India's Digital Landscape with PM-WANI
For Prelims: PM WANI, India's Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
For Mains: Role of PM-WANI in India's Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)
Why in News?
The Prime Minister Wi-Fi Access Network Interface (PM WANI) scheme is set to revolutionize public Wi-Fi in India. PM-WANI can be a potential game-changer for India’s digital public infrastructure.
- The scheme enables public Wi-Fi data service through small retail data offices, which can potentially bring broadband internet to remote locations at a minimum investment.
What is PM-WANI?
- About:
- The PM-WANI, launched by the Department of Telecom (DoT) in December 2020, is one key scheme launched to bolster the penetration of public WiFi hotspots to establish a robust digital communication infrastructure throughout the nation, especially in rural areas.
- It is a framework that enables any entity, such as a shopkeeper, a tea stall owner, or a Kirana store owner, to set up a public Wi-Fi hotspot and provide internet service to customers.
- This framework takes forward the goal of the National Digital Communications Policy, 2018 (NDCP) of creating a robust digital communications infrastructure.
- Importance:
- To facilitate ease of doing business and encourage local shops and small establishments to become Wi-Fi providers, it has been approved that the last-mile Public Wi-Fi providers require no license, no registration and will not need to pay any fees to DoT.
- PM-WANI Ecosystem:
- PM-WANI consists of four elements:
- Public Data Office (PDO): PDO is the entity that establishes, maintains, and operates the Wi-Fi hotspot and provides last-mile connectivity to the users by procuring internet bandwidth from telecom service providers or internet service providers.
- Public Data Office Aggregator (PDOA): PDOA is the entity that provides aggregation services, such as authorization and accounting, to PDOs, and facilitates them in providing services to the end users.
- App Provider: It is the entity that develops an application to register users and discover and display PM-WANI compliant Wi-Fi hotspots in proximity for accessing the internet service and also authenticate the potential users.
- Central Registry: It is the entity that maintains the details of App Providers, PDOAs, and PDOs. It is currently maintained by the Centre for Development of Telematics (C-DoT).
- Status:
- As of November 2022, the PM-WANI central registry reported the existence of 188 PDO aggregators, 109 app providers, and 11,50,394 public WiFi hotspots.
- PM-WANI consists of four elements:
- Benefits of PM-WANI:
- It can expand Internet access in rural and remote areas.
- It can provide an affordable and convenient option for internet access, as compared to mobile technologies like 5G, which require high investment and subscription costs.
- It can stimulate innovation and competition in the internet market.
- Challenges of PM-WANI:
- Ensuring Wi-Fi quality and user experience poses challenges related to bandwidth availability, managing user numbers, device compatibility, and maintaining data security and privacy.
- Security threats like data leakage, hacking, and malware can jeopardize user and provider privacy.
- Mobile telecom companies might face challenges, including market share and revenue loss, due to PM-WANI's affordability and accessibility.
- Expanding and maintaining PM-WANI in rural and remote areas with low internet demand and high operational costs could be challenging.
How can PM-WANI be a Game-Changer for India’s Digital Public Infrastructure?
- PM-WANI is a key part of India's Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI). It can democratize internet access and bridge the digital divide by enabling anyone to become a Wi-Fi provider and anyone to become a Wi-Fi user, without any license, registration, or fee.
- Leverage the existing physical and social infrastructure, such as the shops, the CSCs, the SDCs, the post offices, the schools, the panchayats, etc., to create a distributed and decentralized network of Wi-Fi hotspots, and also utilize the existing digital infrastructure, such as Aadhaar, UPI, e-KYC, e-Sign, etc., to enable seamless and secure authentication and payment of the Wi-Fi services.
- Empower the citizens and the communities by providing them access to information, knowledge, opportunities, and services that can improve their quality of life, and also enable them to participate and contribute to the digital economy and society.
What is Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI)?
- About:
- DPI refers to blocks or platforms such as digital identification, payment infrastructure and data exchange solutions that help countries deliver essential services to their people, empowering citizens and improving lives by enabling digital inclusion.
- DPIs mediate the flow of people, money and information. First, the flow of people through a digital ID System. Second, the flow of money through a real-time fast payment system. Third, the flow of personal information through a consent-based data-sharing system to actualize the benefits of DPIs and to empower the citizens with a real ability to control data.
- These three sets become the foundation for developing an effective DPI ecosystem.
- Operates under open, transparent, and participatory governance.
- India, through India Stack, became the first country to develop all three foundational DPIs, Digital identity (Aadhar), Real-time fast payment (UPI)and Account Aggregator built on the Data Empowerment Protection Architecture (DEPA).
- Constitutes Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI):
- DPI comprises three integral layers:
- Market: Innovative and competitive players designing inclusive products.
- Governance: Legal and institutional frameworks, public programs, and policies.
- Technology Standards: Identity, payments, and data sharing standards for interoperability.
- DPI comprises three integral layers:
- Benefits of DPI's Approach:
- Reduced development costs and modular end-user solutions.
- An ecosystem of diverse applications and lower entry barriers.
- A democratic, non-monopolistic system with built-in scalability.
- Successful DPI Initiatives in India:
- Aadhaar, Unified Payment Interface (UPI), and CoWin. Others like Unified Health Interface (UHI), Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), and Open Network for Digital Commerce are in progress.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- Aadhaar card can be used as a proof of citizenship or domicile.
- Once issued, Aadhaar number cannot be deactivated or omitted by the Issuing Authority.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (d)
Global Report on Hypertension
For Prelims: World Health Organization (WHO), Hypertension, India Hypertension Control Initiative Program (IHCI)
For Mains: Hypertension and its implications on public health, Universal Health Coverage.
Why in News?
Recently, during the United Nations General Assembly’s (UNGA) 78th session, the World Health Organization (WHO) released a report titled "Global report on hypertension: The race against a silent killer."
- It is the first-ever report by the WHO on the worldwide implications of hypertension, commonly referred to as high blood pressure.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- A Global Epidemic:
- One in three adults across the world suffers from hypertension.
- The number of hypertension cases has doubled from 650 million to a staggering 1.3 billion between 1990 and 2019.
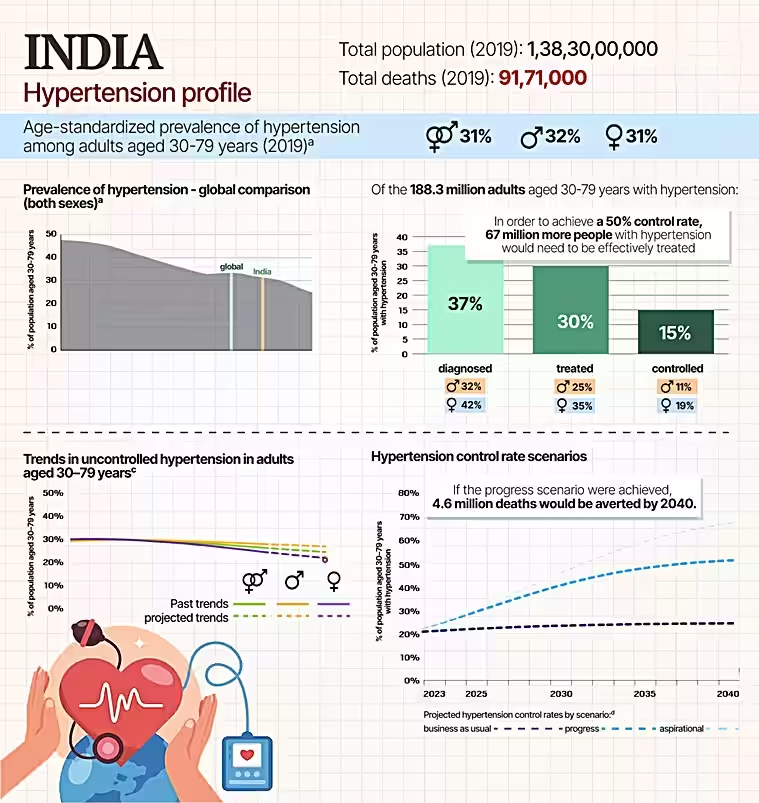
- Hypertension affects approximately 33% of adults aged 30-79 worldwide.
- Approximately four out of every five people with hypertension are not adequately treated.
- India's Hypertension Burden:
- India alone has an estimated 188.3 million adults aged 30–79 years grappling with hypertension.
- The prevalence of high blood pressure in India is slightly lower than the global average of 31%.
- To reach a 50% control rate, India needs to ensure that an additional 67 million people with hypertension receive effective treatment.
- If the progress scenario were achieved, 4.6 million deaths due to high blood pressure would be averted by 2040.
- Inadequate Treatment:
- About 80% of individuals with hypertension do not receive adequate treatment.
- Effective hypertension treatment has the potential to prevent 76 million deaths, 120 million strokes, 79 million heart attacks, and 17 million cases of heart failure by 2050.
- About 80% of individuals with hypertension do not receive adequate treatment.
- Disparities in Treatment Coverage:
- Treatment coverage for hypertension exhibits significant disparities among countries, with high-income nations having a more favourable coverage rate.
- The WHO region of the US leads with a 60% coverage rate, while the African region lags behind at 27%.
- More than three-quarters of adults with hypertension live in low- and middle-income countries.
- Treatment coverage for hypertension exhibits significant disparities among countries, with high-income nations having a more favourable coverage rate.
- The Urgency of Timely Treatment:
- Nearly 30% of individuals with uncontrolled hypertension exhibit blood pressure measurements above the threshold warranting urgent treatment.
- Globally, the percentage of adults aged 30–70 taking medication for hypertension has doubled from 22% in 1990 to 42% in 2019.
- Effective treatment coverage has quadrupled during the same period, reaching 21%.
- Nearly 30% of individuals with uncontrolled hypertension exhibit blood pressure measurements above the threshold warranting urgent treatment.
- The WHO's Call to Action:
- The WHO calls for prioritising the prevention, early detection, and effective management of hypertension as part of national health benefit packages.
- Recommendations:
- There is a need to strengthen hypertension control programs that remain under-prioritized and acutely underfunded.
- Strengthening hypertension control must become an integral part of every country's journey toward universal health coverage.
What is Hypertension?
- About:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) is when the pressure in your blood vessels is too high (140/90 mmHg or higher). It is common but can be serious if not treated.
- Blood pressure is written as two numbers.
- The first (systolic) number represents the pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats.
- The second (diastolic) number represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats.
- Blood pressure is written as two numbers.
- World Hypertension Day is celebrated on May 17 every year to promote awareness about hypertension and encourage people to prevent and control this silent killer.
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) is when the pressure in your blood vessels is too high (140/90 mmHg or higher). It is common but can be serious if not treated.
- Risk Factors:
- High-salt diets, lack of physical activity, and excessive alcohol consumption are significant contributors to hypertension, and genetics are believed to play a role in high blood pressure as well.
- Symptoms:
- Most people with hypertension don’t feel any symptoms. Very high blood pressure can cause headaches, blurred vision, chest pain and other symptoms.
- Complications of Uncontrolled Hypertension:
- Severe heart issues, including chest pain, heart attacks, heart failure, and irregular heartbeats, as well as increase the risk of stroke by affecting blood flow to the brain.
- Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes like adopting a low-salt diet, weight loss, physical activity, and quitting tobacco etc. and medications.
- Initiatives:
- Global:
- To achieve the global target to reduce the prevalence of hypertension by 25% by 2025, WHO and the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention launched the Global Hearts Initiative in 2016.
- The United Nations Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3) aims to ensure healthy lives and promote well-being for all.
- India:
- India Hypertension Control Initiative Program (IHCI):
- Through programmes such as IHCI and the government’s push towards non-communicable disease screening and treatment at the primary healthcare level, India aims to put 75 million patients with hypertension or diabetes on standard care by 2025.
- India Hypertension Control Initiative Program (IHCI):
- Global:
Expediting the Enrolment of Children in Schools
For Prelims: United Nation’s Education transformation Summit, SDG-4, Primary Education, Upper Secondary Education
For Mains: Need for improving the enrolment of children for realization of the 2030 SDG Targets.
Why in News?
Recently, 2023 Global Education Monitoring Report titled ‘SDG 4 Mid-Term Progress Review’ released by UNESCO, paints a grim picture across the underdeveloped and developing countries with respect to enrolment of children at primary levels.
- There are now 250 million children not enrolled in school, up by six million since 2021, according to the report.
- 1.4 million children must be enrolled in preschool every year until 2030, and primary completion rates must be almost tripled, as per the report.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report ?
- About:
- The 2023 Global Education Monitoring Report shows the progress made since 2015 against all SDG 4 targets based largely on the data of the UNESCO Institute for Statistics, which oversees 10 of the 12 global indicators.
- Report Finds that between 2015 and 2021:
- Early Childhood: The percentage of children one year younger than the official primary entry age who are in organized learning programmes has remained constant at 75%.
- Higher Education: The tertiary education gross enrolment ratio increased from 37% to 41%, with women (44%) having a six percentage point gap over men (38%).
- Adult Education: Among 57 mainly high-income countries, the participation rate of adults in formal or non-formal education and training fell by 10%, mostly as a result of Covid-19.
- Gender Parity: The number of young women completing secondary school for every 100 young men increased from 102 to 105 globally and from 84 to 88 in sub-Saharan Africa, which remains the region where young women face the largest disadvantage.
- School Infrastructure: The share of schools with electricity increased from 66% to 76% in primary education and from 88% to 90% in upper secondary education.
- Teachers: The percentage of trained teachers in primary education has remained almost stagnant at 86%. In sub-Saharan Africa, the percentage of trained pre-primary teachers increased from 53% to 60%.
- Inequity in Access: During the Covid-19 Pandemic, the rapid shift to online learning left out at least half a billion students worldwide, disproportionately affecting the poorest and those in rural areas.
- Education Completion Rate:
- Sub-Saharan Countries
- Sub-Saharan Africa remained well below the global average by more than 20% in primary education(64%).
- Whereas, in upper secondary education, it remained below the global average (27%).
- Vietnam:
- In the 31 low- and lower-middle-income countries that measure learning progress at the end of primary school, Vietnam is the only country where a majority of the children achieved minimum proficiency in both reading and mathematics.
- Sub-Saharan Countries
What are Sustainable Development Goals for Education?
- About:
- The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of 17 global goals established by the United Nations in 2015 as part of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- These goals provide a comprehensive framework for addressing social, economic, and environmental challenges to achieve a sustainable future for all.
- SDGs and Education:
- SDG 4 has 10 targets encompassing many different aspects of education.
- There are seven targets which are expected outcomes and three targets which are means of achieving these targets.
- By 2030, ensure that all girls and boys complete free, equitable and quality primary and secondary education leading to relevant and effective learning outcomes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Sustainable Development Goals were first proposed in 1972 by a global think tank called the ‘Club of Rome’.
- The Sustainable Development Goals have to be achieved by 2030.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
- Adopted in 2015, SDGs came into effect in January 2016. They are meant to be achieved by 2030. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The SDGs were born at the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development in Rio de Janeiro in 2012. The Club of Rome advocated resource conservation for the first time in a more systematic way in 1968. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
State of Working India 2023
For Prelims: State of Working India 2023, Social Issues, Covid-19, Unemployment, State of Indian workforce, Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
For Mains: India's Unemployment Situation and Problems
Why in News?
Recently, Azim Premji University's Centre for Sustainable Employment has released the Report titled- "State of Working India 2023" highlighting the State of Indian workforce.
- It covers unemployment rates, women's participation, intergenerational mobility, and caste-wise workforce dynamics.
- The report used various data sources like surveys conducted by the National Statistical Office including Employment-Unemployment Surveys and Periodic Labour Force Surveys along with the India Working Survey.
What are the Highlights of the Report?
- Faster Structural Change:
- After stagnating since the 1980s, the share of workers with regular wage or salaried work started increasing in 2004, going from 18% to 25% for men and 10% to 25% for women.
- Between 2004 and 2017, around 3 million regular wage jobs were created annually. Between 2017 and 2019 this jumped to 5 million per year.
- Since 2019, the pace of regular wage jobs creation has decreased due to the growth slowdown and the pandemic.
- Gender-Based Earnings Disparities Reduced:
- In 2004, salaried women workers earned 70% of what men earned.
- By 2017 the gap had reduced and women earned 76% of what men did. Since then the gap has remained constant till 2021-22.
- Unemployment Rates and Education:
- The overall unemployment rate reduced to 6.6% in 2021-22 from 8.7% in 2017-18.
- However, for graduates under the age of 25, the unemployment rate was strikingly high at 42.3%.
- In contrast, those completing higher secondary education had a lower unemployment rate of 21.4%.
- Women’s Workforce Participation:
- Post the Covid-19 Pandemic, 60% of women were self-employed compared to 50% before.
- However, this increase in workforce participation was accompanied by a decline in self-employment earnings, reflecting the pandemic's distressing impact.
- Intergenerational Mobility:
- Intergenerational upward mobility has shown an upward trend, indicating socio-economic progress.
- However, this trend is weaker for workers from Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes compared to general castes.
- 75.6 % of SC/ST men in casual wage work also had sons involved in casual wage work in 2018. In comparison, the figure stood at 86.5 % in 2004, indicating that sons of casual wage workers belonging to SC/ST category have moved to other kinds of employment, most notably informal regular wage work.
- Caste-wise Workforce Dynamics:
- There are changes in caste-wise workforce participation over the years.
- The share of SC workers in casual wage work has significantly reduced, but this reduction is more pronounced in the general caste category.
- For instance, in 2021, 40% of SC workers were involved in casual employment as compared to 13% of general caste workers.
- Furthermore, around 22 % of SC workers were regular wage workers as opposed to 32% of general caste workers.
- Economic Growth vs. Employment Generation:
- Economic growth has not proportionately translated into job creation, with the capacity to generate jobs declining as GDP (Gross Domestic Product) increases.
- The transition from agriculture to other sectors has not ensured a shift to salaried employment.
- Informal Salaried Work:
- Despite the aspiration for salaried employment, the majority of salaried work is informal, lacking contracts and benefits. Good salaried jobs with proper benefits are becoming less prominent.
- Factors Influencing Graduate Unemployment:
- Graduate unemployment could be attributed to high aspirations and wage demands that the economy may not meet. Additionally, graduates from well-off households might have the luxury to remain unemployed.
What are Government’s Initiatives to Curb Unemployment?
- Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE)
- PM-DAKSH (Pradhan Mantri Dakshta Aur Kushalta Sampann Hitgrahi)
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA)
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
- Start Up India Scheme
- Rozgar Mela
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Disguised unemployment generally means (2013)
(a) large number of people remain unemployed
(b) alternative employment is not available
(c) marginal productivity of labour is zero
(d) productivity of workers is low
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. “While we flaunt India’s demographic dividend, we ignore the dropping rates of employability.” What are we missing while doing so? Where will the jobs that India desperately needs come from? Explain. (2014)
National Medical Commission
Why in News?
The National Medical Commission (NMC) , India has been awarded the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) Recognition Status for 10 years, the highest standards in medical education and accreditation.
- This recognition is a testament to NMC’s unwavering commitment to the highest standards in medical education and accreditation.
- WFME's accreditation program plays a pivotal role in ensuring that medical institutes meet and uphold the highest international standards of education and training.
What is the World Federation for Medical Education (WFME) ?
- WFME was founded in 1972 by the World Medical Association, the World Health Organization, the regional organizations of medical schools and academic teachers, and the International Federation of Medical Students Associations.
- WFME is a global organization dedicated to enhancing the quality of medical education worldwide.
- WFME has developed and published global standards for basic, postgraduate, and continuing medical education, as well as guidelines for distributed and distance learning in medical education.
What are the Benefits of WFME Accreditation ?
- All the 706 existing medical colleges in India will become WFME accredited .
- The new medical colleges that will be set up in the coming 10 years will automatically become WFME accredited.
- It will also enable Indian medical graduates to pursue postgraduate training and practice in other countries that require WFME recognition, such as the US, Canada, Australia, and New Zealand.
- It will increase the international recognition and reputation of Indian medical schools and professionals.
- It facilitates academic collaborations and exchanges and promotes continuous improvement and innovation in medical education.
- It will also make India an attractive destination for international students due to our globally recognized standards.
What is National Medical Commission (NMC) ?
- The NMC has been constituted by an act of Parliament known as National Medical Commission Act, 2019.
- The NMC acts as India's top regulator of medical education and practice.
- Committed to upholding the highest standards in healthcare education, NMC ensures the delivery of quality medical education and training across the nation.
Announcement of New Science Awards
Why in News?
The Central Government has decided to introduce 56 prizes under the category of Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar (3 Vigyan Ratna, 25 Vigyan Shri, 25 Yuva Vigyan Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar, 3 Vigyan Team Awards) to felicitate scientists.
- The awards will be announced annually on National Technology Day, May 11 and will be awarded on National Space Day, August 23 in 2024.
Note:
- Akin to prestigious Padma awards, these awards will not include any cash component.
- The Rashtriya Vigyan Puraskar shall be given in the 13 science-related domains.
What are the Key Highlights About these Awards?
- Included Awards:
- Vigyan Ratna Awards:
- These awards will recognise lifetime achievements & contributions made in any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Shri Awards:
- These awards will recognise distinguished contributions to any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Team Awards:
- These awards are to be given to a team comprising of three or more scientists/researchers/innovators who have made an exceptional contribution working in a team in any field of science and technology.
- Vigyan Yuva-Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar (VY-SSB):
- These awards are the highest multidisciplinary science awards in India for the young scientists (maximum 45 years).
- They are named after Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar, the founder and director of the Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), who was also a renowned chemist and visionary.
- Vigyan Ratna Awards:
- Awards Open to PIOs:
- Persons of Indian origin (PIOs) will now be eligible for the new awards, but only one PIO may receive the Vigyan Ratna.
- Three PIOs each can be selected for the Vigyan Shri and the VY-SSB.
- However, PIOs will not be eligible for the Vigyan Team awards.
What is National Technology Day?
- About:
- The day, which was first observed in 1999, aims to commemorate the scientific and technological achievements of Indian scientists, engineers.
- The day was named by the former Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee.
- Every year, the Technology Development Board of India under the Ministry of Science and Technology celebrates the day by awarding individuals with the National Award for their contribution to science and technology.
- The day, which was first observed in 1999, aims to commemorate the scientific and technological achievements of Indian scientists, engineers.
- Significance:
- It is the day India successfully tested nuclear bombs in Pokhran on 11th May, 1998.
- India successfully test-fired its Shakti-1 nuclear missile in operation called Pokhran-II, also codenamed as Operation Shakti.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. For outstanding contribution to which one of the following fields is Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize given? (2009)
(a) Literature
(b) Performing Arts
(c) Science
(d) Social Service
Ans: (c)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Omega Blocking
The recent devastating floods in Libya can be attributed to the occurrence of an Omega atmospheric blocking event.
- Omega blocking is a meteorological phenomenon that occurs when a high-pressure system gets trapped between two low-pressure systems, creating a pattern that resembles the Greek letter omega (Ω).
- It can cause extreme weather events, such as heat waves, droughts, and floods, depending on the location and season.
- These events are difficult to predict and can cause significant damage and loss of life.
- They have been linked to past extreme weather events, including the Pakistan floods in 2011, extreme rainfall in northwestern Iran in 2008, and heatwaves in France and Germany in 2019.
Read More: Climate Change: A Roadblock to Economic Growth
Indian Visa Service Suspended in Canada
As diplomatic tensions between India and Canada escalate, the Indian government has suspended visa services in Canada, affecting a range of travelers and sparking questions about the future of diplomatic relations.
- Indian-origin Canadians with valid Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) cards or valid long-term Indian visas are not affected by the visa service suspension.
- OCI cardholders have lifetime entry privileges into India, allowing them to live and work in the country indefinitely.
- Canadians who possess valid Indian visas will not be impacted by the suspension. Their visas remain valid until further notice.
- Canada has not yet imposed restrictions on Indian visa applicants but may consider reciprocal measures in response to the current situation.
Read More: India and Canada Ties at a Downturn, The Khalistan Shadow on India-Canada Ties, Overseas Citizen of India (OCI)
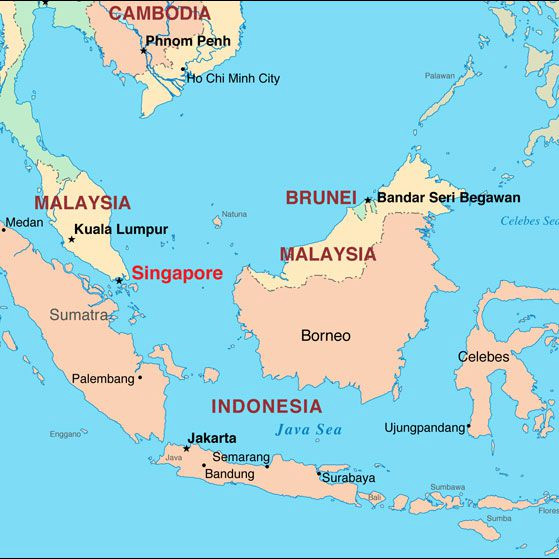
SIMBEX 2023
Indian Naval Ships Ranvijay and Kavaratti and submarine INS Sindhukesari arrived in Singapore to participate in the Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise (SIMBEX), 2023.
- This exercise has been conducted since 1994 and holds the distinction of being the longest naval exercise that the Indian Navy has conducted with another country.
- In addition to naval vessels, the exercise also includes the participation of the Long-Range Maritime Patrol Aircraft P8I.
- Other Exercises between the two countries include exercise Bold Kurukshetra, Trilateral Maritime Exercise SIMTEX (With Thailand) and exercise Agni Warrior (Army).
Read More: Singapore-India Maritime Bilateral Exercise, India-Singapore Relations
Mobile Application and Web Portal for General Crop Estimation Survey (GCES)
Recently, the Mobile Application and the Web Portal for GCES, developed by the Department of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare was launched.
- The aim is to transform agricultural practices across the nation.
- The portal and the app provide a comprehensive repository of yield estimation including village wise GCES plan and plot details where the crop cutting experiments are conducted.
- Geo referencing is one of the key features of the mobile application, which enables the primary worker to draw the boundary of the experimental plot and upload photos of the plot as well as of the crops through it.
Read More: Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare, Digital India