Kakrapar Atomic Power Project
For Prelims: Kakrapar Atomic Power Project, Regulated Fission Reaction, Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB).
For Mains: Kakrapar Atomic Power Project, Ways to Enhance India’s Nuclear Power Capacity.
Why in News?
Recently, the fourth unit of Kakrapar Atomic Power Station (KAPS), Gujarat has achieved its first Criticality — the beginning of the regulated fission reaction — paving the way for its eventual transition to generating power for commercial use.
What is Criticality?
- Criticality is the first step towards power production. A nuclear reactor is said to be critical when the nuclear fuel inside a reactor sustains a fission chain reaction.
- Each fission reaction releases a sufficient number of neutrons to sustain a series of reactions. Heat is produced in the event, which is used to generate steam that spins a turbine to create electricity.
- Fission is a process in which the nucleus of an atom splits into two or more smaller nuclei, and some byproducts.
- When the nucleus splits, the kinetic energy of the fission fragments (primary nuclei) is transferred to other atoms in the fuel as heat energy, which is eventually used to produce steam to drive the turbines.
What is the Significance of Achieving First Criticality?
- Milestone for Power Generation:
- This stage demonstrates that the reactor can produce a controlled and continuous chain reaction, essential for sustained power generation. It's a precursor to full operation and power generation for commercial use.
- Technology Advancements:
- The Kakrapar reactors, particularly Units 3 and 4, boast advanced safety features inspired by lessons from past nuclear incidents like the Fukushima Daiichi disaster.
- These include steel-lined containment systems and passive decay heat removal systems, enhancing safety and reliability.
- Energy Sustainability and Climate Goals:
- Nuclear energy, as a low-carbon source, aligns with India's climate goals to increase its renewable energy share.
- India aims to generate 50% of its electricity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030, as pledged at international forums like the United Nations Convention of Parties (COP26).
What are the Key Points about the Kakrapar Reactor?
- Existing KAPS reactors Unit-1 and Unit-2 have a capacity of 220 MW each. But the new 700MW projects, Unit-3 and Unit-4, are among the safest reactors in the world.
- The Unit-3 and 4 reactors have steel-lined inner containment systems that prevent any radioactive material from escaping in case of an accident.
- They also have passive decay heat removal systems, which safely cool down the reactor even when it is shut down.
How has India's Nuclear Journey Been?
- Early Development:
- India's nuclear program started in the 1940s and gained momentum with the establishment of the Atomic Energy Commission (AEC) in 1948.
- Homi Bhabha, known as the father of India's nuclear program, played a pivotal role in its early stages.
- Peaceful Nuclear Explosions:
- India conducted its first peaceful nuclear explosion as operation Smiling Buddha 1974, in Pokhran, marking its entry into nuclear technology.
- In May 1998 Pokhran-II was conducted as a series of five nuclear tests including one thermonuclear test aimed at demonstrating nuclear weapon capability
- Civil Nuclear Cooperation:
- Despite being outside the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT), India negotiated civil nuclear agreements with various countries, including the Indo-US Civil Nuclear Agreement in 2008, allowing for technology cooperation and nuclear fuel supply.
- Indigenous Nuclear Capabilities:
- India developed indigenous nuclear technology, including Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) and Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs), showcasing self-reliance and scientific prowess.
- India's nuclear power generation capacity grew steadily, with the Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL) leading the construction and operation of nuclear reactors across the country.
- India developed indigenous nuclear technology, including Pressurised Heavy Water Reactors (PHWRs) and Fast Breeder Reactors (FBRs), showcasing self-reliance and scientific prowess.
- Safety and Regulations:
- India focused on stringent safety standards and regulatory measures overseen by the Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) to ensure the safe operation of nuclear facilities.
- Nuclear energy played a role in diversifying India's energy mix, contributing to energy security and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- India focused on stringent safety standards and regulatory measures overseen by the Atomic Energy Regulatory Board (AERB) to ensure the safe operation of nuclear facilities.
- Current Status and Future Plans:
- Currently, India has 23 nuclear power reactors in operation under NPCIL (Nuclear Power Corporation of India), with a total capacity of 7,480 MW.
- NPCIL is constructing nine more reactors, including KAPS Unit-4, with a total capacity of 7,500 MW.
- As of 2023, India has a total generation capacity of 417 GW, out of which 43 percent is from renewable sources.However, nuclear energy still has a small role in India’s total energy generation, despite its rapid growth.
- In 2022-23, nuclear energy formed around 2.8 percent of India’s total energy production, according to government data.
- India has set ambitious targets to significantly increase its nuclear energy production, aiming to triple its capacity by 2031.
- However, challenges such as public concerns over safety, land acquisition, and regulatory hurdles remain.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. The function of heavy water in a nuclear reactor is to (2011)
(a) Slow down the speed of neutrons
(b) Increase the speed of neutrons
(c) Cool down the reactor
b Stop the nuclear reaction
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. With growing energy needs should India keep on expanding its nuclear energy programme? Discuss the facts and fears associated with nuclear energy. (2018)
Artificial Intelligence Mission
For Prelims: Artificial Intelligence, Global Partnership for AI Summit, AI Mission, Machine Learning (ML), INDIAai.
For Mains: Boosting AI innovation and startups, Artificial Intelligence Technology.
Why in News?
India is gearing up for a significant Artificial Intelligence (AI) push with the recent announcement of the AI Mission by the Prime Minister at the Global Partnership for AI Summit.
- The AI Mission is expected to boost India’s innovation ecosystem and position it as a global leader in artificial intelligence by building computational capacity and providing compute-as-a-service to startups.
Note
- Computing capacity, or compute, is a general term that refers to the resources required for a program to be successful. This includes processing power, memory, networking, and storage.
What are the Key Highlights of the AI Mission?
- Mission Objectives:
- The primary objectives of the AI Mission include establishing robust computing powers for AI within India.
- The mission seeks to enhance services for startups and entrepreneurs while fostering AI applications in critical sectors such as agriculture, healthcare, and education.
- Compute Capacity Goals:
- The ambitious plan involves building a substantial compute capacity, ranging between 10,000 to 30,000 Graphic Processing Units (GPUs).
- A GPU is a chip or electronic circuit that can render graphics for display on an electronic device. GPUs are designed to accelerate computer graphics and image processing.
- Additionally, an extra 1,000-2,000 GPUs are slated through the PSU Centre for Development of Advanced Computing (C-DAC).
- The government emphasizes a collaborative approach with the private sector for capacity building within the National Supercomputing Mission.
- The ambitious plan involves building a substantial compute capacity, ranging between 10,000 to 30,000 Graphic Processing Units (GPUs).
Note
- C-DAC's Rudra and Param systems are slated for expansion with the addition of 1,000-2,000 GPUs.
- Rudra is an indigenous server platform built by the C-DAC which has two expansion slots for graphic cards.
- Param Utkarsh is a high-performance computing system setup at C-DAC that offers AI over machine learning and deep learning frameworks, computing and storage as a cloud service.
- Incentive Structures:
- The government is exploring varied incentive models, including capital expenditure subsidies, operational expense-based incentives, and a "usage" fee.
- Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for Startups:
- The government plans to create a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) using the GPU assembly, allowing startups to access computational capacity at a reduced cost.
- Focus on Datasets:
- The introduction of the India Datasets platform is highlighted, offering non-personal and anonymized datasets to startups and researchers.
- The government contemplates issuing a directive to major tech companies, including Facebook, Google, and Amazon, to share anonymized personal data with the India Datasets platform.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
- AI is the ability of a computer, or a robot controlled by a computer to do tasks that are usually done by humans because they require human intelligence and judgement.
- Although no AI can perform the wide variety of tasks an ordinary human can do, some AI can match humans in specific tasks.
- The ideal characteristic of AI is its ability to rationalize and take actions that have the best chance of achieving a specific goal. A subset of AI is Machine Learning (ML).
- Deep Learning (DL) techniques enable this automatic learning through the absorption of huge amounts of unstructured data such as text, images, or video.
What are India's Other Initiatives Related to Artificial Intelligence?
- INDIAai.
- Global Partnership on Artificial Intelligence (GPAI).
- US India Artificial Intelligence Initiative.
- Responsible Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Youth.
- Artificial Intelligence Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation Platform.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. What are the main socio-economic implications arising out of the development of IT industries in major cities of India? (2022)
Q. “The emergence of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (Digital Revolution) has initiated e-Governance as an integral part of government”. Discuss. (2020)
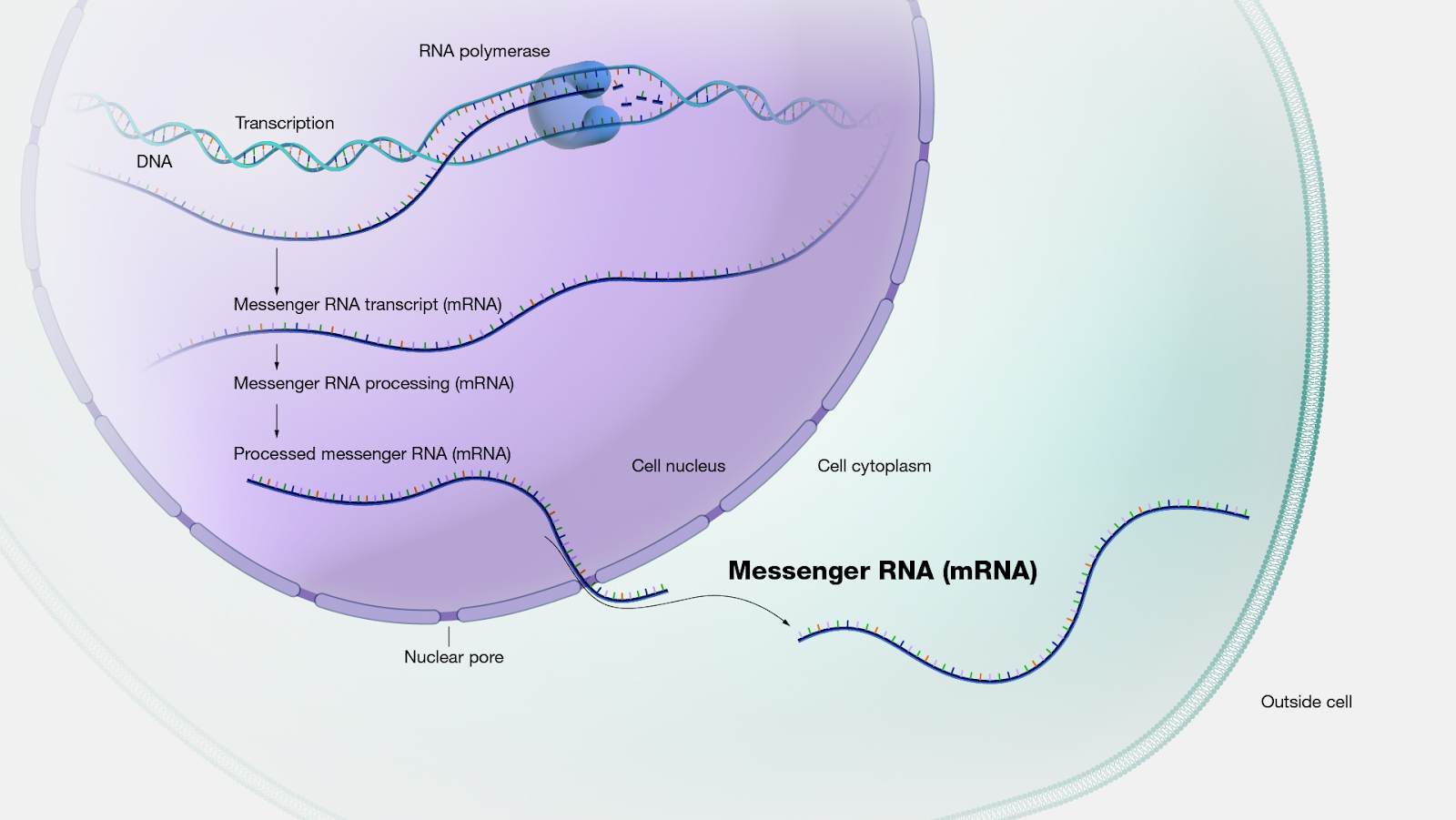
mRNA-Based Medicines
For Prelims: mRNA Vaccines, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), Cancer vaccine, mRNA Therapy.
For Mains: mRNA-Based Medicines, Biotechnology.
Why in News?
The cells in our body create mRNAs that serve as instructions to make specific proteins we need to function. Researchers can create new mRNAs to correct those instructions when they aren’t working.
- While most scientists studying mRNAs are not creating new drugs, this fundamental understanding of how mRNA works laid the foundation for other scientists to create effective mRNA medicines like Covid-19 vaccines.
What does mRNA do?
- mRNA (Messenger RNA) carries important messages from our DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid), to the cell's machinery, telling it how to make specific proteins.
- Imagine DNA as a library of cookbooks filled with recipes (genes) to create different proteins.
- Our bodies need around 100,000 proteins to work properly, helping with tasks like breaking down food and performing vital chemical reactions.
- When a cell needs a specific protein, it doesn't directly read the recipe from DNA. Instead, it makes a copy called mRNA.
- This mRNA serves as a messenger, carrying the protein-making instructions. It's made up of four building blocks (A, U, C, G), forming words of only three letters.
- By reading this mRNA recipe, cells easily know how to create the required protein.
- Cells are quite good at recognizing, using, and then getting rid of mRNA once it's done its job.
- However, changes or mistakes in the DNA's recipe book (mutations) can mess up the mRNA instructions, leading to errors in making essential proteins, which can cause diseases.
What is the Significance of mRNAs in Making Medicine?
- Precision and Customization:
- Scientists comprehend how mRNAs instruct cells to create proteins. This knowledge allows them to easily craft codes for various proteins, modifying these codes to suit individual patient needs.
- Whether it's designing entirely new mRNA codes or adjusting existing ones, the flexibility allows for tailored treatments.
- Scalability and Uniformity:
- Manufacturing mRNA treatments is scalable and consistent. The process to create one mRNA is uniform across different mRNA types.
- Unlike traditional drugs, each having unique chemistry and manufacturing methods, mRNA production follows a standardized process. This uniformity streamlines production, akin to knowing a basic recipe and being able to create countless variations.
- Easy Adaptability:
- Cells naturally eliminate mRNA once its task is complete. This characteristic ensures that mRNA treatments are not permanent.
- Adjusting doses to accommodate changing patient requirements becomes effortless due to this innate ability of cells to degrade unnecessary mRNA.
- Production Capacity:
- Scientists can generate substantial quantities of mRNA in laboratory settings. This ability to produce large amounts facilitates the development and distribution of mRNA-based medicines on a broader scale.
- Expanded Vaccine Development:
- Clinical trials for mRNA-based vaccines extend to diseases like seasonal flu, herpes, respiratory syncytial virus, norovirus, Lyme disease, Zika, and shingles, promising a wider array of preventive treatments.
- mRNA therapies show promise in cancer treatment by leveraging the body's immune response. Cancer vaccines, tailored to target specific mutations in tumors, enhance antibody production to mark and attack cancer cells. This personalized approach seeks to minimize harm to healthy cells.
- Clinical trials for mRNA-based vaccines extend to diseases like seasonal flu, herpes, respiratory syncytial virus, norovirus, Lyme disease, Zika, and shingles, promising a wider array of preventive treatments.
What is the Future of mRNA Based Medicines?
- The future of mRNA-based medicine appears promising, offering highly personalized, effective therapies with fewer side effects.
- This revolutionary approach holds the potential to address diverse diseases by precisely altering cellular processes and correcting protein deficiencies.
- The ease of customization and production positions mRNA as a versatile tool in modern medicine, poised to redefine treatment strategies and improve patient outcomes across various medical conditions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. Widespread resistance of malarial parasite to drugs like chloroquine has prompted attempts to develop a malarial vaccine to combat malaria. Why is it difficult to develop an effective malaria vaccine? (2010)
(a) Malaria is caused by several species of Plasmodium
(b) Man does not develop immunity to malaria during natural infection
(c) Vaccines can be developed only against bacteria
(d) Man is only an intermediate host and not the definitive host
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Malaria is a life-threatening disease caused by Plasmodium parasites that are transmitted to people through infected female Anopheles mosquitoes.
- The malarial parasite has an extraordinary ability to evade the immune system, which explains the difficulty in developing an effective malaria vaccine.
- RTS,S/AS01 (RTS,S) is the first and, to date, the only vaccine to show partial protection against malaria in young children.
- Hence, option (b) is correct.
Q. With reference to recent developments regarding ‘Recombinant Vector Vaccines’, consider the following statements:
- Genetic engineering is applied in the development of these vaccines.
- Bacteria and viruses are used as vectors.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Recombinant vector vaccines are made through genetic engineering. The gene that creates the protein for a bacteria or virus is isolated and placed inside another cell’s genes. When that cell reproduces, it produces vaccine proteins that mean the immune system will recognize the protein and protect the body against it. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Live recombinant bacteria or viral vectors effectively stimulate the immune system as in natural infections and have intrinsic adjuvant properties. They are used as the channel for the entry into the host organism.
- Several bacteria have been used as vectors, such as Mycobacterium bovis BCG, Listeria monocytogenes, Salmonella spp. and Shigella spp.
- Numerous viral vectors are available for vaccine development, such as vaccinia, modified vaccinia virus Ankara, adenovirus, adeno-associated virus, retrovirus/lentivirus, alphavirus, herpes virus, etc. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
2023 Records Lowest Number of CAG Audits
For Prelims: Appointment and Removal of Comptroller and Auditor General, Constitutional Provisions Related to CAG.
For Mains: Role of Audits in Democracy like India, Duties of CAG
Why in News?
In the calendar year 2023, only 18 audit reports on the Union government’s accounts, prepared by the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG), were tabled in Parliament. A year-wise analysis shows that the number of audits on the Union Government tabled in Parliament has been decreasing.
- On average, 22 reports were tabled each year between 2019 and 2023, compared to the 40 reports tabled between 2014 and 2018
What is the Office of CAG?
- About:
- Comptroller and Auditor General of India, is a constitutional authority which heads the Indian Audit and Accounts Department (IA&AD). The two entities are known as the Supreme Audit Institution of India (SAI).
- Mandate:
- As a “Guardian of the Public Purse”, CAG is vested with the responsibility of inspecting and auditing all the expenditure of both the Central and the State Governments as well as of those organizations or the bodies which the government significantly funds.
- This is the reason why Dr. B.R. Ambedkar said that the CAG shall be the most important Officer under the Constitution of India.
- As a “Guardian of the Public Purse”, CAG is vested with the responsibility of inspecting and auditing all the expenditure of both the Central and the State Governments as well as of those organizations or the bodies which the government significantly funds.
- Constitutional Provisions:
- Article 148 provides for an independent office of the CAG.
- Other Provisions Related to CAG include: Articles 149-151 (Duties & Powers, Form of Accounts of the Union and the States and Audit Reports), Article 279 (calculation of net proceeds, etc.) and Third Schedule (Oath or Affirmation) and Sixth Schedule (Administration of Tribal Areas in the States of Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram).
- Article 148 provides for an independent office of the CAG.
- Appointment: The CAG is appointed by the president of India by a warrant under his hand and seal.
- He is provided with the security of tenure. He can be removed by the president only in accordance with the procedure mentioned in the Constitution.
- Tenure: Period of 6 years or until attaining the age of 65 years whichever is earlier.
- Removal: Removal of the CAG from office requires a specific process: an order from the President after receiving an address from each House of Parliament.
- For removal to take effect, the address must be supported by a majority of the total membership of that house and by at least a two-thirds majority of the members present and voting in the same session.
- Grounds for removal include proved misbehavior or incapacity.
- Provisions of Independence: Major provisions include-
- The CAG's salary and expenses are charged upon the Consolidated Fund of India.
- CAG is provided with the security of tenure and does not hold office till the pleasure of the president, though he is appointed by him.
- Upon relinquishing the office, the CAG is barred from holding any subsequent position within either the Government of India or any State Government, maintaining the independence and integrity of the office.
What is the Role of Audits in a Democracy like India?
- Transparency and Accountability:
- Public Trust: Audits instill confidence in the public regarding how taxpayer money is utilized, ensuring transparency in government operations.
- Accountability: They hold government bodies and officials accountable for their financial decisions and actions, preventing misuse or misallocation of public funds.
- Preventing Financial Mismanagement:
- Detecting Errors and Fraud: Audits help uncover errors, discrepancies, or potential fraudulent activities, ensuring corrective actions are taken promptly.
- Budget Compliance: They verify if financial activities align with budgetary allocations, preventing overspending or unauthorized expenditures.
- Improving Efficiency and Effectiveness:
- Identifying Inefficiencies: Audits highlight inefficiencies in processes, allowing for improvements and cost-saving measures.
- Performance Assessment: They assess the effectiveness of government programs and initiatives, guiding future policy decisions for better outcomes.
- Enhancing Decision-Making: Audit reports provide valuable insights for policymakers, aiding in informed decision-making for better governance.
- Global Standards and Collaborations: Audits meeting global standards improve the country's standing in international financial communities, facilitating collaborations and partnerships
Note: The Constitution of India envisions the CAG as both the Comptroller and Auditor General. However, in practice, the CAG primarily functions as an Auditor General only and not Comptroller. In other words, CAG lacks control over fund disbursements. It is involved only during the audit phase, after the expenditure has occurred.
What Should be the Way Forward?
- Streamlining Audit Processes:
- Efficient Workflow: Implement streamlined processes within government departments to facilitate timely and comprehensive reporting, aiding in faster audit completion.
- Digital Transformation: Embrace technological advancements to digitize and expedite audit procedures, minimizing manual intervention and accelerating report generation.
- Promoting Transparency and Accountability:
- Timely Reporting: Set clear timelines and protocols for the submission of audit reports to Parliament, ensuring timely presentation and discussion.
- Enhanced Public Access: Ensure wider accessibility of audit reports through online platforms, promoting greater public scrutiny and understanding.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In India, other than ensuring that public funds are used efficiently and for intended purpose, what is the importance of the office of the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG)? (2012)
1. CAG exercises exchequer control on behalf of the Parliament when the President of India declares national emergency/financial emergency
2. CAG reports on the execution of projects or programmes by the ministries are discussed by the Public Accounts Committee.
3. Information from CAG reports can be used by investigating agencies to press charges against those who have violated the law while managing public finances.
4. While dealing with the audit and accounting of government companies, CAG has certain judicial powers for prosecuting those who violate the law.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 3 and 4 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: C
Mains
Q1: “The Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) has a very vital role to play.” Explain how this is reflected in the method and terms of his appointment as well as the range of powers he can exercise. (2018)
Q2: Exercise of CAG’s powers in relation to the accounts of the Union and the States is derived from Article 149 of the Indian Constitution. Discuss whether audit of the Government’s policy implementation could amount to overstepping its own (CAG) jurisdiction.(2016)
Outcome of SHG Bank Linkage Project
For Prelims: RBI , NABARD, Self-Help Group (SHG), Bank Sakhis, Core Banking Solution (CBS) database, DAY-NRLM, Revolving Fund and Community Investment Fund, Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP)
For Mains: Significance of SHG Bank Linkage Project,Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM), Government Policies & Interventions .
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Rural Development, in a written reply in Rajya Sabha has given information about Self Help Group (SHG) Bank linkage (BL).
- In 2019, the International Initiative for Impact Evaluation assessed DAY-NRLM, finding a 19% income boost and a 28% increase in household savings compared to the baseline.
- The study spanned nine states: Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
What is Self Help Group (SHG) Bank linkage (BL) Project?
- About:
- Components:
- Training and sensitization of Bank Branch Managers
- Training and positioning of Bank Sakhis at Rural Bank Branches
- Initiate Community Based Repayment Mechanism (CBRM) at Rural Bank Branches
- Credit Linkage of SHGs
- Key Factors for SHG-BL’s Success:
- Annual issuance of a Master Circular by RBI and NABARD.
- Specification of minimum loan amounts for each Self-Help Group (SHG) with provisions being modified as needed to meet the scheme's requirements.
- Regular training of staff and community cadres under State Rural Livelihoods Missions (SRLMs) to enhance their capacity.
- Financial education for Self Help Group (SHG) members through trained Financial Literacy Community Resource Persons (FLCRPs) at the village level.
- Bank Sakhis, trained members from SHGs who act as intermediaries, aiding SHG members in transactions and application processes.
- A web portal was created to overcome information asymmetry in SHG-Bank Linkage, incorporating data directly from Banks' Core Banking Solution (CBS) database.
- Annual issuance of a Master Circular by RBI and NABARD.
- Status of Bank Loans:
- The Bank loans to the tune of Rs. 7.68 lakh Crore have been accessed by SHGs since FY 2013-14.
What is Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM)?
- About:
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Programme, launched by the Ministry of Rural Development in 2011.
- It aims to eliminate rural poverty through the promotion of multiple livelihoods and improved access to financial services for the rural poor households across the country.
- Functioning:
- It involves working with community institutions through community professionals in the spirit of self-help which is a unique proposition of DAY-NRLM.
- It impacts livelihoods by
- Mobilizing rural households into SHGs.
- Organizing one-woman member from each rural poor household into SHGs
- Providing training and capacity building to SHG members
- Providing access to financial resources from their own institutions and banks.
- Sub Programs:
- Mahila Kisan Sashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): It aims to promote agro-ecological practices that increase women farmers’ income and reduce their input costs and risks.
- Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP): It aims to support entrepreneurs in rural areas to set up local enterprises.
- Aajeevika Grameen Express Yojana (AGEY): It was launched in August 2017, to provide safe, affordable and community monitored rural transport services to connect remote rural villages.
- Deendayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDUGKY): It aims at building placement-linked skills of the rural youth and placing them in relatively higher wage employment sectors of the economy.
- Rural Self Employment Institutes (RSETIs): DAY-NRLM, in partnership with 31 Banks and State Governments, is supporting Rural Self Employment Institutes (RSETIs) for skilling rural youth to take up gainful self-employment.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. How does the National Rural Livelihood Mission seek to improve livelihood options of rural poor? (2012)
- By setting up a large number of new manufacturing industries and agribusiness centres in rural areas
- By strengthening ‘self-help groups’ and providing skill development
- By supplying seeds, fertilizers, diesel pump-sets and micro-irrigation equipment free of cost to farmers
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. “The emergence of Self-Help Groups (SHGs) in contemporary times points to the slow but steady withdrawal of the State from developmental activities”. Examine the role of the SHGs in developmental activities and the measures taken by the Government of India to promote the SHGs. (2017)
Q. The Self-Help Group (SHG) Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP), which is India’s own innovation, has proved to be one of the most effective poverty alleviation and women empowerment programmes. Elucidate. (2015)
Bihar's Punaura Dham project
Why in News?
The Bihar state government recently approved a project to develop Punaura Dham, a temple complex in Sitamarhi district, as a major tourist attraction.
- Punaura Dham is believed to be the birthplace of Goddess Sita, wife of Lord Rama and a revered figure in Hinduism.
- The initiative aims to promote the culture and heritage of Mithila, the region where Sita was born and raised.
Note:
- According to the Valmiki Ramayana, Sita emerged from a furrow when King Janaka, the ruler of Mithila, was ploughing the land.
- He adopted her as his daughter and named her Sita, which means “furrow” in Sanskrit. He also gave her the name Janaki, meaning “daughter of Janaka”.
What are the Key Cultural Aspects of Mithila?
- Historical Significance:
- Mithila has a rich and ancient history, dating back to the Vedic period (1500-500 BCE) when it was one of the 16 Mahajanapadas of India.
- Mithila, also known as Tirhut or Tirabhukti, is a historically and culturally significant region encompassing Darbhanga, Madhubani, Sitamarhi, Supaul, Saharsa, Madhepura, and adjacent areas of Bihar and Nepal.
- It is bounded by the Himalayas in the north, the Ganges in the south, the Gandaki River in the west, and the Mahananda River in the east.
- It is also known as Mahla and mentioned in revenue records of the United Provinces of Bihar, Bengal, and Orissa.
- It was ruled by the Videha Janak dynasty.
- Language and Literature:
- The main language of Mithila is Maithili which belongs to the Indo-Aryan family.
- Maithili has a rich literary tradition, the poet Vidyapati(1352–1448 AD), wrote famous songs of love and devotion in this language.
- Maithili literature also includes epics, dramas, folktales, and biographies of saints and heroes.
- The main language of Mithila is Maithili which belongs to the Indo-Aryan family.
- Cultural Heritage:
- Mithila is famous for its unique style of painting, known as Madhubani or Mithila painting, which is done using bright earthy natural colours and geometric patterns.
- The paintings depict scenes from Hindu mythology, especially the Ramayana, as well as flora, fauna, and social events.
- Mithila is famous for its unique style of painting, known as Madhubani or Mithila painting, which is done using bright earthy natural colours and geometric patterns.
- GI Tag:
- Mithila Makhana or Makhan (botanical name: Euryale ferox Salisb.) is a special variety of aquatic fox nut cultivated in Mithila region of Bihar and Nepal. It is also recognised with the GI (geographical indication) tag.
National Mathematics Day 2023
National Mathematics Day is celebrated on 22nd December annually since 2012. The day honours the birth anniversary of Srinivasa Ramanujan, a renowned Indian mathematician.
- Ramanujan, born on 22nd December 1887, in Erode, Tamil Nadu, is known for his contributions to number theory, infinite series, and continued fractions.
- The number 1729, known as the Ramanujan number, is the smallest number expressible as the sum of two different cubes in two distinct ways.
- Ramanujan compiled around 3,900 results consisting of equations and identities. One of his most treasured findings was his infinite series for Pi.
- Made significant contributions to hypergeometric series, Riemann series, elliptic integrals, mock theta function, and theory of divergent series.
- The Man Who Knew Infinity is a 2015 biographical film about Ramanujan.
CMFRI Commercializes Seaweed-Based Nutraceuticals
The Indian Council of Agricultural Research(ICAR)- Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI) has successfully commercialized two seaweed-based nutraceutical products, CadalminTM Immunalgin extract (CadalminTM IMe) and CadalminTM Antihypercholesterolemic extract (CadalminTM ACe).
- These products, developed with eco-friendly 'green' technology, aim to boost anti-viral immunity and combat high cholesterol or dyslipidemia (imbalance of cholesterol).
- The product is positioned as a potential remedy against post-Covid complications, exhibiting antiviral properties against the delta variant of SARS CoV-2.
- Seaweeds, primitive marine algae, lacking roots, stems, and leaves, play a vital role in marine ecosystems.
- Seaweeds offer nutritional benefits and medicinal properties, containing anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial agents with potential cancer-fighting effects.
Paat-Mitro App to Facilitate Jute Farmers
Recently, the Ministry of Textiles launched “Paat-Mitro”, a mobile application, developed by the Jute Corporation of India Limited (JCI) during the Jute Symposium.
- The application is available in 6 languages and all the functionalities are made available to the users free of cost.
- The app also offers agronomic practices, Minimum Support Prices (MSP) details, Jute Gradation Parameters, 'Jute-ICARE' schemes, weather forecasts, JCI’s Purchase Centers’ locations, and Procurement Policies. It enables farmers to track their jute payments and uses a Chatbot for queries.
- India is the largest producer of jute followed by Bangladesh and China.
- However, in terms of acreage and trade, Bangladesh takes the lead accounting for three-fourth of the global jute exports in comparison to India’s 7%.
Kashi Tamil Sangamam
The Prime Minister of India inaugurated the Kashi Tamil Sangamam at Namo Ghat, Varanasi, which aims to celebrate the historical and civilizational connections between North and South India.
- The event is a month-long celebration of art, music, handloom, handicrafts, cuisines, and other distinctive products from Tamil Nadu and Varanasi.
- The ancient connection between Kashi (Uttar Pradesh) and Tamil Nadu dates back to the 15th century when King Parakrama Pandya, ruler of the region around Madurai, traveled to Kashi to bring back the lingam for his temple.
- While returning, he stopped to rest under a tree. When he tried to continue his journey, the cow carrying the lingam refused to budge from its spot.
- Parakrama Pandya understood this to be the Lord’s wish and installed the lingam there, a place that today is known as Sivakasi.
- The Pandyas also built the Kasi Viswanathan Temple which is known as Tenkasi in southwestern Tamil Nadu.