Grameen Udyami Project
For Prelims: National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC), Grameen Udyami Project, Ministry of Skill Development and Enterprises (MSDE).
For Mains: Need for Entrepreneurship at Grassroot level.
Why in News?
Recently, National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) in partnership with Seva Bharti and Yuva Vikas Society, launched the second phase of the Grameen Udyami Project.
- Under the initiative, the endeavor is to multiskill India’s youth and impart functional skills to them for enabling livelihoods.
What is the National Skill Development Corporation?
- The National Skill Development Corporation (NSDC) is a non-profit public limited company established on July 31, 2008, under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956.
- The Ministry of Finance established NSDC as a Public Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- The Government of India, through the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), owns 49% of NSDC, while the private sector owns the remaining 51%.
- The organisation provides funding to develop scalable and successful initiatives for vocational training.
What is Grameen Udyami Project?
- About:
- It is a unique multiskilling project, funded by NSDC that aims to train 450 tribal students in Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- The project is being implemented in six states— Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, and Gujarat.
- It is a unique multiskilling project, funded by NSDC that aims to train 450 tribal students in Madhya Pradesh and Jharkhand.
- Significance:
- There is a dire need to increase ownership at the tribal level so that there is awareness built around such schemes and initiatives.
- As there is so much potential and ability in the tribal youth, all we need to do is lay down the right avenues for them to use their talent in the right places.
- This initiative will provide economic empowerment to our tribal population.
- There is a dire need to increase ownership at the tribal level so that there is awareness built around such schemes and initiatives.
- Objectives:
- Increase in Rural/Local Economy.
- Enhance employment opportunities.
- Reduce forced migration due to lack of local opportunities.
- Conservation of natural resources.
How will Grameen Udyami Project Work?
- Phase -1:
- Candidates were mobilized from rural and tribal areas of Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- The transportation, boarding & lodging were provided to candidates so that they do not miss out on the learning opportunity due to lack of resources.
- Candidates were mobilized from rural and tribal areas of Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat.
- Phase-2:
- The phase-II of the pilot project launched in Ranchi, which is being implemented by Yuva Vikas Society, through Seva Bharti Kendra in Ranchi.
- NSDC under the aegis of the Ministry of Skill Development and Enterprises (MSDE) has supported setting up of labs and classrooms through Sector Skill Councils (SSCs) in Seva Bharti Kendra Skill Development Center.
- The phase-II of the pilot project launched in Ranchi, which is being implemented by Yuva Vikas Society, through Seva Bharti Kendra in Ranchi.
- The training under the project will be conducted in the following Job roles which are relevant to the local economy.
- Electrician & Solar PV Installation Technician.
- Plumbing & Masonry.
- Two-Wheeler Repair & Maintenance.
- IT/ITES with e-Governance.
- Farm Mechanization.
What are the Other Initiatives taken by the Government for Skill Development?
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
- Rozgar Mela.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Kendras (PMKK).
- Capacity Building Scheme.
- School Initiatives and Higher Education.
- India International Skill Centres (IISCs).
- Pre-Departure Orientation Training (PDOT).
Way Forward
- Compared to the national average, the contribution of organized sectors to tribal livelihoods is significantly lower due to a lack of skill and education.
- So, projects like the Grameen Udyami project are important for their improvement and to make sure they can make a living.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. ‘Recognition of Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to (2017)
(a) Certifying the skills acquired by construction workers through traditional channels.
(b) Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
(c) Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
(d) Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme.
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), GoI launched the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) in the year 2015. The objective of this Skill Certification Scheme was to enable a large number of Indian youth to take up industry-relevant skill training that will help them in securing a better livelihood.
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL), introduced as a component of PMKVY, largely refers to an assessment process used to evaluate a person’s existing skill set, knowledge and experience gained either by formal, non-formal or informal learning and not under the National Skill Development Program.
- It has threefold objectives: To align the competencies of the un-regulated workforce of the country to the standardized National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF). To enhance the employability opportunities of an individual as well as provide alternative routes to higher education. To provide opportunities for reducing inequalities based on privileging certain forms of knowledge over others. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. Demographic Dividend in India willremain only theoretical unless our manpower becomes more educated, aware,skilled and creative.” Whatmeasures have been taken by the governmentto enhance the capacity of our population to be more productive and employable? (2016)
Women Scientists in India
For Prelims: Department of Science and Technology, Vigyan Jyoti Programme, Science Technology Engineering and Mathematics (STEM), CURIE programme, GATI program.
For Mains: Representation of Women in Science and Associated Government Initiatives.
Why in News?
Data compiled by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) shows that 28% of participants in extramural Research & Development projects in 2018-19 were women, up from 13% in 2000-01 due to various initiatives taken by successive governments.
- The ministry aims to raise women’s participation in S&T to 30% by 2030.
- The recent appointment of Dr N Kalaiselvi as the first woman director general of Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) underlined a significant trend of participation of women in science research.
What are the Key Findings?
- DST Findings:
- The number of women principal investigators in R&D had risen more than four times from 232 in 2000-01 to 941 in 2016-17.
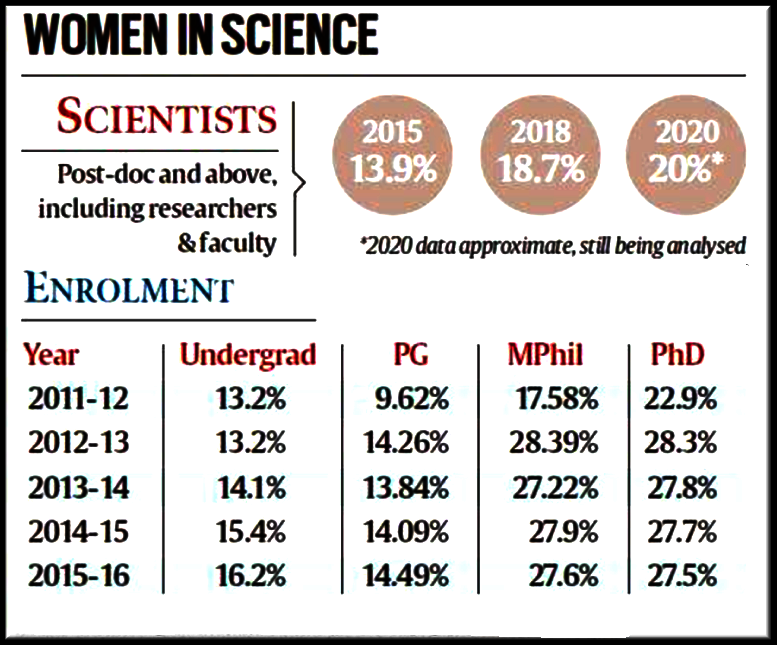
- The percentage of women among researchers went from 13.9% in 2015 to 18.7% in 2018.
- While the overall data show an upward trend, women researchers in engineering and technology are fewer than in natural sciences, health and agriculture.
- The percentage of women researchers in the social sciences and humanities is, however, much higher at 36.4%.
- At the post-doctoral level, there are fewer women researchers than the global average.
- Participation (of women) is healthy till the postgraduate level.
- But there is a drop at the post-doctoral level, where most of the research takes place. Even though this too has increased, it is still far less than the 30% global average
- All India Survey on Higher Education (AISHE) 2019:
- According to AISHE, 53% participation of women in science education at Bachelor’s and 55% at Master’s levels respectively.
- But at doctoral level, women graduates at 44% lagged behind men at 56%.
- According to AISHE, 53% participation of women in science education at Bachelor’s and 55% at Master’s levels respectively.
What is the Overall State of Women Participation in the Science Sector?
- National Figure:
- Number of science researchers in India has doubled from 30,000 in 2014 to over 60,000 in 2022.
- Women’s participation is the highest in biotechnology at 40% and medicine at 35%.
- Department of Science and Technology:
- Out of the 97 scientists in the Department of Science and Technology (DST), 35 are women.
- The big achievement is that 11 out of 18 divisions in the DST are now headed by women, that is 61%, probably the largest percentage of women in leadership in any government department.
- Other Institutions:
- Coalition for Disaster Resilient Infrastructure (CDRI) has 18%, NIPER Hyderabad 21%, and the Defence Bio-Engineering and Electro-Medical Lab (DEBEL) in Bangalore has 33%.
- Delhi University has 33% women’s participation, while Tezpur University in Assam has 17%.
What Initiatives has the Government Taken for Women in Science?
- Gender Advancement for Transforming Institutions (GATI):
- The Gender Advancement for Transforming Institutions (GATI) was launched by the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- It will develop a comprehensive Charter and a framework for assessing Gender Equality in STEM (Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics).
- In the first phase of GATI, 30 educational and research institutes have been selected by DST, with a focus on women’s participation in leadership roles, faculty, and the numbers of women students and researchers.
- Vigyan Jyoti Scheme:
- Vigyan Jyoti Scheme is launched by the Department of Science & Technology (DST).
- It is intended to create a level-playing field for the meritorious girls in high school to pursue Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) in their higher education.
- It also offers exposure for girl students from the rural background to help to plan their journey from school to a job of their choice in the field of science.
- Indo-US Fellowship for Women in STEMM (WISTEMM) program:
- Women scientists can work in research labs in the US.
- Consolidation of University Research for Innovation and Excellence in Women Universities (CURIE) Programme:
- Improving R&D infrastructure and establishing state-of-the-art research facilities in order to create excellence in S&T in women universities.
Pandurang Khankhoje & Swami Vivekananda
For Prelims: Important Personalities of Indian History, India’s Independence Movement, Ghadar Party
For Mains: Significance of Important Personalities in India’s Struggle for Independence
Why in News?
Lok Sabha Speaker will travel to Mexico to unveil statues of Swami Vivekananda and Maharashtra-born freedom fighter and agriculturalist Pandurang Khankhoje (1883-1967).
- The Speaker’s visit is part of India's efforts to honor lesser-known Indian-origin leaders outside India.
Who was Pandurang Khankhoje?
- Birth:
- Pandurang Khankhoje was born in Wardha, Maharashtra, in the late 19th century.
- Revolutionary Connections:
- Pandurang Khankhoje came in contact with other revolutionaries early on.
- Hindu reformer Swami Dayanand and his Arya Samaj movement, which called for a spirit of reform and social change, became the hero to a young student group led by Khankhoje.
- Khankhoje was an ardent admirer of the French Revolution and of the American War of Independence.
- Before leaving India for training in abroad, he visited Bal Gangadhar Tilak, by who he was inspired.
- Pandurang Khankhoje came in contact with other revolutionaries early on.
- Life Abroad:
- Khankhoje decided to go abroad for further training in revolutionary methods and militaristic strategy.
- After spending time with nationalists from Japan and China, Khankhoje eventually moved to the US, where he enrolled in college as a student of agriculture.
- A year later, he joined the Mount Tamalpais Military Academy in California to fulfil his original purpose of leaving India.
How was Khankhoje associated with the Indian Independence Movement?
- Khankhoje & Ghadar Party:
- In the US, Khankhoje met Lala Har Dayal, an Indian intellectual teaching at Stanford University.
- Har Dayal had begun a propaganda campaign, publishing a newspaper that featured patriotic songs and articles in the vernacular languages of India.
- This was the seed from which the Ghadar Party would emerge.
- Har Dayal had begun a propaganda campaign, publishing a newspaper that featured patriotic songs and articles in the vernacular languages of India.
- Khankhoje was one of the founding members of the Ghadar Party, established by Indians living abroad in 1913, mostly belonging to Punjab.
- Its aim was to lead a revolutionary fight against the British in India.
- In the US, Khankhoje met Lala Har Dayal, an Indian intellectual teaching at Stanford University.
What is the Connection between Khankhoje and Mexico?
- Connections with Mexicans in the US:
- At the military academy in the US, Khankhoje met many people from Mexico.
- Khankhoje was inspired by “The Mexican Revolution of 1910” which led to the overthrow of the dictatorial regime.
- While he was reaching out to Indians working on farms in the US with the aim of discussing the idea of Indian independence with them, he met with Mexican workers as well.
- He reached out to Bhikaji Cama in Paris, and met with Vladimir Lenin in Russia among other leaders, seeking support for India's Independence.
- He was facing deportation from Europe and he could not go to India, so he sought shelter in Mexico.
- At the military academy in the US, Khankhoje met many people from Mexico.
- Life in Mexico:
- With the help of some friends in Mexico, he was appointed a professor at the National School of Agriculture in Chapingo, near Mexico City.
- He researched corn, wheat, pulses and rubber, developing frost and drought-resistant varieties, and was part of efforts to bring in the Green Revolution in Mexico.
- Later on in the 20th Century, the American agronomist Dr Norman Borlaug, called the Father of the Green Revolution in India, brought the Mexican wheat variety to Punjab.
- Khankhoje was revered as an agricultural scientist in Mexico.
- The renowned Mexican artist Diego Rivera painted murals that featured Khankhoje, including one titled ‘Our Daily Bread’ that prominently depicted him breaking bread with people seated around a table.
Who was Swami Vivekananda?
- Birth:
- Swami Vivekanand ,original name Narendranath Datta was born on 12th January, 1863.
- National Youth Day is held every year to observe the birth anniversary of Swami Vivekananda.
- In 1893, upon the request of Maharaja Ajit Singh of the Khetri State, he took the name ‘Vivekananda.’
- Contributions:
- Introduced the world to the Indian philosophies of Vedanta and Yoga.
- He preached ‘neo-Vedanta’, an interpretation of Hinduism through a Western lens, and believed in combining spirituality with material progress.
- Laid the greatest emphasis on education for the regeneration of our motherland. Advocated a man-making character-building education.
- Best known for his speech at the World Parliament of Religion in Chicago in 1893.
- Spelt out the four pathways of attaining moksha from the worldly pleasure and attachment in his books:
- Raja-yoga
- Karma-yoga
- Jnana-yoga
- Bhakti-yoga
- Netaji Subhas Chandra Bose had called Vivekananda the “maker of modern India.”
- Introduced the world to the Indian philosophies of Vedanta and Yoga.
- Associated Organisations:
- He was the chief disciple of the 19th-century mystic Ramakrishna Paramhansa and established the Ramakrishna Mission in 1897.
- Ramakrishna Mission is an organization which works in the area of value-based education, culture, health, women's empowerment, youth and tribal welfare and relief and rehabilitation.
- In 1899, he established Belur Math, which became his permanent abode.
- He was the chief disciple of the 19th-century mystic Ramakrishna Paramhansa and established the Ramakrishna Mission in 1897.
- Death:
- He died at Belur Math in 1902.
- Belur Math, located in West Bengal, is the headquarters of Ramakrishna Math & Ramakrishna Mission.
What is the Ghadar Party?
- It was an Indian revolutionary organisation, with the aim to liberate India from British rule.
- ‘Ghadar’ – also written as ‘Ghadr’ in English – is an Urdu word for rebellion.
- The party was formed in the United States in 1913, by migrant Indians, mostly Punjabis. However, the party also included Indians from all parts of India.
- Motive was to wage a nationwide armed struggle against British colonialism in India.
- The party was established as the Hindi Association of Pacific Coast under the leadership of Lala Har Dayal with Baba Sohan Singh Bhakna as its president.
- The party is known for setting the foundation for future Indian revolutionary movements and served as a stepping stone for independence.
- Most members of the Ghadar party came from the peasantry who first began migrating from Punjab to cities in Asia like Hong Kong, Manila and Singapore at the dawn of the 20th century.
- Later, with the rise in the lumber industry in Canada and the US, many moved to North America, where they thrived – but also became victims of institutionalised racism.
- The Ghadar movement ‘inspired to transpose egalitarian values (Egalitarianism) of American culture in the social framework of colonial India’.
- Egalitarianism is a doctrine based on the notion of equality, namely, that all people are equal and deserve equal treatment in all things.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The Ghadr (Ghadar) was a: (2014)
(a) revolutionary association of Indians with headquarters at San Francisco
(b) nationalist organization operating from Singapore
(c) militant organization with headquarters at Berlin
(d) communist movement for India’s freedom with headquarters at Tashkent
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What does each of the following quotations mean to you?
“Every work has got to pass through hundreds of difficulties before succeeding. Those that persevere will see the light, sooner or later.”- Swami Vivekananda. (2021)
“Condemn none: if you can stretch out a helping hand, do so. If not, fold your hands, bless your brothers, and let them go their own way.” – Swami Vivekananda. (2020)
India-Iran Pact on Seafarers
For Prelims: India-Iran Pact on Seafarers, International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping for Seafarers (1978), International Maritime Organization, Tehran Declaration, Iran’s location, Caspian Sea.
For Mains: Significance of India-Ian Relations.
Why in News?
India and Iran signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to smoothen movement of seafarers from both the countries as per the provisions of International Convention on Standards of Training, Certification and Watchkeeping (STCW) for Seafarers (1978).
What is the International Convention on STCW for Seafarers?
- It sets qualification standards for masters, officers and watch personnel on seagoing merchant ships.
- STCW was adopted in 1978 by a conference at the International Maritime Organization (IMO) in London and entered into force in 1984. The Convention was significantly amended in 1995.
- The 1978 STCW Convention was the first to establish basic requirements on training, certification and watchkeeping for seafarers on an international level.
- It prescribes minimum standards relating to training, certification and watchkeeping for seafarers which countries are obliged to meet or exceed.
- One especially important feature of the Convention is that it applies to ships of non-party States when visiting ports of States which are Parties to the Convention.
How have been the India-Iran Relations?
- India and Iran share close civilizational ties since the times of the Persian Empire and Indian kingdoms.
- Iran is an important nation in India’s neighborhood and in fact, the two countries shared a border until India’s partition and independence in 1947.
- The “Tehran Declaration” signed during former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee’s visit to Iran affirmed the shared vision of the two countries for an “equitable, pluralistic and co-operative international order”.
- It recognized the then Iranian President Mohammad Khatami’s vision of a “dialogue among civilisations” as a paradigm of international relations based on principles of tolerance, pluralism and respect for diversity.
What is the Significance of India-Iran Relations?
- Location and Connectivity:
- Iran is located at a strategic and crucial geographical location between the Persian Gulf and the Caspian Sea.
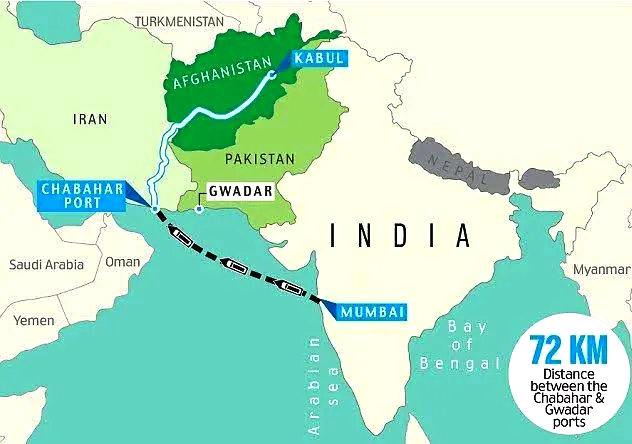
- Iran is important to India as it provides an alternate route of connectivity to Afghanistan and Central Asian republics through Chabahar Port without passing the land route through Pakistan.
- Cheaper Crude Oil:
- Since, Iran is one of the largest deposits of crude oil and natural gas in the world.
- India may well consider restarting oil imports from Iran. If India changes course and resumes imports of Iranian oil, it could potentially encourage some other countries to follow suit and open up additional oil in the market, which could eventually bring prices of crude oil down.
- Connectivity with Eurasia:
- The International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC), aims to connect India, Iran, Afghanistan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe through multi-modal transport, reducing the transit time of goods drastically.
- Although some part of it has been operationalized, again, due to sanctions on Iran, its full potential has not been realised. India and Iran could well play a major part in giving INSTC the required boost to reap the benefits of resultant trade.
- Energy Security:
- The Iran-Oman-India gas pipeline (IOI) too is an ambitious project that has been stuck for a long time. Fortunately, Iran and Oman signed a deal to develop two gas pipelines and an oil field along their maritime borders.
- If this comes through, there is potential for the pipeline being extended to India, which would help overcome the loss of the failed Iran-Pakistan-India (IPI) pipeline and facilitate the supply of natural gas to India.
Way Forward
- There is a need to look forward toward areas of convergence, where both countries have a mutual understanding of each other’s common interests and further work together to achieve the same.
- India and Iran, therefore, have a lot that can be achieved together. The assertive diplomacy being practiced by India, emphasizing on standing by its neighbors and friends and focusing solely on fulfilling its national interests, is a refreshing change.
- If India can extend the same vision toward its engagement with Iran, it could open a huge potential for cooperation between these two great nations and civilizations. Time is therefore ripe for a reset.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
(a) India’s trade with African countries will enormously increase.
(b) India’s relations with oil-producing Arab countries will be strengthened.
(c) India will not depend on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
(d) Pakistan will facilitate and protect the installation of a gas pipeline between Iraq and India.
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. A number of outside powers have entrenched themselves in Central Asia, which is a zone of interest to India. Discuss the implications, in this context, of India’s joining the Ashgabat Agreement, 2018. (2018)
Q. In what ways would the ongoing U.S-Iran Nuclear Pact Controversy affect the national interest of India? How should India respond to this situation? (2018)
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)
Indian Energy Exchange Procurement
For Prelims: Indian Energy Exchange Procurement, Electricity Act 2003, Central Electricity Regulatory Commission
For Mains: Regulation of Discoms & Significance of Power Sector of India
Why in News?
Recently, the managements of power utilities of Telangana (Discoms) were banned from participating in the day ahead market with the Indian Energy Exchange (IEX) for procuring energy.
- They were banned on the grounds of non-payment of dues to Gencos despite making payments.
- However, the ban has now been lifted following reconciliation of accounts pertaining to payments made.
Why do we need to know about the Ban?
- The National Load Dispatch Centre (NLDC) imposed a ban on bidding of Telangana (Discoms) in energy procurement without even reconciling the accounts with the Gencos concerned.
- Telangana (Discoms) have cleared ₹1,360 crore out of ₹1,381 crore dues mentioned by the agency before the imposing of the ban.
- As per the Discoms, the agency was acting beyond its mandate as per the Electricity Act, 2003, which is in force now.
- As per the 2003 Act, the agency has to monitor and maintain only the grid discipline and it is not supposed to be involved in any commercial activity such as its present unilateral decision.
- The ban was lifted officially on 19th August 2022 allowing the Discoms to go for procuring energy.
What is the Indian Energy Exchange?
- About:
- It is the first and largest energy exchange in India providing a nationwide, automated trading platform for physical delivery of electricity, Renewable Energy Certificates and Energy Saving Certificates.
- The exchange platform enables efficient price discovery and increases the accessibility and transparency of the power market in India while also enhancing the speed and efficiency of trade execution.
- It is a publicly listed company with National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE).
- It is approved and regulated by Central Electricity Regulatory Commission (CERC) and has been operating since 2008.
- Mission:
- To leverage technology and innovation to establish transparent and efficient energy marketplaces for delivering affordable, reliable energy to consumers.
- Trading Platform for:
- Electricity Market:
- Day-Ahead Market (DAM):
- It is a physical electricity trading market for deliveries for any/some/all 15-minute time blocks in 24 hours of the next day starting from midnight.
- Term-Ahead Market (TAM):
- The contracts under TAM cover a range for buying/selling electricity for duration up to 11 days.
- It enables participants to purchase electricity for the same day through intra-day contracts, for the next day through day-ahead contingency, on a daily basis for rolling seven days through daily contracts.
- Real Time Market:
- The market features a new auction session every 30 minutes with power to be delivered after 4 time blocks or an hour after gate closure of the auction.
- The price and quantum of electricity trading is determined through a double-sided closed auction bidding process.
- Cross Border Electricity Trade:
- The Cross border in electricity is an endeavour to expand the Indian power market towards building an integrated South Asian Power Market.
- The grid connected south Asian countries such as Nepal, Bhutan and Bangladesh will be able to participate in Day ahead Market and Term ahead Market on the Exchange.
- Day-Ahead Market (DAM):
- Green Market:
- Green Term Ahead Market:
- The Green-Term Ahead Market (G-TAM) is a new market segment for trading in renewable energy following the CERC approval.
- The new market segment features contracts such as:
- Green-Intraday
- Green-Day-ahead Contingency (DAC)
- Green-Daily and Green-Weekly.
- The matching mechanism is continuous/spot trading for Green-Intraday, Green-DAC and Green-Daily contracts whereas double sided open auction process to be implemented for Green-Weekly.
- Green Day-Ahead Market:
- The Green Day ahead Market allows anonymous & double-sided closed collective auction in renewable energy on the day-ahead.
- The Exchange invites bids for conventional and renewable products in an integrated way through separate bidding windows.
- The clearing takes place in a sequential manner – first in the renewable segment having the must-run status, considering the availability of the transmission corridor, followed by conventional segment.
- Green Term Ahead Market:
- Certificate Market:
- Renewable Energy Certificates (REC):
- Under the REC mechanism, a generator can generate electricity through renewable resources in any part of the country.
- For the electricity part, the generator receives the cost equivalent to that from any conventional source while the environment attribute is sold through the exchanges at the market determined price.
- The obligated entity from any part of the country can purchase these RECs to meet its RPO (Renewable Purchase Obligation) compliance.
- Obligated entities may either purchase renewable energy or can purchase RECs to meet their RPO set under the RPO of their respective States.
- Under the REC mechanism, a generator can generate electricity through renewable resources in any part of the country.
- Energy Saving Certificates (ESCerts):
- These are the tradable certificates under the Perform, Achieve, Trade (PAT) Scheme of the Bureau of Energy Efficiency (BEE).
- It is a market-based mechanism to incentivise energy efficiency in large energy-intensive industries.
- Renewable Energy Certificates (REC):
- Electricity Market:
What is the Electricity Act 2003 & Central Electricity Regulatory Commission?
- Electricity Act 2003:
- The Electricity Act, 2003 is the central law regulating the electricity sector.
- The Act provides for Electricity Regulatory Commissions at both the central and state levels (CERC and SERCs).
- Functions of these Commissions include:
- Regulating and determining tariff
- Issuing licenses for transmission
- Distribution, and electricity trading
- Adjudicating upon disputes, within their respective jurisdiction.
- Functions of these Commissions include:
- Central Electricity Regulatory Commission:
- CERC is a regulator of the power sector in India.
- It intends to promote competition, efficiency and economy in bulk power markets, improve the quality of supply, promote investments and advise the government on the removal of institutional barriers to bridge the demand supply gap.
- It is a statutory body functioning with quasi-judicial status under the Electricity Act 2003.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which one of the following is a purpose of ‘UDAY’, a scheme of the Government? (2016)
(a) Providing technical and financial assistance to start-up entrepreneurs in the field of renewable sources of energy
(b) Providing electricity to every household in the country by 2018
(c) Replacing the coal-based power plants with natural gas, nuclear, solar, wind and tidal power plants over a period of time
(d) Providing for financial turnaround and revival of power distribution companies
Ans: (d)
Explanation:
- Ujwal DISCOM Assurance Yojana (UDAY) was launched by the Ministry of Power. It aimed to help to make state electricity distribution companies (DISCOMS) financially and operationally healthy so that they can supply adequate power at affordable rates.
- It envisages financial turnaround, operational improvement, reduction of the cost of generation of power, development of renewable energy, energy efficiency and conservation.
- The scheme seeks to impact financially and operationally sound DISCOMs, increased demand for power, improvement in Plant Load Factor (PLF) of generating plants, reduction in stressed assets, availability of cheaper funds, increased capital investment, development of renewable energy sector.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
New Norms to Invest Overseas
Why in News?
Recently, The Ministry of Finance noticed new norms making it easier for domestic corporates to invest abroad, while making it tougher for loan defaulters and those facing a probe by investigative agencies to invest in overseas entities.
What are the Key Highlights of the New Rules?
- Administered by RBI:
- The Overseas Investment Rules and Regulations, notified under the Foreign Exchange Management Act, will be administered by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and shall subsume all existing norms pertaining to overseas investments as well as the acquisition and transfer of immovable property outside India.
- No Go Sectors:
- A No-Objection Certificate (NOC) will be mandatory for any person who has a bank account classified as a Non-performing asset, or is labelled a wilful defaulter by any bank, or is under investigation by a financial service regulator, the Enforcement Directorate (ED) or the Central Board of Investigation (CBI).
- Further, no Indian resident will be permitted to make investments in foreign entities that are engaged in real estate business, gambling in any form and dealing with financial products linked to the Indian rupee without the central bank’s specific approval.
- Sixty Day Timeline:
- However, if the lenders or the relevant regulatory body or investigative agency fail to furnish the NOC within sixty days of receiving an application, it may be presumed that they have no objection to the proposed transaction.
- Significance:
- The revised regulatory framework for overseas investment provides for simplification of the existing framework for overseas investment and has been aligned with the current business and economic dynamics
- Clarity on overseas direct investment and overseas portfolio investment has been brought in and “various overseas investment-related transactions that were earlier under the approval route are now under automatic route, significantly enhancing ease of doing business.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which of the following is issued by registered foreign portfolio investors to overseas investors who want to be part of the Indian stock market without registering themselves directly? (2019)
(a) Certificate of Deposit
(b) Commercial Paper
(c) Promissory Note
(d) Participatory Note
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- A Participatory Note or P-note is an instrument issued by a registered Foreign Institutional Investor (FII) to an overseas investor who wishes to invest in Indian stock markets without registering themselves with the market regulator, the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
- A Certificate of Deposit is a savings certificate with a fixed maturity date and specified fixed interest rate that can be issued in any denomination aside from minimum investment requirements.
- Commercial Paper is an unsecured money market instrument issued in the form of a Promissory Note. It was introduced in India in 1990 with a view to enable highly rated corporate borrowers to diversify their sources of short-term borrowings and to provide an additional instrument to investors.
- A Promissory Note is a financial instrument that contains a written promise by one party (the note’s issuer or maker) to pay another party (the note’s payee) a definite sum of money, either on demand or at a specified future date.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Online Marketplace Aqua Bazar
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister for Fisheries launched the Online Market Place feature, Aqua Bazar, in the MatsyaSetu mobile app during the ninth general body meeting of the National Fisheries Development Board.
What is Matsya Setu App?
- About:
- The app was developed by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research ICAR-Central Institute of Freshwater Aquaculture (ICAR-CIFA), Bhubaneswar, with the funding support of the National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB), Hyderabad through the Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY).
- Features:
- Through this platform, any registered vendor can list their input materials.
- The listed items will be displayed in the marketplace based on geographical proximity to the app user.
- The listings are categorized into the following major categories, fish seeds, input materials, services, jobs, and table fish.
- Every listing will contain detailed information about the product, price, available quantity, supply area, etc. along with the seller’s contact details.
- The needy farmers/stakeholders can contact the vendors and fulfill their procurements.
- It also allows the fish farmers to list their grown table-size fish/fish seeds for sale with an option to indicate the date of availability along with the price offer.
- Interested fish buyers will contact the farmers and offer their prices.
- Significance:
- The online marketplace will help the fish farmers and stakeholders to source the inputs such as fish seeds, feed, medicines, etc., and services required for fish culture as well as farmers can also list their table-size fish for sale.
- The marketplace aims to connect all stakeholders in the aquaculture sector.
- Reliable information about the timely availability of quality inputs in the right place is very crucial for the success and development of freshwater aquaculture in the country.
- It will certainly help the farmers to receive more business inquiries from buyers or buyer agents who procure fish, paving the way for increased awareness about the market situation and better price realization of farmers' produce.
- The online marketplace will help the fish farmers and stakeholders to source the inputs such as fish seeds, feed, medicines, etc., and services required for fish culture as well as farmers can also list their table-size fish for sale.
What was the Need to Launch this Initiative?
- At times, fish farmers do face problems in sourcing critical, quality inputs such as fish seeds, feed, feed ingredients, fertilizers, nutraceuticals, additives, medicines, etc., during the crop season.
- Any delay in obtaining these inputs would cause significant consequences in the productivity of their fish culture operation.
- Sometimes, farmers also look for services such as farm construction, rental services, manpower for harvesting, etc.
- Similarly, at certain times, fish farmers do face difficulties in selling their produce in the market or they only rely upon a limited number of buyers/agents to procure their fish produced.
What is the National Fisheries Development Board?
- The National Fisheries Development Board (NFDB) was established in 2006 as an autonomous organization under the administrative control of the Department of Fisheries, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying, Government of India to enhance fish production and productivity in the country and to coordinate fishery development in an integrated and holistic manner.
- Headquarters: Telangana, Hyderabad.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Defining the blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)
AK-203 Rifles
Why in News?
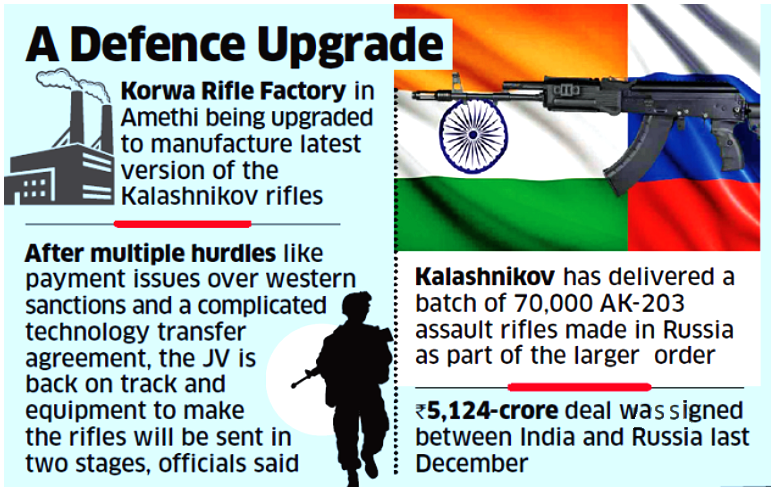
The Indo-Russian joint venture “Indo-Russian Rifles Private Ltd (IRRPL)” will be manufacturing over 6.1 lakh AK-203 assault rifles costing over ₹5,000 crore in Amethi, Uttar Pradesh.
- Training of Indian workers of the factory will begin shortly and the manufacturing process will reach 100% indigenisation in three years.
- The AK-203 assault rifles will replace the India-made INSAS assault rifles and the older AK-47.
What do we know about the Contract?
- Indo-Russian Rifles Private Ltd (IRRPL) was set up jointly between erstwhile Ordnance Factory Board OFB [now Advanced Weapons and Equipment India Limited (AWEIL) and Munitions India Limited (MIL)] of India and Rosoboronexport (RoE) and concern Kalashnikov of Russia.
- The Rs 5,124 crore deal was signed between India and Russia in December 2021.
- It is the biggest defence deal between the two nations in recent years. The deal has a clause for complete technology transfer. The rifles will also be exported to friendly foreign nations.
- Kalashnikov has already delivered a batch of 70,000 rifles made in Russia as part of the larger AK-203 assault rifles order.
How has Indo-Russia Defence and Security Relations been?
- India-Russia military-technical cooperation has evolved from a buyer-seller framework to one involving joint research, development and production of advanced defence technologies and systems.
- Both countries regularly conduct the Tri-Services exercise ‘INDRA‘.
- The joint programmes between India and Russia include:
- BrahMos cruise missile programme
- 5th generation fighter jet programme
- Sukhoi Su-30MKI programme
- Ilyushin/HAL Tactical Transport Aircraft
- KA-226T twin-engine utility helicopters
- The military hardware purchased/leased by India from Russia includes:
- S-400 Triumf
- Kamov Ka-226 200 to be made in India under the Make in India initiative
- T-90S Bhishma
- INS Vikramaditya aircraft carrier programme
- Russia also plays a very important role in assisting the Indian Navy with its submarine programmes:
- Indian Navy’s first submarine, ‘Foxtrot Class’ came from Russia.
- India is dependent on Russia for its nuclear submarine programme.
- INS Vikramaditya, the sole aircraft carrier operated by India, is also Russian in origin.
- Nine of the fourteen conventional submarines operated by India are Russian.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What is the significance of Indo-US defence deals over Indo-Russian defence deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)
Tomato Flu
Why in News?
Recently, some parts of Kerala reported Tomato Flu among children under five years of age.
What is Tomato Flu?
- About:
- The infection has been named ‘tomato flu’ because of the red, painful blisters that appear on a patient’s body and gradually enlarge to the size of a tomato.
- The ‘tomato flu’ is caused by Coxsackievirus A 16.
- It belongs to the Enterovirus family.
- The enteroviruses are an ancient and important group of RNA viruses.
- Humans are the only hosts for the enteroviruses (NPEVs).
- The infectious disease is caused by intestinal viruses and is rare in adults as they usually have immune systems strong enough to defend them from the virus.
- Transmission:
- Tomato flu is very contagious and children are at increased risk of exposure to tomato flu as viral infections are common in this age group and spread is likely to be through close contact.
- If the outbreak of tomato flu in children is not controlled and prevented, transmission might lead to serious consequences by spreading in adults as well.
- Symptoms:
- The primary symptoms observed in children with tomato flu are like those of chikungunya, which include high fever, rashes, and intense pain in joints.
- As with other viral infections, further symptoms include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, dehydration, swelling of joints, body aches, and common influenza-like symptoms, which are similar to those manifested in dengue.
- Treatment:
- This flu is a self-limiting one and there is no specific drug for this.
- The treatment for tomato flu is similar to the treatment of chikungunya, dengue and hand, foot, and mouth disease.
- Patients are advised to isolate, rest, plenty of fluids, and hot water sponge for the relief of irritation and rashes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- In tropical regions, Zika virus disease is transmitted by the same mosquito that transmits dengue.
- Sexual transmission of Zika virus disease is possible.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Zika virus is a flavivirus which was first discovered in 1947 in monkeys and then in humans in Uganda in 1952.
- Both Zika and Dengue have similarities in terms of symptoms of fever, skin rashes, conjunctivitis, muscle and joint pain, malaise, and headache. In addition to this, the mode of transmission is also same for both the diseases, i.e., both are spread by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus species of mosquitoes. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Modes of Zika Transmission
- Mosquito bites
- During pregnancy, from mother to child, which can cause microcephaly and other severe fetal brain defects. Zika virus has also been found in breast milk.
- Sexual transmission from infected partner. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Through blood transfusion.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.