International Relations
India's Interest Arctic Region and the Northern Sea Route
For Prelims: Arctic Region, Northern Sea Route, India’s Energy Security, UN Sustainable Development Goals, Himalayas, Suez Canal, Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor.
For Mains: India's Interest Arctic Region and the Northern Sea Route.
Why in News?
Murmansk, popularly called the capital of the Arctic Region and the beginning point of the Northern Sea Route (NSR), is witnessing the rising trend of Indian involvement in Cargo traffic.
- In the first seven months of 2023, India got a share of 35% of eight million tonnes of cargo handled by the Murmansk port, which is about 2,000 km northwest of Moscow, Russia.
What is the Significance of the Arctic for India?
- Untapped Hydrocarbon Reserves:
- The region constitutes the largest unexplored prospective area for hydrocarbons remaining on the earth. It is estimated that the region may hold over 40% of the current global reserves of oil and gas.
- The region has rich deposits of coal, gypsum and diamonds and also substantial reserves of zinc, lead, placer gold and quartz.
- The Arctic can therefore potentially address India’s energy security needs and deficiency of strategic and rare earth minerals.
- However, the government’s Arctic Policy of 2022 mentions that the country’s approach to economic development of the region is guided by UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- India's Historical Engagement:
- India's engagement with the Arctic dates back to the signing of the Svalbard Treaty in 1920.
- India has conducted various scientific studies and research in the region, focusing on atmospheric, biological, marine, hydrological, and glaciological studies.
- Initiatives like the Himadri research station, multi-sensor moored observatory, and northernmost atmospheric laboratory showcase India's commitment to Arctic research.
- Becoming an observer-state of the Arctic Council in 2013 strengthened India's Arctic presence.
- Geographical Significance:
- The Arctic helps circulate the world's ocean currents, moving cold and warm water around the globe.
- Also, Arctic sea ice acts as a huge white reflector at the top of the planet, bouncing some of the sun's rays back into space, helping keep the Earth at an even temperature.
- Environmental Significance:
- The Arctic and the Himalayas, though geographically distant, are interconnected and share similar concerns.
- The Arctic meltdown is helping the scientific community to better understand the glacial melt in the Himalayas, which has often been referred to as the ‘third pole’ and has the largest freshwater reserves after the North and South poles.
- Therefore, the study of the Arctic is critical to Indian scientists. In line, India launched its first scientific expedition to the Arctic Ocean in 2007 and opened the Himadri research base in the Svalbard archipelago (Norway) and has been actively engaging in research there ever since.
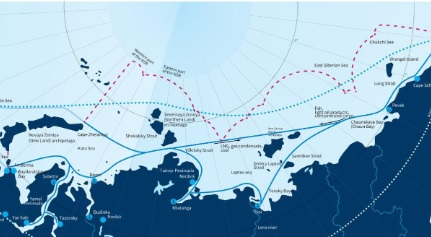
What is the North Sea Route (NSR)?
- About:
- The NSR, the shortest shipping route for freight transportation between Europe and countries of the Asia-Pacific region, straddles the Four Seas (Barents, Kara, Laptev and East Siberian Sea) of the Arctic Ocean.
- Running to 5,600 km, the Route begins at the boundary between the Barents and the Kara seas (Kara Strait) and ends in the Bering Strait (Provideniya Bay).
- It offers potential distance savings of up to 50% compared to traditional routes through the Suez or Panama Canals.
- The 2021 Suez Canal Blockage heightened interest in the NSR as an alternative trade route.
- Russia's Role in NSR Development:
- The Arctic's icebound nature necessitates icebreaking assistance for safe navigation along the NSR. Russia boasts the world's only nuclear-powered icebreaker fleet, ensuring year-round operation. Rosatom, the NSR infrastructure operator, oversees this fleet.
- With Russia's ambitious plans to enhance the NSR's cargo traffic, its nuclear icebreaker fleet remains central to the project.
- Driving Factors for India's NSR Engagement:
- The increasing cargo traffic along the NSR, with a growth rate of approximately 73% during 2018-2022, aligns with India's expanding imports of Russian Crude Oil and coal.
- The NSR's potential as a transit route also suits India's trade-heavy economy.
- The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor (CVMC) project offers a shorter and efficient trade route, further boosting India's interest in the NSR.
- Additionally, India seeks to balance China and Russia's potential collective influence over the NSR.
- Future Developments and Collaborations:
- Russia's NSR development plan aims for significant cargo traffic growth by 2035. The CVMC project, designed to link India and Russia via the NSR, holds promise for reducing transport times and enhancing trade efficiency.
- A forthcoming workshop between the two countries is expected to provide a platform for advancing the CVMC project.
Way Forward
- India's engagement in the Arctic region and its increasing participation in the NSR underscore its strategic interests in economic security, environmental sustainability, and trade efficiency.
- As the Arctic continues to experience transformations, India's role in the region is likely to evolve, shaping its economic and geopolitical interests on the global stage.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The term ‘IndARC’, sometimes seen in the news, is the name of (2015)
(a) an indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence
(b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim
(c) a scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region
(d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.1 Why is India taking keen in resources of Arctic region? (2018)
Q.2 What are the economic significances of discovery of oil in Arctic Sea and its possible environmental consequences? (2015)
Indian Economy
India's Ageing Workforce
For Prelims: India's Ageing Workforce, CMIE's (Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy), Stable employment opportunities, Informal Sector.
For Mains: Concerns over India's Ageing Workforce.
Why in News?
Despite having the largest youth population globally, India's workforce is ageing rapidly according to an analysis of India's workforce using data from CMIE's (Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy)’s Economic Outlook, which is a concerning trend.
- An ageing workforce basically means that if one looks at all the employed people in India, the share of young people is going down while the share of those closer to 60 years of age is going up.
What are the Key Highlights of the Analysis?
- Age Groups and Workforce Composition:
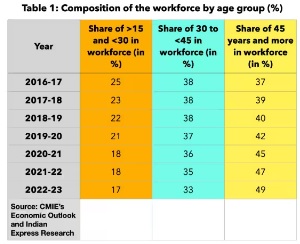
- The analysis categorizes the workforce into three distinct age groups to better understand the ageing workforce trend,
- Aged 15-29 years: The share of this age group in the total workforce has decreased from 25% in 2016-17 to 17% in the financial year 2022-23.
- Aged 30-44 years: The share of individuals in this age group has also declined from 38% to 33% over the same period.
- Aged 45 years and older: This age category's share has grown significantly, increasing from 37% to 49%.
- The analysis categorizes the workforce into three distinct age groups to better understand the ageing workforce trend,
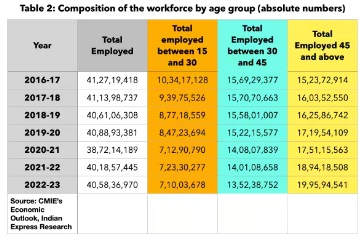
- Falling Employment Rates Among Youth:
- While the youth population has grown by 2.64 crore (from 35.49 crore in 2016-17 to 38.13 crore in 2022-23), the number of employed individuals in this group has fallen by a staggering 3.24 crore.
- Consequently, the employment rate for this age group has plummeted from 29% to 19% over seven years.
- Varying Impact on Different Age Groups:
- While the decline in employment rates is most pronounced among the youth, the trend extends to other age groups as well, albeit to a lesser extent.
- Notably, the oldest age category (45 years and above) has experienced a relatively smaller decline in employment rates and has actually seen an increase in the absolute number of employed individuals.
What are the Factors Contributing to an Ageing Workforce?
- Lack of Adequate Job Opportunities:
- One of the primary reasons for the declining youth employment is the lack of sufficient job opportunities.
- The rapid growth of the youth population has not been matched with a proportional increase in available jobs, leading to intense competition for limited positions.
- Skill Mismatch:
- A mismatch between the skills possessed by the youth and the skills required by the job market can result in higher rates of unemployment.
- The education system may not be adequately preparing young individuals for the evolving job landscape, leading to underemployment or unemployment.
- Informal Sector Dominance:
- A significant portion of India's workforce is engaged in the informal sector, which often lacks stable employment opportunities and social security benefits.
- Youth entering the job market may find it challenging to secure stable and formal employment, leading to instability and underutilization of skills.
- Educational Attainment and Aspirations:
- While educational attainment is rising among the youth, there may be a disconnect between the skills acquired through education and the skills demanded by the job market.
- Aspirations for higher-level jobs might lead to a situation where youth are willing to wait for suitable positions, contributing to a decline in youth employment.
What are the Concerns and Implications of the Ageing Indian Workforce?
- Productivity:
- Older employees might experience reduced productivity due to health issues and declining physical abilities. This could impact overall economic output.
- There may be an increased demand for healthcare services, which could strain the healthcare system and affect both public and private spending.
- Innovation:
- Younger workers often bring fresh perspectives and technological savviness, which can drive innovation in industries.
- An ageing workforce lacks this dynamism.
- Younger workers often bring fresh perspectives and technological savviness, which can drive innovation in industries.
- Economic Growth:
- A declining workforce can impact economic growth potential, as a smaller working-age population contributes less to production and consumption.
- Sectors that rely heavily on manual labor, such as construction and manufacturing, might face labor shortages if younger workers are not available to replace older ones.
- Skill Shortages:
- An aging workforce can create skill shortages, particularly in industries that require specialized knowledge.
- This can hinder technological progress and innovation.
- Consumption Patterns:
- Older individuals often have different consumption patterns, focusing more on savings and essential goods, which can impact consumer demand and industries geared toward luxury goods.
Way Forward
- Policies that discourage early retirement and incentivize older individuals to remain in the workforce can help extend their productive years.
- This could include flexible retirement age, reduced working hours, and financial incentives.
- Companies can adopt age-inclusive workplace policies that address the needs of older workers, such as ergonomic facilities, health support, and opportunities for upskilling
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Performance of welfare schemes that are implemented for vulnerable sections is not so effective due to the absence of their awareness and active involvement at all stages of the policy process – Discuss. (2019)
Agriculture
Scientific Authenticity of Nano Liquid Urea
For Prelims: Scientific Authenticity of Nano Liquid Urea, Indian Farmers and Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO), Climate Change, Ocean Acidification, Ozone Depletion.
For Mains: Scientific Authenticity of Nano Liquid Urea. Issues Related to Using Nano Liquid Urea.
Why in News?
Recently, an opinion paper published in the journal "Plant and Soil" has raised concerns about the scientific validity of Nano Liquid Urea produced by the Indian Farmers and Fertiliser Cooperative (IFFCO).
- The paper questions the claims made about the efficacy and benefits of the product, emphasizing the need for rigorous scientific scrutiny before launching nano fertilizers into the market.
What is Liquid Nano Urea?
- About:
- It is urea in the form of a nanoparticle. It is a nutrient (liquid) to provide nitrogen to plants as an alternative to the conventional urea.
- Urea is a chemical nitrogen fertilizer, white in colour, which artificially provides nitrogen, a major nutrient required by plants.
- It is developed to replace conventional urea and it can curtail the requirement of the same by at least 50%.
- It contains 40,000 mg/L of nitrogen in a 500 ml bottle which is equivalent to the impact of nitrogen nutrient provided by one bag of conventional urea.
- It is urea in the form of a nanoparticle. It is a nutrient (liquid) to provide nitrogen to plants as an alternative to the conventional urea.
- Developed At:
- It has been indigenously developed at Nano Biotechnology Research Centre, Kalol, Gujrat in line with Atmanirbhar Bharat and Atmanirbhar Krishi.
- India is dependent on imports to meet its urea requirements.
- It has been indigenously developed at Nano Biotechnology Research Centre, Kalol, Gujrat in line with Atmanirbhar Bharat and Atmanirbhar Krishi.
- Significance:
- Liquid Nano Urea has been found effective and efficient for plant nutrition which increases production with improved nutritional quality.
- It can boost a balanced nutrition program by reducing the excess use of Urea application in the soil and make the crops stronger, healthier and protect them from the lodging effect.
- It has a positive impact on the quality of underground water, a very significant reduction in global warming with an impact on climate change and sustainable development.
- Liquid Nano Urea has been found effective and efficient for plant nutrition which increases production with improved nutritional quality.
What is the Background?
- IFFCO had asserted that a small quantity of nano liquid urea could replace a substantial amount of conventional urea.
- The central government and IFFCO have ambitious plans to expand nano urea production and export.
- The researchers express concerns about the potential consequences of these plans, as exaggerated claims could lead to severe yield losses, impacting food security and farmer livelihoods.
What are the Concerns Raised By the Paper?
- Discrepancy Between Claims and Outcomes:
- Nano liquid urea was introduced as a promising alternative to traditional granular urea.
- Nano liquid urea has failed to deliver noticeable results in the field. Farmers using the fertiliser have experienced increased input costs without corresponding improvements in crop yield.
- This highlights the discrepancy between product claims and real-world outcomes.
- Environmental Concerns:
- While IFFCO advertised nano urea as environmentally friendly, the paper finds no scientific basis for this claim.
- It emphasizes that nitrogen, a vital compound for crop growth, has been linked to numerous environmental issues such as Climate Change, Ocean Acidification, and Ozone Depletion.
What are the Recommendations of the Study?
- The study underscores the need to address excess nitrogen due to its adverse impact on the environment.
- The opinion paper highlights the importance of transparent and rigorous scientific evaluation before introducing novel agricultural technologies.
- With implications for food security, farmers' livelihoods, and the environment, this controversy underscores the need for responsible innovation and evidence-based decision-making in the agricultural sector.
What is Indian Farmers Fertilizer Cooperative Limited?
- About:
- It is one of India's biggest cooperative societies which is wholly owned by Indian Cooperatives.
- Founded in 1967 with just 57 cooperatives, today it is an amalgamation of over 36,000 Indian Cooperatives with diversified business interests ranging from General Insurance to Rural Telecom apart from its core business of manufacturing and selling fertilizers.
- Objective:
- To enable Indian farmers to prosper through timely supply of reliable, high quality agricultural inputs and services in an environmentally sustainable manner and to undertake other activities to improve their welfare.
Conclusion
- The Nano Liquid Urea controversy underscores the necessity for transparency, and responsible innovation in the agricultural sector.
- Striking a balance between technological advancements and environmental sustainability is vital for the well-being of farmers, Food Security, and the planet.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to chemical fertilizers in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
- At present, the retail price of chemical fertilizers is market-driven and not administered by the Government.
- Ammonia, which is an input of urea, is produced from natural gas.
- Sulphur, which is a raw material for phosphoric acid fertilizer, is a by-product of oil refineries.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Government of India subsidizes fertilizers to ensure that fertilizers are easily available to farmers and the country remains self-sufficient in agriculture production. The same has been achieved largely by controlling the price of fertilizer and the amount of production. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Ammonia (NH3) has been synthesized from natural gas. In this process, natural gas molecules are reduced to carbon and hydrogen. The hydrogen is then purified and reacted with nitrogen to produce ammonia. This synthetic ammonia is used as fertilizer, either directly as ammonia or indirectly after synthesis as urea, ammonium nitrate, and monoammonium or diammonium phosphates. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Sulfur is a major by-product of oil refining and gas processing. Most crude oil grades contain some sulfur, most of which must be removed during the refining process to meet strict sulfur content limits in refined products. This is done through hydrotreating and results in production of H2S gas, which is converted into elemental sulfur. Sulfur can also be mined from underground, naturally-occurring deposits, but this is more costly than sourcing from oil and gas and has largely been discontinued. Sulfuric acid is used in the production of both Monoammonium Phosphate (MAP) and Diammonium Phosphate (DAP). Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option B is the correct answer.
Governance
Rail-Sea-Rail Transportation
For Prelims: Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) transportation, coal, SHAKTI
For Mains: Challenges in Enhancing Coal Evacuation in India, Initiatives Related to Coal
Why in News?
The Ministry of Coal is promoting the Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) transportation strategy, aimed at streamlining the movement of domestic coal.
What is Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR) Transportation?
- About:
- It is an innovative multimodal transportation strategy.
- Integrates rail and sea routes for seamless coal transportation from mines to ports and end-users.
- Aims to enhance logistical efficiency and reduce transportation costs.
- It is an innovative multimodal transportation strategy.
- Addressing Coal Movement Challenges:
- RSR is designed to address challenges related to efficient coal movement from production centers to consumption regions.
- A significant portion of domestic raw coal dispatch, around 75%, is attributed to major coal-producing states like Odisha, Chhattisgarh, and Jharkhand.
- The Ministry of Coal recognizes the need to augment coal production to meet the growing demand for energy. In light of this, the ministry has projected a substantial increase in coal production, targeting a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of approximately 7.7% by FY’30.
- RSR is designed to address challenges related to efficient coal movement from production centers to consumption regions.
- Leveraging Coastal Shipping:
- Coastal shipping has emerged as an economical and environmentally friendly mode of transporting goods, including coal.
- As part of the RSR initiative, efforts are being made to fully utilize the potential of ports along India's Southern and Western coasts.
- This optimisation enables the efficient movement of coal to powerhouses located in states like Gujarat, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Goa, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Andhra Pradesh.
- Coastal shipping has emerged as an economical and environmentally friendly mode of transporting goods, including coal.
- Cost Optimization and Competitive Pricing:
- Opting for RSR could result in significant cost savings.
- Potential savings of around Rs. 760-1300 per ton for end-users in Southern India.
- These cost savings can make domestically produced coal more competitive against the total landed cost of imported coal.
- Opting for RSR could result in significant cost savings.
- Reducing Congestion and Enhancing Logistics:
- Presently, railways handle about 55% of coal evacuation. The Ministry of Coal envisions raising the railways' share in coal evacuation to 75% by FY'30.
- One of the primary goals of this initiative is to reduce congestion on traditional rail routes, which often face bottlenecks due to high traffic. The focus on alternative routes, including Rail-Sea-Rail (RSR), is expected to alleviate this congestion and streamline logistics.
- Presently, railways handle about 55% of coal evacuation. The Ministry of Coal envisions raising the railways' share in coal evacuation to 75% by FY'30.
- Growth and Future Prospects:
- Rail-sea-rail transportation of coal has witnessed remarkable growth, experiencing an increase of approximately 125% over the past four years.
- This growth trajectory indicates the effectiveness and viability of RSR as an alternative mode of transportation. With India's coal production expected to nearly double within the next seven years, the success of RSR becomes even more crucial in ensuring an uninterrupted supply of coal to consumption centres across the country.
- Challenges in Rail-Sea-Rail Coal Evacuation:
- Robust rail and port infrastructure is required for efficient Rail-Sea-Rail coal transport and handle increased capacity.
- There is a need to develop risk mitigation strategies to address potential challenges such as adverse weather conditions, technical glitches, and disruptions in the transportation chain.
- Ensuring seamless collaboration between various Ministries involved in Rail-Sea-Rail strategy implementation for smooth execution.
What are the Initiatives Related to the Coal Sector in India?
- UTTAM (Unlocking Transparency by Third Party Assessment of Mined Coal).
- Scheme for Harnessing and Allocating Koyala (Coal) Transparently in India (SHAKTI).
- Online Coal Clearances System: Provides a single window access to its investors to submit online applications for all the permissions / clearances and approvals granted by the Ministry of Coal.
- Coal Allocation Monitoring System (CAMS): Monitor the allocation of coal by Coal India Limited to States, States to Single Nodal Agency(SNA) and SNA to such consumers in a transparent manner.
- Commercial coal mining: The government has introduced commercial coal mining for private companies, allowing them to bid for coal blocks and sell coal in the open market.
Coal
- It is a type of fossil fuel found in the form of sedimentary rocks and is often known as 'Black Gold'.
- It is a conventional source of energy and is widely available. It is used as a domestic fuel, in industries such as iron and steel, steam engines and to generate electricity. Electricity from coal is called thermal power.
- The leading coal producers of the world include China, US, Australia, Indonesia, India.
- Indian coal has high ash content, which varies from 35 to 45%, compared with that of coal in other parts of the world, which is around 15% while it has low sulphur content, about 0.5%.
- Different Types of Coal in India:
- Anthracite (80-95% carbon content, J&K), Bituminous (60-80% carbon content, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, MP), Lignite (40-55% carbon content, Rajasthan, Assam, Tamil Nadu), Peat (less than 40% carbon content, early wood-to-coal stage).
- Major Coal Producing States:
- Jharkhand, Odisha, Chhattisgarh, West Bengal, Madhya Pradesh, and Telangana.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2019)
- Coal sector was nationalized by the Government of India under Indira Gandhi.
- Now, coal blocks are allocated on lottery basis.
- Till recently, India imported coal to meet the shortages of domestic supply, but now India is self-sufficient in coal production.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Coal sector was nationalised in two phases under Indira Gandhi Government in 1972. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The coal blocks are allocated through auctions and not on a lottery basis. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- The coal sector is the monopolistic sector in India. India holds 5th biggest coal reserves in the world, but due to the incapacity of coal production by monopolistic firms, it imports coal to meet the shortages of domestic supply. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q2. Which of the following is/are the characteristic/characteristics of Indian coal? (2013)
- High ash content
- Low sulphur content
- Low ash fusion temperature
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
National Judicial Data Grid
Why in News?
Recently, the National Judicial Data Grid (NJDG) has gained significant attention for its role in revolutionizing the way judicial proceedings are managed in India.
What is the National Judicial Data Grid?
- About:
- NJDG is a database of orders, judgments and case details of 18,735 District & Subordinate Courts and High Courts created as an online platform under the eCourts Project.
- Data is updated on a near real-time basis by the connected District and Taluka courts. It provides data relating to judicial proceedings/decisions of all computerized district and subordinate courts of the country.
- All High Courts have also joined the NJDG through web services, providing easy access facility to the litigant public.
- Features:
- Aligned with the National Data Sharing and Accessibility Policy (NDSAP), NJDG provides an Open Application Programming Interface (API) to Central & State Governments.
- This API offers streamlined access to NJDG data using designated departmental IDs and access keys.
- This feature is intended for institutional litigants to evaluate and monitor cases, with plans to extend access to non-institutional litigants in the future.
- Significance:
- NJDG works as a monitoring tool to identify, manage & reduce pendency of cases.
- It helps to provide timely inputs for making policy decisions to reduce delays in disposing of cases and helps in reducing case pendency.
- It also facilitates better monitoring of court performance and systemic bottlenecks, and, thus, serves as an efficient resource management tool.
- To track cases related to land disputes, Land Records data of 26 States have been linked with NJDG.
- International Recognition:
- In the Ease of Doing Business report for 2018, the World Bank (WB) commended NJDG for its role in generating case management reports that facilitate contract enforcement.
- This recognition underscores NJDG's significance in improving the business environment.
What are the Other Initiatives under E-court Projects?
Important Facts For Prelims
Eastern Equine Encephalitis
Why in News?
Mosquito-borne illnesses continue to pose a significant threat across various parts of the world, and one of the latest additions to this concern is the emergence of the Eastern equine encephalitis (EEE) virus in the United States.
- This rare virus has recently been reported in Alabama and New York, with serious implications for public health.
What is Eastern Equine Encephalitis?
- About:
- Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). It spreads to people and animals by the bite of an infected mosquito.
- EEE was first identified in horses in Massachusetts, United States, in 1831.
- Eastern Equine Encephalitis (EEE) is a viral disease that causes inflammation of the brain (encephalitis). It spreads to people and animals by the bite of an infected mosquito.
- Causes: EEE is caused by the Eastern Equine Encephalitis Virus (EEEV), which belongs to the genus Alphavirus and the family Togaviridae.
- EEE virus has a single-stranded, positive-sense RNA genome.
- EEEV is primarily transmitted through the bite of infected mosquitoes, particularly species belonging to the Culiseta melanura group.
- These mosquitoes feed on both birds (reservoir hosts) and mammals, including humans and horses (dead-end hosts).
- The virus does not spread between humans or from animals like horses to humans.
- Symptoms: The symptoms associated with EEE can range from mild to severe, often progressing rapidly:
- The virus typically begins with high fever, headache, chills, and nausea.
- As the infection advances, more serious symptoms may develop, including seizures, disorientation, and even coma.
- Effects:
- Roughly 33% of individuals who are infected do not survive, typically passing away between 2 to 10 days after the symptoms first appear.
- Survivors of the virus might experience long-lasting neurological issues, with a greater likelihood of occurrence in individuals above 50 and under 15 years of age.
- Treatment:
- Currently, there are no vaccines available to directly treat Eastern equine encephalitis.
- To mitigate the risk of infection, individuals are advised to take several precautionary steps, including avoiding mosquito bites by using repellents and wearing protective clothing.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
1. In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue.
2. Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: c
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Meta’s New AI model can Translate & Transcribe Nearly 100 Languages
Meta has developed an AI model known as SeamlessM4T, capable of translating and transcribing in over 100 languages, both in text and speech. It's the pioneering all-in-one multilingual and multimodal AI tool for translation and transcription.
- Meta’s goal is to elevate interconnectedness by granting users access to a broader array of multilingual content.
- It also supports speech-to-speech translation in around 100 input languages and around 35 output languages, including English.
- This unified approach of SeamlessM4T minimizes errors and delays, enhancing the efficiency and quality of translation processes.
- Meta's text-to-text machine translation model, known as No Language Left Behind (NLLB), supports approximately 200 languages. Notably, NLLB has been integrated into Wikipedia as one of its translation providers.
Read more: The Future of Metaverse and AI
Rare Black Eagle Spotted at Chail Wildlife Sanctuary
A rare black eagle has been sighted for the first time in Chail wildlife sanctuary located in the Solan district, Himachal Pradesh. This specific type of black eagle has been observed in the Chamba region on prior occasions.
- This eagle is part of the Accipitridae family and stands as the sole member of the Ictinaetus genus.
- They are notable for their substantial size and unique characteristics, often seen in forested mountainous and hilly regions.
- They are found in the Indian states of Himachal Pradesh and Jammu & Kashmir, as well as in the forests of the Eastern and Western Ghats in peninsular India.
- As per the IUCN, their conservation status is categorised as "Least Concern”.
- The Chail Wildlife Sanctuary is home to a variety of animals, including rhesus macaques, leopards, Indian muntjacs, gorals, porcupines, wild boars, langurs, and Himalayan black bears. It has contributed to the preservation of several endangered species of reptiles and birds.
Dibang Multipurpose Project
NHPC Limited, India’s premier hydropower company, has signed an MoU with RITES, a Miniratna Schedule 'A' Central Public Sector Undertaking under the Ministry of Railways, for construction of railway siding at Pasighat, Arunachal Pradesh, for NHPC’s 2,880 MW Dibang MultiPurpose Project.
- Leveraging its core strength, RITES will provide comprehensive and efficient solutions for developing rail infrastructure facilities for NHPC Dibang and other upcoming projects in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Dibang Multipurpose Project is a flood control cum hydroelectric power project planned to be developed on the Dibang River, a tributary of Brahmaputra River, in Arunachal Pradesh.
- It is being developed by India’s state-run National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC).
Read More: Dibang Hydel Project
Hubble Space Telescope Captures Image of Irregular Galaxy
- The Hubble Space Telescope has captured an image of the irregular galaxy ESO 300-16 located at a distance of 28.7 million lightyears in the southern constellation of Eridanus.
- Irregular galaxies do not have a clearly defined shape, and appear as diffuse clouds. A bubble of bright, blue gas is visible towards the galaxy core
- ESO 300-16 was captured as part of an imaging campaign known as Every Known Nearby Galaxy, which aims to create a complete inventory of Hubble images of all galaxies within 10 megaparsecs of the Earth, or 32.6 million lightyears.
- Even the distance that light travels in a year is not convenient for measuring astronomical distances, which is why astronomers use parsecs.
- One parsec is equal to 3.26 lightyears, or 30.9 trillion kilometers. A megaparsec is one million parsecs.
- The Every Known Nearby Galaxy campaign aims to capture the remaining 25% of the galaxies. Hubble has previously captured the lenticular galaxy NGC 6684 and the irregular dwarf galaxy NGC 1156 as part of the campaign.
Read More: Hubble Space Telescope