Governance
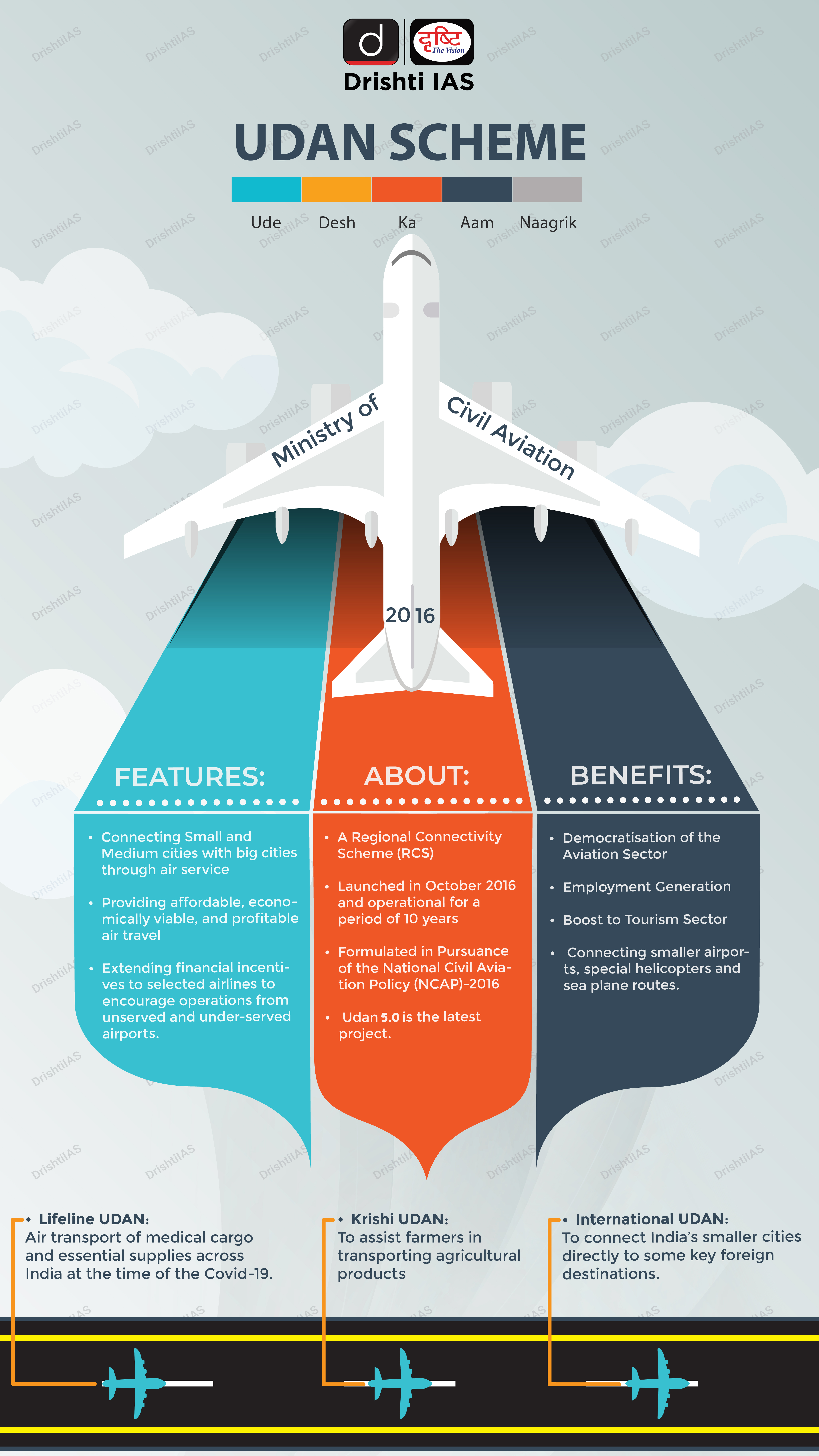
UDAN 5.0 Scheme
For Prelims: UDAN Scheme, UDAN 5.0, Viability Gap Funding (VGF), Regional Connectivity Fund (RCF)
For Mains: UDAN Scheme: Features and achievements, UDAN 5.0
Why in News?
Recently, the government has launched the fifth round of the Regional Connectivity Scheme – UDAN (UDAN 5.0).
What is UDAN (Ude Desh ka Aam Nagrik) Scheme?
- About:
- The scheme was launched by the Ministry of Civil Aviation for regional airport development and regional connectivity enhancement.
- It is a part of the National Civil Aviation Policy 2016.
- The scheme is applicable for a period of 10 years.
- Objectives:
- Improve the air connectivity to remote and regional areas of India.
- Development of remote areas and enhancing trade and commerce and tourism expansion.
- Enable common people to access air travel with affordable rates.
- Employment creation in the aviation sector.
- Key Features:
- Under the scheme, airlines have to cap airfares for 50% of the total seats at Rs. 2,500 per hour of flight.
- This would be achieved through:
- A financial stimulus in the form of concessions from Central and State governments and airport operators and
- Viability Gap Funding (VGF) – A government grant provided to the airlines to bridge the gap between the cost of operations and expected revenue.
- Regional Connectivity Fund (RCF) was created to meet the viability gap funding requirements under the scheme.
- The partner State Governments (other than UTs and NER states where contribution will be 10%) would contribute a 20% share to this fund.
- Previous Phases of the Scheme:
- Phase 1 was launched in 2017, with the objective of connecting underserved and unserved airports in the country.
- Phase 2 was launched in 2018, with the aim of expanding air connectivity to more remote and inaccessible parts of the country.
- Phase 3 was launched in November 2018, with the focus on enhancing air connectivity to hilly and remote regions of the country.
- Phase 4 of the UDAN scheme was launched in December 2019, with a focus on connecting islands and other remote areas of the country.
- Key Features of UDAN 5.0:
- It focuses on Category-2 (20-80 seats) and Category-3 (>80 seats) aircrafts.
- There is no restriction on the distance between the origin and the destination of the flight.
- VGF to be provided will be capped at 600 km stage length for both Priority and Non-Priority areas; earlier capped at 500 km.
- No predetermined routes would be offered; only Network and Individual Route Proposal proposed by airlines will be considered.
- The same route would not be awarded to a single airline more than once, whether in different networks or in the same network.
- Exclusivity of operation provided to an airline will be withdrawn if the average quarterly Passenger Load Factor (PLF) is higher than 75% for four continuous quarters.
- This has been done to prevent exploitation of the monopoly on a route.
- Airlines would be required to commence operations within 4 months of the award of the route; earlier this deadline was 6 months.
- Novation process for routes from one operator to another has been simplified and incentivized.
- Novation - The process of substituting an existing contract with a replacement contract, where the contracting parties reach a consensus.
What are Achievements under UDAN Scheme?
(As per the data released in Aug 2022 by the Ministry of Civil Aviation)
- The scheme has also been able to provide a fair amount of air connectivity to Tier-2 and Tier-3 cities at affordable airfares and has transformed the way travelling was done earlier.
- The number of operational airports has gone up to 141 from 74 in 2014.
- 68 underserved/unserved destinations which include 58 Airports, 8 Heliports & 2 Water Aerodromes have been connected under UDAN scheme.
- With 425 new routes initiated, UDAN has provided air connectivity to more than 29 States/ UTs across the country.
- More than one crore passengers have availed the benefits of this scheme.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Examine the development of Airports in India through joint ventures under Public–Private Partnership (PPP) model. What are the challenges faced by the authorities in this regard? (2017)
International Relations
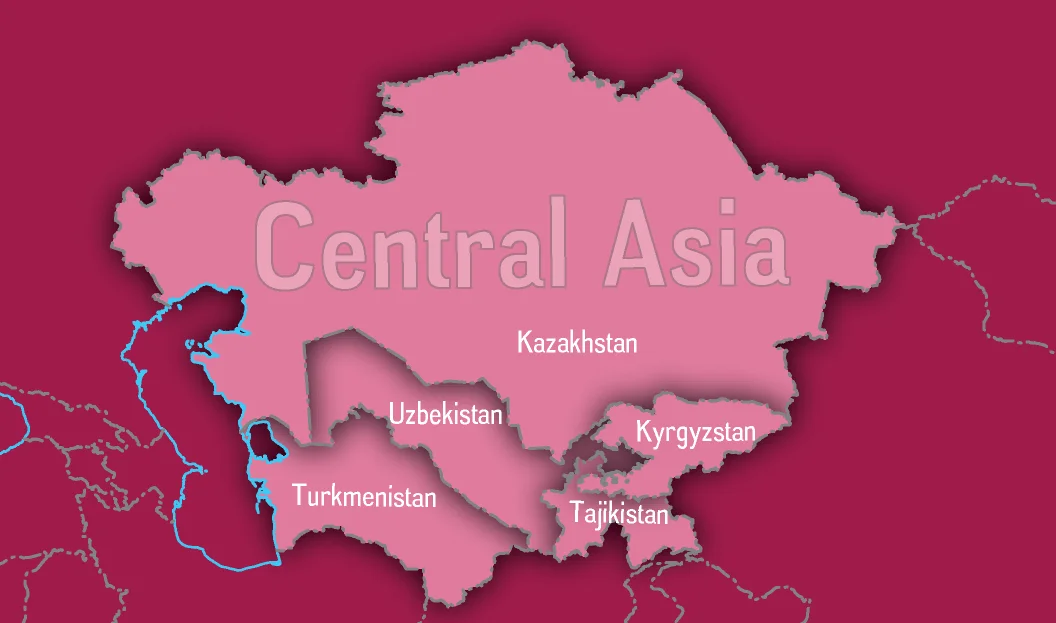
China’s Outreach in Central Asia
For Prelims: C+C5, Buddhism, Silk Route, SCO, Russia-Ukraine, CSTO
For Mains: China’s Outreach in Central Asia and India’s Stand.
Why in News?
Recently, China has conducted a meeting of trade ministers of the grouping known as C+C5 — China and the five Central Asian republics, namely Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Kyrgyzstan.
- It was the latest in a series of diplomatic engagements by China with the region since the Russian invasion of Ukraine.
What is the China-Central Asia Engagement?
- C+C5:
- The first C+C5 summit held in Jan 2022 marked the 30th anniversary of diplomatic relations between China and Central Asian nations.
- China's historical trade and cultural links with the region date back to the ancient Silk Route.
- Significance for China:
- The region provides China with a market for cheap exports and overland access to markets in Europe and West Asia.
- Central Asia is resource-rich, with massive reserves of gas, oil, and strategic minerals such as uranium, copper, and gold.
- China has also prioritized its relationship with these countries to ensure peace in Xinjiang Autonomous Region, which forms its frontier with Central Asia.
- BRI and Investments:
- China has been investing heavily in Central Asia through its Belt and Road Initiative, which includes projects in oil and gas, transportation, digital technology, and green energy.
- While China's investments have provided opportunities for economic growth in the region, there has also been resentment towards China due to its treatment of Muslims in Xinjiang and concerns about its increasing presence and land acquisitions.
- Despite this, Central Asian governments have not joined international campaigns against China's treatment of its Muslim minority.
- China is now the region's foremost trading partner, with talks underway for further transport and logistics projects linking all countries in the region to China's seaports.
How are C5s Balancing their Relationships with Russia, China and West?
- Heavily Dependent on Russia:
- The region is heavily reliant on Russia, which is also the main provider of security through the CSTO (Collective Security Treaty Organisation).
- However, the CSTO's unity is weakening, and the conflict in Ukraine has raised concerns about the consequences of Russia's security relationship with Central Asia.
- In 2022 Kyrgyzstan cancelled a CSTO military exercise that was to be held on its territory last year, and none of the five Central Asian countries have openly taken Russia's side in the conflict.
- Nevertheless, Russia has increased its trade with the region as it seeks to reduce its dependence on European imports.
- China’s Increasing Engagement:
- China has been increasing its engagement with Central Asia, leading some to speculate that Beijing is taking advantage of Russia's preoccupation with Ukraine to expand its influence in the region.
- While Russia may be concerned about Chinese expansion, there was no visible indication of this.
- Seeking towards West:
- Central Asian countries are seeking to develop trade relations with the West, including the European Union and the United States.
- However, the region's landlocked geography and limited transport infrastructure have hindered this effort.
What is India’s Stake in Central Asia?
- Cultural and Ancient Ties:
- The Silk Route connected India with Central Asia from the 3rd century BC to the 15th century AD. From the export of Buddhism to the lasting influence of Bollywood, India has shared old and deep cultural ties with the region.
- Security:
- In December 2022, officials from Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan arrived in India for the first India-Central Asia meeting of national security advisors.
- It highlighted the India-Central Asia relationship, emphasizing their common shared interests, such as stabilizing the security situation in Afghanistan and reinforcing territorial integrity.
- India has also attempted to boost its security presence in the region by renovating military bases in Tajikistan.
- If operational, the airbases would offer India a strategic advantage against its two adversaries: China and Pakistan.
- Tajikistan is located close to the Wakhan Corridor, which connects Afghanistan and China, as well as Pakistan Occupied Kashmir.
- In December 2022, officials from Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan arrived in India for the first India-Central Asia meeting of national security advisors.
- Extended Neighborhood Policy:
- In 2022 India demonstrated its commitment to its “Extended Neighborhood Policy (ENP),” which calls to diversify its geopolitical partners and diplomatic goals, and its willingness to engage its Central Asian partners on a multitude of fronts.
- The ENP was launched in 2014 and seeks to build a web of partnerships and economic cooperation with neighboring countries.
- The policy emphasizes India's commitment to promoting regional stability, peace, and prosperity through mutually beneficial cooperation with its neighbors.
- In 2022 India demonstrated its commitment to its “Extended Neighborhood Policy (ENP),” which calls to diversify its geopolitical partners and diplomatic goals, and its willingness to engage its Central Asian partners on a multitude of fronts.
- Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO):
- India joined SCO, as a full member in 2017.
- SCO also includes Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan.
- The grouping provides India with a forum to establish security relationships with Astana, Bishkek, and Tashkent, adding on to robust ties with Tajikistan.
- India joined SCO, as a full member in 2017.
- Connectivity as a Challenge:
- While India has trading ties with the C5, it is hobbled by the absence of a land route to Central Asia, with Pakistan denying it passage and Afghanistan being uncertain territory after the Taliban takeover.
- The Chabahar port in Iran offers an alternative route, but it is not fully developed yet.
- There have been suggestions that India should provide connectivity for people and trade in Central Asia through “air corridors”, as it had done for Afghanistan.
- While India has trading ties with the C5, it is hobbled by the absence of a land route to Central Asia, with Pakistan denying it passage and Afghanistan being uncertain territory after the Taliban takeover.
Way Forward
- India must prioritize building long-lasting and reliable partnerships with Central Asian states, particularly in the face of ongoing geopolitical challenges. Security will remain a focal point for bilateral relations, but it is important for India to establish links through transit, trade, investment, and people-to-people connections.
- India should take advantage of the vulnerabilities that the region has been exposed to due to crises such as Russia's war in Ukraine and the Taliban takeover in Afghanistan.
- Joint counterterrorism efforts can help New Delhi establish itself as a consistent partner and monitor adversaries from a closer range.
- However, India must also work on other issues to supplement the security aspect and ensure that the relationship with Central Asia is not susceptible to geopolitical, economic, or domestic pressure.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
(a) India’s trade with African countries will enormously increase.
(b) India’s relations with oil-producing Arab countries will be strengthened.
(c) India will not depend on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
(d) Pakistan will facilitate and protect the installation of a gas pipeline between Iraq and India.
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. A number of outside powers have entrenched themselves in Central Asia, which is a zone of interest to India. Discuss the implications, in this context, of India’s joining the Ashgabat Agreement. (2018)
Governance
Logistics Performance Index 2023
For Prelims: Logistics Performance Index (LPI), National Logistics Policy (NLP), PM Gati Shakti initiative.
For Mains: PM Gati Shakti, Significance of National Logistics Policy, Significance Investment in infrastructure for Economic Growth
Why in News?
India has climbed six places on the World Bank's Logistic Performance Index (LPI) 2023, now ranking 38th in the 139 countries index.
- This is a significant improvement from its previous ranking of 44th in 2018 and 54th in 2014.
- Earlier, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry released the Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS) Report 2022.
What is LPI?
- The LPI is an interactive benchmarking tool developed by the World Bank Group.
- It helps countries identify the challenges and opportunities they face in their performance of trade logistics and what they can do to improve their performance.
- It measures the ease of establishing reliable supply chain connections and the structural factors that make it possible. The LPI considers 6 parameters to evaluate logistics performance, namely:
- Customs performance
- Infrastructure quality
- Ease of arranging shipments
- Logistics services quality
- Consignment tracking and tracing
- Timeliness of shipments
- The LPI was reported by the World Bank every two years from 2010 to 2018 with a break in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic and a restructuring of the index methodology, eventually came out in 2023.
- LPI 2023 allows for comparison across 139 countries and for the first time, LPI 2023 measures the speed of trade with indicators derived from big datasets tracking shipments.
What Aspects Led to India's Improved Logistics Performance?
- Policy Interventions:
- PM Gati Shakti Initiative: In October 2021, government announced the PM Gati Shakti initiative, a National Master Plan for multimodal connectivity.
- This initiative aims to reduce logistics costs and boost the economy by 2024-25.
- National Logistics Policy (NLP): The PM launched the National Logistics Policy (NLP) in 2022 to ensure quick last-mile delivery, end transport-related challenges, save time and money for the manufacturing sector and ensure desired speed in the logistics sector.
- These policy interventions are fructifying, which can be seen in India's jump in LPI and its other parameters.
- PM Gati Shakti Initiative: In October 2021, government announced the PM Gati Shakti initiative, a National Master Plan for multimodal connectivity.
- Infrastructure Improvements:
- According to the LPI report, India's rank moved up five places in the infrastructure score from 52nd in 2018 to 47th in 2023.
- The government has invested in trade-related soft and hard infrastructure, connecting port gateways on both coasts to the major economic centers located in the interior regions of the country.
- This investment has paid off, with India climbing to the 22nd spot for international shipments in 2023 from 44th in 2018.
- Technology's Role:
- Technology has been a critical component of India's logistics performance improvement efforts.
- Under a public-private partnership, the government has implemented a supply chain visibility platform, which has contributed to remarkable reductions in delays.
- NICDC Logistics Data Services Limited applies radio frequency identification tags to containers and offers consignees end-to-end tracking of their supply chain.
- The report also states that emerging economies like India are leapfrogging advanced countries due to modernization and digitalization.
- Reduced Dwell Time:
- Dwell time is how long a vessel spends at a specific port or terminal. It may also refer to the amount of time that a container or cargo spends at a port or terminal before being loaded onto a vessel or after being unloaded from a vessel.
- India's very low dwell time (2.6 days) is one example of how the country has improved its logistics performance.
- According to the report, the average dwell time for containers between May and October 2022 was 3 days for India and Singapore, much better than in some of the industrialized countries.
- The dwell time for the U.S. was 7 days and for Germany, it was 10 days.
- With the introduction of cargo tracking, dwell time in the eastern port of Visakhapatnam fell from 32.4 days in 2015 to 5.3 days in 2019.
- Dwell time is how long a vessel spends at a specific port or terminal. It may also refer to the amount of time that a container or cargo spends at a port or terminal before being loaded onto a vessel or after being unloaded from a vessel.
What are India’s Initiatives Related to Logistics?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “Investment in infrastructure is essential for more rapid and inclusive economic growth.” Discuss in the light of India’s experience. (2021)
Social Justice
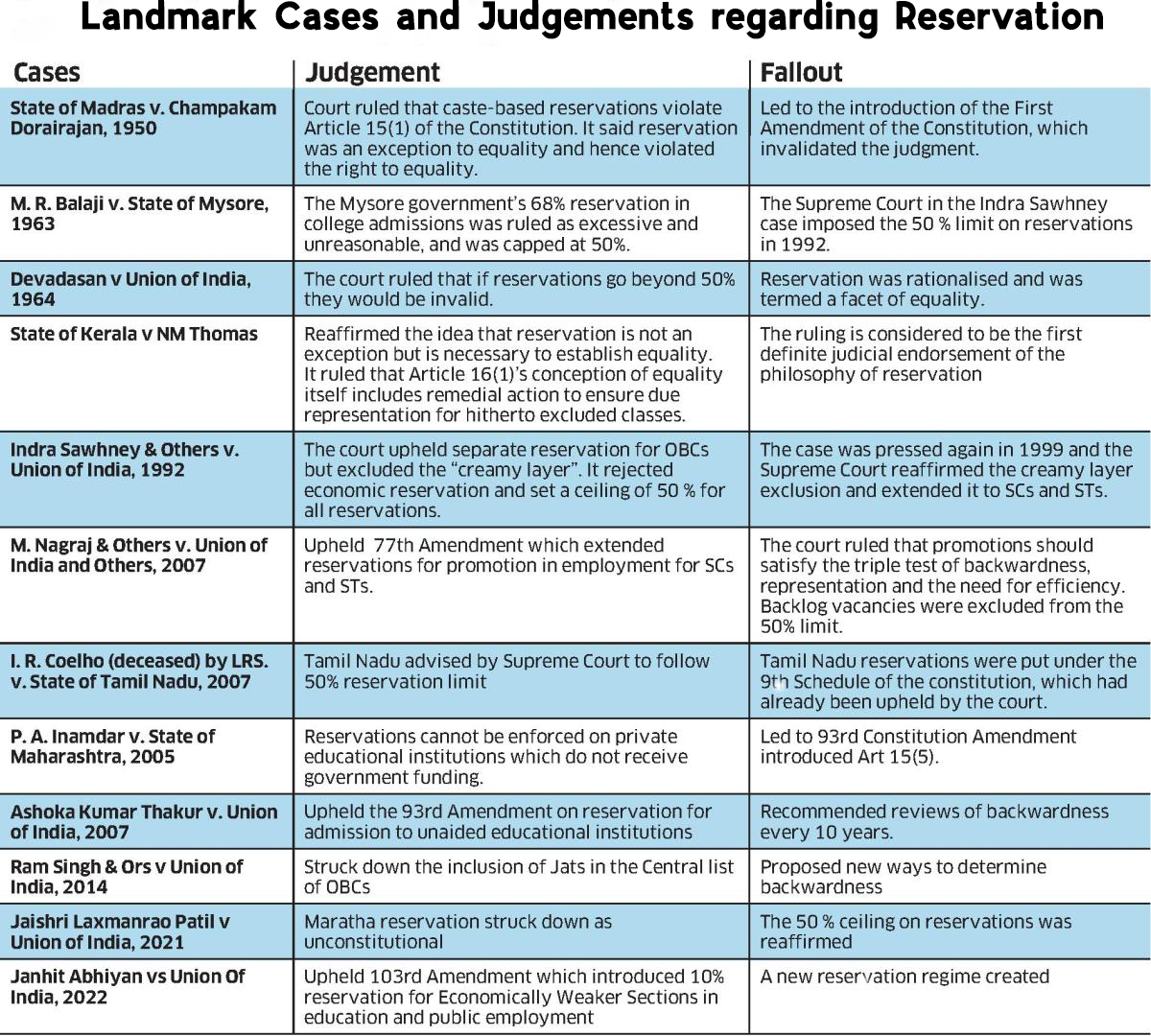
Mandal Commission
For Prelims: Article 15, Article 16, Reservation, Indira Sawney Case, OBC Reservation, Mandal Commission, Rohini G Commission
For Mains: Mandal Commission, Reservation: Benefits and Challenges.
Why in News?
The second phase of the caste survey beginning in Bihar and several other political debates have brought Mandal Politics once again in news.
What is Mandal Politics and Mandal Commission?
- About:
- Mandal politics refers to a political movement that emerged in the 1980s, advocating for the inclusion of socially and economically disadvantaged communities, particularly the Other Backward Classes (OBCs), in government jobs and educational institutions.
- The movement was named after the Mandal Commission.
- Mandal Commission:
- The Mandal Commission or the second Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Commission, was established in India in 1979 with a mandate to "identify the socially or educationally backward classes" of India.
- It was headed by B. P. Mandal and submitted its report in 1980 and was implemented in 1990.
- The Commission reported that 52% of the country’s population was comprised of OBCs. Initially, the commission argued that the percentage of reservations in government service should match this percentage.
- However, this would have gone against the Supreme Court ruling in M.R. Balaji vs State of Mysore case (1963) which had laid down a limit of 50% on. There was already a 22.5% reservation for SCs and STs.
- Therefore, the figure of reservation for OBCs was capped at 27% which when added to keep the reservation below the 50% mark.
- The Commission also identified backward classes among non-Hindus.
- The Mandal Commission or the second Socially and Educationally Backward Classes Commission, was established in India in 1979 with a mandate to "identify the socially or educationally backward classes" of India.
- Recommendations of Mandal Commission:
- OBCs must be provided a reservation of 27% in public sector and government jobs.
- They should be provided with the same 27% reservation in promotions at all levels of public services.
- The reserved quota, if unfilled, should be carried forward for a period of 3 years.
- OBCs should be provided age relaxation similar to SCs and STs.
- Reservations to be made in PSUs, banks, private sector undertakings receiving government grants, colleges, and universities.
- The government to make the necessary legal provisions to implement these recommendations.
- Impact of Mandal Commission:
- Implementation of Mandal Commission by the government resulted in a widespread protest where students committed self-immolation in protest when the government showed its intent to implement it.
- The implementation was finally challenged in Indra Sawhney vs Union of India case.
What did the SC Rule in Indira Sawhney Case?
- In this case the Supreme Court held the 27% reservations for OBCs as constitutionally valid but with certain conditions:
- The court held that the reservation must be in the four walls of 50% cap and should not be extended in promotions.
- The concept of creamy layer was also introduced by the court to exclude well-off people from the community.
- The carry forward rule (by which unfulfilled vacancies are filled in the upcoming year) should not breach 50% ceiling.
What are the Merits of Mandal Commission?
- Increased Representation: The Mandal Commission helped in increasing the representation of SEBCs in government jobs and educational institutions.
- According to Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, OBC representation against total appointment through direct recruitment was consistently above 27% during 2014-2021.
- Access to Education: The reservation policy enabled many OBC students to gain access to higher education. This resulted in a significant increase in the number of OBC students in universities and colleges.
- According to the Ministry of Social Justice during the period of 2014-2021, the enrolment of OBCs in Higher Educational Institutions has been consistently increasing since 2014-15.
- Social Justice: The Mandal Commission's recommendations were based on the principles of social justice and aimed at providing equal opportunities to all sections of society, especially those who have been historically disadvantaged.
What are the Demerits of Mandal Commission?
- Limited Impact on Upliftment: The impact has been limited to a very few communities. According to the Justice Rohini G. Commission, out of almost 6,000 castes and communities in the OBCs, only 40 such communities had gotten 50% of reservation benefits for admission in central educational institutions and recruitment to the civil services.
- Politicisation: The politicians have often used the Reservation as their vote bank politics. During 1980s, the Mandal Commission was highly politicized giving a new form of Politics- Mandal politics.
- Even today, it is used as a political tool. Recently, a politician while campaigning in Karnataka has demanded to lift 50% limit on SC/ST/OBC reservation.
- Negative Impact on Merit: The reservation policy led to a negative impact on merit as many deserving candidates were left out, and the seats were filled by candidates with lesser merit.
Way Forward
- Periodic Review of Reservation Policy: The policy must be reviewed periodically to assess its impact as directed by the Supreme Court in Indira Sawhney vs Union of India case (1992).
- Improve Early Level of Education: The government must improve education at earlier levels so that the reservations at higher levels could easily be phased out.
- Increase Job Opportunities in Private Sector: The government should thrive to increase job opportunities in private sector to reduce dependence on public sector and reservation for employment.
Biodiversity & Environment
State of the Global Climate 2022: WMO
For Prelims: WMO, GHG, Glaciers, Ocean Acidification, Rainfall, Heatwave
For Mains: State of the Global Climate 2022.
Why in News?
Recently, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) has released the State of the Global Climate Report 2022.
- The report focuses on key climate indicators – Greenhouse Gasses, Temperatures, Sea level rise, Ocean Heat and Acidification, Sea ice and Glaciers. It also highlights the impacts of climate change and extreme weather.
- Earlier, the WMO released the provisional State of the Global Climate report, 2022.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Temperature
- Global mean temperature in 2022 was 1.15 °C above the 1850-1900 average.
- The years 2015 to 2022 were the eight warmest in the instrumental record back to 1850.
- This was despite three consecutive years of a cooling La Niña – such a “triple-dip” La Niña has happened only three times in the past 50 years.
- Greenhouse Gasses:
- Concentrations of the three main GHG, Carbon dioxide, Methane, and Nitrous oxide, reached record highs in 2021.
- The annual increase in methane concentration from 2020 to 2021 was the highest on record.
- Sea Level Rise:
- Global mean sea level (GMSL) continued to rise in 2022, reaching a new record high for the satellite altimeter record.
- For the period 2005-2019, total land ice loss from glaciers, Greenland, and Antarctica contributed 36% to the GMSL rise, and ocean warming contributed 55%.
- Ocean Heat:
- Ocean heat content reached a new record high in 2022.
- Around 90% of the energy trapped in the climate system by greenhouse gases goes into the ocean, somewhat ameliorating even higher temperature increases but posing risks to marine ecosystems.
- Ocean Acidification:
- CO2 reacts with seawater resulting in a decrease of pH referred to as ‘ocean acidification’, threatening organisms and ecosystem services.
- The IPCC Sixth Assessment Report concluded that “There is very high confidence that open ocean surface pH is now the lowest it has been for at least 26 [thousand years] and current rates of pH change are unprecedented since at least that time.
- Sea Ice:
- Sea ice in Antarctica dropped to 1.92 million km2 in February 2022, the lowest level on record and almost 1 million km2 below the long-term (1991-2020) mean.
- Glaciers:
- Glaciers are losing a lot of ice, with a thickness change of over (-) 1.3 meters on average between October 2021 and October 2022, which is much larger than the average of the past decade.
- The European Alps saw record glacier melt due to a lack of winter snow, dust from the Sahara in March 2022, and heatwaves from May to early September.
What are the Impacts of Such Record Highs In Climate Indicators?
- Drought in East Africa:
- Rainfall has been below-average in five consecutive wet seasons, the longest such sequence in 40 years. As of January 2023, it was estimated that over 20 million people faced acute food insecurity across the region, under the effects of the drought and other shocks.
- Record Breaking Rain in Pakistan:
- Total damage and economic losses were assessed at USD 30 billion.
- July (181% above normal) and August (243% above normal) were each the wettest on record nationally.
- The flooding in Pakistan affected some 33 million people, including about 8,00,000 Afghan refugees hosted in affected districts.
- Total damage and economic losses were assessed at USD 30 billion.
- Heat Waves in Europe:
- In some areas, extreme heat was coupled with exceptionally dry conditions. Excess deaths associated with the heat in Europe exceeded 15, 000 in total across Spain, Germany, the UK, France, and Portugal.
- China had its most extensive and long-lasting heatwave since national records began, extending from mid-June to the end of August and resulting in the hottest summer on record by a margin of more than 0.5 °C. It was also the second-driest summer on record.
- Food Insecurity:
- As of 2021, 2.3 billion people faced food insecurity, of which 924 million people faced severe food insecurity.
- Projections estimated 767.9 million people facing undernourishment in 2021, 9.8% of the global population.
- Half of these are in Asia and one third in Africa.
- Pre-Monsoon Heat Waves in India and Pakistan:
- Pre-monsoon season Heatwaves in India and Pakistan in caused a decline in crop yields.
- This, combined with the banning of wheat exports and restrictions on rice exports in India after the start of the conflict in Ukraine, threatened the availability, access, and stability of staple foods within international food markets and posed high risks to countries already affected by shortages of staple foods.
- Displacement:
- In Somalia, almost 1.2 million people became internally displaced by the catastrophic impacts of drought on pastoral and farming livelihoods and hunger during the year, of whom more than 60,000 people crossed into Ethiopia and Kenya during the same period. Concurrently, Somalia was hosting almost 35,000 refugees and asylum seekers in drought-affected areas.
What is the World Meteorological Organization (WMO)?
- The WMO is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 192 Member States and Territories.
- India is a member of WMO.
- It originated from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which was established after the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress.
- Established by the ratification of the WMO Convention on 23rd March 1950, WMO became the specialized agency of the United Nations for meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology and related geophysical sciences.
- WMO is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
Important Facts For Prelims
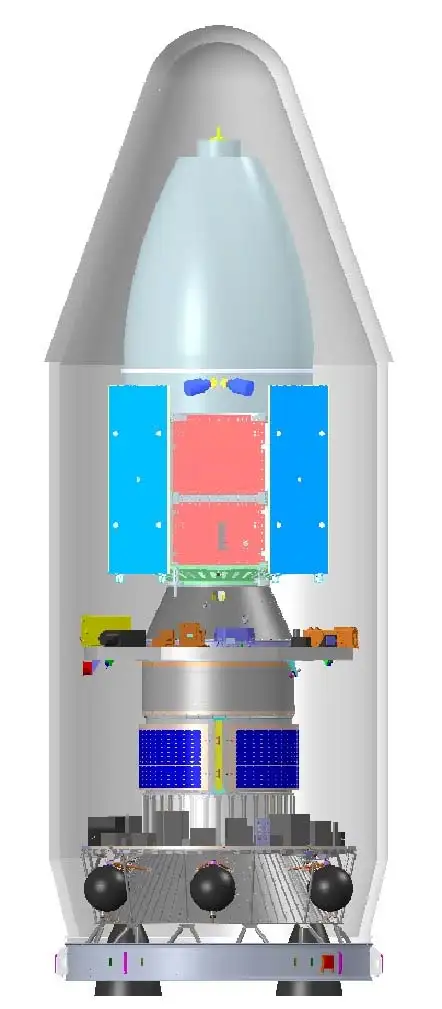
PSLV C55 and TeLEOS-2 Satellite
Why in News?
Recently, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organization) has successfully launched the PSLV (Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle)-C55/TeLEOS-2 mission from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota in Andhra Pradesh.
What is the PSLV C55/TeLEOS-2 Mission?
- About:
- This is the 57th flight of PSLV and 16th mission using the PSLV Core Alone configuration (PSLV-CA).
- It is a dedicated commercial mission through NSIL (NewSpace India Limited) with TeLEOS-2 as primary satellite and Lumelite-4 as a co-passenger satellite, both belonging to Singapore.
- The scientists used PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-2 (POEM-2) as an orbital platform to carry out the scientific experiments through non-separating payloads carried by it.
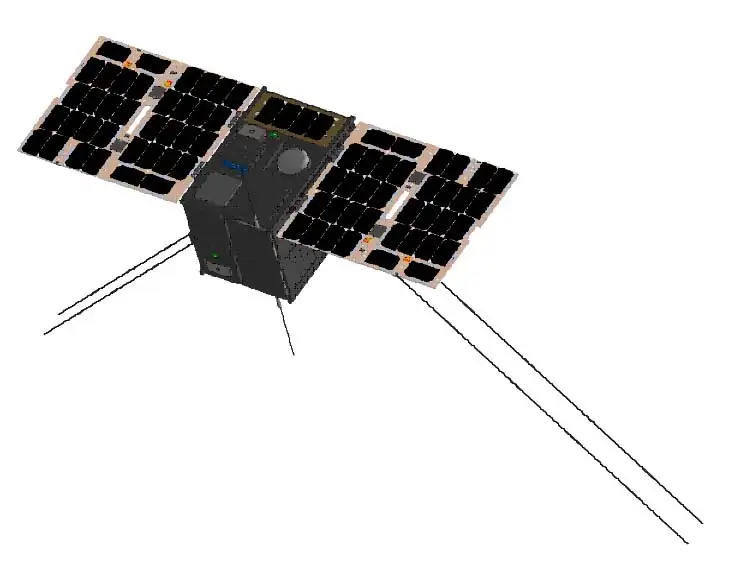
- TeLEOS-2:
- It is an Earth Observation Satellite (EOS) and will be the primary satellite being carried by the rocket.
- In 2015, ISRO launched TeLEOS-1, which was launched into a low Earth orbit for remote sensing applications. ISRO has so far launched nine satellites belonging to Singapore.
- TeLEOS-2 carries a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payload capable of imaging at 1m full-polarimetric resolution. It will be able to provide all-weather day and night coverage.
- SAR is a type of active radar imaging technology that uses the motion of the radar antenna to create a high-resolution 3D image of the target area.
- It is an Earth Observation Satellite (EOS) and will be the primary satellite being carried by the rocket.
- LUMILITE-4:
- It is an advanced 12U satellite developed for the technological demonstration of the High-Performance Space-borne VHF Data Exchange System (VDES).
- "12U" refers to a standardized form factor for CubeSats, which are small satellites with a modular design.
- In the 12U form factor, the CubeSat measures 24 x 24 x 36 cm and has a volume of 20.7 liters.
- It aims to augment Singapore’s e-navigation maritime safety and benefit the global shipping community.
- It is the co-passenger satellite being sent along with TeLEOS-2
- It is an advanced 12U satellite developed for the technological demonstration of the High-Performance Space-borne VHF Data Exchange System (VDES).
What is POEM?
- POEM is an experimental mission by ISRO which performs in-orbit scientific experiments during the 4th stage of the PSLV launch vehicle as an orbital platform.
- The PSLV is a four-stage rocket where the first three spent stages fall back into the ocean, and the final stage (PS4) — after launching the satellite into orbit — ends up as space junk.
- POEM has a dedicated Navigation Guidance and Control (NGC) system for attitude stabilization, which stands for controlling the orientation of any aerospace vehicle within permitted limits.
- The NGC will act as the platform’s brain to stabilize it with specified accuracy.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors; and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)
Important Facts For Prelims
India's Fighter Jets
Why in News?
The Indian Air Force (IAF), one of the world’s largest Air Forces, face challenges in modernizing its fleet, as delays in procurement have led to a shortfall in its fighter squadrons.
- An IAF representative informed the Parliamentary standing committee on Defence that the IAF has only 31 fighter squadrons, against the sanctioned strength of 42.
What is Fighter Squadron?
- About:
- A fighter squadron is a military unit consisting of fighter aircraft and the pilots who fly them.
- It is a fundamental component of an air force and is responsible for conducting air operations in a combat zone.
- A typical fighter squadron consists of 18 fighter aircraft.
- They are an essential component of any modern air force and are tasked with a wide range of missions, including air superiority, and ground attack.
- A fighter squadron is a military unit consisting of fighter aircraft and the pilots who fly them.
- Reasons for the Shortfall:
- Delays in procurement have contributed to the shortfall, as many of the IAF's fighter jets are ageing and need to be replaced.
- Status of the Procurement of Fighter Jets:
- India has an ambitious plan to acquire over 500 fighter jets, with most of them being for the IAF.
- Many of these jets are still in various stages of development, and their manufacturing and timely deliveries are critical.
- The IAF has in total contracted 272 SU-30s.
- A deal to procure 12 additional SU-30MKI aircrafts to replace the ones lost in accidents and 21 additional MIG-29s from Russia has been stuck, though both IAF and Russian officials state that it has only been delayed but is on track.
- India has an ambitious plan to acquire over 500 fighter jets, with most of them being for the IAF.
What Different Types of Aircrafts India Has?
- Light Combat Aircraft (LCA):
- Designed to replace ageing Mig 21 fighter planes
- Developed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) under the Department of Defence Research and Development.
- Manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- Lightest, smallest and tailless multi-role supersonic fighter aircraft in its class.
- Can carry a range of air-to-air, air-to-surface, precision-guided weapons.
- Air-to-air refueling capability, maximum payload capacity of 4000 kg, maximum speed of Mach 1.8 and Range of 3000 km.
- Multi-Role Fighter Aircraft (MRFA):
- Designed to perform various missions such as air-to-air combat, air-to-ground attack, and electronic warfare.
- IAF pursuing the procurement of 114 MRFA to replace the aging fleet of Soviet-era MiG-21.
- Procurement will be carried out under the Make in India initiative.
- Selected vendor will have to set up a production line in India and transfer technology to local partners.
- MiG-21:
- Supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft designed by the erstwhile USSR in the 1950s.
- Widely used combat aircraft in history, with more than 11,000 units built and over 60 countries operating it.
- IAF acquired its first MiG-21 in 1963 and has since inducted 874 variants of the aircraft
- Involved in several wars and conflicts involving India. Involved in many accidents and crashes, earning it the nickname “flying coffin”.
- IAF plans to phase out the MiG-21 by 2024 and replace it with more modern fighters.
- Supersonic jet fighter and interceptor aircraft designed by the erstwhile USSR in the 1950s.
- Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA):
- An Indian program to develop a 5thgeneration stealth, multirole combat aircraft for the IAF and the Indian Navy
- Designed and developed by the ADA of the DRDO, in collaboration with Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL) and other public and private partners.
- Expected to have features such as a stealth airframe, internal weapons bay, advanced sensors, data fusion, supercruise capability and swing-role performance
- Started in 2008 as a successor to the Sukhoi Su-30MKI
- First flight planned for 2025 and production is expected to start after 2030.
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI:
- Twin-engine, two-seat, multirole fighter aircraft developed by Russia’s Sukhoi and built under license by India’s HAL for the IAF.
- Designed to perform air superiority, ground attack, electronic warfare, and maritime strike missions
- Entered service with the IAF in 2002 and has been deployed in several conflicts and exercises
- Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter (TEDBF):
- Manufactured for the Navy to replace the Navy's MiG-29K.
- First twin-engine aircraft project in India for dedicated carrier-based operations.
- Equipped predominantly with domestic weapons.
- Maximum mach number of 1.6, service ceiling of 60,000 feet, maximum takeoff weight of 26 tons, unfolded wing.
- Rafale:
- French twin-engine and multirole fighter aircraft.
- India procured 36 Rafale jets for Rs 59,000 crore in 2016.
- Equipped to perform air supremacy, interdiction, aerial reconnaissance, ground support, in-depth strike, anti-ship strike, and nuclear deterrence missions.
- The weapons package of Rafale jets includes Meteor missile, Scalp cruise missile, and MICA missile system.
- Meteor missile is the next generation of Beyond Visual Range air-to-air missile designed to revolutionize air-to-air combat, capable of targeting enemy aircraft from 150 km away.
- SCALP Cruise Missiles can hit targets 300 km away, while MICA missile system is a versatile air-to-air missile capable of hitting targets up to 100 km away.
- Flight hour capacity of 30,000 hours in operations.
Note:
- In a more recent move, INS Vikrant, India’s first indigenous aircraft carrier, was commissioned in Sept 2022 and is currently in the process of getting operationalised.
- Recently, the Naval variant of India’s indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) made its maiden landing on board the INS Vikrant.
Important Facts For Prelims
Hakki Pikki Tribal Community
Why in News?
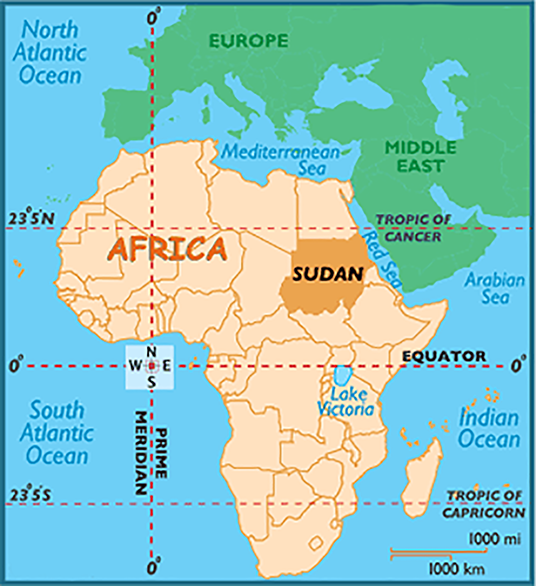
More than 181 members of the Hakki Pikki tribal community from Karnataka are stuck in violence-hit Sudan.
What are the Characteristics of the Hakki Pikki Tribe?
- About:
- The Hakki Pikki tribe is a semi-nomadic tribe traditionally engaged in bird catching and hunting, living in forest areas in west and south India.
- It is a Scheduled Tribe in Karnataka and their origin is said to be an ancestral relation with the legendary Ranapratap Singh.
- Origination and Settlement:
- The Hakki Pikki tribe is believed to have originated from Gujarat and Rajasthan and migrated to south India via Andhra Pradesh.
- The tribe is divided into four clans and has a population of 11,892 in Karnataka.
- The 4 clans are Gujaratia, Panwar, Kaliwala and Mewaras and can be equated with castes in the traditional Hindu society.
- Society:
- The usual age of marriage among the tribe is 18 for women and 22 for men, and cross-cousin marriages are preferred.
- The society is matriarchal, and Monogamy is the norm.
- Hakki Pikkis in Karnataka follow Hindu traditions and celebrate all Hindu festivals.
- Education levels among the Hakki Pikkis are still low.
- The usual age of marriage among the tribe is 18 for women and 22 for men, and cross-cousin marriages are preferred.
- Livelihood:
- The forest is the main natural resource of the Hakki Pikki.
- The tribe has faced challenges due to stricter wildlife protection laws, leading them to shift from hunting to selling herbal oils, spices, and plastic flowers in local temple fairs.
- Migration to Africa:
- In recent years, members of the Hakki Pikki tribe have been travelling to African countries to sell their products as there is a huge demand for Ayurvedic products in the continent.
- African countries offer better market opportunities, with the potential for higher returns on investment in raw materials such as hibiscus powder, oil extraction, gooseberry, Ayurvedic plants, etc.
To know more about Various Tribes of India – Click Here
What led to the Violence in Sudan?
- There was violence recently in the country due to tense negotiations between two forces, Sudan Armed Forces (SAF) and the Rapid Support Forces (RSF).
- The negotiations were about merging the forces into a single national army, as part of a political agreement for the military to hand over power to civilian leaders.
- This created mounting tensions because hardline factions within the military were resistant to the incorporation and led to violence.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Under which Schedule of the Constitution of India can the transfer of tribal land to private parties for mining be declared null and void? (2019)
(a) Third Schedule
(b) Fifth Schedule
(c) Ninth Schedule
(d) Twelfth Schedule
Ans: (b)
Important Facts For Prelims
Starship
Why in News?
Recently, SpaceX launched an uncrewed test flight of its Starship cruise vessel from the Super Heavy rocket. However, the vehicle exploded when the upper-stage Starship failed to separate from the lower-stage Super Heavy.
- SpaceX is a private company founded in 2002 by Elon Musk.
What is the Starship Project?
- SpaceX’s Starship spacecraft and Super Heavy rocket – collectively referred to as Starship – represent a fully reusable transportation system designed to carry both crew and cargo to Earth orbit, the Moon, Mars and beyond.
- Starship will be able to carry up to 150 metric tonnes fully reusable and 250 metric tonnes expendable.
- Starship Super Heavy is powered by an array of Raptor engines, which are fueled by liquid methane (CH4) and liquid oxygen (LOX).
- A total of 33 Raptor engines power the first-stage booster.
- It leverages tanker vehicles (essentially the Starship spacecraft minus the windows) to refill the Starship spacecraft in low-Earth orbit.
- Development and manufacturing of Starship takes place at Starbase, one of the world’s first commercial spaceports designed for orbital missions.
What are the other Major Projects of Space X?
- Falcon 9:
- Falcon 9 is a reusable, two-stage rocket for the reliable and safe transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond.
- Falcon Heavy:
- SpaceX claims Falcon Heavy to be the most powerful rocket in the world by a factor of two.
- It is composed of three Falcon 9 nine-engine cores whose 27 Merlin engines together generate more than 5 million pounds of thrust at liftoff.
- Merlin engines use a rocket grade kerosene (RP-1) and liquid oxygen as rocket propellants in a gas-generator power cycle.
- Starlink and Starshield:
- Starlink provides high-speed, low-latency broadband internet across the globe.
- Its high-speed, low-latency service is made possible via the world’s largest constellation of highly advanced satellites operating in a low orbit around the Earth.
- Starshield leverages Starlink technology and launch capability to support national security efforts.
- While Starlink is designed for consumer and commercial use, Starshield is designed for government use.
- Starlink provides high-speed, low-latency broadband internet across the globe.
What are India’s Efforts in Commercialisation of Space?
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
The Black Sea Grain Deal
The Group of Seven (G7) agriculture ministers have issued an official statement calling for the extension, full implementation, and expansion of the Black Sea Grain Initiative (BSGI) deal that allows Ukraine to export over 27 million Tonnes of grain from its Black Sea ports.
The deal was brokered by the United Nations and Turkey in July 2022 but Russia, which invaded Ukraine in February 2022, has signaled that it will not allow the deal to continue beyond 18th May 2023 because its demands to facilitate its own grain and fertilizer exports have not been met.
The G7 ministers strongly disapprove of Russia using food as a way to create problems and force Ukraine to do what they want. They promise to stand with Ukraine and help those who are most affected by Russia's use of food as a weapon. The G7 members have also pledged to provide support for the recovery and reconstruction of Ukraine, including expertise in demining agricultural land and reconstruction of agricultural infrastructure.
Read more: Black Sea Grain Initiative (BSGI)
Basava Jayanthi
The Prime Minister paid tribute to Jagadguru Basaveshwara on Basava Jayanthi. It is a festival celebrated in honor of the philosopher, statesman, social reformer, and saint in the Shaivism Bhakti movement during the 12th century. Basaveshwara is well-known for his teachings of gender equality, social reforms, eradication of social discrimination, clarification of superstitions, and unnecessary rituals.
Basava Jayanthi is celebrated on the third of the bright half or Shukla paksha during the month of Vaisakha by Lingayats in the State of Karnataka, marking the birth anniversary of Basaveshwara.
Basaveshwara introduced the practice of wearing the Ishtalinga necklace, which symbolizes Lord Shiva and is worn by all Lingayats. The Anubhava Mantapa established by Basava laid down the foundation of social democracy.
Read more: Basava Jayanthi
Earth Day
Earth Day is an annual event celebrated on 22nd April to raise awareness about the need to protect our planet and its environment. In 2009, the United Nations designated 22nd April as ‘International Mother Earth Day. The theme for Earth Day 2023 is “Invest in our planet,” which calls on businesses, investors, financial markets, and governments to lead the way in building a healthier and more equitable global system. The private sector can use its power to promote green innovation and practices, while governments can incentivize citizens, businesses, and institutions to work toward environmental conservation. Individual citizens can also contribute by voting for politics that prioritize the environment and by supporting environmentally conscious businesses.
Earth Day was first observed in 1970 as a response to environmental degradation caused by issues such as smog, polluted rivers, and oil spills. Today, Earth Day is globally coordinated by EARTHDAY.ORG, a non-profit organization formerly known as Earth Day Network. It aims to build the world’s largest environmental movement to drive transformative change for people and the planet.
The landmark Paris Agreement, which aims to reduce global greenhouse emissions, was signed on Earth Day 2016, demonstrating the significance of this day in driving meaningful change for our planet.
Read more: Earth Day
National Panchayati Raj Day
National Panchayati Raj Day is observed on 24th April every year to commemorate the 73rd constitutional amendment that came into effect on the same day in 1993, which accorded panchayats a constitutional status as the third tier of local self-governance in India.
Although some states such as Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh and West Bengal had already recognized panchayats as local self-governance institutions, the 73rd and 74th amendments made this a pan-India phenomenon.
Panchayati Raj has been far more successful in giving women a fair share of representation, with one-third of total seats reserved for women at the local level, and some states providing 50% reservations to women in elections for the local bodies. This increased representation of women at the local level has various policy outcomes, including increased spending on community-based welfare for women and financial independence for women through self-help groups in many places.
There is significant variation in the degree of fiscal autonomy granted to local government bodies across states, with some having greater devolution of financial powers than others. For instance, Kerala and Maharashtra are ranked as the best in terms of following devolution, while Odisha and Assam are ranked the lowest among major states.
Read more: National Panchayati Raj Day, Panchayati Raj Institution (PRI)