Infographics
International Relations
India's Jet Engine Deal with the US
For Prelims: LCA Tejas Mk2, F414 engine, Defence Research Development Organisation (DRDO), critical technologies
For Mains: Significance of India's efforts to achieve self-reliance in critical technologies, Potential benefits of cooperation in critical and emerging technology
Why in News?
Recently, India has announced a significant agreement between the American multinational corporation General Electric (GE) and Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL), during Indian PM's state visit to the US. The deal involves the transfer of critical jet engine technologies and the manufacturing of GE's F414 engine for India's indigenous Light Combat Aircraft (LCA) Tejas Mk2.
- This development marks a crucial milestone in India's pursuit of advanced combat jet engine technology.
Note:
- The India-US Defence Acceleration Ecosystem (INDUS-X) was also launched during the ongoing visit of the PM.
- INDUS-X is meant as a platform for Indian and U.S. start-ups and tech companies to collaborate for the co-development and co-production of advanced technologies.
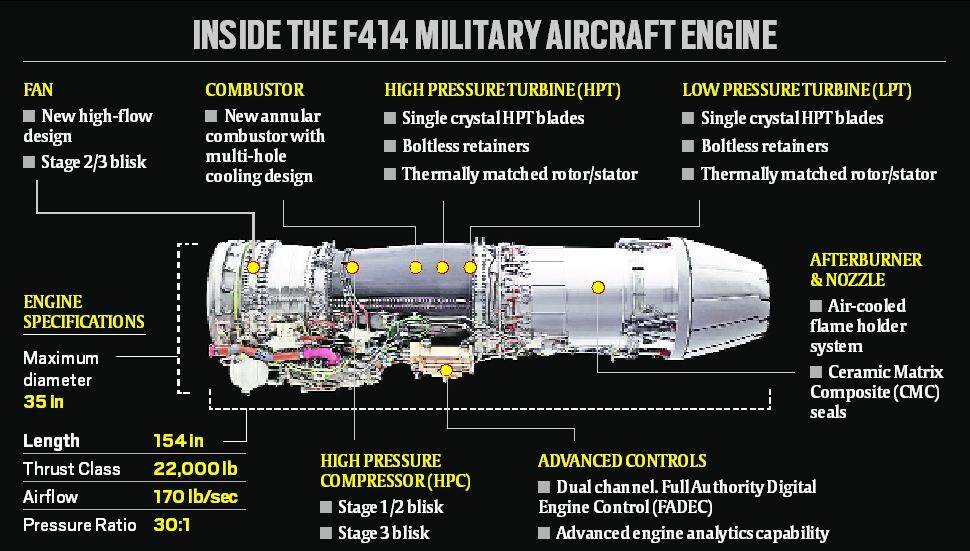
What is GE's F414 engine?
- About:
- GE's F414 engine is a turbofan engine used by the US Navy for over 30 years.
- It is equipped with a dual-channel full authority digital engine control (FADEC), a six-stage high-pressure compressor, an advanced high-pressure turbine, and a "fueldraulic" system for nozzle area control.
- It offers exceptional throttle response, excellent afterburner light and stability, and unrestricted engine performance when required.
- The F414 engine has powered military aircraft in eight nations, making it a trusted choice for modern fighter jets.
- GE's F414 engine is a turbofan engine used by the US Navy for over 30 years.
- India's Engine Requirements:
- For India, the F414 engine holds great significance, particularly in the context of the LCA Tejas Mk2.
- The Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA) of the DRDO has selected the India-specific version of the engine, known as F414-INS6, for the LCA Tejas Mk2.
- This strategic decision reflects India's aim to bolster its indigenous defence capabilities and reduce dependence on foreign suppliers.
- Furthermore, there are prospects of utilizing F414 engines for the Advanced Medium Combat Aircraft (AMCA), India's ambitious fifth-generation fighter aircraft.
- For India, the F414 engine holds great significance, particularly in the context of the LCA Tejas Mk2.
What is LCA Tejas Mk2?
- The LCA Tejas Mk2 is an upgraded version of the indigenous fighter aircraft developed in India.
- It has the capability to carry eight Beyond-Visual-Range (BVR) missiles simultaneously and integrate both native and advanced weapons from other countries.
- The LCA Mk2 offers improved range and mission endurance compared to its predecessor, with a mission endurance of 120 minutes, as opposed to 57 minutes for the LCA Tejas Mk1.
- It is intended to serve as a replacement for the Jaguars, MiG-29s, and Mirage 2000s as they retire in the coming decade. Manufacturing has already begun, and the aircraft is expected to be rolled out by 2024.
Why is the India-US Jet Engine Deal Significant?
- Self-reliance in Critical Technologies:
- Manufacturing engines for combat aircraft requires advanced technology and metallurgy, which only US, Russia, UK and France have mastered.
- India, despite its push for self-reliance in critical technologies, including cryogenic rocket engines, has not been able to join this list.
- The countries that have the technology to manufacture advanced engines for fighter aircraft have been traditionally unwilling to share them which is also why the deal is pathbreaking.
- Manufacturing engines for combat aircraft requires advanced technology and metallurgy, which only US, Russia, UK and France have mastered.
- A Significant Component of iCET:
- The agreement for the transfer of technology was discussed in the talks between India's Defence Minister and the US Secretary of Defence earlier in June 2023 and was a key highlight of India's National Security Advisor’s meeting with his US counterpart when the US-India iCET was operationalized.
- Development Efforts by DRDO:
- The DRDO's Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) initiated the development of the GTX-37 engine for the LCA, followed by the ambitious Kaveri engine project in 1989.
- Despite the development of 9 full prototype engines and 4 core engines and extensive testing, the engines did not meet the requirements for fighter aircraft making this deal crucial for its defence capabilities.
- The DRDO's Gas Turbine Research Establishment (GTRE) initiated the development of the GTX-37 engine for the LCA, followed by the ambitious Kaveri engine project in 1989.
- End of Technology Denial Regime:
- This pact finally lays to rest what former PM of India (in 2008) had described in as the “technology denial regime” imposed on India by the West, led by the US.
- The Nuclear Suppliers’ Group’s waiver to the Indo-US nuclear deal marked the end of India’s decades long isolation from the nuclear technology.
- This jet engine technology transfer agreement is another one of the important milestones in this journey.
- This pact finally lays to rest what former PM of India (in 2008) had described in as the “technology denial regime” imposed on India by the West, led by the US.
What are India's Recent Developments in Defence Sector?
- India's Indigenous Developments:
- Successful testing of indigenous weapons and systems, including:
- Launch and commissioning of indigenous naval vessels, including:
- INS Karanj submarine
- OPV Vijaya patrol vessel
- INS Dhruv nuclear missile tracking ship
- INS Himgiri stealth frigate
- India's Defence Collaboration with Other Countries:
- Procurement and signing of contracts for defence equipment and platforms from foreign countries, such as:
- Aside from GE, India has been talking to other global jet engine makers for technology transfer such as Safran SA of France and Rolls-Royce of the United Kingdom for the AMCA.
Governance
Coal India and CCI
For Prelims: Competition Commission of India, Supreme Court, Coal Mines (Nationalisation) Act, of 1973, Competition Act, 2002
For Mains: Significance of Competition Commission due to the changing dynamics of the market,
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has recently dismissed Coal India Ltd (CIL)’s appeal, which affirmed the Competition Commission of India (CCI)’s authority to examine CIL’s conduct under the Competition Act, 2002.
- The court found no merit in excluding CIL from the purview of the Competition Act, which was earlier accused of engaging in abusive practices.
What is the Case About?
- About:
- In 2017, the CCI imposed a penalty of Rs. 591 crores on CIL for imposing unfair and discriminatory conditions in fuel supply agreements (FSAs) with power producers.
- The company was found to be supplying lower quality coal at higher prices and placing opaque conditions in the contract regarding supply parameters and quality.
- The CCI argued that Coal India and its subsidiaries operated independent of market forces and enjoyed market dominance in the production and supply of non-coking coal in India.
- In 2017, the CCI imposed a penalty of Rs. 591 crores on CIL for imposing unfair and discriminatory conditions in fuel supply agreements (FSAs) with power producers.
Note:
- Coal India Ltd (CIL) is a public sector undertaking that is the largest coal producer and supplier in India.
- It operates under the Coal Mines (Nationalisation) Act, of 1973, which gives it a monopoly over coal mining and distribution in the country.
- CIL was a fully government-owned entity until it's disinvestment in 2010. Currently, the government holds a majority shareholding with a share percentage of 67%.
- Arguments of CIL and CCI:
- CIL’s Stance:
- Principles of "Common Good":
- CIL operates based on the principles of promoting the "common good" and ensuring equitable distribution of coal, a vital natural resource.
- Monopoly Status:
- CIL refers to the Nationalization Act of 1973 to assert its position as a "monopoly" established for efficient coal production and distribution.
- Differential Pricing:
- CIL implements differential pricing to incentivise captive coal production, aiming to sustain the larger operating ecosystem and pursue welfare objectives.
- Implications for National Policies:
- CIL's coal supply supports national policies, such as promoting growth in economically disadvantaged regions through increased allocation.
- Principles of "Common Good":
- CCI’s Stance:
- Raghavan Committee Report (2020):
- The CCI referred to the Raghavan Committee report (2020), which concluded that state monopolies like CIL are not in the best interests of the nation and should not operate without competition.
- This highlights the need to promote competition and accountability in the market.
- Non-Essential Commodity Classification:
- The CCI emphasized that coal is no longer classified as an "essential commodity" since 2007.
- The Nationalisation Act too was removed from the Ninth Schedule (laws that cannot be challenged in court) in 2017.
- This indicates that coal is subject to market dynamics and should not be exempted from the Competition Act, 2002.
- The CCI emphasized that coal is no longer classified as an "essential commodity" since 2007.
- Impact on Consumers:
- The CCI highlighted the significant impact of irregular prices and supply of coal on power generation companies, which indirectly affects consumers.
- Unfair pricing or supply practices by CIL would directly impact consumers' interests.
- Government Ownership and Supply Allocation:
- CIL's significant coal supplies to power companies connect coal supply to the welfare of the nation.
- The CCI argued that ensuring continuous coal supply, adherence to contracts, reasonable pricing, and quality serve the common good.
- Raghavan Committee Report (2020):
- CIL’s Stance:
- Ruling of the Supreme Court:
- The SC dismissed CIL's argument for exemption based on the Nationalization Act of 1973, ruled that it cannot be exempted from the Competition Act.
- The court emphasized the need for fair competition and equality among entities, regardless of their sector and reinforced the principle of "competitive neutrality" and the need for a level playing field.
- It highlights the importance of competition in fostering a vibrant and efficient economy.
What is the Coal Mines (Nationalisation) Act, of 1973?
- The Coal Mines (Nationalisation) Act, of 1973, was enacted by the Indian Parliament to ensure rational, coordinated, and scientific development of coal resources.
- Under this act, coal mining was exclusively reserved for the public sector.
- Exceptions were introduced in 1976 for captive mining by private companies in iron and steel production and sub-leasing in isolated small pockets.
- In 1993, amendments allowed private sector participation in captive coal mining for power generation, coal washing, and other notified end uses.
- Allotment of coal mines for captive use was based on recommendations from a high-powered committee.
- Mining of coal for captive use in cement production was permitted by government notification.
- The Act established government control over coal mining in India, with limited provisions for private sector involvement in specific sectors and purposes.
What is the Competition Commission of India?
- About:
- Statutory body responsible for enforcing the Competition Act, 2002.
- Established in March 2009, replacing the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, of 1969.
- Quasi-judicial body giving opinions and dealing with cases.
- Composition:
- One Chairperson and six members appointed by the Central Government.
- Competition Act, 2002:
- The Competition Act, initially passed in 2002 and later amended by the Competition (Amendment) Act of 2007, has been further modified by the Competition Amendment Act of 2023.
- This latest amendment aims to regulate mergers and acquisitions based on transaction value, establish a framework for quicker resolution of investigations through settlement and commitment, and decriminalize specific offenses under the Act.
- Prohibits anti-competitive agreements and abuse of dominant position.
- Regulates combinations causing an adverse effect on competition within India.
- In accordance with the provisions of the Amendment Act, the Competition Commission of India and the Competition Appellate Tribunal (COMPAT) have been established.
- The government replaced the COMPAT with the National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT) in 2017.
- The Competition Act, initially passed in 2002 and later amended by the Competition (Amendment) Act of 2007, has been further modified by the Competition Amendment Act of 2023.
- Functions and Role of CCI:
- Eliminating practices with adverse effects on competition and protecting consumer interests.
- Giving opinions on competition issues referred by statutory authorities.
- Undertaking competition advocacy, creating public awareness, and providing training on competition issues.
- Ensuring consumer welfare and fair competition for economic growth and development.
- Implementing competition policies for efficient utilization of economic resources.
What are the other Judgements Related to Market Monopoly in India?
- Competition Commission of India v. Steel Authority of India Ltd (SAIL) (2010):
- The SC upheld the CCI’s order to investigate SAIL for anti-competitive practices in supplying rails to Indian Railways.
- SC ruled that SAIL was not exempt from the Competition Act and that its order was not appealable at the initial stage.
- The Court also said that the CCI was a necessary or proper party in any appeal before the COMPAT.
- Competition Commission of India v. Google LLC & Ors (2021):
- CCI appealed against Karnataka HC's order, investigating alleged anti-competitive practices by Google in India's smart TV and Android app store markets.
- The HC quashed CCI's order due to lack of jurisdiction and the absence of Google's opportunity to present its case.
- The SC stayed CCI's investigation and issued notices to all parties involved.


Social Justice
UNDP and DAY-NULM for Women Entrepreneurs
For Prelims: United Nations Development Programme, DAY-NULM, Biz-Sakhis, Care economy
For Mains: Women Entrepreneurs in India, Challenges Faced by Female Entrepreneurs in India, Facilitating Women Entrepreneurship in India
Why in News?
Recently, the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) and the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NULM) have joined hands to empower women entrepreneurs in India.
What are the Key Highlights of the Partnership?
- Aim:
- The partnership aims to provide support for women looking to start or expand their own enterprises in various sectors, such as care economy, digital economy, electric mobility, waste management, food packaging and more.
- To enhance the implementation of national-level schemes for urban poverty alleviation and livelihood promotion by providing capacity building support to DAY-NULM.
- To pilot innovative solutions, particularly in the care economy domain, to address the challenges and opportunities faced by women entrepreneurs.
- Coverage and Time Span:
- The project will cover eight cities in the initial phase and will span over three years, with the possibility of extension beyond 2025.
- Role of UNDP:
- UNDP will offer national-level capacity building support to DAY-NULM, focusing on knowledge generation and management, such as compiling compendiums of best practices related to urban poverty.
- UNDP and DAY-NULM will jointly engage in on-ground mobilization activities that involve identifying pockets of urban poverty and potential entrepreneurs, as well as facilitating access to business development services.
- UNDP will also contribute to the initiative by developing community business mentors called Biz-Sakhis in selected project locations.
- These mentors can support new and existing enterprises and serve as a resource for DAY-NULM at a later stage.
- Importance:
- Women entrepreneurship is a proven strategy for poverty alleviation, financial independence, and reshaping gender norms.
- Today, women account for only 15% of the total entrepreneurs in India. By increasing this number, the partnership not only empowers women, but also accelerates economic growth and ensures a happy and healthy society.
- The partnership leverages UNDP’s experience in linking over 200,000 women with better employment opportunities, and DAY-NULM’s mandate of uplifting urban communities through sustainable livelihood opportunities.
- Women entrepreneurship is a proven strategy for poverty alleviation, financial independence, and reshaping gender norms.
What is Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Urban Livelihoods Mission?
- The mission was launched in 2014 and is being implemented by the Urban Ministry of Housing & Poverty Alleviation.
- It aims to uplift urban poor by enhancing sustainable livelihood opportunities through skill development.
- It is Centrally Sponsored Scheme. Funding will be shared between the Centre and the States in the ratio of 75:25. For North eastern and Special Category – the ratio will be 90:10.
- DAY-NULM has mobilized more than 8.4 million urban poor women across India, forming over 8,31,000 Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in over 4,000 towns till 2023.
What Challenges do Women Entrepreneurs Face?
- Lack of female mentors and role models.
- Difficulty in maximizing the value of business networks traditionally dominated by men.
- Gender stereotypes and biases regarding logical and empathetic capabilities.
- Societal barriers imposed by patriarchal constructs and familial constraints.
- Challenges in raising finance and lack of creditworthiness.
- Limited avenues for financial management and reliance on others.
What are the Initiatives Related to Women Entrepreneurship in India?
- The Government of India and many state governments are running schemes to improve financial inclusivity for women. Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana is one such high-potential scheme for women because it offers collateral free loans.
- The Dena Shakti Scheme provides loans up to ₹20 lakh for women entrepreneurs in agriculture, manufacturing, micro-credit, retail stores, or small enterprises.
- The scheme also provides a concession of 0.25% on the rate of interest.
- The Government of India also launched the Stand Up India Scheme to leverage the institutional credit structure to reach out to the underserved sector of people such as SCs, STs and Women Entrepreneurs.
- Stree Shakti Yojana and Orient Mahila Vikas Yojana support women who have majority of ownership in the business.
- Women who want to enroll themselves in catering business can attain loan via the Annapurna Yojana.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q.1 “Empowering women is the key to control population growth”. Discuss. (2019)
Q.2 Discuss the positive and negative effects of globalization on women in India? (2015)
Q.3 Male membership needs to be encouraged in order to make women’s organization free from gender bias. Comment. (2013)


Important Facts For Prelims
China Blocks Proposal to Blacklist Pakistan-Based Terrorist
Why in News?
China's recent move to block a proposal at the United Nations (UN) to designate a Pakistan-based LeT terrorist as a global terrorist has drawn attention and raised concerns among the international community.
- In September 2022, China had put a hold on the proposal to designate the terrorist at the UN.
What is the Concern Raised Regarding China's Decision to Block the Proposal?
- The blocked proposal, brought forward by India and the United States, aimed to blacklist a wanted individual for his involvement in the 26/11 Mumbai terror attacks, under the 1267 Al Qaeda Sanctions Committee of the UN Security Council.
- This is not the first time China has blocked efforts to blacklist Pakistan-based terrorists under the UN Security Council's sanctions committee.
- China has consistently placed holds on listings that target individuals associated with terrorism in Pakistan including in 2009, 2016, 2017.
- China's actions have raised concerns among countries that seek to combat terrorism globally, as it appears to prioritise its relationship with Pakistan over international security cooperation.
- It also highlights the challenges of achieving consensus within the UN Security Council on sensitive issues related to terrorism.
What is the 1267 Al Qaeda Sanctions Committee?
- The committee is part of the UN Security Council and its job is to implement international sanctions against terrorists.
- The other two committees with similar roles are the Counter-Terrorism Committee and the Security Council Committee.
- The Al Qaeda committee was established as the Al-Qaida and Taliban Sanctions Committee on October 15, 1999, after Security Council Resolution 1267 designated al-Qaeda and the Taliban as terrorist bodies.
- In 2011, a separate committee was formed for the Taliban.
- Under the Committee regime, any UN member state can propose the name of an individual or group to be designated as a terrorist.
- Decisions are made by consensus in the 1267 Sanctions Committee, which comprises all members of the UNSC.
- A committee member can block blacklisting proposals by raising objections or applying a “technical hold” on a proposal.
- An individual or entity listed as a terrorist is subjected to an assets freeze, travel ban, and arms embargo.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The Security Council of UN consists of 5 permanent members, and the remaining 10 members are elected by the General Assembly for a term of (2009)
(a) 1 year
(b) 2 years
(c) 3 years
(d) 5 years
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
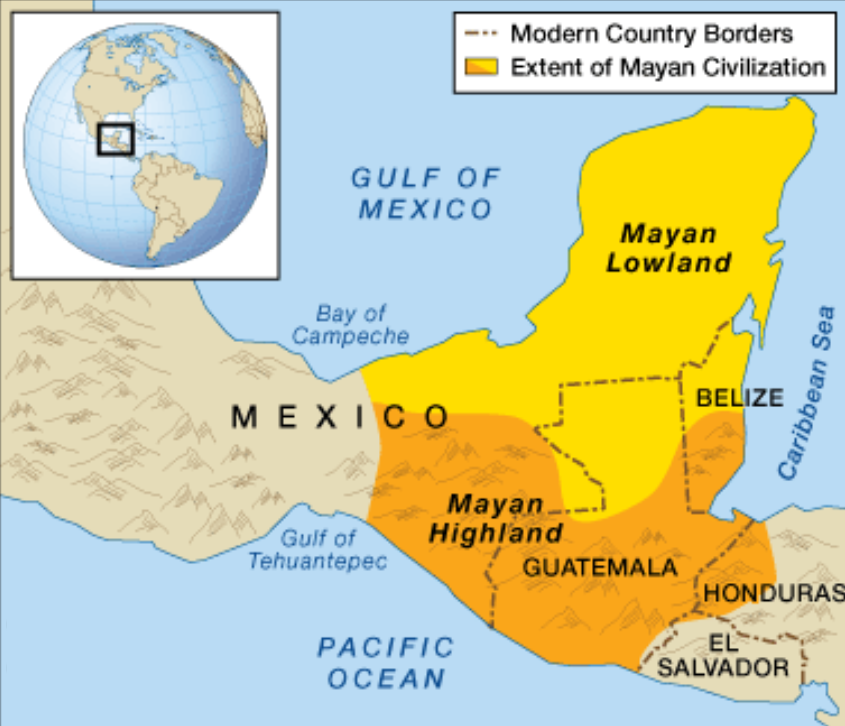
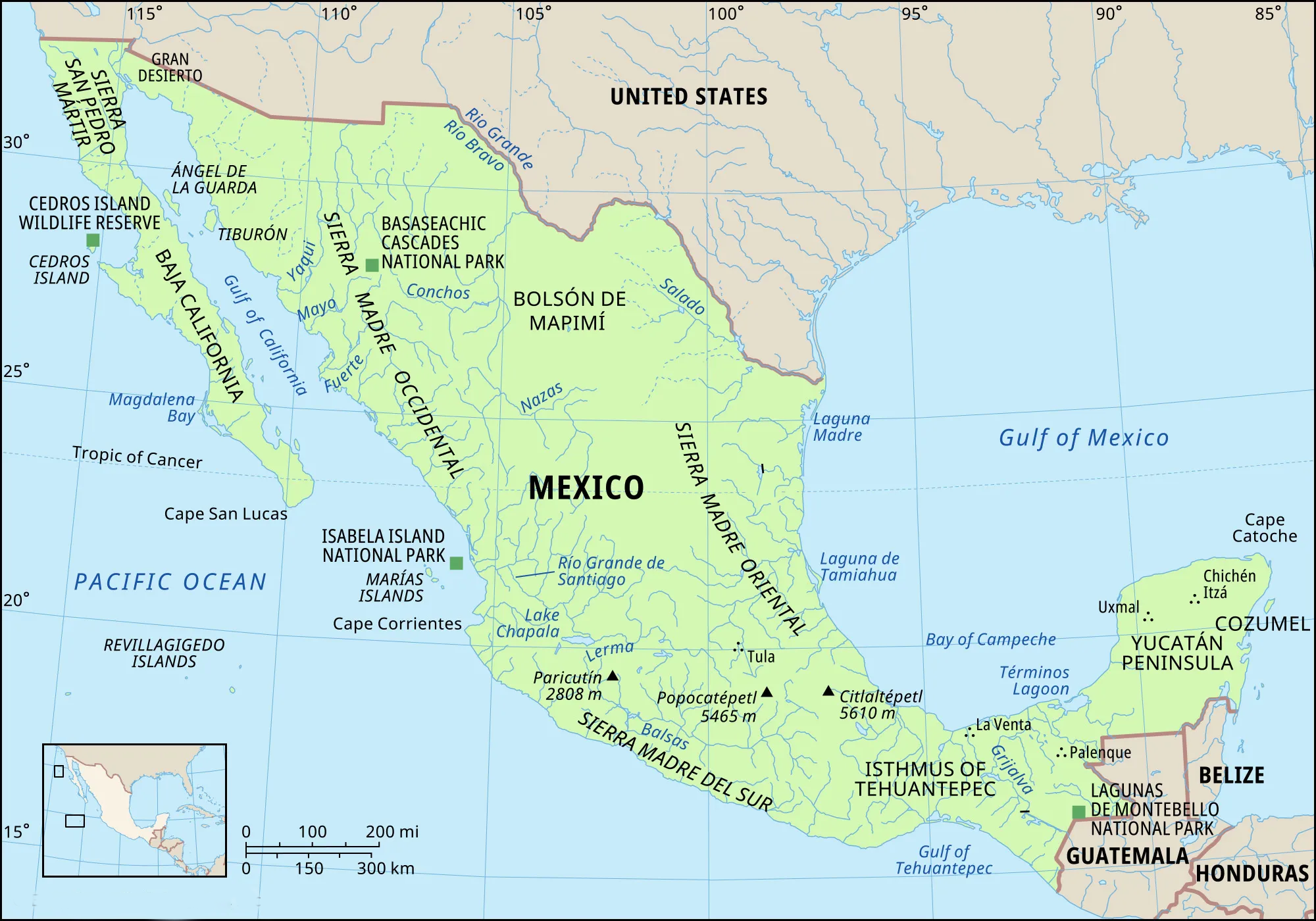
Discovery of Ancient Maya City
Why in News?
Archaeologists in Mexico have made a significant discovery in the dense jungle of the Yucatan Peninsula, uncovering the remains of an ancient Maya city.
What are the Major Findings Related to Ancient Maya City?
- About:
- The National Institute for Anthropology and History (INAH) in Mexico led the expedition to Ocomtún.
- The research team used airborne laser scanning to identify pre-Hispanic structures throughout the region.
- Named Ocomtun, meaning "stone column" in the Yucatec Maya language, this newly discovered city is believed to have been a prominent centre in the central lowland region of the Yucatan Peninsula between 250 and 1000 AD.
- It also provides invaluable insights into the advanced societal and religious practices of the Maya civilization, known for its sophisticated mathematical calendars.
- The National Institute for Anthropology and History (INAH) in Mexico led the expedition to Ocomtún.
- Major Findings:
- Elevated Terrain: One of the most surprising findings was an elevated terrain surrounded by wetlands, suggesting a unique and strategic settlement pattern.
- Pottery: Pottery fragments found at the site indicate that Ocomtún was inhabited during the Late Classic period (600-900 A.D.)
- Central Altars: It was discovered near the La Riguena river, possibly used for community rituals.
- Central altars suggest the presence of community rituals, highlighting the spiritual and communal aspects of Maya life.
- Pre-Hispanic Ball Games: It was played throughout the Maya region, representing a religious practice.
- The game involved passing a rubber ball, symbolising the sun, through a stone hoop without using hands.
- Decline of the City: The site likely underwent significant changes between 800 and 1000 AD.
- This period coincided with the decline and collapse of the Lowland Maya civilization, which was marked by a decline in population, urban centres, and political instability.
- The fall of Ocomtún and other Maya cities was part of a larger regional collapse, signifying a transformative period in Maya history.
What is Maya Civilization?
- The Maya are an indigenous people of Mexico and Central America. Originating in the Yucatán, they rose to prominence around A.D. 250 in present-day southern Mexico, Guatemala, northern Belize and western Honduras.
- The rise of the Maya began about 250 CE, and what is known to archaeologists as the Classic Period of Mayan culture lasted until about 900 CE.
- The Maya civilization was one of the most advanced and influential cultures.
- They developed complex systems of writing, astronomy, mathematics, art, architecture, and religion.
- They also built impressive cities with pyramids, palaces, temples, and plazas. However, many aspects of their history and culture remain mysterious and unknown.
What are the Other Major Ancient Civilizations?
- The Indus Valley Civilization- Northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India
- The Mesopotamian Civilization- Iraq, Syria, and Turkey
- The Incan Civilization- Ecuador, Peru, and Chile
- The Aztec Civilization- Mexico
- The Persian Civilization- Iran
- The Ancient Greek Civilization- Greece
- The Ancient Egyptian Civilization- Egypt
What are the Key Facts of Mexico?
- Form of Government: Republic of federated states
- Capital: Mexico City
- Official Language: Spanish
- Money: Peso
- Major Mountain Ranges: Sierra Madre
- Major Rivers: Rio Grande, Yaqui


Important Facts For Prelims
Star Rating Registration Process for Coal Mines
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Coal has announced the commencement of the Star Rating Registration process of Coal and Lignite Mines for the financial year 2022-23.
What is the Process of Registration?
- Parameters:
- The Star Rating policy aims to evaluate mines based on various factors across seven key parameters namely,
- Mining Operations,
- Environment-related parameters,
- Adoption of Technologies,
- Best Mining Practices,
- Economic performance,
- Rehabilitation & Resettlement,
- Worker-related Compliance and Safety & security.
- The Star Rating policy aims to evaluate mines based on various factors across seven key parameters namely,
- Process:
- Participating mines will undergo a self-evaluation process, and the top 10% performing mines will be further validated through inspections conducted by a committee.
- While the remaining 90% of the mines will undergo an online review process, all participants can contribute to the evaluation by reviewing other mines.
- The evaluation will be conducted by the Coal Controller’s Organization.
- The ratings awarded range from Five Star to NO Star, comprehensively evaluating each mine’s achievements.
- Aim:
- It aims to foster competitiveness among mines and recognize their outstanding performance based on compliance of statutory provisions, adoption of advanced mining technology and economic achievements.
What is Coal?
- About:
- It is a type of fossil fuel found in the form of sedimentary rocks and is often known as 'Black Gold'.
- It is a conventional source of energy and is widely available. It is used as a domestic fuel, in industries such as iron and steel, steam engines and to generate electricity. Electricity from coal is called thermal power.
- The leading coal producers of the world include China, US, Australia, Indonesia, India.
- Indian coal has high ash content, which varies from 35 to 45%, compared with that of coal in other parts of the world, which is around 15% while it has low sulphur content, about 0.5%.
- Distribution of Coal in India:
- Gondwana Coal Fields (250 million years old):
- Gondwana coal makes up to 98% of the total reserves and 99% of the production of coal in India.
- Gondwana coal forms India’s metallurgical grade as well as superior quality coal.
- It is found in Damodar (Jharkhand-West Bengal), Mahanadi (Chhattisgarh-Odisha), Godavari (Maharashtra), and Narmada valleys.
- Tertiary Coal Fields (15 – 60 million years old):
- Carbon content is very low but is rich in moisture and Sulphur.
- Tertiary coalfields are mainly confined to extra-peninsular regions
- Important areas include Assam, Meghalaya, Nagaland, Arunachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir, Himalayan foothills of Darjeeling in West Bengal, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Kerala.
- Gondwana Coal Fields (250 million years old):
- Classification:
- Anthracite (80 - 95% carbon content, found in small quantities in J&K).
- Bituminous (60 - 80% carbon content and is found in Jharkhand, West Bengal, Odisha, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh).
- Lignite (40 to 55% carbon content, high moisture content and is found in Rajasthan, Lakhimpur (Assam) and Tamil Nadu).
- Peat (less than 40% carbon content and it is in the first stage of transformation from organic matter (wood) to coal).
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Which of the following is/are the characteristic/characteristics of Indian coal? (2013)
- High ash content
- Low sulphur content
- Low ash fusion temperature
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Licensing and Regulation of Submarine Cable Landing in India
Why in News?
The Department of Telecom (DoT) raised concerns about Indian International Long-Distance Operators (ILDOs) without any stake in submarine cable systems seeking clearances for laying and maintaining submarine cables in India.
- In this context, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has released recommendations on the "Licensing Framework and Regulatory Mechanism for Submarine Cable Landing in India”.
What are the Recommendations of TRAI?
- Two Categories of CLS:
- Amending the ILD/ISP-A (international long distance/Internet service provider Category A) permits to include two categories of Cable Landing Station (CLS) locations — Main CLS and CLS “point of presence”.
- Main CLS facility be mandated to seek all approvals for an international submarine cable (SMC) landing in India.
- CLS ‘point of presence’ needs to allow lawful interception and meet the requisite security drill.
- Amending the ILD/ISP-A (international long distance/Internet service provider Category A) permits to include two categories of Cable Landing Station (CLS) locations — Main CLS and CLS “point of presence”.
- Critical and Essential Service:
- The submarine cable operations should be recognized as critical and essential services due to their crucial role in maintaining seamless national and international communication networks.
- Submarine cable operations should have the highest level of importance for obtaining necessary permissions and security clearances.
- Proposed Legislative Amendment:
- Addition of a section on "Submarine cable" and "Cable Landing Station" in the Indian Telecommunication Bill, 2022.
- It will provide legal and regulatory support, contributing to the growth and robustness of the digital communications sector.
- Addition of a section on "Submarine cable" and "Cable Landing Station" in the Indian Telecommunication Bill, 2022.
- Custom Duty and GST Exemptions:
- TRAI proposes exemption from custom duty and GST for goods and items required for CLS, submarine cable operation, and maintenance.
- This will address critical challenges in the sector, particularly related to cable repair and maintenance.
What is the Significance of the Recommendations?
- Strengthening Data Flow:
- TRAI's recommendations have the potential to unlock the full potential of cross-border data flow, fuel innovation, and fortify India's position as a data powerhouse.
- Reduced Reliance on Foreign Providers:
- The requirement for Indian entity-owned vessels for undersea cable maintenance will reduce delays and decrease reliance on foreign providers for repairing subsea cables.
What is a Submarine Communications Cable?
- About:
- It is a cable laid on the seabed between land-based stations to transmit telecommunication signals across stretches of ocean and sea.
- Modern submarine cables use fiber-optic technology. The optical fibre elements are typically coated with plastic layers and contained in a protective tube suitable for the environment where the cable will be deployed.
- Significance:
- Compared to satellites, using internet connection through submarine cables is more reliable, cost efficient and of larger capacity.
- Examples:
- MIST Submarine Cable System (connecting India with Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia and Singapore)
- Reliance Jio Infocomm’s India Asia Xpress (IAX) (India to the Maldives, Singapore, Sri Lanka and Thailand)
- India Europe Xpress (IEX) (India to Italy via Saudi and Greece)
- SeaMeWe-6 project (Singapore to France via India, Bangladesh, Maldives)
- Africa2 Cable (India with the UK via several African countries
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
'Made-in-Surat' Eco-Friendly Diamond
During the Indian Prime Minister's visit to the White House, US, an eco-friendly lab-grown diamond (LGD) was presented as a gift to US First Lady Jill Biden. Produced in Surat, India, the diamond showcases the excellence of the country's diamond industry.
LGD are synthetic diamonds produced in laboratories, possessing the same chemical composition and physical properties as naturally occurring diamonds. They are manufactured through High Pressure, High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) methods using a seed diamond, a slice of another diamond. Lab-grown diamonds have applications in industrial tools and machinery due to their hardness, and pure synthetic diamonds are used as heat spreaders in electronics.
Read more: Lab-Grown Diamonds
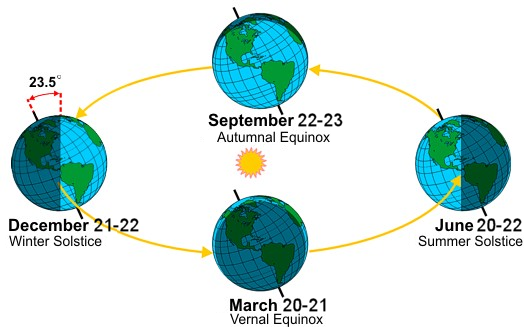
Summer Solstice
The summer solstice, occurring on June 21 in the Northern Hemisphere, signifies the longest day of the year. This astronomical event is a result of the Earth's tilt on its axis. This tilt, always at 23.5 degrees with respect to the Sun, creates the phenomenon known as the solstice. The solstice, derived from the Latin phrase meaning "sun stands still,". The Northern Hemisphere receives more direct sunlight between March and September, leading to the summer season in this region. The amount of sunlight received during the summer solstice varies based on latitude, with areas further north experiencing more daylight. In fact, at the Arctic Circle, the sun remains visible throughout the entire day during the solstice.
In contrast, the Southern Hemisphere receives most sunlight on December 21, 22 or 23 when the northern hemisphere has its longest nights– or the winter solstice.
Read more: Summer Solstice: 21st June
National Florence Nightingale Award
Recently, the President of India presented the National Florence Nightingale Awards for the years 2022 and 2023 to the Nursing professionals at a function held at Rashtrapati Bhavan.
The National Florence Nightingale Award was instituted by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India in the year 1973 as a mark of recognition for the meritorious services rendered by the nurses and nursing professionals to the society.
Read more: International Nurses Day
Legal Counsel Challenges ED's Authority in PMLA Arrest Case
A senior counsel representing a petitioner before the Madras High Court questioned the Directorate of Enforcement (ED) jurisdiction to insist on custodial interrogation in a case related to the Prevention of Money Laundering Act (PMLA).
The counsel argued that the PMLA does not grant ED officials the powers of a Station House Officer (SHO), making their demand for custody of the arrested person legally questionable. Additionally, a Supreme Court ruling was cited that restricts custodial interrogation beyond 15 days from the date of arrest, regardless of circumstances.
The ED is a multi-disciplinary organisation mandated with investigation of offences of money laundering and violations of foreign exchange laws. It functions under the Department of Revenue of the Ministry of Finance.
Read more: Directorate of Enforcement, Prevention of Money Laundering Act.