Governance
AI Chatbot for PM-KISAN Scheme
For Prelims: Chatbot, Artificial Intelligence (AI), PM-Kisan
For Mains: Launch of the AI-Chatbot and its impact on addressing the problems of farmers and beneficiaries.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare launched an AI chatbot — the first of its kind to be integrated with a major flagship scheme of the central government — for the Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi Yojana(PM-KISAN scheme).
- The Chatbot will provide the farmers with “prompt, clear and accurate” responses to their queries.
What are the Key Features of the AI Chatbot for PM KISAN?
- It has been developed and improved with the support of EkStep foundation and Bhashini.
- In the first phase of the development, the AI Chatbot will assist farmers in seeking information related to their application status, payment details, ineligibility status etc.
- The AI Chatbot, accessible through the PM-KISAN mobile application, is integrated with Bhashini which offers multilingual support, catering to the linguistic and regional diversity of the PM-KISAN beneficiaries.
- This integration of advanced technology will not only enhance transparency but also empower farmers to make informed decisions.
What is an AI Chatbot?
- About:
- Chatbots, also called chatterbots, is a form of Artificial Intelligence (AI) used in messaging apps.
- This tool helps add convenience for customers—they are automated programs that interact with customers like a human would and cost little to nothing to engage with.
- Key examples are chatbots used by businesses in Facebook Messenger, or as virtual assistants, such as Amazon's Alexa and ChatGPT etc.
- Chatbots tend to operate in one of two ways—either via machine learning or with set guidelines.
- However, due to advancements in AI technology, chatbots using set guidelines are becoming a historical footnote.
- Machine Learning Chatbot:
- A chatbot that functions through machine learning have an artificial neural network inspired by the neural nodes of the human brain.
- The bot is programmed to self-learn as it is introduced to new dialogues and words.
- In effect, as a chatbot receives new voice or textual dialogues, the number of inquiries that it can reply to and the accuracy of each response it gives increases.
- Meta (as Facebook's parent company is now known) has a machine learning chatbot that creates a platform for companies to interact with their consumers through the Messenger application.
What is PM KISAN Scheme?
- About:
- It was launched on 24th February, 2019 to supplement financial needs of land holding farmers.
- Financial Benefits:
- Financial benefit of Rs 6000/- per year, in three equal installments every four months, is transferred into the bank accounts of farmers’ families across the country through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode.
- Scope of the Scheme:
- The scheme was initially meant for Small and Marginal Farmers (SMFs) having landholding upto 2 hectares but scope of the scheme was extended to cover all landholding farmers.
- Funding and Implementation:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Objectives:
- To supplement the financial needs of the Small and Marginal Farmers in procuring various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- To protect them from falling in the clutches of moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities.
- PM-KISAN Mobile App:
- It was developed and designed by the National Informatics Centre in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Physical Verification Module:
- A mandatory physical verification of 5% beneficiary every year is being done as per the provisions laid down in the scheme.
- Excluded Category: The following categories of beneficiaries of higher economic status shall not be eligible for benefit under the scheme:
- All Institutional Land holders.
- Farmer families which belong to one or more of the following categories:
- Former and present holders of constitutional posts.
- Former and present Ministers/ State Ministers and former/present Members of LokSabha/ RajyaSabha/ State Legislative Assemblies/ State Legislative Councils,former and present Mayors of Municipal Corporations, former and present Chairpersons of District Panchayats.
- All serving or retired officers and employees of Central/ State Government Ministries /Offices/Departments and its field units Central or State PSEs and Attached offices /Autonomous Institutions under Government as well as regular employees of the Local Bodies
(Excluding Multi Tasking Staff /Class IV/Group D employees) - All superannuated/retired pensioners whose monthly pension is Rs.10,000/-or more (Excluding Multi Tasking Staff / Class IV/Group D employees) of above category
- All Persons who paid Income Tax in last assessment year.
- Professionals like Doctors, Engineers, Lawyers, Chartered Accountants, and Architects registered with Professional bodies and carrying out profession by undertaking practices.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)


Indian Polity
Supreme Court to Revisit Legislative Immunity on Bribery
For Prelims: Article 105(2), Article 194(2), Parliamentary Privileges
For Mains: The Privileges of Members of Parliament.
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has referred the 1998, 5-judge Constitution Bench judgement P V Narasimha Rao case to a 7-judge Bench for reconsideration.
- The case deals with the interpretation of Articles 105(2) and 194(2) of the Constitution, which extends parliamentary privilege and immunity to members of Parliament and State Legislatures against criminal prosecution on bribery charges for any speech or vote in the House.
- The decision was taken in another case related to bribery charges against an MLA, who had relied on Article 194(2) for quashing the charge sheet and criminal proceedings.
What is the Case of PV Narasimha Rao v/s State,1998?
- Case:
- The P V Narasimha Rao case refers to the 1993 Jharkhand Mukti Morcha(JMM) bribery case. In this case, Shibu Soren and some of his party MPs were accused of taking bribes to vote against a no-confidence motion against the then P V Narasimha Rao government.
- No-confidence motions are significant political events that usually occur when there is a perception of the government losing majority support.
- The Supreme Court had quashed the case against the JMM MPs, citing immunity under Article 105(2) of the Constitution.
- The P V Narasimha Rao case refers to the 1993 Jharkhand Mukti Morcha(JMM) bribery case. In this case, Shibu Soren and some of his party MPs were accused of taking bribes to vote against a no-confidence motion against the then P V Narasimha Rao government.
- Articles 105(2) and 194(2) of the Constitution:
- Article 105(2):
- No member of Parliament shall be liable to any proceedings in any court in respect of anything said or any vote given by him in Parliament or any committee thereof, and no person shall be so liable in respect of the publication by or under the authority of either House of Parliament of any report, paper, votes or proceedings.
- The purpose of Article 105(2) is to ensure that members of Parliament can perform their duties without fear of consequences.
- Article 194(2):
- No member of the Legislature of a State shall be liable to any proceedings in any court in respect of anything said or any vote given by him in the Legislature or any committee thereof, and no person shall be so liable in respect of the publication by or under the authority of a House of such a Legislature of any report, paper, votes or proceedings
- Article 105(2):
Why did the Supreme Court Refer the Matter to a 7-Judge Bench?
- The Supreme Court referred the matter to a 7-judge Bench because it recognized the need to reexamine the correctness of its previous 1998 constitution bench ruling in the PV Narasimha Rao case.
- The purpose of Articles 105(2) and 194(2) is to ensure that members of Parliament and the State Legislatures can discharge their duties freely, without fear of consequences for their speech or vote.
- The objective is not to give legislators higher privileges in terms of immunity from the general criminal law of the land.
- The purpose of Articles 105(2) and 194(2) is to ensure that members of Parliament and the State Legislatures can discharge their duties freely, without fear of consequences for their speech or vote.
What are the Parliamentary Privileges?
- About:
- Parliamentary privileges are special rights, immunities and exemptions enjoyed by the two Houses of Parliament, their committees and their members.
- These privileges are defined in Article 105 of the Indian Constitution.
- Under these privileges, the members of Parliament are exempted from any civil liability (but not criminal liability) for any statement made or act done in the course of their duties.
- The privileges are claimed only when the person is a member of the house.
- As soon as s/he ends up being a member, the privileges are said to be called off.
- Parliamentary privileges are special rights, immunities and exemptions enjoyed by the two Houses of Parliament, their committees and their members.
- Privileges:
- Freedom of Speech in Parliament:
- The freedom of speech and expression guaranteed to a citizen under Article 19(2) is different from the freedom of speech and expression provided to a member of the parliament.
- It has been guaranteed under Article 105(1) of the Indian constitution. However, freedom is subject to rules and orders that regulate the proceedings of the parliament.
- Limitations:
- Freedom of speech should be in accordance with the constitutional provisions and subject to rules and procedures of the parliament, as stated under Article 118 of the Constitution.
- Article 121 of the Indian Constitution states that members of parliament cannot discuss the conduct of Supreme Court or High Court judges while they are performing their duties.
- The only exception is if there is a motion to present an address to the President requesting the judge's removal.
- The freedom of speech and expression guaranteed to a citizen under Article 19(2) is different from the freedom of speech and expression provided to a member of the parliament.
- Freedom from Arrest:
- Members enjoy immunity from arrest in any civil case 40 days before and after the adjournment of the house or during a session.
- Arrest within the Parliament's limits requires the house's permission.
- If the detention of any members of the parliament is made, the chairman or the speaker should be informed by the concerned authority, of the reason for the arrest.
- But a member can be arrested outside the limits of the house on criminal charges against him under the Preventive Detention act, the Essential Services Maintenance Act (ESMA), the National Security Act (NSA), or any such act.
- Members enjoy immunity from arrest in any civil case 40 days before and after the adjournment of the house or during a session.
- Right to Prohibit the Publication of Proceedings:
- Article 105(2) of the Constitution, no person shall be held liable for publishing any reports, discussions etc. of the house under the authority of the member of the house.
- For paramount and national importance, it is essential that the proceedings should be communicated to the public to aware them of what is going on in the parliament.
- Article 105(2) of the Constitution, no person shall be held liable for publishing any reports, discussions etc. of the house under the authority of the member of the house.
- Right to Exclude Strangers:
- The members of the house have the power and right to exclude strangers who are not members of the house from the proceedings. This right is very essential for securing free and fair discussion in the house.
- Freedom of Speech in Parliament:


Governance
Transforming India's Ceiling Fan Market
For Prelims: Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), Star Rating Program, UJALA Programme
For Mains: challenges associated with making '5-star' electric appliances affordable for consumers in India, Government initiatives aimed at enhancing energy efficiency.
Why in News?
India's fan market is undergoing a transformative evolution, driven by changes in policy and a growing commitment to sustainable energy practices.
What are the Reasons for the Ceiling Fan Market Transformation?
- India's commitment to transitioning to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources is a primary driver for change in the fan market.
- Growing awareness of climate change and its impacts necessitates a reduction in energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
- India's goal of reducing harmful emissions per unit of Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by 45% by 2030, relative to 2005, necessitates energy-efficient solutions in various sectors.
- Households account for nearly one-third of all electricity consumed in India, making energy efficiency in appliances like ceiling fans crucial.
- Ceiling fans are used by 90% of households in India as as per a Council on Energy, Environment and Water (CEEW) survey of 2020, making them a significant contributor to electricity consumption
- The India Cooling Action Plan (ICAP) projects growth in the number of fans in use in India, from about 500 million to a billion by 2038, underscores the need for energy-efficient cooling solutions.
- The ICAP aims to reduce cooling demand across sectors by 20-25% by 2037-38. The plan also aims to reduce refrigerant demand by 25-30% and cooling energy requirements by 25-40% by 2037-38.
- Mandatory star ratings for ceiling fans and regulatory changes are driving manufacturers to produce more energy-efficient fan models.
What are the Government Initiatives to Enhance Ceiling Fan Energy Efficiency?
- Star Rating Program:
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), India’s energy efficiency regulator under the Union Ministry of Power, made the Standards and Labelling (S&L) programme, popularly known as the ‘star-rating’ programme mandates labelling of ceiling fans based on their energy efficiency.
- Informs consumers about a fan's energy performance through star ratings.
- Encourages manufacturers to produce more energy-efficient fans.
- Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE), India’s energy efficiency regulator under the Union Ministry of Power, made the Standards and Labelling (S&L) programme, popularly known as the ‘star-rating’ programme mandates labelling of ceiling fans based on their energy efficiency.
- Energy Efficiency Services Limited (EESL):
- ‘5-star’ fans (the star rating) cost twice as much as typical unrated fans. To address the Cost challenge of ‘5-star’ fans (the star rating), EESL is planning a demand aggregation programme to sell 10 million '5-star' ceiling fans.
- The programme hopes to transform the fans market much like it did for LED lamps under the famous Unnat Jyoti by Affordable Light Emitting Diode (LED) for All (UJALA) programme.
- ‘5-star’ fans (the star rating) cost twice as much as typical unrated fans. To address the Cost challenge of ‘5-star’ fans (the star rating), EESL is planning a demand aggregation programme to sell 10 million '5-star' ceiling fans.
UJALA Programme:
- Launched in 2015 and initially labeled as the LED-based Domestic Efficient Lighting Programme (DELP), it aims to promote the efficient usage of energy for all i.e., its consumption, savings and lighting.
- The program was spearheaded by the EESL.
- The programme has evolved to be the world’s largest zero subsidy domestic lighting programme that addresses concerns like high electrification costs and high emissions that result from inefficient lighting.
- The program's goal was to replace 77 million incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs.
- The program was successful in lowering the retail price of LED bulbs from INR 300-350 to INR 70-80. The program also resulted in significant energy savings. As of 5th January 2022, 47,778 million kWh per annum energy has been saved.
Way Forward
- Technology-Agnostic Policy:
- Maintain a technology-agnostic policy that accommodates various fan technologies, recognizing their trade-offs and advantages.
- Allow manufacturers to offer different technologies under a single procurement framework, promoting competition and cost-effectiveness.
- Balancing Price Reduction and Quality:
- Manage the balance between reducing fan prices and maintaining product quality.
- Avoid intense price pressure that might lead to the introduction of lower-quality fans with higher failure rates.
- Allow market actors to determine the pace of price reduction, fostering consumer trust in the new technology.
- Manage the balance between reducing fan prices and maintaining product quality.
- Boosting Domestic Manufacturing:
- Foster high-quality domestic manufacturing capacity for high-efficiency fans.
- Leverage India's massive domestic market to achieve economies of scale for fan products and components.
- Explore opportunities for fan exports to countries enforcing minimum energy performance standards.
- Strengthening the Standard and Labeling Program:
- Allocate resources to enhance the standard and labelling program, ensuring the authenticity of energy performance labels.
- Utilize market monitoring powers to ensure that compliant products reach consumers while non-compliant models are removed from the market.
- Lower barriers to selling new energy-efficient fan models in the market.
- Promoting Energy-Efficient Fans' Role:
- Highlight the importance of energy-efficient fans in providing critical services for coping with extreme heat while reducing electricity bills.
- Emphasize the central role of energy-efficient fans in India's clean energy transition and their potential contribution to economic growth.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. On which of the following can you find the Bureau of Energy Efficiency Star Label? (2016)
- Ceiling fans
- Electric geysers
- Tubular fluorescent lamps
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Indian Economy
India’s Inclusion in JPMorgan GBI-EM Index
For Prelims: India’s Inclusion in JPMorgan GBI-EM Index, Government Bond, Sovereign Bonds, Fiscal Deficits, Yield Curve, Reserve Bank of India.
For Mains: Significance of India’s Inclusion in JPMorgan GBI-EM Index and Challenges.
Why in News?
Recently, JPMorgan Chase & Co. will include India in its Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) index from June 2024, anticipating significant inflows to India. This move is expected to widen the investor base and potentially lead to the appreciation of the Rupee.
What is the JPMorgan Government Bond Index-Emerging Markets (GBI-EM) index?
- About:
- The JP Morgan GBI-EM is a widely followed and influential benchmark index that tracks the performance of local-currency-denominated Sovereign Bonds issued by emerging market countries.
- It is designed to provide investors with a representative measure of the fixed income market within emerging market economies.
- It Includes government bonds issued by various emerging market countries.
- The composition may change over time based on eligibility criteria.
- India’s Inclusion:
- JPMorgan has identified 23 Indian government bonds with a combined nominal value of USD 330 billion as eligible for inclusion in the GBI-EM.
- India's weight is expected to reach the maximum weight threshold of 10% in the GBI-EM Global Diversified, and approximately 8.7% in the GBI-EM Global index.
- India's local bonds will become part of the GBI-EM index and its suite of indices, which serve as benchmarks for approximately USD 236 billion in global funds, as per JPMorgan.
What is the Significance of India’s Inclusion in GBI-EM Index?
- Enhanced Investment Attractiveness:
- India's inclusion in the GBI-EM index positions India as a coveted investment destination.
- It can attract global investors seeking opportunities in emerging markets, potentially resulting in substantial inflows of USD 45-50 billion over the next 12-15 months.
- Economic Stability and Financing Ease:
- It can ease financing constraints related to India's Fiscal and current account deficits by providing an alternative source of funds.
- It structurally lowers India's risk premia and funding costs, fostering economic stability.
- Risk premia refers to the amount by which the return of a risky asset is expected to outperform the known return on a risk-free asset.
- Equity market exposure is the best-known risk premium, rewarding investors for taking exposure to long-only equity investments.
- Positive Impact on Various Sectors:
- Corporate Sector: The inclusion is expected to lower the entire Yield Curve, reducing the cost of financing for the corporate sector. Narrower corporate bond spreads will stimulate investment and business growth.
- The Yield Curve is a graphical representation of the interest rates on debt for a range of maturities.
- Banking Sector: With lesser pressure to absorb government bonds, banks can allocate more resources for lending to the private sector, promoting economic expansion.
- Infrastructure Development: India's ongoing infrastructure development initiatives receive a boost as the inclusion provides a sustainable source of long-term financing through government securities.
- Corporate Sector: The inclusion is expected to lower the entire Yield Curve, reducing the cost of financing for the corporate sector. Narrower corporate bond spreads will stimulate investment and business growth.
- Currency Appreciation and Stability:
- The inclusion will lead to an appreciation of the Indian rupee due to increased investor confidence.
- A stable exchange rate enhances the attractiveness of investing in India.
- Market Development and Innovation:
- Integration into global markets, supported by ongoing reforms and increased market access, propels market development and encourages long-term capital inflows.
- It sets the stage for the introduction of innovative financial products.
- Par with other Countries:
- India is expected to reach a maximum weightage of 10 % in the GBI-EM Global Diversified Index, putting it at par with others like China, Brazil, Indonesia and Malaysia.
What are the Challenges of India’s Inclusion in GBI-EM Index ?
- Market Fluctuations:
- Inclusion may introduce volatility in local debt markets, especially during global economic turmoil or uncertainty, requiring the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to manage and stabilize the markets effectively.
- The RBI will need to carefully manage its monetary policy decisions to balance the impact of increased foreign investment while also ensuring domestic economic stability and growth.
- Geopolitical Risks:
- High foreign holding of debt exposes Indian markets not only to external macro-economic shocks but also to geo-political risks. The recent experience of how Russia was ousted from international currency markets and the SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunications) is a cautionary tale of how geopolitics can impact financial flows and hence economic well-being.
- Currency Management:
- The inclusion may impact the domestic currency's value, posing challenges in managing exchange rates and ensuring the rupee remains competitive to support exports.
- Transparency and Fiscal Responsibility:
- It may subject India to increased scrutiny regarding government finances, necessitating greater transparency and fiscal responsibility in managing the fiscal deficit.
- Taxation Challenges:
- Unresolved tax treatment for foreign investors may deter potential investors, necessitating clarity and favorable tax policies to attract foreign capital into Indian government bonds.
- The behavior of foreign investors, especially during global economic shifts, could result in sudden surges or withdrawals of funds, impacting market stability and capital flows.
Way Forward
- There is a need to work on resolving operational challenges related to custody, settlement, and tax implications to facilitate smooth participation of foreign investors.
- Strengthen the regulatory environment to ensure market integrity, transparency, and investor protection, encouraging long-term participation.
- Strengthen India's economic fundamentals to better withstand global economic shifts and fluctuations, minimizing risks associated with external factors.


Important Facts For Prelims
Bima Sugam
Why in News?
Recently, the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) has formed a steering committee to act as the apex decision-making body for the creation of its ambitious ‘Bima Sugam’ online platform.
- IRDAI says Bima Sugam is an electronic marketplace protocol which would universalise and democratize insurance. This protocol will be connected with India Stack.
What is Bima Sugam?
- About:
- It’s an online platform where customers can choose a suitable scheme from multiple options given by various companies.
- All insurance requirements, including those for life, health, and general insurance (including motor and travel) will be met by Bima Sugam.
- Features:
- It will simplify and digitize the insurance marketplace— right from buying policies, to renewals, claim settlement, and agent and policy portability.
- It will assist consumers with all insurance related queries.
- Role:
- The proposed platform would act as a single window for the policyholder to manage his/her insurance coverage.
- It will provide end-to-end solutions for customers’ insurance needs i.e., purchase, service, and settlement.
- Utility:
- It will facilitate insurance companies to access the validated and authentic data from various touch points on a real-time basis.
- The platform will interface for the intermediaries and agents to sell policies and provide services to policyholders, among others, and reduce paperwork.
- Stakeholders:
- Life insurance and general insurance companies will own a 47.5% stake each, while brokers and agent bodies will own 2.5% each in Bima Sugam Platform.
What is IRDAI?
- IRDAI, founded in 1999, is a regulatory body created with the aim of protecting the interests of insurance customers.
- It is a statutory body under the IRDA Act 1999 and is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of Finance.
- It regulates and sees to the development of the insurance industry while monitoring insurance-related activities.
- The powers and functions of the Authority are laid down in the IRDAI Act, 1999 and Insurance Act, 1938.
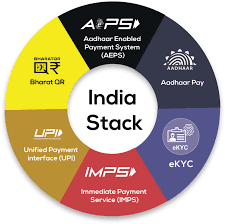
What is India Stack?
- About:
- India Stack is a set of APIs (Application programming interface) that allows governments, businesses, startups and developers to utilize a unique digital Infrastructure to solve India’s hard problems towards presence-less, paperless, and cashless service delivery.
- It aims to unlock the economic primitives of identity, data, and payments at population scale.
- Features:
- Digital transactions through India Stack often have lower transaction costs compared to traditional methods. This benefits businesses, consumers, and the government by reducing the cost of conducting various transactions.
- Bridging the wealth gaps and building an efficient and resilient digital economy that drives economic growth and social development.
- Components:
- The key components of INDIA STACK include Aadhaar (unique biometric-based identification system), Unified Payments Interface (UPI) for instant digital payments, and Digital Locker for secure storage of personal documents.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The Aadhaar platform helps service providers authenticate identity of residents electronically, in a safe and quick manner, making service delivery more cost effective and efficient. According to the GoI and UIDAI, Aadhaar is not proof of citizenship.
- However, UIDAI has also published a set of contingencies when the Aadhaar issued by it is liable for rejection. An Aadhaar with mixed or anomalous biometric information or multiple names in a single name (like Urf or Alias) can be deactivated. Aadhaar can also get deactivated upon non-usage of the same for three consecutive years.


Important Facts For Prelims
International Day of Sign Languages 2023
Why in News?
On the occasion of International Day of Sign Languages (23rd September), the Government of India has introduced several initiatives to improve communication and accessibility for the hearing-impaired.
- Initiatives for the hearing-impaired include online Indian Sign Language (ISL) courses, introduction of 267 signs for financial terms in ISL, a comprehensive ISL dictionary, tailored courses for special schools, and a WhatsApp-based video relay service for improved communication.
What is International Day of Sign Languages?
- About:
- International Day of Sign Languages is an annual event that promotes the linguistic and cultural diversity of deaf communities around the world.
- In 2017, the United Nations General Assembly proclaimed 23rd September as the official day to celebrate the International Day of Sign Languages.
- It is an opportunity to raise awareness of the importance of sign languages in the lives of deaf communities and the need to protect them as an essential part of human diversity.
- Millions of people around the world use sign language as their primary means of communication.
- They are complex visual-gestural communication systems with their own grammar and syntax.
- Theme of 2023:
- A World Where Deaf People Can Sign Anywhere.
- History:
- The World Federation of the Deaf (WFD), a federation of 135 national federations of the deaf, proposed the idea for the day on behalf of the estimated 70 million deaf people around the world.
- The Permanent Mission of Antigua and Barbuda to the United Nations, along with 97 other UN Member States, sponsored a resolution, which was unanimously adopted in December, 2017.
- The date of September 23 was chosen to honour the day in 1951 when the WFD was established.
- In 2018, as part of the International Week of the Deaf, the International Day of Sign Languages was observed for the first time.
- Status of Deaf People:
- According to the World Federation of the Deaf, there are over 70 million deaf people in the world.
- More than 80% of them live in underdeveloped countries. They collectively use more than 300 different sign languages.


Important Facts For Prelims
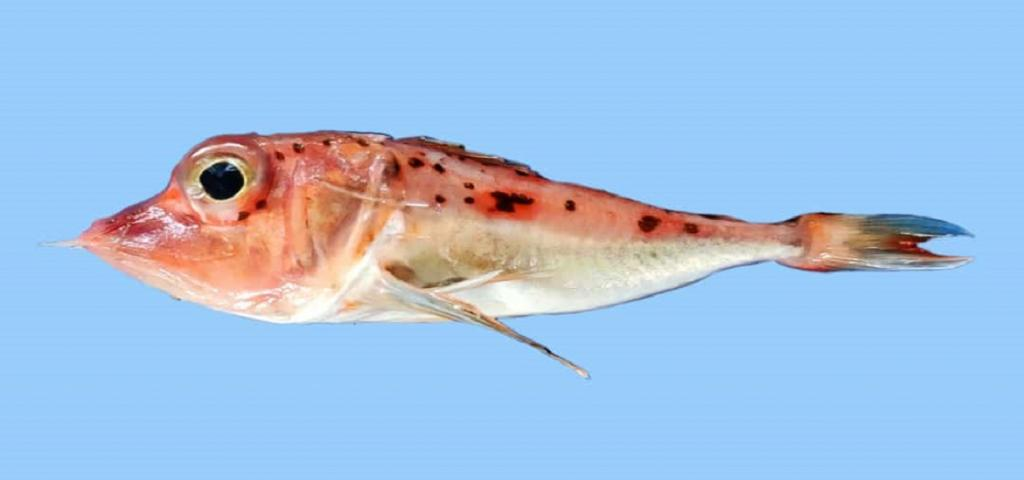
New Fish Species Discovered
Why in News?
Recently, the scientists of the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI) have discovered a new species of a vibrant orange coloured deep water marine fish from Digha Mohana in West Bengal.
Which Fish Species is Discovered?
- About:
- The new species, commonly known as gurnards or sea-robins, belongs to the family Triglidae.
- Fish is named Pterygotrigla Intermedica, it has characters quite similar to species like Pterygotrigla hemistictus. There are a total 178 species of the Triglidae family worldwide.
- Distinct Characteristics:
- A distinct pectoral-fin with black membranes on the inner surface, a white posterior margin, and three small white spots basally in the fin.
- Significance of this Discovery:
- The newfound marine fish represents the fourth species of the “Pterygotrigla” genus to be reported in India.
- This contributes to the growing knowledge of the unique marine ecosystems in Indian waters and underlines the country’s strong footprint in terms of marine biodiversity.
What is the Zoological Survey of India (ZSI)?
- The ZSI, a subordinate organization of the Ministry of Environment and Forests was established in 1916.
- It is a national centre for faunistic survey and exploration of the resources leading to the advancement of knowledge on the exceptionally rich faunal diversity of the country.
- It has its headquarters at Kolkata and 16 regional stations located in different geographic locations of the country.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q Recently, our scientists have discovered a new and distinct species of banana plant which attains a height of about 11 meters and has orange coloured fruit pulp. In which part of India has it been discovered? (2016)
(a) Andaman Islands
(b) Anaimalai Forests
(c) Maikala Hills
(d) Tropical rain forests of northeast
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Combing Operations held in Mukurthi National Park
In recent times, the Forest Department has been conducting combing operations in the Mukurthi National Park in Tamil Nadu and adjoining forest areas to ensure that there was no illegal movement of people and poachers.
- Mukurthi National Park is located in the northwest corner of Tamil Nadu in the Western Ghats.
- It is a part of Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve (UNESCO World Heritage Site) along with Mudumalai Wildlife Sanctuary, Bandipur National Park, Nagarhole National Park, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary and Silent Valley.
- Keystone Species : The park was created to protect its keystone species, the Nilgiri Tahr.
- Forest Type: The park is characterized by montane grasslands and shrublands interspersed with sholas in a high altitude area of high rainfall, near-freezing temperatures and high winds.
- Peaks: The Park is also home to Mukurthi Peak, one of the highest peaks in the Nilgiri Hills.
- Tribes Living Inside: Todas (a pastoral tribe of the Nilgiri Hills).
Read More:- National Parks, Wayanad Wildlife Sanctuary
Tracking Newborn Immunization in U.P
Recently, an immunization wheel, a job aid that helps frontline health workers calculate dates for childhood vaccinations (for children under five), has been launched in Uttar Pradesh.
- The immunization wheel, called a teekakaran chakra in Hindi, is a simple plastic laminated cardboard construction developed and funded by the Clinton Foundation, under the Clinton Health Access Initiative (CHAI).
- It consists of two discs, placed one on top of the other, one bigger than the other, and attached with a rivet. The smaller one has details of the vaccines and arrows; the larger one has a calendar with days and months.
- Health workers register a child’s birth in what they call the ASHA diary. They use the wheel to match a birth date to the first vaccine and other dates get aligned accordingly.
Read More: Accredited Social Health Activist, National Health Mission
Maiden India, Indonesia, and Australia Trilateral Maritime Exercise
- The Indian Navy's warship, INS Sahyadri, participated in the first trilateral Maritime Partnership Exercise with the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) and Indonesian Navy from September 20-21, 2023.
- The exercise allowed the three nations to strengthen their partnership and improve their collective capability to support a stable, peaceful, and secure Indo-Pacific region.
- INS Sahyadri, the third ship of the indigenously designed and built Project-17 class multirole stealth frigates was built at Mazagon Dock Ltd, Mumbai.
- The Project 17 class, also known as the Shivalik class. These frigates were the first stealth warships built in India.
- Shivalik is fitted with a mix of indigenous Russian, Indian, and Western weaponry and sensor systems.
Read more: Indo-Pacific region
Kaobal Gali-Mushkoh Valley
- Kaobal Gali-Mushkoh Valley, once a battleground during the Kargil war, is now welcoming tourists. This transformation is attributed to the enduring ceasefire between India and Pakistan sparking hope that tourism-driven commerce will thrive in the region.
- The Gurez valley in north Kashmir, which was once prone to frequent shelling from Pakistan, is now all set to connect with the Mushkoh valley in Kargil's Drass Sector, Ladakh.
- The 130-km road has been opened up for tourists and Kaobal Gali, the highest pass at a height of 4,166.9 meters in Gurez, connects the two valleys.
- The Gurez Valley is close to the Line of Control (LoC) with the Kishanganga River demarcating the line in several parts.
- The Gurez valley is one of few habitations in Kashmir where villages with only log houses exist, with no intervention of urban concrete materials.