2nd CII India Nordic-Baltic Business Conclave 2023
For Prelims: 2nd CII India Nordic-Baltic Business Conclave 2023, Nordic Baltic (NB) 8, Blue Economy to enhance Global Supply Chain Resilience,Renewable Energy, Global South through G20, CII (Confederation of Indian Industries).
For Mains: 2nd CII India Nordic-Baltic Business Conclave 2023, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, the 2nd CII (Confederation of Indian Industries) India Nordic-Baltic Business Conclave 2023 was held in New Delhi, aiming to foster collaboration between India and the Nordic Baltic Eight (NB8) countries, known for their prowess in innovation and technology.
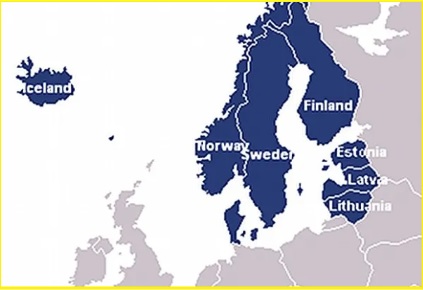
What is Nordic Baltic (NB) 8?
- The NB8 is a regional cooperation format that brings together the Nordic countries and the Baltic states.
- It comprises five Nordic countries: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden, along with three Baltic states: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania.
- The group shares historical, cultural, and geographical ties, fostering collaboration and cooperation in various fields, including politics, economics, trade, security, and culture.
- While the Nordic countries are located in Northern Europe and share similarities in governance, social systems, and values, the Baltic states are situated in Northeastern Europe and have their unique historical backgrounds and geopolitical positioning.
What are the Key Highlights of the Conclave?
- Food Processing and Sustainability:
- Discussions focused on transforming food systems towards sustainability by sharing experiences, innovations, and best practices between India and the Nordic-Baltic nations.
- Collaboration aimed to address global challenges with a holistic approach encompassing economic, social, and environmental dimensions.
- Blue Economy and Maritime Cooperation:
- Emphasis was placed on efficient management of the Blue Economy to enhance Global Supply Chain Resilience, promote sustainable marine practices, encourage innovation, and foster greater maritime cooperation between India and the Nordic-Baltic countries.
- Renewable Energy Integration:
- Deliberations centered around India's push for Renewable Energy integration, identifying resources, policy support, energy storage, and advanced technology initiatives.
- The aim was to seek support from innovative Nordic-Baltic economies in identifying and implementing clean energy-related technologies.
- Transition to Industry 5.0:
- Collaboration discussions focused on leveraging advanced technologies like AI (Artificial Intelligence), IoT, and smart manufacturing to enhance productivity and efficiency in the manufacturing sector.
- The aim was to explore how cooperation between India and Nordic-Baltic nations could contribute to India's goal of becoming a developed nation by 2047.
- Green Financing for Climate Action:
- The conclave highlighted the significance of climate finance in achieving green and sustainable transitions. Discussions aimed at exploring strategies and solutions to drive funding and investments, fostering greater collaboration between India and the Nordic-Baltic countries in advancing climate action.
- Information Technology and AI Collaboration:
- Emphasis was placed on exploring potential areas of cooperation between India and the Nordic-Baltic countries in leveraging IT and AI to address complex societal challenges. Skill development initiatives were also discussed to enable inclusive AI and IT growth.
- Resilient Supply Chain and Logistics:
- Discussions revolved around the need to build efficient and resilient supply chains, aligning with India's Logistics Policy. The conclave aimed to explore how India and the Nordic-Baltic countries could collaborate to strengthen global value chains using technological advancements.
How have the Economic Relations between India and the Nordic-Baltic countries been?
- Trade and Investments:
- Cumulative Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) received from Nordic countries has reached a significant figure, demonstrating mutual investment interests.
- India's combined trade in goods with the NB8 countries is currently around USD 7.3 billion and the cumulative FDI received from Nordic countries from 2000 to 2023 is USD 4.69 billion.
- Moreover, the presence of over 700 Nordic companies in India and close to 150 Indian companies in the Nordic-Baltic region showcases the bilateral investment and trade partnerships.
- Cumulative Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) received from Nordic countries has reached a significant figure, demonstrating mutual investment interests.
- Bilateral Collaborations:
- Specific collaborations and partnerships have been established in various domains.
- Examples include sustainability partnerships with Finland, a green strategic partnership with Denmark focusing on water solutions, wind energy, and agriculture, and joint projects with Iceland in harnessing geothermal energy.
- Sectoral Engagements:
- Collaboration in sectors such as renewable energy, food processing, logistics, IT, AI, maritime cooperation, and blue economy initiatives has been identified as potential areas for joint efforts and investments.
- The alignment of India's ambitious renewable energy targets with the technological expertise of the Nordic-Baltic countries offers opportunities for collaboration.
- Space Technology and Polar Research:
- There is potential for collaboration in space technology, geospatial sectors, and polar and climate research, with discussions around joint research projects and opportunities in the Arctic and Antarctic regions.
- Global Engagement and Partnerships:
- Both India and the Nordic-Baltic countries are actively engaged in global partnerships, such as India's engagement with the Global South through G20, which provides opportunities for collaboration in finding solutions for sustainable growth.
- Additionally, exploration of partnerships in joint development projects, especially in Africa, underlines the potential for expanding their collective global footprint.
Way Forward
- There is a need to expand bilateral trade by diversifying the range of traded goods and services. Focusing on sectors like renewable energy, technology, healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing can foster mutual growth. Reducing trade barriers and enhancing market access will be crucial.
- Encourage and facilitate investments between India and the Nordic-Baltic countries. Promote joint ventures, collaborations, and technology transfer across sectors of mutual interest.
- Ensure a conducive environment for investments through favorable policies, regulatory frameworks, and ease of doing business.
Antarctic Ozone Hole
For Prelims: Antarctic Ozone Hole, Montreal Protocol, Ozone Depletion, Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
For Mains: Antarctic Ozone Hole, Environmental pollution and degradation.
Why in News?
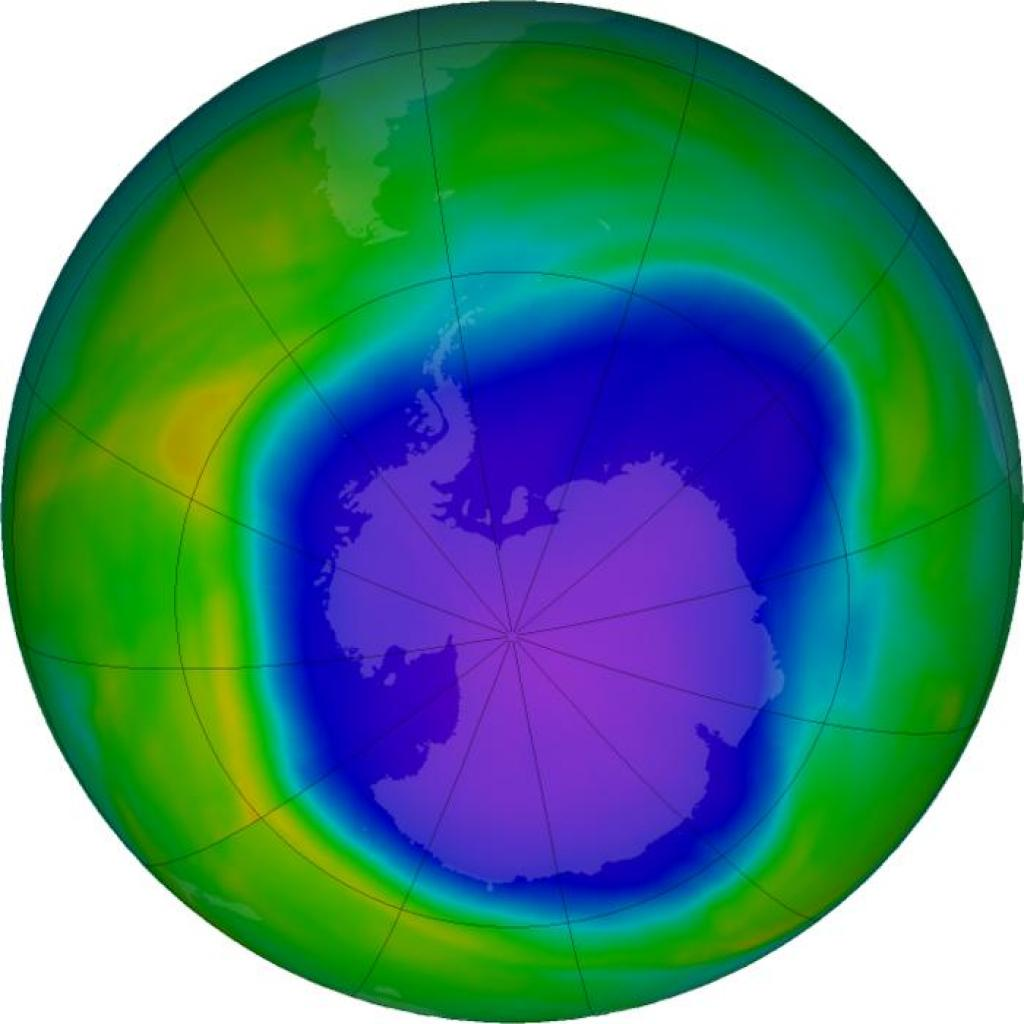
- According to a recent study, published in Nature Communications, stated that the Antarctic Ozone Hole has been massive in the last four years.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Ozone Depletion:
- The Antarctic ozone hole has been consistently large and has shown thinning over recent years, contrary to the expected recovery trend observed since the 2000s.
- The concentration of ozone at the center of the hole has notably reduced, indicating significant thinning of the ozone layer.
- The concentration of ozone at the core of the ozone hole has decreased by 26% from 2004 to 2022, despite the efforts outlined in the Montreal Protocol, which aimed to reduce human-generated chemicals that deplete the ozone layer.
- Polar Vortex Influence:
- The Antarctic ozone hole exists within the polar vortex, a circular wind pattern in the stratosphere that forms during winter and is maintained until late spring.
- Within this vortex, the Antarctic air from the mesosphere (the atmospheric layer above the stratosphere) falls into the stratosphere. This intrusion of air brings natural chemicals (nitrogen dioxide, for example) which impact ozone chemistry in October.
- Factors Affecting Ozone Depletion:
- The role of meteorological conditions, such as temperature, wind patterns, aerosols from wildfires and volcanic eruptions, and changes in the solar cycle, influenced the size and behavior of the Antarctic ozone hole.
- Recommendations:
- There's a need for further research to understand the descent of air from the mesosphere and its specific impacts on ozone chemistry.
- Investigating these mechanisms will likely shed light on the future behavior of the Antarctic ozone hole.
What is an Ozone Hole?
- About:
- An Ozone Hole refers to a severe depletion of the ozone layer—a region in the Earth's stratosphere containing a higher concentration of ozone molecules.
- Ozone molecules (O3) in this layer play a crucial role in shielding the Earth from harmful Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun.
- The ozone layer depletion leads to the formation of an area with significantly reduced ozone concentrations, often observed over Antarctica.
- This phenomenon occurs primarily during the Southern Hemisphere's spring months (August to October), though it can also be influenced by global factors.
- Reasons for Ozone Hole:
- The depletion is caused by human-generated chemicals known as ozone-depleting substances (ODS), including Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), halons, carbon tetrachloride, and methyl chloroform.
- These substances, once released into the atmosphere, rise to the stratosphere, where they break down due to the sun's ultraviolet radiation, releasing chlorine and bromine atoms that destroy ozone molecules.
- The Antarctic ozone hole is the most famous and severe example of this phenomenon. It's characterized by a drastic reduction in ozone levels, allowing increased amounts of harmful UV radiation to reach the Earth's surface.
- Impact:
- The increased UV radiation poses health risks to humans, including higher rates of skin cancers, cataracts, and compromised immune systems.
- UV radiation can harm various organisms and ecosystems. Ozone depletion can indirectly influence climate change. Changes in the stratosphere due to ozone depletion can impact atmospheric circulation patterns, potentially affecting weather and climate in certain regions.
What are the Global Initiatives to Curb Ozone Depletion?
- The 1985 Vienna Convention for the Protection of the Ozone Layer was an international agreement in which United Nations members recognized the fundamental importance of preventing damage to the stratospheric ozone layer.
- The 1987 Montreal Protocol on Substances that deplete the Ozone Layer and its succeeding amendments were subsequently negotiated to control the consumption and production of anthropogenic (ODSs) and some hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs).
- The Protocol was signed by 197 parties in 1987 to control the use of ozonedepleting substances, mainly chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs). Montreal Protocol deals with the development of replacement of substances, firstly hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) and then HFCs, in a number of industrial sectors.
- While HFCs have only a minor effect on stratospheric ozone, some HFCs are powerful greenhouse gases (GHGs).
- The adoption of the 2016 Kigali Amendment to the Montreal Protocol will phase down the production and consumption of some HFCs and avoid much of the projected global increase and associated climate change.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which one of the following is associated with the issue of control and phasing out of the use of ozone depleting substances? (2015)
(a) Bretton Woods Conference
(b) Montreal Protocol
(c) Kyoto Protocol
(d) Nagoya Protocol
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The Bretton Woods Conference, officially known as the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference was a gathering of delegates from 44 nations that met in 1944 in Bretton Woods (USA) to agree upon a series of new rules for the post-World War-II international monetary system.
- The two major accomplishments of the conference were the creation of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD).
- The Montreal Protocol is an international environmental agreement to protect the earth’s ozone layer by eliminating the use of ozone depleting substances. Adopted on 15th September 1987, the protocol is to date the only UN treaty that ever has been ratified by every country on Earth – all 197 UN member states.
- The Kyoto Protocol is an international agreement linked to the UNFCCC, which commits its Parties by setting internationally binding GHGs (Greenhouse Gases) emission reduction targets.
- The Kyoto Protocol was adopted in Kyoto, Japan on 11th December 1997 and entered into force on 16th February 2005.
- The detailed rules for the implementation of the protocol were adopted as CoP7 in Marrakesh, Morocco in 2001 and referred as the Marrakesh Accord.
- India has ratified the second commitment period (2008‑2012) of the Kyoto protocol, that commits countries to contain emissions of greenhouse gases, reaffirming its stand on climate action.
- The Nagoya Protocol on Access to Genetic Resources and the Fair and Equitable Sharing of Benefits Arising from their Utilization provides a transparent legal framework for the effective implementation of one of the three objectives of the Convention on Biological Diversity: the fair and equitable sharing of benefits arising out of the utilization of genetic resources, to promote sustainable use of biological diversity. India signed the protocol in 2011.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Child Pornography
For Prelims: Child Pornography, Child Abuse, Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM), NCRB (National Crime Report Bureau), Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act, 2012, Child Abuse Prevention and Investigation Unit, The Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act.
For Mains: Child Pornography, Mechanisms, laws, institutions and Bodies constituted for the protection and betterment of the vulnerable sections.
Why in News?
Recently, the EU lawmakers agreed to draft rules requiring Alphabet’s Google, Meta and other online services to identify and remove Online Child Pornography, stating that end-to-end encryption would not be affected.
- The draft rule on Child Sexual Abuse Material (CSAM), proposed by the European Commission in 2022, has been a bone of contention between advocates of online safety measures and privacy activists worried about surveillance.
- The European Commission proposed rules requiring online services to identify and remove CSAM, addressing the inadequacy of voluntary detection and reporting systems by tech companies.
What is Child Pornography?
- About:
- Child pornography refers to the creation, distribution, or possession of sexually explicit material involving minors. In India and globally, it's a heinous crime with severe implications, perpetuating the sexual exploitation and abuse of children.
- Online child pornography is the manifestation of digital exploitation, refers to the production, distribution, or possession of sexually explicit material involving minors through digital platforms.
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (Amendment) Act, 2019 defines child pornography as any visual depiction of sexually explicit conduct involving a child including photograph, video, digital or computer generated image indistinguishable from an actual child.
- Indian Scenario:
- The spike in cases of child pornography reflects the grim picture of online child sexual abuse in India. According to NCRB (National Crime Report Bureau) 2021 the cases have increased from 738 (2020) to 969 (2021).
- Impact:
- Psychological Impact: Porn creates a psychological impact on children. It is associated with depression, anger and anxiety. It can lead to mental distress. It also impacts day to day functioning of children, their biological clock, their work, and their social relationship.
- Impact on Sexuality: When seen regularly, it gives a sense of sexual gratification and sexual obsession, which leads to a willingness to do the same things in real life.
- Sexual Addiction: According to some experts, pornography is like an addiction. It produces a similar effect on the brain as produced by consumption of drugs or alcohol on a regular basis.
- Behavioral Impact: Adolescent pornography use is associated with stronger beliefs in gender stereotypes, particularly for males. Male adolescents who view pornography frequently are more likely to view women as sex objects.
- Pornography may strengthen attitudes supportive of sexual violence and violence against women.
What are the Challenges to Deal with Pornography?
- The effect of pornography is different in children belonging to the lower class compared to children belonging to the high class. A single approach won't be able to handle the issue effectively.
- In India, sex is seen as negative (something which should be hidden). There is no healthy family dialogue regarding sex. It leads the child to learn this from outside which leads to an addiction to pornography.
- It's very difficult for agencies to detect the activities of child pornography and monitor them effectively.
- Availability of obscene content on regular websites and OTT (over the top) services like Amazon Prime, Netflix, Hotstar, etc, make it difficult to differentiate between the non-vulgar content and vulgar content.
What are the Indian Initiatives to Check Child Pornography and Child Abuse?
- Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act, 2012:
- The Posco act has been amended in 2019, the amended POCSO included stringent measures such as the death penalty for aggravated sexual assault on children.
- The Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (Amendment) Act, 2019 has introduced several provisions to curb child pornography in India.
- According to the amended act, whoever uses a child or children for pornographic purposes shall be punished with imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than five years and shall also be liable to fine, and in the event of second or subsequent conviction with imprisonment for a term which shall not be less than seven years and also be liable to fine.
- Other Initiatives:
Way Forward
- Child porn should be banned immediately. Most of the time, the first exposure of porn to a child is accidental for eg. in the form of advertisement while browsing for other things on the internet. The government should try to find technological solutions to stop accidental exposure.
- Awareness and sex education is a must and should be made compulsory in schools. Parents and teachers must be skilled to deal with children in the modern era and technology.
Legal Insights: POCSO Act is Gender Neutral
Changing Dynamics of China-US Relations
For Prelims: Changing Dynamics of China-US Relations, Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Clean Energy, World Trade Organization (WTO), South China Sea, Human Rights.
For Mains: Changing Dynamics of China-US Relations, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, China and the US have held a Bilateral Meeting on the sidelines of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) summit, in San Francisco, US, raising concerns for India about Changing Dynamics in China-US Relations.
- China-US relations have undergone significant shifts and complexities over recent decades, reflecting a mix of cooperation, competition, and periods of tension.
What are the Key Highlights of the Meeting?
- New Areas of Engagement:
- The summit discussed emerging areas of US-China collaboration, particularly in regulating Artificial Intelligence (AI), which could profoundly impact global AI regulations and technological advancements.
- Agreement on Energy:
- The US and China announced an agreement to sharply increase Clean Energy, displace Fossil Fuels and reduce emissions that are warming the planet.
- Together, they account for 38% of the world’s greenhouse gases.
- The countries agreed to “pursue efforts to triple renewable energy capacity globally by 2030,” with the intention “to accelerate the substitution for coal, oil and gas generation.”
- The US and China announced an agreement to sharply increase Clean Energy, displace Fossil Fuels and reduce emissions that are warming the planet.
How have China-US relations been in Recent Years?
- In recent years the US adopted a more confrontational approach, initiating a Trade War, targeting Chinese tech firms, and challenging China's territorial claims. Human rights issues, especially regarding Xinjiang and Hong Kong, further strained relations.
- The US has maintained a tough stance on various fronts, particularly on trade, technology, and human rights, while seeking cooperation on global issues like climate change.
What are India’s Concerns over Changes in US-China Relations?
- Potential G-2 Dynamics:
- India remains cautious about the emergence of a dominant Sino-American collaboration in Asia (termed 'G-2') that might sideline other global players, affecting India's strategic interests.
- US-China Engagement in AI Regulation:
- India is attentive to new areas of US-China engagement, particularly in regulating Artificial Intelligence (AI).
- Potential understandings between the two nations in this field could significantly impact Global AI Regulations and technological advancements, influencing India's tech landscape.
- US Business Relations with China:
- China’s attempts to allure US business leaders back to China raise concerns for India. If successful, it might undermine India's attractiveness for Western capital, affecting economic engagements and investments.
- India cannot afford complacency assuming the 'China option' is no longer viable for Western businesses.
- Sustaining India's appeal for Western capital remains crucial, necessitating continuous efforts to engage productively with Western economic interests.
- Indo-Pacific Dynamics and Taiwan Issue:
- The lack of substantial breakthroughs in regional security discussions, especially on sensitive issues like Taiwan, is a concern.
- India observes the US-China dialogue on the Indo-Pacific closely, understanding its implications for regional stability and security dynamics.
Way Forward
- India must continuously assess the changes in great power relations, especially among the US, China, and Russia.
- India’s emphasis should be on taking advantage of the new possibilities to strengthen its ties with the US, maintaining its long-standing ties with Russia, and managing the difficult ties with China.
- India's forward path involves a balanced and proactive approach, leveraging global partnerships, economic growth, strategic maneuvering, and robust diplomacy to navigate a changing world order while safeguarding its national interests and contributing positively to global stability and progress.
Materialism
For Prelims: Materialism, Lokāyata, Chárváka, Bhautikvad, and Jadavāda, Material nature of existence, Atomism of Democritus and Epicurus
For Mains: Materialism, Contributions of Moral Thinkers and Philosophers from India and World
Why in News?
Materialism, traced back to ancient origins, provides a coherent framework that centers on matter as the basis of existence.
What is Materialism?
- About:
- Materialism asserts that all existence originates from and is fundamentally composed of matter.
- It refutes the existence of non-material entities, considering all other phenomena, even intelligence, as transformations or products of matter following inherent natural laws.
- Historical Context:
- Materialism has roots in ancient philosophies worldwide. In India, it found expression in Lokāyata, Chárváka, Bhautikvad, and Jadavāda, among other names.
- Lokāyata, meaning the philosophy of the people, emphasizes worldliness and instinctive materialism. Lokāyata was pioneered by philosophers like Brhaspati, Ajita, and Jābāli.
- Chárváka highlights hedonism, the belief that pleasure is the most important thing in life.
- Bhautikvad focuses on the physical or material nature of existence.
- Jadavāda reflects the materialists' inclination to seek the material roots of existence.
- Early Greek philosophers also pursued materialistic explanations for the cosmos, notably through the atomism of Democritus and Epicurus.
- Various names in different cultures signify materialist philosophies.
- Materialism has roots in ancient philosophies worldwide. In India, it found expression in Lokāyata, Chárváka, Bhautikvad, and Jadavāda, among other names.
- Evolution of Thought:
- Ancient materialists pondered the four classical elements (Mahābhūtas) and explained reality's diversity through 'svabhāva' or self-becoming.
- The four fundamental elements were considered to be agni (fire), apa (water), vāyu (wind) and prthvī (earth).
- They rejected divine providence and denied the existence of any world beyond the singular, observable reality, meaning they didn't believe in a higher power guiding events or the universe's destiny.
- They also denied the existence of any world beyond what could be directly observed or experienced, emphasizing the importance of empirical reality as the sole reality.
- Ancient materialists pondered the four classical elements (Mahābhūtas) and explained reality's diversity through 'svabhāva' or self-becoming.
- Ethics of Materialism:
- The ethics of materialism did face criticism for allegedly promoting a hedonistic lifestyle, as reflected in the Sanskrit dictum “yāvat jīvēt sukham jīvēt,” which means “as long as you live, live happily”.
- Materialism did not accept any moral or ethical principles that were derived from religious or metaphysical doctrines.
- Materialism did not deny the existence of ethics, but rather argued that ethics should be based on human reason and experience, and that the goal of ethics should be the maximization of pleasure and the minimization of pain for oneself and others.
What is the Philosophical Significance of Materialism?
- Materialism offers a comprehensive worldview that emphasizes empirical observation and natural laws governing existence.
- It challenges religious dogma and encourages a critical examination of reality based on tangible, observable phenomena.
- It advocated for freedom of thought, challenging societal norms and conventions.
- Despite shifts in dominant philosophies over time, materialist ideas persist and continue to shape contemporary scientific inquiry, particularly in understanding the fundamental nature of reality.
- Its influence spans cultures and epochs, encouraging a rational exploration of the universe and rejecting supernatural explanations in favor of empirical observation and understanding.
NASA's Atmospheric Waves Experiment
Why in News?
NASA's unveiling of the Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) emerges amidst escalating disruptions in satellite communication and GPS systems, spotlighting the critical need to comprehend space weather.
- With Earth's extreme weather events influencing space phenomena via Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGWs), AWE's imminent launch promises groundbreaking insights into these interconnected dynamics.
What is Space Weather?
- Space weather is the term used to describe the dynamic conditions in the space environment around the Earth and other planets, which are influenced by the activity of the Sun and the interactions between the solar wind and the planetary magnetic fields.
- Space weather can affect various aspects of human activities and technologies, such as satellite-based communication, navigation, and power systems, as well as astronaut health and safety, and aviation and space exploration.
What are Atmospheric Gravity Waves (AGWs)?
- Gravity Waves: In a stable atmosphere, gravity waves are created when temperature contrasts between rising air and the surrounding atmosphere generate a force that pushes the air back to its initial location.
- Atmospheric Gravity Waves: AGWs are waves that travel within a stable atmospheric layer, particularly thriving in regions where air is moving upward, facilitating the creation of distinctive cloud formations.
- Remarkably, these AGWs extend into space, playing a role in shaping space weather.
- They are mostly generated by extreme weather events or disturbances causing vertical displacement of stable air.
- Thunderstorms,hurricanes, and regional topography contribute to the generation of AGWs in the lower atmosphere.
What is NASA’s Atmospheric Waves Experiment?
- About: As a pioneering NASA experiment under the Heliophysics Explorers Program, AWE aims to study the connections between lower atmospheric waves and space weather.
- Operational Mechanism: Mounted on the International Space Station (ISS), AWE will observe the colorful air glows in the Earth's atmosphere, specifically at the mesopause (about 85 to 87 km above the Earth’s surface).
- Equipped with an Advanced Mesospheric Temperature Mapper (ATMT), AWE will scan the mesopause using imaging radiometers to capture specific wavelengths' brightness.
- Mission Objective: Understanding the forces driving space weather and investigating the potential impact of terrestrial weather on it.
- Data obtained by AWE will contribute as inputs for weather models, improving weather forecasts.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. If a major solar storm (solar flare) reaches the Earth, which of the following are the possible effects on the Earth?(2022)
- GPS and navigation systems could fail.
- Tsunamis could occur at equatorial regions.
- Power grids could be damaged.
- Intense auroras could occur over much of the Earth.
- Forest fires could take place over much of the planet.
- Orbits of the satellites could be disturbed.
- Shortwave radio communication of the aircraft flying over polar regions could be interrupted.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5 only
(b) 2, 3, 5, 6 and 7 only
(c) 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Ans: (c)
59th Session of the International Tropical Timber Council
Why in News?
The 59th session of the International Tropical Timber Council (ITTC), the governing body of the International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO), recently concluded with significant decisions shaping the future of sustainable tropical forest management and the trade of sustainably produced tropical timber.
What are the Key Outcomes of the 59th session of the ITTC?
- The countries agreed to endorse eight projects related to sustainable forest management and related objectives.
- The session also approved and adopted a budget of USD 7.1 million for the coming financial year 2024-25.
- The council also approved a trial measure that will allow ineligible members to submit project proposals and concept notes.
- Members who have fallen behind on their financial contributions and are thus ineligible will be allowed to submit one project and concept note for every two years of arrears paid.
- The Council also adopted the work programme for 2024-25, which emphasizes collaboration with the members of Collaborative Partnership on Forests and other partners for effective implementation.
What is the International Tropical Timber Organization (ITTO)?
- About:
- The ITTO is an intergovernmental organization promoting the sustainable management and conservation of tropical forests and the expansion and diversification of international trade in tropical timber from sustainably managed and legally harvested forests.
- ITTO was established under the International Tropical Timber Agreement 1983 (ITTA 1983), negotiated under the auspices of the United Nations Conference on Trade and Development.
- It is governed by ITTC, a group that meets at least once a year to discuss a wide-ranging agenda aimed at promoting sustainable tropical forest management(SFM) and the trade of sustainably produced tropical timber
- Members:
- It has 75 countries, including India.
- Its members manage about 80% of the world's tropical forests and are responsible for 90% of the global tropical timber trade.
- Functions:
- ITTO develops internationally agreed policy guidelines and norms to encourage SFM and sustainable tropical timber industries and trade.
- Assists tropical member countries to adapt such guidelines and norms to local circumstances and to implement them in the field through projects and other activities.
- Collects, analyzes and disseminates data on the production and trade of tropical timber. Promotes sustainable tropical timber supply chains.
- Headquarters: Yokohama, Japan.
2D Protein Monolayer Unravels Amyloidosis
Source: PIB
Why in News?
Recently, researchers have achieved a significant breakthrough in disease study through the creation of a two-dimensional (2D) protein monolayer using lysozyme molecules.
What are Lysozyme and Amyloidosis ?
- Lysozyme is a naturally occurring enzyme found in various bodily secretions like tears, saliva, mucus. It plays a crucial role in the body's defense system against bacteria.
- This enzyme works by breaking down the cell walls of certain bacteria, essentially disrupting their structure and leading to their destruction.
- It is also the principal component of airway fluid, serving as a model protein in investigating diseases like Amyloidosis, which trigger multi-organ dysfunction.
- Amyloidosis refers to a group of rare conditions characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein clumps called amyloids in various organs and tissues throughout the body.
- These amyloid proteins, typically made up of misfolded proteins, can disrupt normal organ function such as the heart, kidneys, liver, spleen and cause damage over time.
What are the Major Highlights of the Research?
- Scientists assembled lysozyme molecules into a 2D monolayer at the interface of a pure water subphase.
- These meticulously arranged layers of lysozyme, positioned at different interfaces, provide an exceptional model for delving into the complexities of Amyloidosis.
- Employing the sophisticated Langmuir-Blodgett (LB) technique was crucial in forming this specialized two-dimensional protein layer.
- The Langmuir-Blodgett technique is a process used to create monolayers of molecules, including proteins, at air-water and air-solid interfaces.
- The changes observed in the structure and shape of lysozyme molecules under different pH conditions remarkably mirror the abnormalities seen in Amyloidosis.
- This groundbreaking research not only paves the way for a more profound comprehension of Amyloidosis but also establishes a versatile platform for probing disease mechanisms.
- Furthermore, it presents exciting possibilities for exploring nanotechnology applications within the realm of protein science.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Kambala Buffalo Race
The traditional buffalo race, Kambala, is set to take place for the first time in Bengaluru, Karnataka.
- Kambala is a buffalo race held in Coastal Karnataka districts (Udupi and Dakshina Kannada) during the winter months when farmers harvest their paddy crops.
- The race is held on two parallel tracks filled with mud and water. Each pair of buffaloes will also have a jockey, or 'Kambala runner' to control and command the animals on the track.
- The team that wins qualifies for higher rounds till a champion emerges.
- Apart from winning the race, targets also include splashing water; in fact, some winners are even declared on the amount of water splashed; this is called 'kolu'.
Read more: Kambala
Justice M. Fathima Beevi
Justice M. Fathima Beevi, the first female Judge to be appointed to the Supreme Court of India, passed away.
- She was also the first Muslim woman to be appointed to the higher judiciary in the country.
- She served as a member of the National Human Rights Commission and then as Governor of Tamil Nadu.
Guru Tegh Bahadur Martyrdom Day
Guru Tegh Bahadur Martyrdom Day is observed every year on 24th November. He is the ninth guru in the lineage of Sikh saints.
- He was born as Tyag Mal in 1621 in Amritsar. His teachings against divisive practices and emphasis on unity in faith garnered widespread resonance across North India.
- His travels, including visits to far-reaching places like Dhaka and Puri, showcased his commitment to spreading his message of fearlessness and unity.
- However, his confrontation with Aurangzeb's regime, culminating in his martyrdom on 24th November, 1675, symbolized unyielding resilience and refusal to compromise on principles.
Read more: Guru Tegh Bahadur
16th World Wushu Championship
The 16th World Wushu Championships recently concluded in Fort Worth, Texas, USA.
- It was organized by the United States of America Wushu-Kungfu Federation (USAWKF) under the auspices of the International Wushu Federation (IWUF).
- Wushu is a martial art that originated in China and encompasses various forms and styles. It's a disciplined and highly stylized form of combat and self-defense.
- Among the standout performers from India, Roshibina Devi (silver) , Kushal Kumar (bronze) and Chavi (bronze) demonstrated remarkable skill and resilience in their respective weight categories.
Read more: Martial Art forms in India