Governance
ODOP Sampark Event in Nagaland
For Prelims: Department for the Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade, One District One Product, PM Gati Shakti, Krishi UDAN scheme, Krishi UDAN scheme, World Economic Forum, Bharatmala, Sagarmala, Inland waterways
For Mains: Features of ODOP Initiative and PM Gati Shakti
Why in News?
Recently, the Department for the Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) and Invest India, in collaboration with the Department of Industries and Commerce, Nagaland organised the ODOP Sampark Event in Nagaland.
- The event aimed to create awareness about the One District One Product (ODOP) and PM Gati Shakti (Logistics) initiatives.
What are the Major Highlights of the Event?
- Enhancing Market Access: One of the primary objectives of the event was to improve market access for Indian products, particularly from Nagaland, in foreign markets like the European Union (EU), Switzerland, and others.
- Infrastructure Development: To support the ODOP products from Nagaland, various measures to improve logistics facilities were highlighted such as:
- Leveraging Krishi UDAN scheme for better transportation
- Expanding railway connectivity
- The Union Budget 2023-24 has allocated INR 5000 crores for the construction of Unity Malls across the country, which will act as centralised marketplaces for ODOP products.
- Infrastructure Development: To support the ODOP products from Nagaland, various measures to improve logistics facilities were highlighted such as:
- ODOP Exhibition: The event showcased various ODOP products from Nagaland, including chili, fish, coffee, and turmeric.
What is One District One Product Initiative?
- About:
- ODOP is an initiative to boost economic growth at the district level by promoting and branding one product from each district of the country.
- The idea is to leverage the local potential, resources, skills, and culture of each district and create a unique identity for them in the domestic and international markets.
- Over 1000 products have been selected from all 761 districts in the country. The initiative covers a wide range of sectors, including textiles, agriculture, processed goods, pharmaceuticals, and industrial items.
- Also, multiple ODOP products were displayed at the World Economic Forum in January 2023 in the Indian Pavilion at Davos in Switzerland.
- ODOP is an initiative to boost economic growth at the district level by promoting and branding one product from each district of the country.
- Background:
- The concept of ODOP was first launched by the Uttar Pradesh government in January 2018.
- The scheme was successful in reviving the traditional industries and crafts of the state, such as chikankari embroidery, brassware, pottery, carpets, leather goods, etc.
- Inspired by it, the central government adopted the concept and launched it as a national initiative.
- The concept of ODOP was first launched by the Uttar Pradesh government in January 2018.
- Implementation:
- The Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI) implements the scheme for the food processing sector.
- The Ministry of Textile inaugurated the ‘Lota Shop’ at National Crafts Museum, New Delhi under the Central Cottage Industries Corporation of India Limited (CCIC) to showcase and sell the products of ODOP scheme.
- The Directorate General of Foreign Trade (DGFT) also aligned its Districts as an Export Hub initiative with ODOP to boost exports.
- Significance:
- Economic Development: ODOP aims to strengthen the local economy by identifying a unique product or craft for each district and developing it as a specialty.
- This approach helps in creating a diversified and sustainable economic base at the grassroots level, leading to increased income generation, employment opportunities, and overall economic growth.
- Entrepreneurship and Skill Development: The initiative encourages local entrepreneurship by focusing on specific products and crafts.
- It aims to provide skill development, capacity building, and technical support to artisans and entrepreneurs, enabling them to enhance their production capabilities, product quality, and market reach.
- This, in turn, empowers individuals and communities by promoting self-employment and fostering a culture of innovation.
- Preserving Traditional Knowledge and Heritage: India has a rich heritage of traditional crafts and products that are deeply rooted in the cultural fabric of each district.
- The ODOP initiative aims to preserve and promote these traditional arts, crafts, and industries, which often face challenges due to globalization and changing consumer preferences.
- Market Linkages and Branding: ODOP focuses on providing market linkages and creating a robust marketing ecosystem for local products.
- By leveraging the unique characteristics of each district's product, the initiative helps in creating niche markets, attracting buyers, and increasing exports, thereby boosting the local economy.
- Economic Development: ODOP aims to strengthen the local economy by identifying a unique product or craft for each district and developing it as a specialty.
- One District One Product Awards:
- Recognizing the efforts of various stakeholders in promoting economic development and realising the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat, DPIIT has instituted the One District One Product Awards.
- These awards will acknowledge the outstanding work done by States/UTs, Districts, and Indian Missions Abroad.
- The awards will be launched on the Rashtriya Puraskar Portal.
- Recognizing the efforts of various stakeholders in promoting economic development and realising the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat, DPIIT has instituted the One District One Product Awards.
What is PM Gati Shakti?
- About:
- PM Gati Shakti is a National Master Plan for Multi-modal Connectivity, a digital platform to bring 16 Ministries, including Railways, Civil Aviation, MEITY, Shipping, and Road Transport, together for integrated planning and coordinated implementation of infrastructure connectivity projects.
- Features:
- The plan incorporate the infrastructure schemes of various Ministries and State Governments like Bharatmala, Sagarmala, inland waterways, dry/land ports, UDAN etc. and cover economic zones like textile clusters, pharmaceutical clusters, defence corridors, electronic parks, industrial corridors, fishing clusters, agri zones etc. to improve connectivity and make Indian businesses more competitive.
- The plan also leverage technology extensively including spatial planning tools with ISRO imagery developed by BiSAG-N (Bhaskaracharya National Institute for Space Applications and Geoinformatics) and enable transparency in monitoring current projects.
Governance
Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY), Blue Revolution , Kisan Credit Card
For Mains: Fisheries sector in India, Steps Taken to Improve the Fisheries Sector in India
Why in News?
As Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY) enters its 4th year of implementation, the Department of Fisheries plans to expedite the pace of implementation of the scheme.
- As part of this plan, the Department has scheduled a series of review meetings with states and Union Territories (UTs). The first review meeting recently took place in the Northeastern Region (NER) of India.
What is PMSSY?
- About:
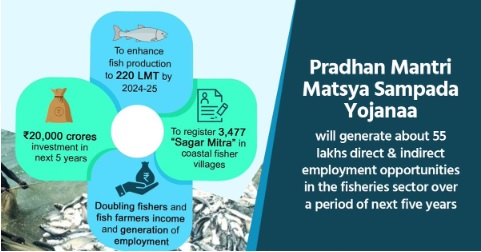
- It aims to bring about the Blue Revolution through sustainable and responsible development of the fisheries sector in India.
- PMMSY was introduced as part of the ‘Atma Nirbhar Bharat’ package with an investment of Rs. 20,050 crores, the highest-ever investment in this sector.
- The scheme is being implemented in all States and UTs for a period of 5 years from FY 2020-21 to FY 2024-25.
- In order to facilitate access to institutional credit, fishermen are provided with insurance coverage, financial assistance and a facility of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) as well.
- Implementation:
- It is implemented as an umbrella scheme with two separate components namely:
- Central Sector Scheme: The project cost will be borne by the Central government.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme: All the sub-components/activities will be implemented by the States/UTs, and the cost will be shared between the Centre and State.
- It is implemented as an umbrella scheme with two separate components namely:
- Objectives:
- Harness the potential of the fisheries sector in a sustainable, responsible, inclusive and equitable manner
- Enhance fish production and productivity through expansion, intensification, diversification and productive utilisation of land and water
- Modernise and strengthen the value chain including post-harvest management and quality improvement
- Double fishers' and fish farmers’ incomes and generate meaningful employment
- Enhance the contribution of the fisheries sector to agricultural Gross Value Added (GVA) and exports
- Ensure social, physical and economic security for fishers and fish farmers
- Build a robust fisheries management and regulatory framework
- Significance:
- The fisheries sector plays an important role in the Indian economy. It contributes to national income, exports, food and nutritional security as well as employment generation.
- The sector provides a livelihood for more than 2.8 crore fishers and fish farmers at the primary level and several more along the fisheries value chain.
- It is a major source of income for a large proportion of the country's economically disadvantaged population.
- To improve fish production, it is important to conduct integrated fish farming and diversify fish production.
- Further, the fisheries sector has been a major contributor to foreign exchange earnings, with India being one of the world's leading seafood exporters.
- In FY20, aquaculture products accounted for 70–75% of the country's total fishery exports.
- The fisheries sector plays an important role in the Indian economy. It contributes to national income, exports, food and nutritional security as well as employment generation.
- Achievements:
- As of 2023, under PMMSY, projects worth Rs 14,654.67 crore have been approved from 2020-21 to 2022-23.
- As the 3rd largest fish producer and the 2nd largest aquaculture producer globally, India recognizes the significance of the fisheries and aquaculture industry.
- The fish production reached an all-time high of 16.25 MMT during FY 2021-22 with marine exports touching Rs. 57,586 Crores.
Note:
- Aquaculture refers to the breeding, rearing, and harvesting of fish, shellfish, algae, and other organisms living in all types of water environments whereas Pisciculture refers to the breeding, rearing, and transplantation of fish by artificial means.
What are the Challenges in Implementation of the Scheme?
- Infrastructural and Technological Gap:
- The fisheries sector faces a lack of adequate infrastructure and technology for fish production, processing, storage, transportation and marketing.
- Lack of Human Resource Development:
- Lack of skilled and trained manpower and extension services for fish farmers and fishermen affects the adoption of best practices, innovations and standards in the sector.
- Financial Inclusion and Social Protection:
- Inadequate access to timely credit and insurance for fish farmers and fishermen exposes them to various risks and vulnerabilities such as natural disasters, diseases, market fluctuations, etc.
- Regulatory and Legal Compliance:
- The fisheries sector faces a lack of awareness and compliance with the regulatory and legal framework for fisheries management such as fishing rights, licenses, quotas, conservation measures, quality control, traceability, etc. This affects the sustainability and competitiveness of the sector.
What are the Other Initiatives Related to Fisheries Sector?
What is the Blue Revolution?
- About:
- The Blue Revolution, with its multi-dimensional activities, focuses mainly on increasing fisheries production and productivity from aquaculture and fisheries resources, both inland and marine.
- Objectives:
- To increase overall fish production in a responsible and sustainable manner for economic prosperity
- To modernise the fisheries with a special focus on new technologies
- To ensure food and nutritional security
- To generate employment and export earnings
- To ensure inclusive development and empower fishers and aquaculture farmers
What is the Kisan Credit Card Scheme?
- About:
- The scheme was introduced in 1998 for providing adequate and timely credit support from the banking system, under a single window with flexible and simplified procedures to farmers for their cultivation and other needs like the purchase of agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides etc. and draw cash for their production needs.
- The scheme was further extended for the investment credit requirement of farmers viz. allied and non-farm activities in the year 2004.
- In the Budget-2018-19, the government announced the extension of the facility of KCC to fisheries and animal husbandry farmers to help them to meet their working capital needs.
- The scheme was introduced in 1998 for providing adequate and timely credit support from the banking system, under a single window with flexible and simplified procedures to farmers for their cultivation and other needs like the purchase of agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides etc. and draw cash for their production needs.
- Implementing Agencies:
- Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Small Finance Banks
- Cooperatives
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Mains:
Governance
UPI Payments: Empowering Users, Challenging Banks
For Prelims: Unified Payments Interface, National Payments Corporation of India
For Mains: Infrastructure challenges associated with UPI
Why in News?
The rapid rise in Unified Payments Interface (UPI) transactions in India has led to the introduction of various daily limits by banks and apps, creating a complex landscape of limitations in terms of value and volume.
- The surge in UPI transactions has revealed the need for continuous development and improvement of banking infrastructure and technological capabilities.
What are the Daily Limits on UPI Payments?
- The National Payments Corporation of India (NCPI) set a limit of 20 transactions per day and ₹1 lakh per day in 2021. However, banks and apps have implemented their own limits, adding to the complexity.
- For instance, ICICI bank allows 10 transactions in 24 hours, while Bank of Baroda and HDFC Bank allow 20 transactions in the same period.
- Certain specific categories of transactions, such as capital markets, collections, insurance, and forward inward remittances, have a higher limit of ₹2 lakh.
- For UPI-based ASBA (Application Supported by Blocked Amount system) IPO and retail direct schemes, the limit for each transaction was increased to ₹5 lakh in December 2021.
What is the National Payments Corporation of India?
- About:
- It is an umbrella organisation for all retail payments systems in India.
- It was set up with the guidance and support of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and Indian Banks’ Association (IBA).
- Objectives:
- To consolidate and integrate the existing multiple systems into a nation-wide uniform and standard business process for all retail payment systems.
- To facilitate an affordable payment mechanism to benefit the common man across the country and propel financial inclusion.
How has the Number of UPI Payments Increased Over Time?
- UPI gained popularity as an alternative to cash after demonetization in India.
- The surge in transactions from May 2018 to May 2023 was primarily in terms of volume rather than value.
- In May 2018, the value of UPI transactions was ₹33,288 crore (₹1,756 per transaction).
- In May 2023, the value rose to Rs.14,89,145 crore (Rs.1,581 per transaction), representing a decrease of Rs.175 per transaction in five years.
Recent developments in UPI ecosystem:
- New Rules:
- Introduction of interchange fee for Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs) wallet transactions via UPI, applicable from April 2023. The fee is up to 1.1% on merchants for Person to Merchant transactions above ₹2,000 and will be shared between banks involved in the transaction.
- UPI AutoPay feature for recurring payments up to ₹5,000, enhancing customer convenience and merchant retention.
- Collaboration:
- NPCI has partnered with several countries such as Singapore, UAE, Bhutan and Japan to enable cross-border payments using UPI.
What are the Effects of these Trends for Users and Banks?
- Positive Impacts:
- Convenience and Efficiency: Quick and hassle-free digital transactions through smartphones.
- Financial Inclusion: Access to digital payments for individuals.
- Reduced Cash Dependency: Minimizing risks and combating illicit transactions.
- Enhanced Transparency: Tracking and monitoring financial activities.
- Boost to Digital Economy: Promoting digital entrepreneurship and innovation.
- Negative Impacts:
- Users:
- UPI as an Alternative to Petty Cash:
- Consumers are increasingly using UPI for smaller transactions, replacing petty cash. The declining value per transaction over time reflects this trend.
- Limited Transaction Flexibility:
- The complex web of limitations set by different apps and banks on UPI transactions creates confusion and restricts users' flexibility in terms of transaction volume and value.
- Users have to navigate through varying limits, impacting their ability to carry out transactions according to their needs.
- Increased Transaction Failures:
- The struggle of banks to upgrade their infrastructure and technical systems to keep up with the surge in UPI payments can result in transaction failures. This can frustrate users and hinder their seamless payment experience.
- UPI as an Alternative to Petty Cash:
- Banks:
- Infrastructure Challenges for Banks:
- Banks face difficulties in keeping up with the surge in UPI payments, leading to transaction failures.
- Upgrading banking infrastructure and technical systems is crucial to meet the growing demand.
- Banks need to ensure that their servers are able to handle the increasing volume and frequency of UPI transactions without any glitches or downtime.
- Security and Fraud Prevention:
- With the rise in UPI transactions, the risk of cyber threats and fraudulent activities also increases.
- Banks need robust security measures, including encryption, two-factor authentication, and fraud detection mechanisms, to safeguard user data and prevent unauthorized access.
- Infrastructure Challenges for Banks:
- Users:
Way Forward
- Agile Infrastructure Development:
- Invest in robust infrastructure and advanced technology solutions to handle the increasing volume and frequency of UPI transactions.
- Embrace edge computing, and distributed ledger technology (DLT),
- DLT is a decentralized digital system that enables secure and transparent recording, storing, and sharing of information across multiple participants in a network to ensure scalability, security, and real-time transaction processing.
- Personalized Financial Insights:
- Leverage data analytics and artificial intelligence to provide personalized financial insights to UPI users.
- Offer real-time spending analysis, budgeting tools, and tailored recommendations to empower users in making informed financial decisions.
- Blockchain Integration:
- Explore the integration of blockchain technology into the UPI infrastructure to enhance transparency, security, and scalability.
- Smart contracts can automate transaction processes, reduce intermediaries, and enable seamless cross-border transactions.
- AI-Powered Fraud Prevention:
- Harness the power of artificial intelligence and machine learning to detect and prevent fraudulent UPI transactions in real-time.
- Implement advanced anomaly detection algorithms that analyze user behavior patterns and transaction data to identify suspicious activities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to digital payments, consider the following statements: (2018)
- BHIM app allows the user to transfer money to anyone with a UPI-enabled bank account.
- While a chip-pin debit card has four factors of authentication, BHIM app has only two factors of authentication.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Q2. Which of the following is a most likely consequence of implementing the ‘Unified Payments Interface (UPI)’? (2017)
(a) Mobile wallets will not be necessary for online payments.
(b) Digital currency will totally replace the physical currency in about two decades.
(c) FDI inflows will drastically increase.
(d) Direct transfer of subsidies to poor people will become very effective.
Ans: (a)
Q3. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) helps in promoting the financial inclusion in the country.
- NPCI has launched RuPay, a card payment scheme.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Science & Technology
Paper-based Supercapacitor for Rapid Device Charging
For Prelims: Supercapacitor, Lithium-Ion batteries, Seaweeds, Exclusive Economic Zone, Algal blooming, Bio-ethanol
For Mains: Significance of Seaweeds
Why in News?
Scientists at the Gujarat Energy Research and Management Institute (GERMI) have achieved a breakthrough in energy storage technology with the development of a paper-based supercapacitor.
- This cutting-edge supercapacitor, derived from seaweed, boasts remarkable attributes such as being lightweight, biodegradable, and capable of fully charging a device within a mere 10 seconds.
What is a Paper-based Supercapacitor?
- About:
- The paper-based supercapacitor developed by GERMI researchers is the thinnest and most lightweight of its kind.
- By leveraging cellulose nanofibers derived from seaweed, the team successfully created an anodic paper supercapacitor that exhibits exceptional tensile strength, performance, and cost-effectiveness.
- Applications and Business Prospects:
- The applications of this innovative supercapacitor are vast, spanning electronics, memory backup systems, airbags, heavy machinery, and electric vehicles.
- Consequently, it presents a lucrative business prospect for industries seeking high-performance energy storage solutions.
- The technology's versatility and eco-friendly nature make it an attractive option for both manufacturers and consumers.
- The Potential of Marine Cellulose:
- The paper supercapacitor owes its remarkable properties to the marine cellulose-based material derived from seaweed.
- This material holds immense potential for integration into various smart electronic devices.
- Additionally, the cultivation of seaweed can serve as a source of revenue for coastal communities, creating economic opportunities and sustainable development.
- The paper supercapacitor owes its remarkable properties to the marine cellulose-based material derived from seaweed.
What is a Supercapacitor?
- A supercapacitor is an electrochemical charge storage device. They are also known as ultracapacitors.
- It has significant advantages such as high-power density, long durability, and ultrafast charging characteristics as compared to conventional capacitors and Lithium-Ion batteries (LIB).
- Main components of supercapacitors include electrode, electrolyte, separator, and the current collector.
What are Seaweeds?
- About:
- Seaweeds are macroalgae attached to rock or other substrata and are found in coastal areas.
- They are classified as chlorophyta (green), rhodophyta (red) and phaeophyta (brown) on the basis of their pigmentation.
- Among them, chlorophyta holds more potential components — carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and bioactive compounds.
- Significance:
- Nutritional Value: Seaweeds are rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals and dietary fibre.
- For Medicinal Purpose: Many seaweeds contain anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial agents. Certain seaweeds possess powerful cancer-fighting agents.
- Bioindicator: When waste from agriculture, industries, aquaculture and households are let into the ocean, it causes nutrient imbalance leading to algal blooming, the sign of marine chemical damage.
- Seaweeds absorb the excess nutrients and balance out the ecosystem.
- Oxygen Production: Seaweeds, as photosynthetic organisms, play a vital role in marine ecosystems by producing oxygen through photosynthesis, sustaining the respiration and survival of marine life.
- Cellulose Content: Green seaweed that is collected from the Porbandar coast of Gujarat has a high amount of a particular type of cellulose in its cell wall.
- Cellulose is found to be the most suitable biopolymer material for manufacturing paper-based electrode materials such as batteries for energy storage applications.
- Cellulose itself is an insulating material that requires to be coated with conductive material to make a paper-based energy storage device.
- Cellulose is found to be the most suitable biopolymer material for manufacturing paper-based electrode materials such as batteries for energy storage applications.
- Seaweed Cultivation:
- Out of the global seaweed production of around 32 million tons of fresh weight valued around USD 12 billion.
- China produces approximately 57%, Indonesia 28% followed by South Korea, whereas India has a mere share of ~0.01-0.02%.
- By an estimate, if cultivation is done in ~10 million hectares or 5% of the Exclusive Economic Zone area of India, it can provide employment to ~ 50 million people, contribute to national GDP, lead to ocean productivity, abates algal blooms, sequesters millions of tons CO2, and could produce bio-ethanol of 6.6 billion litres.
- Out of the global seaweed production of around 32 million tons of fresh weight valued around USD 12 billion.
Governance
Face Authentication for PM-Kisan Scheme
For Prelims: PM-Kisan scheme, Bhashini, UIDAI, Central Sector Scheme, NIC.
For Mains: PM-Kisan Scheme.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Government of India has rolled out Face Authentication Feature in the PM-Kisan app to enhance the efficiency and accessibility of welfare schemes.
- The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) is also integrating with Bhashini to provide farmers information in their native language.
- Bhashini is the government’s National Public Digital Platform for languages to develop services and products for citizens by leveraging the power of artificial intelligence and other emerging technologies.
What are the Key Points of the Feature?
- About:
- The face authentication feature utilizes the iris data available with the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), which maintains Aadhaar-related information.
- The Ministry collaborated with UIDAI to gain access to this feature, thereby ensuring accuracy and reliability.
- The face authentication feature utilizes the iris data available with the Unique Identification Authority of India (UIDAI), which maintains Aadhaar-related information.
- Benefits:
- Enhanced Accessibility: The face authentication feature eliminates the need for physical biometric verification, enabling farmers to complete the e-KYC process conveniently from their mobile phones.
- Addressing Mobile-Aadhaar Linkage Issues: By utilizing facial recognition, the scheme accommodates farmers whose mobile numbers are not linked with their Aadhaar, ensuring a smoother process for all eligible beneficiaries.
- Simplified Process for Elderly Farmers: The new feature overcomes the challenges faced by elderly farmers, eliminating the need for them to visit designated centers for biometric authentication.
What is PM-KISAN?
- About:
- Under the scheme, the Centre transfers an amount of Rs 6,000 per year, in three equal installments, directly into the bank accounts of all landholding farmers irrespective of the size of their land holdings.
- It was launched in February 2019.
- Under the scheme, the Centre transfers an amount of Rs 6,000 per year, in three equal installments, directly into the bank accounts of all landholding farmers irrespective of the size of their land holdings.
- Funding and Implementation:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Identification of Beneficiaries:
- The entire responsibility of identification of beneficiary farmer families rests with the State / UT Governments.
- Objective:
- To supplement the financial needs of the Small and Marginal Farmers in procuring various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- To protect them from falling in the clutches of moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities.
- PM-KISAN Mobile App:
- The PM-KISAN Mobile App developed and designed by the National Informatics Centre in collaboration with the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology has been launched.
- The farmers can view the status of their application, update or carry out corrections of their Aadhaar cards and also check the history of credits to their bank accounts.
- Achievements So Far:
- Over 11 crore farmers across the country have availed the PM-Kisan scheme, indicating its widespread reach and impact.
- More than 3 crore women farmers have been included in the scheme, highlighting its emphasis on gender inclusivity and women empowerment in the agricultural sector.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- The Aadhaar platform helps service providers authenticate identity of residents electronically, in a safe and quick manner, making service delivery more cost effective and efficient. According to the GoI and UIDAI, Aadhaar is not proof of citizenship.
- However, UIDAI has also published a set of contingencies when the Aadhaar issued by it is liable for rejection. An Aadhaar with mixed or anomalous biometric information or multiple names in a single name (like Urf or Alias) can be deactivated. Aadhaar can also get deactivated upon non-usage of the same for three consecutive years.
Important Facts For Prelims
Textile Wastewater Treatment Plant
Why in News?
In a collaborative effort, NIT Warangal, Prime Textiles, and IMPRINT have developed an eco-friendly solution to treat wastewater in the textile and apparel industry located in Hanumakonda district, Telangana, through a pilot-scale textile effluent treatment plant.
- This innovative technology holds immense potential for transforming toxic wastewater into a valuable irrigation source for nearby agricultural areas, while also offering a sustainable alternative to existing treatment methods.
Why is Efficient Treatment of Textile Effluent Necessary?
- Textile effluent contains high levels of pollutants such as dyes, dissolved solids, suspended solids, and toxic metals.
- Robust and efficient technologies are essential to treat this effluent before it is discharged into the environment.
How Does this Innovative Technology Work?
- The innovative technology developed for treating textile wastewater combines biosurfactants, cavitation, and membrane technologies.
- Biosurfactants:
- Biosurfactants are natural compounds produced by microorganisms, and they possess surface-active properties.
- In the textile effluent treatment plant, biosurfactants are used in the Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR) to aid in the removal of dyes from the wastewater.
- The use of biosurfactants in the MBBR not only improves the efficiency of dye removal but also reduces operational time and cost compared to other biological treatment methods.
- Cavitation:
- Cavitation is an advanced oxidation process (AOP) utilized in the treatment plant.
- It involves the creation of pressure variations in a liquid, leading to the formation and implosion of countless small cavities.
- The cavitation phenomenon helps destroy various pollutants in the wastewater, generating oxidizing radicals in-situ, which play a crucial role in the degradation of pollutants.
- This process contributes to reducing installation costs and the carbon footprint of the treatment plant.
- Membrane Technology:
- Membrane technology is employed in the textile effluent treatment plant to enhance the separation and removal of pollutants.
- The membrane's surface is modified using a sol-gel process with boehmite sol, which reduces the pore size from micro-scale to nano-scale.
- This modification significantly improves the membrane's performance by effectively separating and trapping pollutants, leading to cleaner treated water.
- Biosurfactants:
- Overall Treatment Process:
- The overall treatment process involves coagulation to remove suspended solids' turbidity, biofilm growth in MBBR for heavy metal reduction and degradation of biodegradable pollutants, cavitation for pollutant destruction and energy generation, and the use of surface-modified membranes for efficient pollutant separation.
- The pilot plant, with a capacity of 200 Litres Per Day, successfully treats the effluent for agricultural use and cleaning purposes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is a standard criterion for (2017)
(a) Measuring oxygen levels in blood
(b) Computing oxygen levels in forest ecosystems
(c) Pollution assay in aquatic ecosystems
(d) Assessing oxygen levels in high altitude regions
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) is the amount of Dissolved Oxygen needed by aerobic organisms to decompose organic material in a given sample of water at a certain temperature over a particular time period.
- BOD is one of the most common measures of pollutive organic material in water. BOD indicates the amount of putrescible organic matter present in water. Therefore, a low BOD is an indicator of good quality water, while a high BOD indicates polluted water.
- Sewage and untreated water discharge results in the decreased amount of Dissolved Oxygen as much of the available dissolved oxygen is consumed by aerobic bacteria in the degradation process, robbing other aquatic organisms of the Oxygen they need to live.
- Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Q2. In the context of solving pollution problems, what is/are the advantage/advantages of bioremediation technique? (2017)
- It is a technique for cleaning up pollution by enhancing the same biodegradation process that occurs in nature.
- Any contaminant with heavy metals such as cadmium and lead can be readily and completely treated by bioremediation using microorganisms.
- Genetic engineering can be used to create microorganisms specifically designed for bioremediation.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Bioremediation is a treatment process that uses naturally occurring microorganisms (yeast, fungi, or bacteria) to break down, or degrade, hazardous substances into less toxic or nontoxic substances.
- The microorganisms break down the organic contaminants into harmless products-mainly Carbon Dioxide and water. It is a cost effective, natural process applicable to many common organic wastes. Many bioremediation techniques can be conducted on-site. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- All contaminants cannot be easily treated by bioremediation using microorganisms. For example, heavy metals such as Cadmium and Lead are not readily absorbed or captured by microorganisms. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Genetic engineering can be used to create microorganisms designed for specific purposes for bioremediation. For example, Bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans (the most radioresistant organism known) has been modified to consume and digest Toluene and ionic Mercury from highly radioactive nuclear waste. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option C is the correct answer.
Important Facts For Prelims
Manipur Invokes RBI’s Riot Provisions
Why in News?
Recently, the Manipur government has invoked the Riot Provision of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in response to a Grave Situation in the State marked by riots and violence.
- The order acknowledged the borrowers' inability to repay loans due to the crisis and sought relief measures for the affected individuals.
- While typically applied in areas affected by natural calamities, this move marks the first instance of its utilization in response to a law-and-order situation.
What are the Provisions?
- RBI Directions 2018:
- The Provisions are as per Chapter No. 7 of the "Reserve Bank of India (Relief Measures by Banks in Areas Affected by Natural Calamities) Directions, 2018."
- Whenever RBI advises the banks to extend rehabilitation assistance to the riot/disturbance affected persons, the aforesaid guidelines may broadly be followed by banks for the purpose.
- The Provisions specifically addresses "Riots and Disturbances".
- The rules specify several norms that must be followed for Restructuring the Loans, providing fresh loans and other measures, including KYC norms.
- According to the directions, all the short-term loans, except those overdue at the time of the occurrence of riots, will be eligible for restructuring.
- The Provisions are as per Chapter No. 7 of the "Reserve Bank of India (Relief Measures by Banks in Areas Affected by Natural Calamities) Directions, 2018."
- Applicability:
- The provisions of these Directions shall apply to every Scheduled Commercial Bank (including Small Finance Banks (SFBs) and excluding Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) licensed to operate in India by RBI.
- Crop Loans:
- In the case of crop loans, if the loss ranges between 33% and 50%, borrowers are eligible for a maximum repayment period of two years. If the crop loss exceeds 50%, the repayment period can be extended up to a maximum of five years.
- Additionally, all restructured loan accounts will have a moratorium period of at least one year.
- Long Term Agri Loan:
- If the crop is damaged without harm to productive assets, banks can reschedule installment payments for the affected year and extend the loan period by one year.
- Additionally, banks have the option to postpone interest payments by borrowers. However, if productive assets are also damaged, a new loan may be required.
- Fresh loans:
- Banks will evaluate borrowers' credit needs, follow loan approval procedures, and may offer collateral-free consumption loans up to Rs 10,000 to existing borrowers without personal guarantees, even if the value of assets is lower than the loan amount.
- Relaxation in KYC Norms:
- For the people who have lost their documents due to the calamity of riots, the banks need to open new accounts for such people.
- This will be applicable where the balance in the account does not exceed Rs 50,000. The total credit in the account should not exceed Rs 1,00,000.
What is Loan Restructuring?
- About:
- Loan restructuring allows businesses, people, and governments to avoid bankruptcy by negotiating lower interest rates on their debts. When a debtor has trouble paying their bills, loan restructuring is less expensive than going bankrupt. It can help both the debtor and the creditor.
- Companies can avoid bankruptcy by renegotiating their debt commitments' terms to acquire flexibility quickly and manage their overall debt load.
- Benefits:
- The main goal of debt restructuring is to save and keep the business going.
- It protects the business from creditors through the law.
- If the company doesn't go bankrupt, creditors get back more money. When it comes to people who want to borrow money, a debt-restructuring personal loan helps creditors get better results.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following statements best describes the term ‘Scheme for Sustainable Structuring of Stressed Assets (S4A)’, recently seen in the news? (2017)
(a) It is a procedure for considering ecological costs of developmental schemes formulated by the Government.
(b) It is a scheme of RBI for reworking the financial structure of big corporate entities facing genuine difficulties.
(c) It is a disinvestment plan of the Government regarding Central Public Sector Undertakings.
(d) It is an important provision in ‘The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code’ recently implemented by the Government.
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Kalasa Banduri Project on Mahadayi River
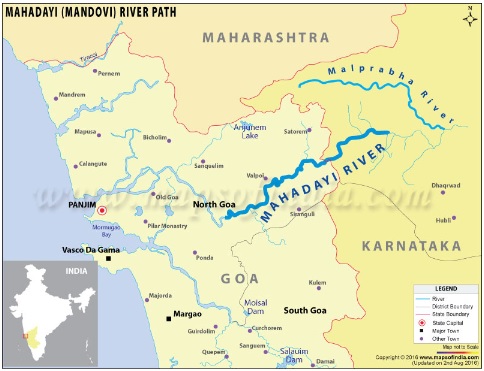
Tenders for the controversial Kalasa Banduri Project, initiated by the previous Karnataka government just before its Assembly elections, might face difficulties due to the absence of forest and environment clearance.
Kalasa-Banduri project aims to improve the drinking water supply to the Belagavi, Dharwad, Bagalkot and Gadag districts in Karnataka. It involves building barrages across Kalasa and Banduri, two tributaries of the Mahadayi River to divert water to the Malaprabha river (a tributary of Krishna River).
Mahadayi or Mhadei, the west-flowing river, originates in Bhimgad Wildlife Sanctuary (Western Ghats), Belagavi district of Karnataka. The river is Spread across the Districts of Goa, Karnataka and Maharashtra.
The Kalasa-Banduri project is controversial due to inter-state water disputes, environmental concerns, and opposition from local communities.
Read More: Mahadayi River & Kalasa-Banduri Project
Assam Flood & Beki River
According to a daily flood report by the Assam State Disaster Management Authority (ASDMA), the flood situation in Assam remains critical, with approximately 20 districts being affected by continuous rainfall.
The tributary of the Brahmaputra River, Beki, is currently flowing above the danger mark. The floodwaters have caused significant damage to various infrastructure, including embankments, roads, and bridges.
The Beki River, originating in Bhutan (also known as Kurissu River), is one of the right-bank tributaries of the River Brahmaputra. A significant portion of this river flows through Assam. It serves as a source of livelihood and mode of transport for the many communities in Assam.
Read More: Brahmaputra River
Biodegradable Utensils: BIS
Recently, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) published IS 18267: 2023 "Food Serving Utensils Made from Agri By-Products – Specification”, aimed at reducing plastic pollution and promoting sustainability.
The standard covers various aspects, including raw materials, manufacturing techniques, performance, and hygiene requirements for the production of biodegradable utensils. These utensils are free from harmful additives and ensure consumer well-being. The standard also creates economic opportunities for farmers and supports sustainable agricultural practices, contributing to rural development and promoting circular economy.
BIS has been established for the harmonious development of the activities of standardisation, marking and quality certification of goods and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto. It was established by the BIS Act, 1986 and works under the aegis of the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution. A new BIS Act 2016 was brought into force with effect from October 2017. The Act establishes the BIS as the National Standards Body of India.
Read More: Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), Plastic Pollution
Canary Islands
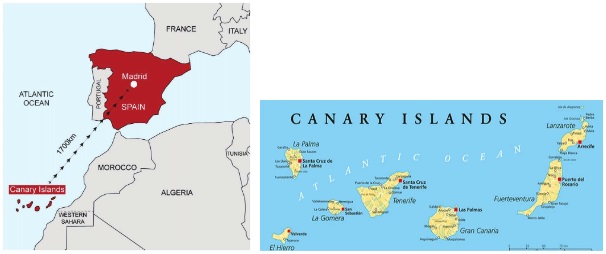
According to information shared by two organizations that focus on migration, over 30 migrants died when a small boat traveling towards Spain's Canary Islands sank.
The Canary Islands of Spain consist of an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean. Canaries comprise the Spanish provinces of Las Palmas and Santa Cruz de Tenerife. The Canary Islands were formed by volcanic eruptions millions of years ago.
Read More: Canary Islands