Raisina Dialogue 2024
For Prelims: Raisina Dialogue, Observer Research Foundation (ORF), Chaturanga: Conflict, Contest, Cooperate, Create.
For Mains: Raisina Dialogue, Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Why in News
Recently, the 9th edition of the Raisina Dialogue took place in New Delhi, with over 2,500 participants from approximately 115 countries attending the conference in person.
- Greece’s Prime Minister Kyriakos Mitsotakis joined the inauguration session as the chief guest.
What is Raisina Dialogue?
- About:
- The Raisina Dialogue is an annual conference on geopolitics and geoeconomics, which aims to address the most challenging issues faced by the world. It was structured along the lines of the Shangri-La Dialogue.
- It is a component of India's "intelligence diplomacy," which, though not prominently featured in the public eye, plays a crucial role in the national security framework, alongside the diplomatic corps and the armed forces.
- The conference takes place in New Delhi and is attended by people from political, business, media, and civil society backgrounds.
- The Dialogue is structured as a multi-stakeholder, cross-sectoral discussion, involving heads of state, cabinet ministers and local government officials, who are joined by thought leaders from the private sector, media and academia.
- Delhi-based think tank Observer Research Foundation (ORF), in partnership with the Ministry of External Affairs, hosts the conference.
- The Raisina Dialogue is an annual conference on geopolitics and geoeconomics, which aims to address the most challenging issues faced by the world. It was structured along the lines of the Shangri-La Dialogue.
- 2024 Theme and Thematic Pillars:
- Chaturanga: Conflict, Contest, Cooperate, Create.
- The participants engaged with each other over six “thematic pillars”. These include:
- Tech Frontiers: Regulations & Realities
- Peace with the Planet: Invest & Innovate
- War & Peace: Armouries & Asymmetries
- Decolonising Multilateralism: Institutions & Inclusion
- The Post 2030 Agenda: People & Progress
- Defending Democracy: Society & Sovereignty.
- Similar Dialogues around the World:
- Munich Security Conference (MSC): Held annually in Munich, Germany, the MSC is one of the most prominent forums for discussing international security policy.
- Shangri-La Dialogue: Organized by the International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) and held annually in Singapore, the Shangri-La Dialogue focuses on security issues in the Asia-Pacific region.
- Oslo Freedom Forum: It is an annual conference focused on human rights, democracy, and freedom. It brings together activists, journalists, and policymakers to share ideas and strategies for advancing human rights globally.
What are the Key Takeaways of Raisina Dialogue 2024?
- Geopolitical Shifts:
- Participants discussed ongoing geopolitical shifts, including the evolving power dynamics between major players such as the United States, China, Russia, and European countries.
- With the emergence of new challenges and opportunities, discussions revolved around how nations are adapting their strategies and alliances.
- India a Bridging Power:
- India’s External Affairs Minister called India a “bridging power”, a country seeking common ground through a “multi-vector” policy, and playing the role of a “Vishwamitra” or friend of the world.
- India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor:
- The Greek Prime Minister spoke about the importance of connectivity projects such as the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor.
- Baltic-Nordic Forum:
- The ministerial contingent from Central and Eastern Europe, which included all Ministers of the Baltic-Nordic forum, enabled a new diplomatic outreach for the government.
- This outreach aims to establish trade agreements and investment ties with this part of Europe, which is often soft-overlooked but economically competitive.
- The ministerial contingent from Central and Eastern Europe, which included all Ministers of the Baltic-Nordic forum, enabled a new diplomatic outreach for the government.
- Global Conflicts:
- The greater part of the conversations focused on global conflicts. The heavy presence of European dignitaries turned the spotlight on the Russian war in Ukraine.
- Panels on military and naval strategy concentrated on the need to handle an aggressive China, including discussions on "grey warfare."
- European Ministers urged India to reconsider trade and ties with Russia and to press the case for Ukraine’s sovereignty ahead of the second anniversary of the Russian invasion of Ukraine that falls on 24th February.
- In particular, they urged India to join a “Peace Conference” in Switzerland, set to be held shortly, at the request of Ukraine President Volodymyr Zelensky.
- Regional Security Concerns:
- The conference addressed various regional security concerns, including tensions in regions like the Indo-Pacific, Middle East, and Eastern Europe.
- Participants discussed strategies for conflict resolution, peace-building efforts, and managing regional rivalries.
- Technology and Innovation:
- The role of technology and innovation in shaping geopolitics and global governance would have been a significant theme.
- Discussions have covered topics such as cybersecurity, digital transformation, artificial intelligence, and their implications for national security and international relations.
Observer Research Foundation
- It is an independent think tank based in New Delhi with three centres in Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata.
- It seeks to lead and aid policy thinking towards building a strong and prosperous India in a fair and equitable world and helps discover and inform India’s choices. It carries Indian voices and ideas to forums shaping global debates.
- It provides non-partisan, independent, well-researched analyses and inputs to diverse decision-makers in governments, business communities, academia and civil society worldwide.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q.1 Consider the following pairs: (2020)
International agreement/set-up : Subject
1. Alma-Ata Declaration : Healthcare of the people
2. Hague Convention : Biological and chemical weapons
3. Talanoa Dialogue : Global climate change
4. Under2 Coalition : Child rights
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 4 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Veer Savarkar
Recently, the Prime Minister paid tribute to freedom fighter Veer Savarkar on his Punya tithi (26th February).
- Birth: Born on 28th May,1883 in Bhagur, a village near Nashik in Maharashtra.
- Related Organisations and Work:
- Founded a secret society called Abhinav Bharat Society.
- He was the president of Hindu Mahasabha from 1937 to 1943.
- The famous book includes ‘The History of the War of Indian Independence’ and ‘Hindutva: who is Hindu?’.
- Trial and Sentences:
- He was arrested in 1909 on charges of plotting an armed revolt against the Morley-Minto reform (Indian Councils Act 1909).
- Arrested in 1910 for his connections with the revolutionary group India House.
- Following the two trials, Savarkar was convicted and sentenced to 50 years imprisonment and transported in 1911 to the Cellular Jail in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (also known as Kala Pani).
- Death: He died on 26th February 1966 due to fasting on his wish of death.
INDUS-X Summit 2024
For Prelims: Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX), Indo-Pacific Region, Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET), INDUS-X Summit, Yudh Abhyas, Vajra Prahar, Malabar, Cope India, Red Flag, Rim of the Pacific (RIMPAC)
For Mains: Cooperation Between India and US, Effect of Policies & Politics of Countries on India's Interests
Why in News?
Recently, the United States Department of Defense (DoD) and the Indian Ministry of Defense (MoD) participated in the second India-U.S. Defense Acceleration Ecosystem (INDUS-X) Summit in New Delhi, India.
- The summit was jointly organized by Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX), MoD, and the DoD, and coordinated by the US-India Business Council (USIBC) and Society of India Defense Manufacturers (SIDM).
What are the Key Highlights of the Second INDUS-X Summit?
- Focus on Indo-Pacific Security:
- The summit emphasised the critical role India and the US play as key partners in ensuring a free and open Indo-Pacific region.
- Discussions centred on co-producing advanced military capabilities, strengthening defence supply chains, and enhancing interoperability to address shared security challenges.
- Promoting Innovation and Collaboration:
- Emphasis was placed on fostering innovation in defence technologies through collaborative efforts between Indian and American industries.
- The summit provided a platform for startups and Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in the defence sector to engage with established players, facilitating knowledge exchange and partnerships.
- Emphasis was placed on fostering innovation in defence technologies through collaborative efforts between Indian and American industries.
- Defence Partnership Between India and the United States:
- The summit highlighted the strong defence partnership between India and the US, citing initiatives like Initiatives on Critical and Emerging Technologies (iCET) aimed at fostering innovation across key sectors, including defence.
- Emphasis on Technological Innovation:
- The Summit emphasised the crucial role of technological innovation in defence within the broader context of the U.S.-India Strategic Partnership, fostering collective progress for defence industries across borders.
- Joint IMPACT Challenges:
- The Summit highlighted the introduction of Joint IMPACT Challenges, aiming to advance defence and aerospace co-development and co-production collaboratively, involving startups in pioneering solutions.
Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX):
- Launched in 2018, iDEX is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Defence. It is funded and managed by the Defence Innovation Organization (DIO), established as a 'not-for-profit' company under Section 8 of the Companies Act 2013.
- iDEX, aims to foster innovation and technology development in the Defence and Aerospace sector.
- It provides grants, funding, and other support to carry out research and development projects with potential for future adoption in Indian defence and aerospace needs.
- It is currently engaged with around 400+ Startups and MSMEs. Recognized as a game-changer in the defence ecosystem, iDEX has received the PM Award for Innovation in the defence sector.
The US-India Business Council:
- It aims to foster bilateral trade between India and the US, bridging industry and government for long-term commercial partnerships, job creation, and global economic growth.
Society of India Defense Manufacturers:
- SIDM is India's leading Defence Industry association, advocating policy reforms and facilitating collaboration with the government and Armed Forces.
What are the Key Developments in India-US Defence Cooperation?
- Framework and Partnership Renewal:
- The foundation of India-US defence cooperation lies in the "New Framework for India-US Defence Cooperation," renewed for a decade in 2015.
- In 2016, the partnership was upgraded to a Major Defence Partnership (MDP).
- India's elevation to Tier-1 status under the US Department of Commerce’s Strategic Trade Authorization license exception occurred on July 2018.
- Institutionalised Dialogue Mechanisms:
- The 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue, involving the Ministers of External Affairs and Defence from both nations along with their US counterparts, serves as the apex platform for addressing political, military, and strategic issues.
- The 5th Edition of the India-US 2+2 Ministerial Dialogue took place, Novemebr 2023 in New Delhi.
- Defence Policy Group (DPG):
- The DPG, led by the Defence Secretary and Under Secretary of Defence (Policy), facilitates a comprehensive review of defence dialogues and mechanisms.
- The 17th DPG convened in Washington D.C. in May 2023.
- The DPG, led by the Defence Secretary and Under Secretary of Defence (Policy), facilitates a comprehensive review of defence dialogues and mechanisms.
- Defence Procurements and Platforms:
- Defence procurements from the US are on the rise, amounting to nearly US$20 billion.
- Key US-origin platforms in use by India include Apache, Chinook, MH60R helicopters, and P8I aircraft.
- Recently, the US State Department has approved a possible foreign military sale of 31 MQ-9B Sky Guardian to India.
- Important Defence Agreements:
- Significant agreements include Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (2016), Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement (2018), Industrial Security Agreement (2019), Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement (2020), and Memorandum of Intent for Defence Innovation Cooperation (2018).
- Military-to-Military Exchanges:
- High-level visits, exercises, training courses, and service-specific bilateral mechanisms facilitate military-to-military exchanges.
- India participates in a growing number of military exercises with the US, including Yudh Abhyas, Vajra Prahar, Malabar, Cope India, and Tiger Triumph, among others.
- Participation in multilateral exercises like Red Flag, Rim of the Pacific (RIMPAC), CUTLASS Express, Sea Dragon, and Milan further strengthens cooperation.
- INS Satpura marked the first Indian naval ship to visit the US mainland as part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav in August 2022.
- India joined the multilateral Combined Maritime Force (CMF) as an Associate Partner in April 2022, based in Bahrain.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. From which one of the following did India buy the Barak anti-missile defence systems? (2008)
(a) Israel
(b) France
(c) Russia
(d) USA
Ans: (a)
Q. Recently, the USA decided to support India’s membership in multi-lateral export control regimes called the “Australia Group” and the “Wassenaar Arrangement”. What is the difference between them? (2011)
1. The Australia Group is an informal arrangement which aims to allow exporting countries to minimize the risk of assisting chemical and biological weapons proliferation, whereas the Wassenaar Arrangement is a formal group under the OECD holding identical objectives.
2. The Australia Group comprises predominantly of Asian, African and North American countries whereas the member countries of Wassenaar Arrangement are predominantly from the European Union and American Continents.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)
Q. ‘What introduces friction into the ties between India and the United States is that Washington is still unable to find for India a position in its global strategy, which would satisfy India’s National self-esteem and ambitions’. Explain with suitable examples. (2019)
Journey of Spices in India
For Prelims: Journey of Spices in India, Indus Valley Civilization, British East India Company, International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
For Mains: Raisina Dialogue, Effect of policies and politics of developed and developing countries on India’s interests.
Why in News?
The history of spices in India reflects a fascinating journey of cultural exchange, economic prosperity, and the integration of Indian flavours into the global culinary landscape.
What is the History of Indian Spices?
- Ancient Origins:
- The use of spices in India can be traced back to ancient times, with evidence dating as far back as the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Spices were used for culinary and medicinal purposes even in these early civilizations.
- Trade Routes:
- India's strategic location on ancient trade routes, including the Silk Road, facilitated the exchange of spices with other civilizations.
- Spices like black pepper, cardamom, and cinnamon were highly sought after, contributing to India's economic prosperity.
- Ayurvedic Influence:
- Spices have been integral to traditional Indian medicine, Ayurveda, for centuries. Many spices were believed to possess medicinal properties and were used to treat various ailments.
- Arab and Persian Influence:
- During the mediaeval period, Arab and Persian traders played a crucial role in further disseminating Indian spices to the West.
- The spice trade flourished, and spices became luxury commodities in Europe.
- European Spice Trade:
- In the 15th century, European powers, particularly the Portuguese, Dutch, and later the British, sought direct access to India's spice-producing regions.
- This led to the exploration and establishment of maritime trade routes, contributing to the Age of Exploration.
- Colonial Control:
- European colonial powers aimed to control the spice trade, leading to the establishment of trading posts and colonies in India. Competition for dominance in spice-producing regions, especially in Kerala, was fierce among the Portuguese, Dutch, and British.
- Monopoly of the British East India Company:
- The British East India Company played a significant role in monopolising the spice trade during the colonial period.
- They controlled spice production, distribution, and trade routes, impacting the livelihoods of local spice farmers.
- Spice Plantations:
- The British introduced large-scale spice plantations in India, particularly in regions like Kerala and Karnataka, focusing on spices like black pepper, cardamom, and cinnamon for export.
- Post-Independence Revival:
- After gaining independence in 1947, India continued to be a major player in the global spice market. Government policies supported spice cultivation, and India remained a significant exporter of various spices.
- Diverse Spice Production:
- Today, India is known for producing a wide variety of spices due to its diverse climate and geography. Spices like black pepper, cardamom, cinnamon, cloves, turmeric, cumin, and coriander are cultivated in different regions of the country.
- Global Influence:
- Indian spices have not only shaped the country's culinary traditions but have also left a significant impact on global cuisine. The use of Indian spices is widespread in international cooking, contributing to the globalization of culinary practices.
What is the Scenario of the Indian Spice Market?
- Production:
- India is the world’s largest spice producer. It is also the largest consumer and exporter of spices.
- The production of different spices has been growing rapidly over the last few years.
- Production in 2021-22 stood at 10.87 million tonnes. During 2022-23, the export of spices from India stood at USD 3.73 billion from USD 3.46 billion in 2021-22.
- During 2021-22, the single largest spice exported from India was chilli followed by spice oils and oleoresins, mint products, cumin, and turmeric.
- Exports:
- India is the largest exporter of spice and spice items. During 2022-23, the country exported spices worth USD 3.73 billion.
- India exported 1.53 million tonnes of spices. From 2017-18 to 2021-22, the total export quantity from India grew at a CAGR of 10.47%.
- Varieties:
- India produces about 75 of the 109 varieties which are listed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
- The most produced and exported spices are pepper, cardamom, chilli, ginger, turmeric, coriander, cumin, celery, fennel, fenugreek, garlic, nutmeg & mace, curry powder, spice oils and oleoresins. Out of these spices, chilli, cumin, turmeric, ginger and coriander make up about 76% of the total production.
- The largest spice-producing states in India are Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Assam, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh, West Bengal, Tamil Nadu and Kerala.
What are the Government Initiatives to Promote Spices?
- Export Development and Promotion of Spices:
- This initiative by the Spices Board of India aims to support the exporter to adopt high-tech processing technologies and upgrade the existing level of technology for the development of industry and to meet the changing food safety standards of the importing countries.
- The Spices Board of India is set up for the development and global promotion of Indian spices.
- It acts as a link between Indian exporters and importers abroad. The main activities of the board involve promotion, maintenance and monitoring of quality, financial and material support to growers, infrastructure facilitation and research.
- Spices Parks:
- Spices Board has launched eight crop-specific Spices Parks in key production/market centres intending to facilitate the farmers to get an improved price realisation and wider reach for their produce.
- The purpose of the park is to have an integrated operation for cultivation, post-harvesting, processing, value-addition, packaging and storage of spices and spice products.
- Spice Complex Sikkim:
- The Spices Board submitted a project proposal to the state’s cell for setting up a Spice Complex in Sikkim seeking financial assistance for facilitating and demonstrating common processing and value addition in spices to help farmers and other stakeholders in the state.
- Codex Committee on Spices and Culinary Herbs (CCSCH):
- The CCSCH is a subsidiary body of the Codex Alimentarius Commission, which is a joint initiative of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
- The Codex Alimentarius Commission is responsible for setting international food standards to ensure the safety, quality, and fairness of food trade. India is its member since 1964.
- The CCSCH is a subsidiary body of the Codex Alimentarius Commission, which is a joint initiative of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The staple commodities of export by the English East India Company from Bengal in the middle of the 18th century were: (2018)
(a) Raw cotton, oil-seeds and opium
(b) Sugar, salt, zinc and lead
(c) Copper, silver, gold, spices and tea
(d) Cotton, silk, saltpetre and opium
Ans: (d)
Q. In making the saffron spice, which one of the following parts of the plant is used? (2009)
(a) Leaf
(b) Petal
(c) Sepal
(d) Stigma
Ans: (d)
- Safron is one of the most expensive spices in the world. It is made from the stigma of the flower Saffron crocus.
- Female reproductive part of a flower, pistel, consists of ovary, style, and stigma. Stigma is the part that gets pollen from the pollinating agents.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
Eased FDI Policy for Space Sector
For Prelims: Foreign Direct Investment, Indian Space Policy 2023, Aditya L1. Chandrayaan-3, Mars Orbiter Mission, Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre, Recent Trends Related to FDI
For Mains: Key Amendments in FDI Policy Related to the Space Sector, FDI Prohibited Sectors in India
Recently, the Union Cabinet approved amendments in the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy pertaining to the space industry.
- This development comes in alignment with the Indian Space Policy 2023, which seeks to unlock the nation's potential in the space domain through enhanced private participation.
What are the Recent Amendments in FDI Policy for the Space Sector?
- 100% FDI Allowed: Under the amended policy, 100% FDI is permitted in the space sector, aiming to attract potential investors to Indian space companies.
- Liberalised Entry Routes: The entry routes for various space activities are as follows:
- Up to 74% under Automatic Route: Satellites-Manufacturing & Operation, Satellite Data Products, Ground Segment & User Segment.
- Beyond 74%, the government route applies.
- Up to 49% under Automatic Route: Launch Vehicles, associated systems or subsystems, Creation of Spaceports.
- Beyond 49%, the government route applies.
- Up to 100% under Automatic Route: Manufacturing of components and systems/sub-systems for satellites, ground segment, and user segment.
- Up to 74% under Automatic Route: Satellites-Manufacturing & Operation, Satellite Data Products, Ground Segment & User Segment.
What are the Major Developments in the Space Sector in India?
- About:
- India constitutes 2-3% of the global space economy (US: 40%, UK: 7%) and is expected to enhance its share to more than 10% by 2030.
- ISRO is one of the six largest space agencies in the world.
- India constitutes 2-3% of the global space economy (US: 40%, UK: 7%) and is expected to enhance its share to more than 10% by 2030.
- Recent Major Successful Missions:
- Advancements in Launch Vehicles:
- Missions for International Clients
- Other Key Developments:
What are the Key Features of Indian Space Policy 2023?
- Transition of ISRO's Role: ISRO to transition out from manufacturing operational space systems and concentrate on research and development in advanced technologies.
- Private Participation Encouragement:
- Non-government entities (NGEs) permitted to offer national and international space-based communication services through self-owned, procured, or leased satellite systems.
- NGEs encouraged to manufacture and operate space transportation systems, including launch vehicles, shuttles, and develop reusable, recoverable, and reconfigurable technologies and systems for space transportation.
- NGEs permitted to engage in the commercial recovery of asteroid resources or space resources.
- Entitled to possess, own, transport, use, and sell obtained resources in accordance with applicable laws.
- Industry Collaboration and Commercialisation: Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe) mandated to promote, handhold, guide, and authorise space activities autonomously.
- NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) is tasked with commercialising space technologies and platforms, manufacturing, leasing, or procuring space components, and servicing space-based needs on commercial principles.
What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- About: FDI is an investment made by a foreign entity into a business or corporation in another country.
- FDI can be in the form of equity instruments, or it can be a controlling ownership stake in a business.
- FDI in India:
- In India, FDI is defined as an investment made by a person who is not a resident of India. This can be in the form of:
- An investment in an unlisted Indian company
- An investment in 10% or more of the post-issue paid-up equity capital of a listed Indian company.
- Total FDI inflows in India in FY 22-23 is USD 70.97 billion.
- According to the Reserve Bank of India, The United States was the largest source of FDI in India in 2022-23.
- It was followed by Mauritius, the United Kingdom and Singapore.
- In India, FDI is defined as an investment made by a person who is not a resident of India. This can be in the form of:
- Also, during 2022-23, market value of FDI in India increased by 6.9% in rupee terms, primarily due to the rise in FDI in unlisted companies.
- Routes of FDI in India:
- Automatic Route: Under the Automatic Route, the non-resident investor or the Indian company does not require any approval from the Government of India for the investment.
- Government Route: Prior to investment, approval from the Government of India is required.
- Proposals for FDI under this route are considered by the respective Administrative Ministry/ Department.
- FDI Prohibited Sectors in India:
- Gambling and Betting
- Chit Funds
- Nidhi Company
- Trading in Transferable Development Rights (TDR)
- Real Estate Business
- Manufacturing of Tobacco Products
- Sectors Not Open to Private Sector Investment: Includes atomic energy and railway operations (except for permitted activities under the Consolidated FDI policy).
- Lottery Business: Including government or private lotteries, and online lotteries.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following: (2021)
- Foreign currency convertible bonds
- Foreign institutional investment with certain conditions
- Global depository receipts
- Non-resident external deposits
Which of the above can be included in Foreign Direct Investments?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 4
(d) 1 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
SC’s Interim Order on the Forest Conservation Act 2023
For Prelims: Supreme Court, 1996 T.N. Godavarman Thirumulpad case, Forest Conservation Act of 2023, Indian Forest Act, 1927, Deemed Forest, Permitted Activities in Forest Land, India State of Forest Report 2021.
For Mains: Major Provisions of Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023, Concern Regarding Varying Definitions of Forests in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court has instructed the government to maintain the broad interpretation of "forest" as per the 1996 T.N. Godavarman Thirumulpad case until a final decision is reached on a petition challenging the amended Forest Conservation Act of 2023.
What is the Forest Conservation Act, 1980?
- About: The Forest Conservation Act of 1980 was enacted to streamline forest-related laws, regulate deforestation, oversee the transportation of forest products, and levy duties on timber and other forest produce.
- Under the provisions of this Act, prior approval of the Central Government is required for diversion of forest land for non-forest purposes.
- It primarily applied to forest lands recognized by the Indian Forest Act, 1927 or State records since 1980.
- Under the provisions of this Act, prior approval of the Central Government is required for diversion of forest land for non-forest purposes.
- Supreme Court’s Interpretation: The 1996 Godavarman judgement by the Supreme Court mandated the protection of forests regardless of classification or ownership.
- This introduced the concept of deemed forests or forest-like tracts referring to areas resembling forests but not officially classified as such in government or revenue records.
- Concern Regarding Varying Definitions of Forests: States in India interpret 'forests' differently based on surveys and expert reports, leading to diverse definitions.
- For example, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh base their definitions on size, tree density, and natural growth, while Goa relies on forest species coverage.
- Varying definitions result in estimates of deemed forest ranging from 1% to 28% of India's official forest area.
- Recent Amendment to Forest Conservation Act:
- The recent Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023, passed in July-August 2023, aimed to bring clarity and address concerns surrounding deemed forests.
- It focused on defining the scope of forest land under the Act's purview, exempting certain categories of land from its provisions.
- However, the Supreme Court's interim directive maintains the traditional approach to forest governance, unaffected by the recent amendment enacted by the Centre.
- Also, the Supreme Court ruled that the creation of zoos or safaris by any government or authority must receive final approval from the court.
- The recent Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023, passed in July-August 2023, aimed to bring clarity and address concerns surrounding deemed forests.
What are the Major Provisions of the Forest (Conservation) Amendment Act, 2023?
- Land Under the Purview of the Act: It defines two categories of land under its purview:
- Land declared as forest under the Indian Forest Act or any other law, or notified as a forest after 25th October 1980.
- Land converted from forest to non-forest use before 12th December 1996.
- Exemptions from the Act: It includes allowing up to 0.10 hectares of forest land for connectivity purposes along roads and railways, up to 10 hectares for security-related infrastructure, and up to 5 hectares in Left Wing Extremism Affected Districts for public utility projects.
- Additionally, strategic projects related to national security within 100 kilometres of international borders, Line of Actual Control (LAC), and Line of Control (LoC) are also exempted.
- Permitted Activities in Forest Land: It includes conservation, management, and development efforts, with additional activities like zoos, ecotourism facilities, silvicultural operations, and specified surveys being exempted from non-forest purposes.
- Assignment/Leasing of Forest Land: It extends the prerequisite for obtaining prior approval from the central government for the assignment of forest land to any entity, broadening the scope beyond private entities.
- Furthermore, it grants the central government the authority to stipulate the terms and conditions governing such assignments.
What is the Current Status of Forest Cover in India?
- According to the India State of Forest Report 2021, the total forest and tree cover in India accounts for 24.62% of the country's geographical area.
- Specifically, the total forest cover constitutes 21.71% of the country's geographical area, while the tree cover constitutes 2.91%.
- Madhya Pradesh has the largest forest cover (in terms of area) in the country, followed by Arunachal Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, and Maharashtra.
- In terms of forest cover as a percentage of the total geographical area, the top five states are Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Manipur, and Nagaland.
- States with a positive change in forest cover include Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Odisha, Karnataka and Jharkhand.
- States with a negative change include Arunachal Pradesh, Manipur, Nagaland, Mizoram & Meghalaya.
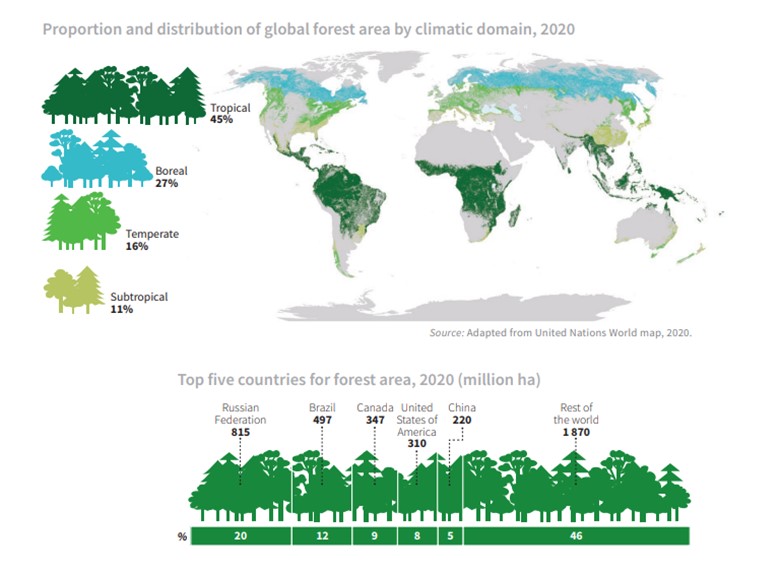
- According to the Global Forest Resources Assessment (FRA) 2020 report by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), India ranks 3rd in the world for net gain in average annual forest area between 2010 and 2020.
- Also, more than half (54%) of the world’s forests are in only five countries: Russian Federation, Brazil, Canada, the United States of America and China.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- As per recent amendment to the Indian Forest Act, 1927, forest dwellers have the right to fell the bamboos grown on forest areas.
- As per the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, bamboo is a minor forest produce.
- The Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006 allows ownership of minor forest produce to forest dwellers.
- Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. “The most significant achievement of modern law in India is the constitutionalization of environmental problems by the Supreme Court.” Discuss this statement with the help of relevant case laws. (2022)
Astronomers Uncover Hot Helium Stars
Why in News?
Astronomers have recently identified a group of hot, helium-covered stars found in binary systems, potentially deepening our understanding of stellar dynamics and evolution.
What are the Major Outcomes of the Discovery?
- Utilising a telescope capable of detecting ultraviolet light, astronomers observed around half a million stars in the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds.
- The Large Magellanic Cloud and the Small Magellanic Cloud are two dwarf galaxies that are companions to the Milky Way.
- Some stars exhibited unusual speeds, hinting at the presence of companions (binary nature) affecting their motion.
- Subsequent analysis of the optical spectra of 25 stars revealed their elemental composition, leading to the identification of different star classes.
- Stars were categorised into three classes:
- Class 1 (helium-rich, hydrogen-depleted)
- Class 2 and Class 3 (helium-rich, with hydrogen)
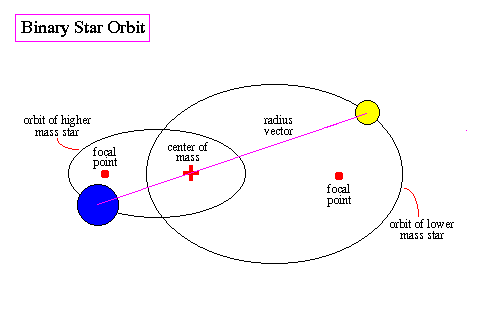
What is the Binary System of Stars?
- About: It refers to the pair of stars that are gravitationally bound to each other and orbit around a common centre of mass.
- An estimated 85% or more of stars are actually part of binary or even multiple-star systems.
- Classification:
- Visual Binaries: These are the easiest to identify and consist of two stars that can be directly resolved and separated using a telescope.
- Spectroscopic binaries: These stars are too close together to be resolved visually even with powerful telescopes.
- However, their presence can be detected by observing periodic shifts in their spectral lines.
- Eclipsing Binaries: These binary systems are aligned in a way that one star periodically passes in front of the other from our perspective.
- This event creates a temporary dip in the brightness of the combined system, allowing astronomers to confirm the presence of the unseen companion and study its properties.
- Astrometric Binaries: These binary systems are detected indirectly by measuring the wobbling motion of a single star.
- This wobbling is caused by the gravitational pull of the unseen companion star.
- Confirmation of Binary Systems: When a star exhausts its fuel, gravity takes over, leading to a supernova explosion that strips its outer layers.
- Some supernova lack hydrogen, suggesting pre-explosion stripping of the outer layer.
- This can happen in binary systems, where one star's gravity removes the outer hydrogen layer from its companion, leaving behind a helium-rich star.
- Astronomers have only found one such binary system so far.
- Some supernova lack hydrogen, suggesting pre-explosion stripping of the outer layer.
How do Stars Maintain their Presence Over Billions of Years?
- Stars maintain their presence over billions of years through a delicate balance between two opposing forces: nuclear fusion and gravity.
- For example, despite Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation suggesting the Sun's gravitational collapse, nuclear fusion at its core acts as a vital stabilising force.
- Nuclear Fusion involves the merging of nuclei of light elements like hydrogen and helium, releasing substantial heat energy.
- This energy, in turn, creates internal pressure, counteracting the gravitational force, thus maintaining equilibrium.
- Therefore, Stars like the Sun sustain this balance between outward fusion energy and inward gravitational pull, ensuring their enduring presence over billions of years.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The terms ‘Event Horizon’, ‘Singularity’, ‘String Theory’ and ‘Standard Model’ are sometimes seen in the news in the context of (2017)
(a) Observation and understanding of the Universe
(b) Study of the solar and the lunar eclipses
(c) Placing satellites in the orbit of the Earth
(d) Origin and evolution of living organisms on the Earth
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q.How does the Juno Mission of NASA help to understand the origin and evolution of the Earth? (2017)
Parhyale Odian
Why in News?
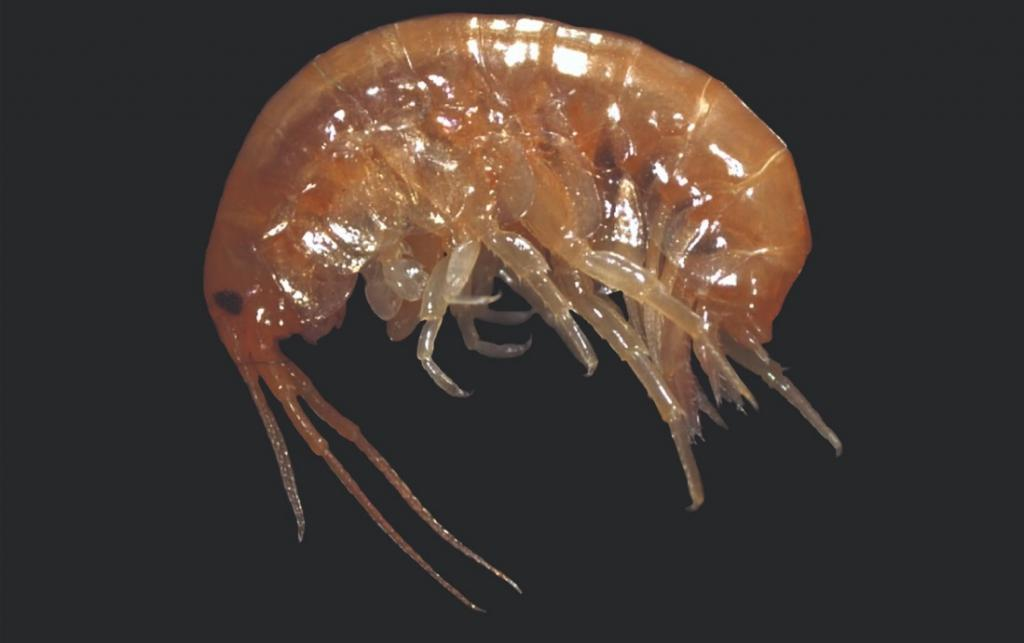
Researchers from Odisha’s Berhampur University discovered a new species of marine amphipod in Chilika Lake. It has been named Parhyale Odian after Odisha’s native language, Odia.
What are Amphipods?
- Amphipods are a diverse group of malacostracan crustaceans, meaning they share some features with crabs, lobsters, and shrimp.
- They have a laterally compressed body, meaning they are flattened from side to side, and a curved body shape.
- The whale lice found on the bodies of whales and dolphins are actually a type of amphipod.
- Amphipods, including those of the genus Parhyale, play a vital role in the marine ecosystem.
- They contribute to the marine food chain and serve as indicators for studying the impact of climate change and the health of coastal ecosystems.
- In 2023, researchers discovered three new marine amphipods: Quadrivisio chilikensis and Demaorchestia alanensis in Chilika Lake and Talorchestia buensis on the West Bengal coast.
What are the Characteristics of Genus Parhyale and Parhyale Odian?
- Genus Parhyale:
- The genus Parhyale, first reported in 1899 from the Virgin Islands (US), comprises 15 species globally.
- The present contribution has added one more species to the genus Parhyale, raising the global species number in the group to 16.
- These amphipods inhabit both marine and brackish water environments.
- They are cosmopolitan, found in intertidal and littoral environments across tropical and warm temperate regions.
- They are commonly found underneath stones with attached vegetation or in the burrows of isopods.
- The genus Parhyale, first reported in 1899 from the Virgin Islands (US), comprises 15 species globally.
- Parhyale Odian:
- It is a shrimp-like crustacean of the genus Parhyale.
- It is brown in colour, approximately 8 millimetres in length, and possesses 13 pairs of legs.
- The first pair of legs is specialized for capturing prey and feeding.
- Unlike the other 15 known species in the genus, Parhyale Odian stands out due to a stout robust seta- a spine-like structure on the surface of the male gnathopod (first pair of legs).
Note: Chilika Lake is the largest brackish water lagoon in Asia and the second-largest coastal lagoon in the world.
- It is located on the east coast of India, at the mouth of the Daya River, which flows into the Bay of Bengal.
- Due to its rich biological diversity, Lake Chilika was the first Indian wetland of international importance to be designated under the Ramsar Convention in 1981.
- The unusual hydrological diversity gives Lake Chilika the characteristics of a lake, estuary and lagoon.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Q. Which one of the following is the correct sequence of a food chain? (2014)
(a) Diatoms-Crustaceans-Herrings
(b) Crustaceans-Diatoms-Herrings
(c) Diatoms-Herrings-Crustaceans
(d) Crustaceans-Herrings-Diatomsol
Ans: (a)
Exercise Dharma Guardian 2024
The 5th edition of Joint Military Exercise 'Dharma Guardian' between the Indian Army and the Japan Ground Self Defence Force started on 25th February and will conclude on 9th March 2024 at Mahajan Field Firing Ranges in Rajasthan.
- Exercise 'Dharma Guardian’ is an annual exercise conducted alternatively in India and Japan.
- The Exercise aims to foster military cooperation and enhance combined capabilities to execute joint operations in the semi-urban environment under Chapter VII of the United Nations Charter.
- The exercise will emphasise high physical fitness, joint planning, tactical drills, and basic special arms skills, including establishing a temporary operating base, creating an ISR grid, setting up mobile vehicle checkposts, conducting cordon and search operations, heliborne operations, and house intervention drills.
- The exercise will enhance defence cooperation and bilateral relations by fostering camaraderie and sharing best practices in tactical operations.
- A Weapon and Equipment Display will also be organised showcasing the ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’ initiative and the growing defence industrial capability of the country.
- India and Japan's defence forces also organise a series of bilateral exercises such as:
- JIMEX (naval), Malabar exercise (Naval Exercise), ‘Veer Guardian’ and SHINYUU Maitri (Air Force), and Dharma Guardian (Army).
Cyclone Shelter HAMs Excel in IOTA Expedition
A dedicated team of amateur radio operators (HAMs) advocating last-mile connectivity, aimed to integrate HAM education in schools for enhanced disaster response, embarked on a significant journey from cyclone shelters in Nachugunta Island, Andhra Pradesh, to participate in the Island on the Air (IOTA) expedition.
- The expedition's success showcases HAM operators' technical prowess, emphasises community engagement and preparedness for natural disasters, and demonstrates India's amateur radio capabilities while enhancing emergency communication resilience in vulnerable regions.
- Amateur Radio (HAM Radio) is a widely enjoyed hobby that uses radio frequencies for non-commercial purposes, fostering technical learning, community engagement, and global connectivity through radio waves.
- Islands On The Air (IOTA), is a program connecting global radio amateurs with island stations, managed by IOTA Ltd and Radio Society of Great Britain (RSGB), categorising islands into communication groups since 1964.
Initiative for Flue-cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco Farmers
- Flue-cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco is predominantly cultivated in India, primarily in Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka, with the current crop season underway.
- The Michaung cyclone caused heavy rains in Andhra Pradesh, severely affecting the FCV tobacco crop across several districts.
- Against this backdrop, the Government of India has approved an interest-free loan of Rs 10,000 from the Grower Welfare Fund of the Tobacco Board for FCV Tobacco growers in Andhra Pradesh.
- Flue-cured Virginia (FCV) Tobacco:
- FCV tobacco is an important commercial crop grown during kharif as rainfed crop predominantly on red sandy loam soils.
- The FCV tobacco cultivated in Karnataka Light Soils is known as ‘Mysore style tobacco’.
- Curing prepares harvested tobacco for market by standardising the process to achieve desired leaf qualities and remove moisture.
- India grows ten distinct types of tobacco in 15 states, including cigarette (FCV, burley, Oriental) and non-cigarette types (Bidi, chewing, hookah and cigar), making it the world's second-largest producer and exporter of tobacco.