulatory Commission and not by Solar Energy Corporation of India. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
World Immunization Week 2022
Why in News?
Recently, World Immunization Week 2022 was celebrated from 24th to 30th April 2022.
- The theme of 2022 is Long Life for All and it aims to unify people around the idea that vaccines make it possible for us to follow our dreams, protect our loved ones and live a long, healthy life.
What is World Immunization Week?
- World Immunization Week is a health campaign coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO) and celebrated in the last week of April, every year.
- It aims to promote the use of vaccines to protect people of all ages against disease.
- Immunization saves millions of lives and is widely recognized as one of the world’s most successful and cost-effective health interventions.
- Yet, there are still nearly 20 million unvaccinated and under-vaccinated children in the world today.
Why Does Immunization Matter Now More Than Ever?
- For over 200 years, vaccines have protected us against diseases that threaten lives and prohibit our development.
- For more than two centuries, vaccines have helped keep people healthy—from the very first vaccine developed to protect against smallpox to the newest vaccines used to prevent severe cases of Covid-19.
- With their help, we can progress without the burden of diseases like smallpox and polio, which cost humanity hundreds of millions of lives.
- Vaccines themselves continue to advance, bringing us closer to a world free from the likes of tuberculosis and cervical cancer, and ending suffering from childhood diseases like tetanus and measles.
How does Vaccine Work?
- Vaccines train the immune system to create antibodies, just as it does when it’s exposed to a disease.
- This is because vaccines contain only killed or weakened forms of germs, they do not cause the disease or put you at risk of its complications.
- Vaccines are given at different ages, from birth to childhood and to maintain this record a vaccination card is given.
- It is important to make sure that all these vaccines are up to date.
- Children can safely be given combined vaccinations (e.g., for diphtheria, pertussis and tetanus) — it means fewer injections and reduced discomfort for the child.
- Vaccines can cause mild side effects, such as a low-grade fever, pain or redness at the injection site. Mild reactions go away within a few days on their own.
- Severe or long-lasting side effects are extremely rare.
- Vaccines can safely be given during any mild illnesses. But children with moderate or severe illness with or without fever may need to wait until they are better to get the dose.
What are recent Immunization Initiatives in India?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant Vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements:
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
- Recombinant vector vaccines are made through genetic engineering. The gene that creates the protein for a bacteria or virus is isolated and placed inside another cell’s genes. When that cell reproduces, it produces vaccine proteins that mean the immune system will recognize the protein and protect the body against it.
Kisan Bhagidari Prathmikta Hamari campaign
Why in News?
The Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare of India will conduct ‘Fasal Bima Pathshala’ under ‘Kisan Bhagidari Prathmikta Campaign’ as a Jan Bhagidari movement.
What is the Kisan Bhagidari Prathmikta Hamari campaign?
- About:
- Under the campaign all Implementing Insurance Companies will organize ‘PMFBY (Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana)- Fasal Bima Pathshala’ at Block/Gram Panchayat/village on all 7 days of the campaign period with participation of at least 100 farmers.
- The detailed information on crop loss intimations during localized calamities and post-harvest losses, tracking of farmers’ application, whom farmers can approach for grievance redressal etc. may be shared and explained in detail to farmers for maximum benefit of the scheme.
- Objectives:
- It aims to make the farmers aware of key scheme aspects of PMFBY like basic scheme provisions, importance of ensuring the crops and how to avail scheme benefits etc. in the ongoing Kharif Season 2022 along with facilitating farmers in getting benefit of the PMFBY scheme.
- The broader focus will be on the importance of PMFBY/RWBCIS (Restructured Weather Based Crop Insurance Scheme) and how farmers can enroll under the scheme and avail the benefit of the scheme.
What is Pradhan Matri Fasal Bima Yojna?
- Launch:
- Launched in 2016 and is being administered by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- It replaced the National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (NAIS) and Modified National Agricultural Insurance Scheme (MNAIS).
- Launched in 2016 and is being administered by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Aim:
- To provide comprehensive insurance cover against the failure of the crop thus helping in stabilizing the income of the farmers.
- Scope:
- All food & oilseed crops and annual commercial/horticultural crops for which past yield data is available.
- Premium:
- The prescribed premium is 2% to be paid by farmers for all Kharif crops and 1.5% for all rabi crops. In the case of annual commercial and horticultural crops, the premium is 5%.
- Premium cost over and above the farmer share was equally subsidized by States and GoI.
- However, GoI shared 90% of the premium subsidy for Northeastern States to promote the uptake in the region.
- Implementation:
- By empanelled general insurance companies. The selection of the Implementing Agency (IA) is done by the concerned State Government through bidding.
- Revamped PMFBY:
- The revamped PMFBY is often called PMFBY 2.0, it has the following features:
- Completely Voluntary: Enrolment 100% voluntary for all farmers from 2020 Kharif.
- Earlier, it was compulsory for loanee farmers to avail a Crop Loan/Kisan Credit Card (KCC) account for notified crops.
- Limit to Central Subsidy: The Centre has decided to limit the PMFBY premium rates - against which it would bear 50% of the subsidy - to a maximum of 30% in un-irrigated and 25% in irrigated areas.
- More Flexibility to States: The government has given the flexibility to states/UTs to implement PMFBY and given them the option to select any number of additional risk covers/features.
- Investing in ICE Activities: Insurance companies must now spend 0.5% of the total premium collected on Information, Education and Communication (IEC) activities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to ‘Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana’, consider the following statements: (2016)
- Under this scheme, farmers will have to pay a uniform premium of two percent for any crop they cultivate in any season of the year.
- This scheme covers post-harvest losses arising out of cyclones and unseasonal rains.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)