Governance
Bharat New Car Assessment Programme
For Prelims: Bharat New Car Assessment Programme, Global NCAP, Ministry of Road Transport & Highways
For Mains: Positive Outcomes and Challenges Related to Bharat NCAP.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Government of India, has introduced the Bharat New Car Assessment Programme (Bharat NCAP).
- This indigenous star-rating system aims to evaluate the safety of vehicles in the event of a collision, empowering consumers to make informed decisions while purchasing cars.
- This comprehensive program is set to come into effect from October 1, 2023, and will play a pivotal role in curbing the alarming number of road fatalities in India.
What is Bharat NCAP?
- About: Under the Bharat NCAP initiative, vehicles, particularly passenger cars, will be subjected to rigorous crash testing procedures, and based on their performance as per protocols laid down in the soon-to-be-published Automotive Industry Standard 197, they will be assigned a safety rating ranging from one to five stars.
- The programme is applicable to passenger vehicles with not more than eight seats in addition to the driver’s seat with gross vehicle weight not exceeding 3,500 kgs.
- The test procedure involves Frontal Offset Test, Side Impact Test and Pole-Side Impact Test.
- This rating will provide consumers with a clear indication of a vehicle's safety standards in the event of a collision.
- Notably, Bharat NCAP is voluntary, encouraging manufacturers to nominate their vehicles for testing, thereby driving the production of safer cars in the Indian market.
- Testing Parameters: Bharat NCAP evaluates vehicles based on three crucial parameters:
- Adult Occupant Protection: This parameter assesses the level of protection a vehicle offers to adult passengers in the event of a crash.
- Child Occupant Protection: The safety of child occupants is equally vital. This parameter gauges a vehicle's effectiveness in safeguarding young passengers during collisions.
- Safety Assist Technologies: Modern vehicles are equipped with a range of safety assist technologies. This parameter examines the presence and effectiveness of these technologies in preventing accidents or minimizing their impact.
- Mandatory and Recommended Testing: While the Bharat NCAP is voluntary, certain scenarios can trigger mandatory testing:
- Base Model Testing: The base model of a popular variant, with a minimum sale of 30,000 units, may be subjected to testing.
- Ministry Recommendations: If recommended by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways based on market feedback or public safety concerns, certain models might undergo testing.
- Evolution and Alignment with Global Standards: The Bharat NCAP draws inspiration from the Global NCAP, a project initiated by the U.K.-based NGO Towards Zero Foundation.
- The Global NCAP acts as a collaborative platform for new car assessment programs worldwide including countries such as the U.S. which has the world’s oldest crash testing regime since 1978. .
- Over the years, India's testing protocols have evolved, with more than 50 crash test results published for the Indian market.
- Notably, Tata achieved India's first 5-star car rating in 2018.
- Possible Outcomes:
- Reduced Fatalities: With India witnessing around 1.5 lakh road fatalities annually, Bharat NCAP aims to reduce casualties by encouraging the production of safer vehicles.
- Healthcare and Insurance Relief: Improved vehicle safety would lead to a reduction in the burden on healthcare and insurance sectors, resulting in positive societal and economic impacts.
- Manufacturer Reputation: Manufacturers can enhance their brand reputation through consumer-centric practices, fostering higher consumer loyalty.
- Challenges:
- Diverse Road Conditions: India's road infrastructure varies greatly, from congested urban roads to poorly maintained rural highways.
- Different road conditions can impact the way vehicles behave during crashes, making it challenging to design a one-size-fits-all safety assessment framework.
- Affordability and Market Dynamics: A substantial portion of the Indian population seeks budget-friendly vehicles, which might pose a challenge for manufacturers in implementing advanced safety features.
- Striking a balance between affordability and safety could be a complex task, requiring innovative engineering solutions.
- Variety of Vehicles: India's automotive market is diverse, featuring a wide range of vehicle types and sizes.
- Designing crash tests that effectively evaluate safety across this diversity, from compact cars to SUVs, requires thorough consideration of different vehicle dynamics.
- Consumer and their Preferences: While the Bharat NCAP aims to empower consumers, the challenge lies in creating awareness about safety ratings and convincing buyers to prioritize safety over other features.
- Consumer preferences might still lean towards design, features, and price, limiting the immediate impact of safety ratings.
- Diverse Road Conditions: India's road infrastructure varies greatly, from congested urban roads to poorly maintained rural highways.
Way Forward
- Collaborative Safety R&D Hubs: There is a need to establish safety research and development hubs in collaboration with academic institutions and manufacturers.
- These hubs can focus on addressing specific safety challenges unique to India, fostering innovation through joint research.
- Road Safety Awareness through Art: There is a need to collaborate with local artists to create safety-themed public art installations near accident-prone areas that can raise awareness about the importance of safe driving.
- "Safety Score" Integration: Insurance companies can assign a safety score to each vehicle model based on its NCAP rating.
- This safety score can be displayed prominently on advertisements and dealerships, making safety a focal point of consumer decisions.


International Relations
15th BRICS Summit
For Prelims: BRICS, New Development Bank
For Mains: Groupings and Agreements, BRICS Summit,
Why in News?
The 15th BRICS summit hosted by South Africa in Johannesburg, holds significant importance against the backdrop of geopolitical changes and global economic dynamics.
- Notably, this summit marks the first in-person gathering since 2019 due to the Covid -19 pandemic.
- The theme for the 15th BRICS Summit is “BRICS and Africa: Partnership for Mutually Accelerated Growth, Sustainable Development and Inclusive Multilateralism”.
What are the Key Highlights of the 15th BRICS Summit?
- BRICS Expansion:
- BRICS marked its 15th summit by expanding its membership from five to eleven countries, reflecting a concerted effort to enhance its global standing.
- Egypt, Iran, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Ethiopia, and Argentina joined the BRICS fold, amplifying the group's representation across the Middle East, Africa, and South America.
- Full membership will take effect on January 1, 2024.
- The original BRIC members had two things in common: large economies, and high potential growth rates.
- The expanded BRICS-11 is a less coherent group; some are going through crises, and others are thriving. This could signal an expansion of the agenda beyond economics.
- BRICS marked its 15th summit by expanding its membership from five to eleven countries, reflecting a concerted effort to enhance its global standing.
- India's Stakes in the BRICS Summit:
- The summit is important for India, as it is the first in-person meeting since the India-China military standoff at the Line of Actual Control.
- After the bilateral talks between the Prime Minister (PM) of India and President of China, both nations have agreed to step up efforts for the disengagement of troops and de-escalation of tensions along the LAC.
- India played a key role in drafting membership criteria and promoting strategic partnerships among new entrants.
- India leverages BRICS to expand its network of allies and enhance its geopolitical influence.
- India sees BRICS as a "non-western" rather than an "anti-western" group, emphasizing the platform's diversity of perspectives.
- India aims to enhance cooperation with China and Russia for the Leader's declaration.
- The Indian PM proposed to establish a BRICS space exploration consortium to advance cooperation in the field of space technology and research.
- India called for BRICS collaboration under the International Big Cat Alliance in protecting the endangered big cats that live in their countries .
- The summit is important for India, as it is the first in-person meeting since the India-China military standoff at the Line of Actual Control.
- Geopolitical Context and Significance:
- The summit gains new importance as it follows the Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022, impacting global stability and security.
- BRICS discussions are perceived to carry a "counter-western" perspective.
- Amidst attempts to "isolate" Russia over the Ukraine conflict, BRICS deliberations gain importance.
- United Nations Reform:
- India and other BRICS members support comprehensive reform of the United Nations, including the Security Council, to make it more democratic, representative, effective and efficient.
- Climate Change:
- BRICS members agreed to address the challenges posed by climate change while also ensuring a just, affordable and sustainable transition to a low-carbon and low-emission economy.
- The five nations called on developed countries to lead by example and support developing countries towards such transitions.
- BRICS nations opposed trade barriers imposed by certain developed countries under the pretext of tackling climate change.
- BRICS members agreed to address the challenges posed by climate change while also ensuring a just, affordable and sustainable transition to a low-carbon and low-emission economy.
What is BRICS?
- About:
- BRICS is an acronym for the grouping of the world’s leading emerging economies, namely Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa.
- In 2001, the British Economist Jim O’Neill coined the term BRIC to describe the four emerging economies of Brazil, Russia, India, and China.
- The grouping was formalized during the first meeting of BRIC Foreign Ministers in 2006.
- South Africa was invited to join BRIC in December 2010, after which the group adopted the acronym BRICS.
- Share of BRICS:
- The BRICS brings together five of the largest developing countries of the world, representing 41% of the global population, 24% of the global GDP and 16 % of the global trade.
- Chairmanship:
- The chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members, in accordance with the acronym B-R-I-C-S.
- India hosted the chair for the 2021 BRICS Summit.
- The chairmanship of the forum is rotated annually among the members, in accordance with the acronym B-R-I-C-S.
- Initiatives of the BRICS:
- New Development Bank:
- During the Sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (Brazil) in 2014, the leaders signed the Agreement establishing the New Development Bank (NDB - Shanghai, China).
- It has so far approved 70 infrastructure and sustainable development projects worth.
- Contingent Reserve Arrangement:
- In 2014, the BRICS governments had signed a treaty on the setting up of the contingent reserve arrangement
- The arrangement is aimed at forestalling short-term balance of payments pressures, providing mutual support and strengthening the financial stability of the BRICS nations.
- Customs Agreements:
- Customs agreements were signed to coordinate and ease trade transport between BRICS countries
- Launched of Remote Sensing Satellite:
- In August 2021, the five space agencies signed an agreement on the Cooperation on BRICS Remote Sensing Satellite Constellation.
- The constellation is made up of six existing satellites: Gaofen-6 and Ziyuan III 02, both developed by China, CBERS-4, jointly developed by Brazil and China, Kanopus-V type, developed by Russia, and Resourcesat-2 and 2A, both developed by India.
- In August 2021, the five space agencies signed an agreement on the Cooperation on BRICS Remote Sensing Satellite Constellation.
- New Development Bank:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- New Development Bank has been set up by APEC.
- The headquarters of New Development Bank is in Shanghai.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- The New Development Bank (NDB) was formed referred to as the BRICS Development Bank.
- It is a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states (Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The bank is headquartered in Shanghai, China. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- During the sixth BRICS Summit in Fortaleza (2014), the New Development Bank (NDB) was established by the Fortaleza Declaration to strengthen cooperation among BRICS and supplement the efforts of multilateral and regional financial institutions for global development.
- It had an initial authorized capital of US$ 100 billion, with an initial subscribed capital of US$ 50 billion, equally shared among founding members.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.

International Relations
20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting
For Prelims: 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting, ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership, Pandemic, Supply Chains, Food Security, Free Trade Agreement.
For Mains: 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ Meeting, India-ASEAN Relations.
Why in News?
Recently, the 20th ASEAN-India Economic Ministers’ meeting was held in Semarang, Indonesia, marking a significant step in enhancing economic cooperation between India and the ASEAN member countries.
What are the Key Highlights of the Meeting?
- Strengthening Economic Partnership:
- The meeting underscored the shared commitment to fortify the ASEAN-India Comprehensive Strategic Partnership, ensuring substantial benefits for both sides.
- The ministers highlighted the importance of fostering economic collaboration amid the challenges posed by the Pandemic.
- The bilateral trade between India and ASEAN in 2022-23 amounted to USD 131.5 billion, constituting 11.3% of India's global trade for the same period.
- ASEAN-India Business Council (AIBC):
- The ministers acknowledged AIBC's endeavors throughout 2023, including the 5th ASEAN-India Business Summit held in Kuala Lumpur in March, 2023.
- AIBC is an organization formed by the Governments of ASEAN and India in 2005 with the aim to foster closer business linkages and provide an industry perspective to the broadening and deepening of economic linkages between ASEAN and India.
- Recognition was given to the concerns raised by businesses regarding Non-Tariff Barriers (NTBs), highlighting the growing exchanges and interactions among stakeholders from both sides.
- NTB refers to any obstacle or restriction that hinders international trade but does not involve the imposition of a direct tariff or customs duty on imported goods. Some examples of NTB are General or product-specific quotas, Quality conditions imposed by the importing country on the exporting countries, Unjustified Sanitary and Phyto-sanitary conditions etc.
- The ministers acknowledged AIBC's endeavors throughout 2023, including the 5th ASEAN-India Business Summit held in Kuala Lumpur in March, 2023.
- Addressing Regional and Global Challenges:
- Amidst the intricate landscape of regional and global challenges, the ministers engaged in discussions about the multi-dimensional effects of the Covid-19 pandemic, climate change, financial market volatility, inflation, and geopolitical tensions.
- Key areas for cooperation were identified, such as robust Supply Chains, Food Security, energy security, health, and financial stability.
- AITIGA Review - A Key Agenda:
- A pivotal point of this year's meeting was the thorough review of the ASEAN-India Trade in Goods Agreement (AITIGA), originally signed in 2009.
- The discussions were preceded by a meeting of the AITIGA Joint Committee, which deliberated on the review's roadmap.
- The Term of Reference and Work Plan for AITIGA Review Negotiations were finalized during this process.
- Endorsement and Commencement of Review:
- The ministers officially endorsed the review documents for AITIGA, paving the way for the formal commencement of negotiations with predefined modalities.
- The initiation of the AITIGA review addresses a longstanding demand from Indian businesses and promises to make the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) more conducive to trade and mutually beneficial.
- A quarterly schedule of negotiations was agreed upon, with the aim of concluding the AITIGA review by 2025.
- This review process is anticipated to bring about enhancements in trade diversification while also addressing existing trade imbalances.
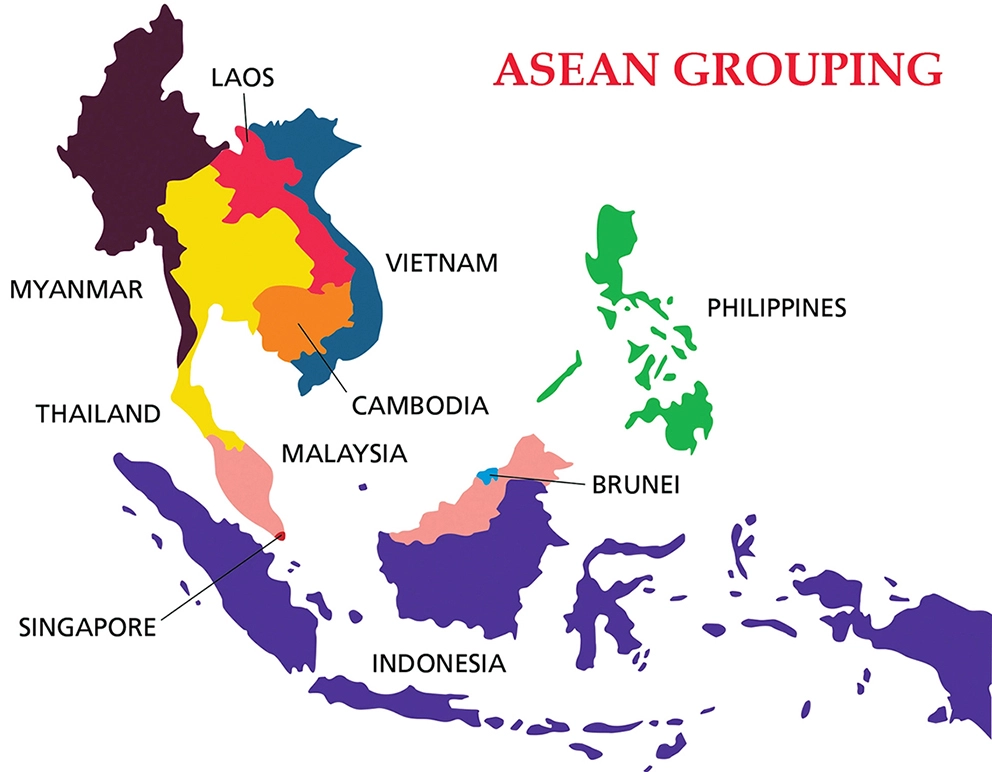
What is the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)?
- About:
- It is a regional grouping that promotes economic, political, and security cooperation.
- It was established in August 1967 in Bangkok, Thailand with the signing of the ASEAN Declaration (Bangkok Declaration) by the founding members of ASEAN, namely Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and Thailand.
- Its chairmanship rotates annually, based on the alphabetical order of the English names of Member States.
- ASEAN countries have an estimated 666.19 million people and a combined Gross Domestic Product (GDP) of USD USD 3.2 Trillion.
- Commodity trade between India and ASEAN region has reached 98.39 billion in the period April 2021- February 2022. India’s main trading ties are with Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam and Thailand.
- Members:
- ASEAN brings together ten Southeast Asian states – Brunei, Cambodia, Indonesia, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam – into one organisation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Q2. The term ‘Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership’ often appears in the news in the context of the affairs of a group of countries known as (2016)
(a) G20
(b) ASEAN
(c) SCO
(d) SAARC
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Evaluate the economic and strategic dimensions of India’s Look East Policy in the context of the post-Cold War international scenario. (2016)


International Relations
India-Bangladesh Relations
For Prelims: India and Bangladesh, Exercise Sampriti, Exercise Bongosagar, Akhaura-Agartala rail link, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation, Indian Ocean Rim Association, Rohingya refugees, Belt and Road Initiative
For Mains: Major Areas of Cooperation Between India and Bangladesh
Why in News?
The 14th Joint Group of Customs (JGC) meeting between India and Bangladesh was convened recently, in New Delhi.
- The India-Bangladesh Joint Group of Customs meetings serves as a critical platform for fostering collaboration on customs-related matters and enhancing the facilitation of cross-border trade.
What are the Key Outcomes of the 14th JGC Meeting?
- Expansion of Land Customs Stations: The meeting deliberated on the establishment of new land customs stations, which play a pivotal role in facilitating cross-border trade.
- The meeting explored the possibility of entering into a bilateral agreement on customs cooperation, which could serve as a comprehensive framework for future collaboration.
- Easing Port Restrictions: The discussion revolved around measures to simplify port restrictions, thereby enhancing the overall efficiency of port operations and reducing trade barriers.
- India expressed appreciation for Bangladesh's completion of trial runs and the subsequent notification for operationalizing the Agreement on Use of Chattogram and Mongla Ports (ACMP), as agreed upon in the 13th JGC meeting.
- Electronic Connectivity of Transit Modules: Discussions were initiated concerning the electronic connectivity of the respective transit modules of ACMP, signifying a step toward efficient digital collaboration.
- Pre-Arrival Customs Data Exchange: Both parties engaged in talks regarding the pre-arrival exchange of customs data. This step aims to expedite the customs clearance process by enabling authorities to prepare in advance.
What are the Major Areas of Cooperation Between India and Bangladesh?
- About:
- India was the first country to recognise Bangladesh as a separate and independent state and established diplomatic relations with the country immediately after its independence in December 1971.
- India's links with Bangladesh are civilisational, cultural, social and economic.
- Bangladesh's geographical location as India's eastern neighbor gives it strategic importance.
- It provides India with access to the Bay of Bengal and an important route for trade and connectivity with Southeast Asia.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Bangladesh is India’s biggest trading partner in the subcontinent. India’s export to Bangladesh stood at USD 8 billion during April –November 2022.
- India enabled the export of cargo from ICDs within India to Bangladesh through inland waterways.
- Also, the transshipment of containerized export cargo from Bangladesh to third countries through India gained a streamlined process.
- Utilizing both riverine and land routes, this measure reinforces trade routes and opens up new possibilities for cargo movement.
- India has provided duty free quota free access to Bangladesh on all tariff lines except tobacco and alcohol under South Asian Free Trade Area (SAFTA) since 2011.
- Bangladesh and India in July 2023 launched a trade transaction in rupees, a move aimed at reducing dependence on the US dollar and strengthening regional currency and trade.
- Bangladesh is India’s biggest trading partner in the subcontinent. India’s export to Bangladesh stood at USD 8 billion during April –November 2022.
Note: According to the India Tourism Statistics Report 2022 of Ministry of Tourism, Bangladesh has been the second largest amongst tourist generating markets for India in the year 2021.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India and Bangladesh share 4096.7 km. of border; the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbors.
- Assam, West Bengal, Mizoram, Meghalaya, and Tripura share borders with Bangladesh.
- The two also conduct Joint Exercises - Army (Exercise Sampriti) and Navy (Exercise Bongosagar)
- India and Bangladesh share 4096.7 km. of border; the longest land boundary that India shares with any of its neighbors.
- Energy and Connectivity:
- The India-Bangladesh Friendship Pipeline connecting Siliguri in West Bengal and Parbatipur in Dinajpur district of Bangladesh, will transport one million Metric Tonnes Per Annum (MMTPA) of High-Speed Diesel to Bangladesh.
- India and Bangladesh have been cooperating in developing cross-border infrastructure projects, such as the Akhaura-Agartala rail link and Maitri Setu.
- The India-Bangladesh Friendship Pipeline connecting Siliguri in West Bengal and Parbatipur in Dinajpur district of Bangladesh, will transport one million Metric Tonnes Per Annum (MMTPA) of High-Speed Diesel to Bangladesh.
- Multilateral Cooperation:
- India and Bangladesh are also engaged in regional cooperation through multilateral forums such as SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation), BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) and Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA).
What are the Current Major Issues Between India and Bangladesh?
- Sharing of Transboundary River Waters: India and Bangladesh share 54 common rivers, but only two treaties have been signed so far of Ganga Waters Treaty and The Kushiyara River Treaty.
- The other major rivers, such as the Teesta and Feni are still under negotiation.
- Illegal Migration: Illegal migration from Bangladesh to India, involving refugees and economic migrants, remains a pressing issue.
- This influx strains Indian border states, impacting resources and security. The problem intensified with Rohingya refugees entering India through Bangladesh.
- The National Register of Citizens (NRC), aimed at curbing such migration, has raised concerns in Bangladesh.
- Drug Smuggling & Trafficking: There have been many incidences of cross border drug smuggling & trafficking. Humans ( especially children & women) are trafficked & various animal & bird species are poached through these borders.
- Growing Chinese Influence in Bangladesh: At present, Bangladesh is an active partner in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) (India is not a part of BRI).
- China's increasing involvement with Bangladesh could potentially undermine India's regional standing and impede its strategic aspirations.
Way Forward
- Joint Task Forces: There is a need to establish joint task forces comprising law enforcement agencies from both countries to effectively combat cross-border drug smuggling and human trafficking. Shared intelligence and coordinated operations can disrupt illegal networks.
- Smart Border Management: Implementing smart border management solutions that utilize artificial intelligence and data analytics can streamline cross-border movements while ensuring security and efficiency.
- Digital Connectivity Corridor: There is a need to establish a digital connectivity corridor between the two countries, focusing on high-speed internet connectivity, digital services, and e-commerce. This can create new avenues for trade, collaboration, and technological exchange.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to river Teesta, consider the following statements: (2017)
- The source of river Teesta is the same as that of Brahmaputra but it flows through Sikkim.
- River Rangeet originates in Sikkim and it is a tributary of river Teesta.
- River Teesta flows into Bay of Bengal on the border of India and Bangladesh.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


Social Justice
Supreme Court Allows Termination of Pregnancy for Rape Survivor
For Prelims: Supreme Court of India, Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971, Abortion Law in India, Reproductive Rights, Shantilal Shah Committee.
For Mains: Legal Provisions Related to Abortion in India, Major Issues Related to Women.
Why in News?
Observing that pregnancy outside marriage, especially in cases of sexual assault, is injurious and a cause of stress, the Supreme Court of India allowed a rape survivor from Gujarat to terminate her 27-week pregnancy.
- The court overruled the Gujarat High Court’s order that denied her request and directed the hospital to carry out the procedure without any delay.
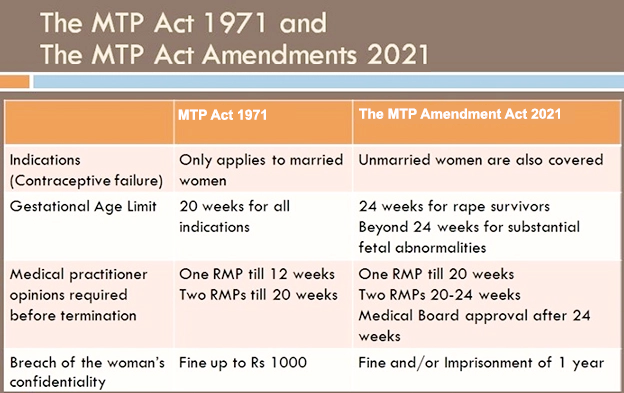
- Under the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Amendment Act 2021, the upper limit for termination of pregnancy is 24 weeks.
What are the Legal Provisions Related to Abortion in India?
- Until the 1960s, abortion was prohibited in India, and violating this led to imprisonment or fines under Section 312 of the Indian Penal Code.
- The Shantilal Shah Committee was set up in the mid-1960s to investigate the need for abortion regulations.
- Based on its findings, the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, 1971 was enacted, allowing safe and legal abortions, safeguarding women's health, and reducing maternal mortality.
- The MTP Act, 1971, allows abortion up to 20 weeks of gestation, with the consent of the woman and on the advice of one registered medical practitioner (RMP). However, the law was updated in 2002 and 2021.
- The 2021 amendment permits abortion from 20 to 24 weeks of gestation for specific cases like rape survivors, with approval from two doctors.
- It sets up state level Medical Boards to decide if a pregnancy may be terminated after 24 weeks in cases of substantial fetal abnormalities.
- The 2021 amendment permits abortion from 20 to 24 weeks of gestation for specific cases like rape survivors, with approval from two doctors.
- It extends the failure of contraceptive clauses to unmarried women( initially only married women), allowing them to seek abortion services on grounds of their choice, irrespective of their marital status.
- Consent requirements vary based on age and mental state, ensuring medical practitioner oversight.
- Recent Supreme Court judgments reaffirm women's bodily autonomy. Courts recognized abortion rights in cases of rape and acknowledged reproductive choice as a component of personal liberty.
Note:
In Justice K.S. Puttaswamy (Retd.) vs. the Union Of India And Others (2017), the Supreme court recognized the constitutional right of women to make reproductive choices, as a part of personal liberty under Article 21 of the Indian Constitution, which, despite laying a robust jurisprudence on reproductive rights and the privacy of a woman, does not translate into a fundamental shift in power from the doctor to the woman seeking an abortion.


Important Facts For Prelims
Demon Particle
Why in News?
Recently, a team of researchers from the University of Illinois discovered a unique particle, known as a "demon particle," within a metal called strontium ruthenate. This discovery has the potential to pave the way for the development of superconductors capable of operating at room temperature.
What is a Demon Particle?
- The demon particle is a name given to a type of quasiparticle, which is not a real particle, but rather a collective excitation or vibration of many electrons in a solid.
- Quasiparticles are useful for describing the complex behavior of electrons in solids, such as metals and semiconductors.
- The demon particle was first predicted by theoretical physicist David Pines in 1956.
- He believed that electrons would behave strangely when passed through a solid. Electric interactions make electrons combine to form collective units. This can make them lose individuality in solids.
- However, with such a large mass, plasmons (collective oscillation of conduction electrons in metals) cannot form with energies available at room temperature.
- However, demons do not contain mass, they can form with any energy and at room temperature as well.
- He believed that electrons would behave strangely when passed through a solid. Electric interactions make electrons combine to form collective units. This can make them lose individuality in solids.
- The demon particle could have many applications in computing, medical imaging, transportation, and energy.
Superconductors
- About:
- A superconductor is a material that can conduct electricity or transport electrons from one atom to another with no resistance.
- No heat, sound or any other form of energy would be released from the material when it has reached critical temperature (Tc), or the temperature at which the material becomes superconductive.
- The critical temperature for superconductors is the temperature at which the electrical resistivity of metal drops to zero.
- Superconductors also exhibit the Meissner effect, which is the expulsion of a magnetic field from the interior of a material during the process of becoming a superconductor.
- Examples: Aluminium, niobium, magnesium diboride, etc.
- Applications:
- Superconductors are used in operations such as levitating trains and highly accurate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines.
- Limitations:
- Their usefulness is still limited by the need for bulky cryogenics (production of and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures) as the common superconductors work at atmospheric pressures, but only if they are kept very cold.
- Even the most sophisticated ones like copper oxide-based ceramic materials work only below −140°C.
- Their usefulness is still limited by the need for bulky cryogenics (production of and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures) as the common superconductors work at atmospheric pressures, but only if they are kept very cold.


Important Facts For Prelims
Mission Amrit Sarovar
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Rural Development has provided insights into the advancements made in the implementation of Mission Amrit Sarovar, an initiative aimed at enhancing water security across various regions.
What is the Mission Amrit Sarovar?
- About:
- On April 24, 2022, Mission Amrit Sarovar was launched as part of India's "Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav" celebrations for the 75th year of independence.
- The mission aims to construct/rejuvenate at least 75 Amrit Sarovars in each district across India to overcome the water crisis in rural areas.
- The target for these water bodies serves as a crucial step towards ensuring water sustainability at the local level.
- Eight Central Ministries/Departments, including Dept. of Rural Development, Department of land resources, Department of Drinking Water and Sanitation, Department of Water resources, Ministry of Panchayati Raj, Ministry of Forest, Environment and Climate changes, Ministry of Railway, Ministry of Road, Transport & Highways, actively contribute to the mission's execution.
- Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Application and Geo-informatics (BISAG-N) has been engaged as Technical partner for the Mission.
- BISAG-N is an autonomous scientific society registered under the Societies Registration Act, of 1860. It comes under the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology.
- Geospatial data and technology play a pivotal role in identifying and executing the construction and rejuvenation of Amrit Sarovar.
- Progress and Achievements:
- So far, out of over 1 lakh identified Amrit Sarovars, the work has been started for over 81,000 Amrit Sarovars and a total of over 66,000 Amrit Sarovars have been constructed/ rejuvenated.
- The national target of 50,000 Amrit Sarovars has been accomplished, demonstrating the dedication and efficacy of the mission.
- State-Specific Challenges and Advancements:
- Several states have made commendable strides towards achieving the goal of 75 Amrit Sarovars per district.
- While some states like West Bengal, Punjab, Telangana, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Bihar, and Rajasthan are still working to meet this target, their determination remains unwavering.
- Bridging Resource Gaps:
- Mission Amrit Sarovar leverages various existing schemes and financial grants to realize its objectives.
- The Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act, Pradhan Mantri Kisan Sampada Yojana sub-schemes, and state-specific initiatives are channelled to mobilize resources for the mission's success.
- Empowering Local Participation:
- The mission encourages citizen engagement and collaboration with non-governmental resources.
- By fostering community involvement, the initiative seeks to harness additional support for the cause.
- Water Security through Collaboration:
- The mission's collaborative nature, combining governmental departments, technical partners, and local communities, highlights its multi-faceted approach to water security.
- The ultimate goal is to transform the water landscape, enhance livelihoods, and ensure water availability for generations to come.


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
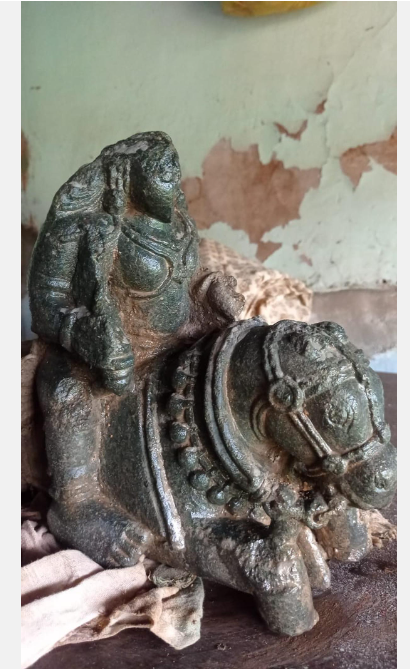
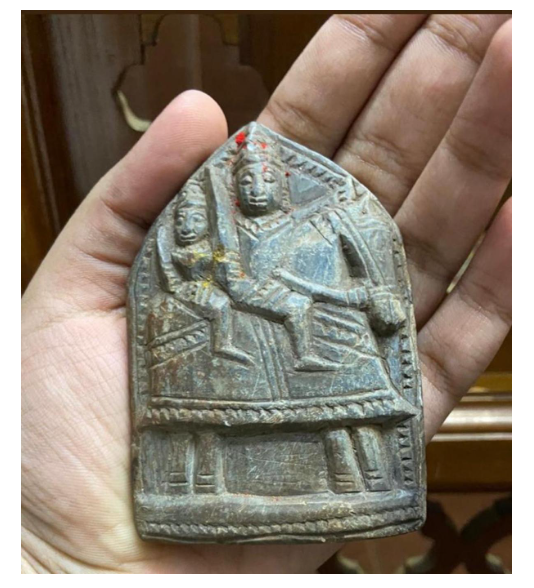
Mylara Cult
The discovery of two ancient sculptures in Basrur, Karnataka, has led to the revelation that the Mylara cult existed in the coastal region.
- Two sculptures resembling those from the 15th and 17th centuries were found in Basrur (historical trading city of the Medieval period).
- A unique sculpture depicting a royal hero sitting on a horse holding a sword and a bowl was found in a well.
- Another stone tablet containing Mylara and Mylaladevi sitting on an ornate horse and holding swords was found in a tank.
- The Mylara cult was a religious tradition in the Deccan region during the medieval period.
- The cult is centered around the worship of a goddess named Mylara, believed to be a form of Lord Shiva.
 |
 |
African Union Suspends Niger from All Institutions Following Coup
The African Union (AU) has suspended Niger from all of its institutions and activities following the recent coup that overthrew the democratically elected president of Niger.
- The AU is a continental body consisting of the 55 member states that make up the countries of the African Continent.
- In 1963, African states established the Organisation of African Unity to enhance cooperation.
- In 2002, the Organisation of African Unity was succeeded by the AU, with one of its goals to accelerate the "economic integration of the continent”.
- The AU called on member nations and the international community to reject the unconstitutional change of government.
- This action could impact diplomatic relations and foreign forces' activities in Niger.
- The West African regional bloc Economic Community of West African States(ECOWAS) demanded the reinstatement of the President.
Read more: Coup in Niger
Revolutionizing Sectors with Next-Gen Photonic RF Conversion
The Next-Generation Photonic Analog-to-Digital Converters (NG-PADC) project has developed new prototypes with the capability to instantly measure, generate, and transport Radio Frequency (RF) signals using optical methods.
- This breakthrough technology has the potential to revolutionize the way RF signals are transported through optical means.
- It can also facilitate faster digital communication, improved satellite communication, better medical imaging, and photonic radars.
- Radio frequency refers to the range of electromagnetic frequencies that are commonly used for wireless communication and various other applications.
- RF signals typically range from around 3 kilohertz (kHz) to 300 gigahertz (GHz).
- They are used for transmitting and receiving wireless signals, such as those used in radio broadcasting, television and cellular communication.
India's First Carbon Negative Garrison Achieves Milestone with Solar Power
The College of Military Engineering (CME) in Pune, Maharashtra has achieved a remarkable feat by becoming India's inaugural carbon-negative garrison through its recent implementation of a 5-megawatt (MW) solar power plant, elevating its total solar power generation capacity to 7 MW.
- In addition to fiscal savings of approximately Rs 6.5 crore per annum, the power generated at CME is distributed to various defense establishments in Pune, contributing to the realization of the 'National Clean Air Programme' and reducing dependency on conventional thermal power plants.
- Established in 1948 as a premier institute for the armed forces, the CME trains personnel from the Indian Army, Navy, Air Force, and foreign counterparts.
Read more: India’s Solar Power Dream, National Clean Air Programme
Annual Capacity Building Plan of Minister of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj
Recently, the Minister of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj launched the Annual Capacity Building Plan (ACBP) of the Department of Rural Development, Department of Land Resources and Ministry of Panchayati Raj.
- It is a plan document that is developed based on the competency enhancement requirements of the officials of the Ministry/Department/Organization (MDO), that is ascertained through carrying out Competency Need Analysis (CNA).
- The ACBP aligns itself closely with the Vision of New India @2047 and is designed under the guidance of the Capacity Building Commission.
- This framework follows a triad of lenses, focusing on National Priorities, Citizen Centricity, and Emerging Technology.
- It is complemented by the three pillars of Individual, Organizational, and Institutional development/
Read more: Mission Karmayogi