Biodiversity & Environment
India's Maiden Winter Arctic Research
For Prelims: National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM), Climate Change, Space Weather, Sea-Ice , Ocean Circulation Dynamics, Ecosystem, Himadri, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Inter Tropical Convergence Zone
For Mains: Significance of India's Winter Arctic Research, Arctic Region.
Why in News?
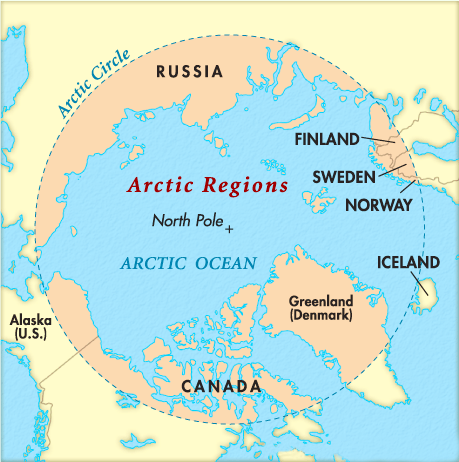
Recently, the Union Minister of Earth Sciences flagged off India’s first winter scientific expedition to Himadri, the nation's Arctic Research Station situated in Ny-Ålesund within the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard in the Arctic.
- The first batch of the maiden Arctic winter expedition comprises researchers from the host National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Mandi, Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) and Raman Research Institute.
What is the Importance of The Winter Arctic Scientific Expedition?
- Indian scientific expeditions to the Arctic during the winter will allow researchers to conduct unique scientific observations during polar nights, where there is no sunlight for nearly 24 hours and sub-zero temperatures.
- It opens more avenues for India to expand our scientific capabilities in Earth’s poles.
- This will aid in expanding understanding of the Arctic, especially climate change, space weather, sea-ice and ocean circulation dynamics, ecosystem adaptations, etc. which affect weather and climate in the tropics, including monsoons.
- India has operated a research base in the Arctic named Himadri since 2008, which has been mostly hosting scientists during the summer (April to October).
- Priority research areas include atmospheric, biological, marine, and space sciences, environmental chemistry, and studies on cryosphere, terrestrial ecosystems, and astrophysics.
- India will join a small group of countries that operate their Arctic research bases through the winter.
- In recent years, climate change and global warming research has been attracting scientists to the Arctic region.
What is the Impact of Warming on the Arctic?
- Temperatures in the Arctic region have risen by about 4 degree Celsius on average over the last 100 years 2023 was the warmest year on record.
- The extent of Arctic sea-ice has been declining at the rate of 13%/ decade, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change.
- The melting sea ice can have global impacts reaching beyond the Arctic region.
- Rising sea levels can influence atmospheric circulation.
- An increase in tropical sea surface temperatures could lead to increased precipitation in the tropics, a shift in the Inter Tropical Convergence Zone and high chances of an increase in extreme rainfall events.
- Milder weather due to global warming could make the Arctic a more habitable and a less hostile place.
- There could be a rush to explore and exploit the Arctic’s resources, including its minerals, and countries will seek to control trade, navigation and other strategic sectors in the region.
Note
- Dakshin Gangotri in Antarctica was set up much earlier in 1983. Dakshin Gangotri is now submerged under ice, but India’s two other stations, Maitri and Bharti, are in use.
- Indian scientific expeditions to the Earth’s poles (the Arctic and the Antarctic) are facilitated under the PACER (Polar and Cryosphere) scheme of the MoES, solely through the aegis of the National Centre for Polar and Ocean Research (NCPOR), Goa, an autonomous institution of the MoES.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The term ‘IndARC’, sometimes seen in the news, is the name of (2015)
(a) an indigenously developed radar system inducted into Indian Defence
(b) India’s satellite to provide services to the countries of Indian Ocean Rim
(c) a scientific establishment set up by India in Antarctic region
(d) India’s underwater observatory to scientifically study the Arctic region
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q.1 Why is India taking keen in resources of Arctic region? (2018)
Q.2 What are the economic significances of discovery of oil in Arctic Sea and its possible environmental consequences? (2015)


Governance
The Post Office Bill, 2023
For Prelims: Post Office Act, 1898, Public Order, Emergency, Public Safety, Land Revenue, Freedom of Speech and Expression, Right to Privacy
For Mains: Significance of The Post Office Bill, 2023.
Why in News?
Recently introduced, the Post Office Bill, 2023 aims to repeal the Indian Post Office Act, 1898, which has been in existence for 125 years.
- The Act regulates India Post, a departmental undertaking of the central government. The Bill contains provisions that allow the Centre to intercept, open, or detain any item, and deliver it to customs authorities.
What are the Key Highlights of the Bill?
- Post officers can “intercept” any item:
- The Bill allows the Centre to empower any officer to “intercept, open or detain any item” in the interest of state security, friendly relations with foreign states, public order, emergency, public safety, or contravention of other laws.
- This provision also allows post officers to hand over postal items to customs authorities if they are suspected to contain any prohibited item, or if such items are liable to duty.
- The Post Office exempt from liability
- The bill exempts the Post Office and its officer from “any liability by reason of any loss, mis-delivery, delay, or damage in course of any service provided by the Post Office except such liability as may be prescribed.
- Removal of Offenses and Penalties:
- The Bill removes all penalties and offenses under the 1898 Act.
- For example, offenses committed by post office officials such as misconduct, fraud, and theft, among others, have been deleted entirely.
- At the same time, if anyone refuses or neglects to pay the charges for availing a service provided by the Post Office, such amount shall be recoverable as if it were an arrear of land revenue.
- The Bill removes all penalties and offenses under the 1898 Act.
- Removes Centre’s exclusivity:
- The present Bill has removed Section 4 of the 1898 Act, which allowed the Centre the exclusive privilege of conveying all letters by post.
- However, courier services have been bypassing the 1898 law by simply calling their couriers “documents” and “parcels”, rather than “letters.”
- The present Bill has removed Section 4 of the 1898 Act, which allowed the Centre the exclusive privilege of conveying all letters by post.
- Regulates Private Courier Services:
- The 2023 Bill, for the first time, regulates private courier services by bringing it under its ambit.
What is the Criticism of the Bill?
- The Bill does not specify procedural safeguards for interception of articles transmitted through India Post.
- Lack of safeguards may violate freedom of speech and expression, and the right to privacy of individuals.
- The grounds for interception include ‘emergency’, which may be beyond reasonable restrictions under the Constitution.
- The Bill exempts India Post from liability for lapses in postal services.
- Liability may be prescribed through Rules by the central government, which also administers India Post. This may lead to conflict of interest.
- The Bill does not specify any offenses and penalties.
- There are no consequences for unauthorized opening of postal articles by a postal officer. This may have adverse implications for the Right to Privacy of consumers.
Way Forward
- Incorporate Robust Procedural Safeguards:
- Introduce clear and comprehensive procedural safeguards for the interception of articles transmitted through India Post. This should include oversight mechanisms, judicial warrants, and adherence to constitutional principles to protect the freedom of speech, expression, and the right to privacy of individuals.
- Define the Grounds for Interception:
- Refine and clearly define the grounds for interception, especially the term 'emergency,' to ensure it aligns with reasonable restrictions under the Constitution. Limit the exercise of emergency powers to prevent potential misuse and uphold individual rights.
- Balanced Liability Framework:
- Ensure the Post Office's accountability by setting clear rules for liability without jeopardizing its independence and efficiency. Address concerns about potential misuse and prevent conflicts of interest.
- Addressing Unauthorized Opening:
- Reintroduce specific offenses and penalties within the Bill, addressing unauthorized opening of postal articles by postal officers. Establish a legal framework that holds individuals accountable for misconduct, fraud, theft, and other offenses to safeguard the right to privacy of consumers.


Social Justice
UNODC’s Global Study on Homicide Report 2023
For Prelims: Global Study on Homicide Report 2023, United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC), Homicide, Sustainable Development Goals.
For Mains: UNODC’s Global Study on Homicide Report 2023, Issues relating to poverty and hunger.
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) has released a Global Study on Homicide 2023 report, which found that homicide is a bigger killer than armed conflict and terrorism combined.
- Homicide is the killing of a person, whether lawful or unlawful, intentional or unintentional while Murder is the unlawful killing of a person with intent or malice aforethought.
- The report examines homicides related to criminal activities and interpersonal conflict, as well as “socio-politically motivated homicides” such as the deliberate killing of human rights activists, humanitarian workers and journalists.
What are the Key Findings of the Global Study on Homicide 2023?
- Homicide Trends:
- An average of around 440,000 deaths annually occurred due to homicide between 2019 and 2021.
- 2021 was exceptionally lethal, witnessing 458,000 homicides. Economic repercussions from the Covid-19 pandemic and a surge in organized crime, gang-related, and socio-political violence contributed to this increase.
- Despite a more than 95% surge in conflict deaths between 2021 and 2022, available data shows that the global homicide burden in 2022 was twice that of conflict deaths.
- Factors Contributing to Homicide:
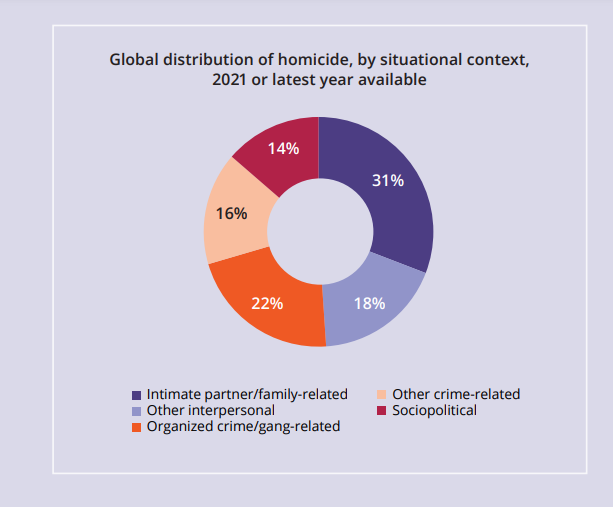
- Organized Crime accounted for 22% of global homicides, reaching 50% in the Americas. Competition among organized crime groups and gangs can escalate intentional homicides significantly.
- Factors like climate change, demographic shifts, inequality, urbanization, and technological changes influence homicide rates differently across regions.
- Regional Variances:
- America has the highest regional homicide rate per capita (15 per 100,000 population in 2021).
- Africa recorded the highest absolute number of homicides (176,000) with a rate of 12.7 per 100,000 population. Rates in Africa did not show a declining trend compared to other regions.
- Asia, Europe, and Oceania had homicide rates far below the global per capita average of 5.8 per 100,000 population in 2021.
- Victims:
- Men constituted 81% of homicide victims and 90% of suspects, while women were more likely to be killed by family members or intimate partners.
- 15% of homicide victims in 2021 were children, amounting to 71,600 boys and girls.
- Targeted Killings and Impact on Aid Workers:
- Deliberate killings of human rights defenders, journalists, aid workers, etc., accounted for 9% of global homicides.
- Humanitarian aid workers faced a higher average number of fatalities during 2017-2022 compared to 2010-2016, indicating increased threat levels.
- Projections and Vulnerability:
- The global homicide rate is projected to decrease to 4.7 in 2030, though this falls short of the Sustainable Development Goals target.
- Africa is projected as the most vulnerable region due to its younger population, persistent inequality, and climate-related challenges.
What are the Key Highlights Related to India?
- Motives Behind Murders:
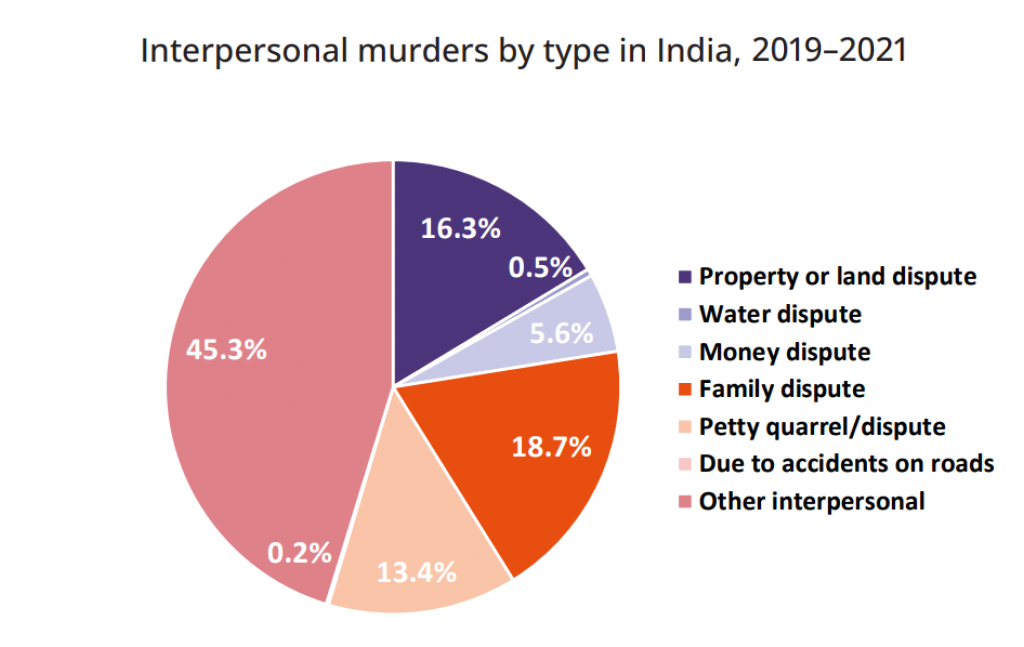
- Nearly 16.8% of murder cases recorded in India between 2019 and 2021 were linked to disputes over property, land, or access to water.
- About 0.5% (300 cases) of recorded murders in India between 2019 and 2021 were specifically attributed to water-related conflicts, highlighting the emergence of this issue as a significant driver of homicides.
- Factors Amplifying Water-Related Conflicts:
- Population Growth, Economic Expansion, and Climate Change: These factors were identified as exacerbating tensions over water access, contributing to increased violence related to disputes over water resources.


Science & Technology
Nicotine Addiction Treatment
For Prelims: Nicotine, Nicotine Replacement Therapy, National Tobacco Control Programme
For Mains: Nicotine Addiction and Burden on Public Health, Government policies and interventions
Why in News?
In a recent study set to redefine nicotine addiction treatment, researchers have unveiled a breakthrough method leveraging Vitamin C and cotinine, a nicotine metabolite.
- This approach goes beyond conventional Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT).
Note
- Nicotine is a plant alkaloid that contains nitrogen, which is found in several types of plants, including the tobacco plant and can also be produced synthetically.
- Nicotine is both a sedative and a stimulant. It is the main psychoactive ingredient in tobacco products.
- Cotinine is formed as a major metabolite of nicotine after tobacco smoking.
What are the Key Highlights of the Study?
- Utilizing Cotinine:
- Current NRT relies on providing additional nicotine to the body through patches or lozenges(medicinal tablets).
- Individuals find it challenging to quit smoking due to nicotine withdrawal, which manifests as cravings, irritability, anxiety, increased appetite, and difficulty concentrating.
- Researchers explore cotinine, nicotine's oxidative metabolite, as an alternative approach.
- In humans, generally, 80% of nicotine accumulates as cotinine in the body, while the remaining 20% is eliminated in urine. Cotinine can cause cancer.
- Researchers used Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) as a reducing agent to convert cotinine back to nicotine which is recirculated in blood to prevent the nicotine urge.
- Researchers made a dissolvable film with Vitamin C for smokers to use when tempted to smoke.
- Ascorbic acid in the specified dose facilitates the conversion of cotinine to nicotine within the smokers' plasma(liquid portion of blood).
- Current NRT relies on providing additional nicotine to the body through patches or lozenges(medicinal tablets).
- Results:
- Vitamin C helps turn cotinine into nicotine without side effects. The body gets rid of toxins at the end without needing extra nicotine.
- Future Considerations and Study Requirements:
- The converted nicotine, as indicated by the study, may be recirculated to induce Central Nervous System (CNS) effects, potentially aiding in the treatment of nicotine withdrawal.
- The research team acknowledges the need for further studies with larger samples to validate their findings.
Nicotine Replacement Therapy (NRT)
- It is a treatment to help people stop smoking. It uses products that supply low doses of nicotine.
- These products do not contain the other toxins found in smoke. The goal of therapy is to cut down on cravings for nicotine and ease the symptoms of nicotine withdrawal.
- NRT products come in several forms, including Gum, Transdermal patches, Nasal sprays, Oral inhalers, and Tablets.
What is the Status of Tobacco Consumption in India?
- Nearly 267 million adults (15 years and above) in India (29% of all adults) are users of tobacco, according to the Global Adult Tobacco Survey India, 2016-17.
- The most prevalent form of tobacco use in India is smokeless tobacco and commonly used products are khaini, gutkha, betel quid with tobacco and zarda.
- Smoking forms of tobacco used are bidi, cigarette and hookah.
- Tobacco use is a major risk factor for many chronic diseases, including cancer, lung disease, cardiovascular disease and stroke.
- It is one of the major causes of death and disease in India and accounts for nearly 1.35 million deaths every year.
- India is also the second largest consumer and producer of tobacco. A variety of tobacco products are available at very low prices in the country.
- The total economic costs attributed to tobacco use from all diseases in India in the year 2017-18 for persons aged 35 years and above amounted to USD 27.5 billion.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Tobacco Consumption?
- Cigarettes and Other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Act(COTPA), 2003:
- The Act applies to all tobacco-containing products outlined in the Act's Schedule. Prohibits advertising and regulates trade, commerce, production, supply, and distribution of cigarettes and other tobacco products in India.
- National Tobacco Control Programme(NTCP):
- It was launched in the year 2007-08 during the 11th five-year plan, to create awareness about the harmful effects of tobacco consumption, reduce the production and supply of tobacco products, ensure effective implementation of the provisions under COTPA 2003, help the people quit tobacco use, and facilitate implementation of strategies for prevention and control of tobacco advocated by WHO Framework Convention of Tobacco Control.
- National Tobacco Quitline Services (NTQLS):
- The objective of NTQLS is to provide telephone-based information, advice, support, and referrals for tobacco cessation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following are the reasons/factors for exposure to benzene pollution? (2020)
- Automobile exhaust
- Tobacco smoke
- Wood burning
- Using varnished wooden furniture
- Using products made of polyurethane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
WHO Prequalification to R21/Matrix-M Vaccine
Why in News?
In a significant development in the global fight against malaria, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recently added the R21/Matrix-M malaria vaccine to its list of prequalified vaccines.
- Developed by Oxford University and manufactured by the Serum Institute of India, this vaccine holds promise in preventing malaria in children.
- The R21/Matrix-M vaccine became the second malaria vaccine to achieve WHO prequalification, the first one was the RTS, S/AS01 vaccine.
What is the Significance of WHO Prequalification?
- WHO prequalification of the R21 vaccine serves as a robust assurance of the safety and efficacy of the vaccine.
- Products that achieve WHO prequalification gain credibility and are more readily accepted in international markets, as WHO applies rigorous international standards to evaluate their safety, effectiveness, and manufacturing compliance.
- WHO prequalification is often a prerequisite for procurement by international organizations, such as the United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF).
- It enhances the likelihood of a vaccine being included in global immunization programs, ensuring a wider reach.
- WHO prequalification is instrumental in securing Gavi support, enabling the implementation of vaccination programs in regions with limited resources.
- Gavi, the Vaccine Alliance, created in 2000 provides funding support for the deployment of vaccines in developing countries.
What is Malaria?
- About:
- It is a life-threatening mosquito-borne blood disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. It is preventable and curable.
- Predominantly found in tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, South America, and Asia.
- Malaria spreads through infected female Anopheles mosquito bites, with parasites multiplying in the liver and subsequently attacking Red Blood Cells.
- Among the five parasite species causing malaria, Plasmodium falciparum and Plasmodium vivax present the highest threat to human health.
- Symptoms of malaria include fever and flu-like illness, including shaking chills, headache, muscle aches, and tiredness.
- It is a life-threatening mosquito-borne blood disease caused by Plasmodium parasites. It is preventable and curable.
- Malaria Burden:
- Malaria places a particularly high burden on children in the African region, where nearly half a million children die from the disease each year.
- In 2022, there were an estimated 249 million malaria cases in the world and 6,08,00 malaria deaths across 85 countries.
- Initiatives to Curb Malaria:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria. Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine? (2010)
(a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
(b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
(c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
(d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Hindustan Republican Association and the Kakori Train Action
Why in News?
Ninety-six years ago, in December, 1927, four revolutionaries of the Indian independence movement were hanged 2 years after the Kakori Train Action, in which members of the Hindustan Republican Association (HRA) had looted a train transporting money to the British treasury.
- It serves as a poignant reminder of their sacrifice and bravery, reigniting reflections on their pivotal roles in shaping the course of India's fight for freedom.
What are the Key Points Related to Hindustan Republican Association?
- Background: Mahatma Gandhi initiated the Non-Cooperation Movement in 1920, advocating non-violence and urging Indians to withdraw support from British activities in India.
- However, the movement's trajectory shifted after the Chauri Chaura Incident in 1922, where police firing led to protesters' deaths and a subsequent mob attack resulted in the death of policemen.
- Gandhi, despite internal dissent within the INC, abruptly halted the movement.
- Foundation: The decision to halt Non-Cooperation Movement disillusioned a group of young men who founded the Hindustan Republican Association (HRA).
- Ram Prasad Bismil and Ashfaqulla Khan, both of whom had a flair for poetry, were among the group’s founders. Others included Sachindra Nath Bakshi and trade unionist Jogesh Chandra Chatterjee.
- Figures such as Chandra Shekhar Azad and Bhagat Singh also joined the HRA.
- Manifesto: Their manifesto released on 1st January, 1925, was titled Krantikari (Revolutionary). It proclaimed the revolutionary party's aim: to establish a federal Republic of the United States of India through an organized, armed revolution.
- It characterized the revolutionaries as neither terrorists nor anarchists, rejecting terrorism for its own sake while considering it as a potent retaliatory measure when necessary.
- HRA's Vision: They envisioned a republic grounded in universal suffrage and socialist principles, prioritizing the abolition of systems enabling human exploitation.
- Evolution of HRA: HRA transformed into the Hindustan Socialist Republican Association (HSRA) in 1928 due to a shift toward socialist ideologies, broadening its focus from political independence to encompass socio-economic equality.
- Led by figures like Bhagat Singh, the HSRA merged nationalist aspirations with socialist principles, altering the trajectory of India's freedom struggle.
What was the Kakori Train Action Incident?
- The train robbery at Kakori was the HRA’s first major action, in August 1925. The Number 8 Down Train ran between Shahjahanpur and Lucknow.
- As the train approached Kakori, a revolutionary (Rajendranath Lahiri) pulled the emergency chain to stop the train and overpowered the guard. The train was carrying treasury bags containing government funds that were to be deposited in the British treasury in Lucknow.
- The revolutionaries planned to rob this money, which they believed legitimately belonged to Indians anyway.
- Their objective was both to fund the HRA and garner public attention for their work and mission.
- The British authorities launched a harsh crackdown, leading to the arrest of numerous HRA members.
- Among the forty arrested individuals, four received death sentences ( Rajendranath Lahiri on 17th December and Ashfaqullah Khan, Ram Prasad Bismil, Thakur Roshan Singh on 19th December) and others faced lengthy imprisonments.
- Chandrashekhar Azad was the only prominent HRA leader who managed to evade capture.


Important Facts For Prelims
Sahitya Akademi Awards 2023
Why in News?
Recently, the Sahitya Akademi announced the Sahitya Akademi Award 2023 in 24 languages.
- Nine books of poetry, six novels, five short story collections, three essays and one literary study have won the Sahitya Akademi Awards this year.
- The award, in the form of a casket containing an engraved copper-plaque, a shawl, and RS 1,00,000, will be presented to the awardees.
What is the Sahitya Akademi Award?
- About:
- Sahitya Akademi award established in 1954, is a literary honour that is conferred annually by Sahitya Akademi, India’s National Academy of letters.
- Akademi gives 24 awards annually to literary works in the languages it has recognized and an equal number of awards to literary translations from and into the languages of India.

- Besides the 22 languages enumerated in the Constitution of India, the Sahitya Akademi has recognised English and Rajasthani as languages in which its programme may be implemented.
- The Sahitya Akademi award is the second-highest literary honour by the Government of India, after the Jnanpith award.
- Criteria for Choosing Awardee:
- The author must be of Indian Nationality.
- Book/work eligible for the award must be an outstanding contribution to the language and literature to which it belongs.
- When equal merit for books of two or more are found, certain criteria like total literary contribution and standing of authors shall be taken into consideration for declaring the award.
- Other Sahitya Akademi Awards:
- Sahitya Akademi Bal Sahitya Puraskar is given to an author based on his/her total contribution to children literature and relates to books first published during the five years immediately preceding the year of Award.
- Sahitya Akademi Yuva Puraskar relates to books published by an author of the age of 35 and below.


Rapid Fire
Kraft Process: A Paper-Maker’s Craft
The kraft process is used to produce cellulose fibers from wood chips, which are then used to make paper and other everyday materials.
- It is a chemical process involving the treatment of wood chips with water, sodium hydroxide, and sodium sulfide at high temperatures.
- The mixture of sodium hydroxide and sodium sulfide creates white liquor, which breaks the bonds between lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose in the wood chips.
- This process is the most common method for paper production, yielding stronger paper determined by its sulphidity, indicating the relative sulfur content.
- The process releases substances like lignin, dissolved carbon, alcohol ions, and heavy metals into the water, making it environmentally unfriendly.


Rapid Fire
NHRC Directs Inquiry on Salwa Judum Victims
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) has responded to a petition, directing the Union Ministry of Home Affairs and six state governments to provide information on victims affected by Salwa Judum.
- It was argued that the displaced individuals, residing in forest areas across several states, have been deprived of essential welfare schemes, including land rights, tribal status, social welfare benefits, and Forest Rights Act entitlements.
- Salwa Judum is a group of tribal persons mobilized for resistance against outlawed armed naxalites.The group was reportedly backed by government machinery in Chhattisgarh.
- In 2011, Supreme Court of India ruled against arming civilians in this manner banned Salwa-Judum and directed Chhattisgarh government to disband any militia force founded to combat Maoist guerrillas.


Rapid Fire
Queen of Millet
Raimati Ghiuria, a tribal farmer from Odisha’s Koraput district, has preserved 30 varieties of millets and trained hundreds of women in cultivating rare millets.
- She was invited to the G20 Summit held to commemorate the ‘International Year of Millets’.
- She has preserved 72 traditional paddy varieties and at least 30 varieties of millets including Kundra bati mandia, jasra, juana, and jamkoli.
- At the G20 Summit she was called the ‘Queen of Millet’. She has been recognized as a pioneer in native seed conservation.
- Millets are drought-resistant, require less water and can grow in poor soil conditions.
- Millets are a good source of fiber, protein, vitamins, and minerals.
- Millets are naturally gluten-free, making them suitable for people with celiac disease or gluten intolerance.


Rapid Fire
Working of Touchscreens
A touchscreen is a surface that combines two functions: to receive inputs for a computer (say, tapping on an app) and to display the output (launching the app).
- There are two most common types of touchscreens: capacitive and resistive.
- Capacitive touchscreens are used in most smartphones and tablets.They work by sensing the electrical properties of the human body when a finger touches the screen.
- Such a touchscreen consists of a surface with a grid of capacitors. Capacitor stores electric charges and when a finger touches the screen, sensors detect the distortion and relay the information to determine the touch location.
- Resistive touchscreens are pressure-sensitive and work by sensing the pressure applied to the screen.
- Resistive touchscreens are cheaper to make and require less power to operate.
- A resistive touchscreen uses resistance. That is, there are two sheets, both conductors, separated by a small gap. When a finger touches one sheet, it moves it at that point to touch the underlying sheet, allowing a current to pass there.
- Capacitive touchscreens are used in most smartphones and tablets.They work by sensing the electrical properties of the human body when a finger touches the screen.