Gender Parity and Women's Empowerment Gap
For Prelims: United Nations, Women's Empowerment Index (WEI), Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI)
For Mains: Challenges and gaps in achieving women's empowerment and gender parity, Issues Related to Women
Why in News?
A recent report by the United Nations sheds light on the status of women's empowerment and gender parity around the world.
- The comprehensive analysis, jointly created by UN Women and UN Development Programme, evaluated 114 countries based on the Women's Empowerment Index (WEI) and the Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI).
- The findings emphasize the urgent need for comprehensive policy action to address the existing gaps and propel progress toward a more equitable and inclusive world.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- Only 1% of women globally live in countries with high women's empowerment and gender parity.
- Leadership roles and decision-making remain predominantly male-dominated, restricting opportunities for women.
- On average, women achieve only 60% of their full potential, according to the WEI.
- Women lag behind men by 28% across key dimensions of human development, as measured by the GGPI.
- None of the 114 countries analyzed achieved complete women's empowerment or gender parity.
- Over 90% of women worldwide reside in countries with low or middle women's empowerment and low or middle performance in achieving gender parity.
- Gender equality challenges persist even in highly developed countries. Among the 114 countries analyzed, over 85, including more than half in the high or very high human development categories, show low or moderate women's empowerment and gender parity. Economic progress alone does not ensure gender equality.
- India has low women's empowerment and gender parity despite moderate human development, highlighting the need for concerted efforts to bridge the gender gap and uplift women's status.
- Gender equality alone does not guarantee women's empowerment. The report shows that no country with a gender gap has achieved high women's empowerment.
- Additionally, about 8% of women live in countries with low empowerment but high gender parity.
UN Women:
- UN Women was established in 2010 by the UN General Assembly to accelerate progress on meeting the needs and rights of women and girls worldwide.
- UN Women supports UN Member States as they set global standards for achieving gender equality and works with governments and civil society to design and implement laws, policies, programs and services that benefit women and girls.
- UN Women focuses on four strategic priorities: women’s leadership and political participation, women’s economic empowerment, ending violence against women, and peace, security and humanitarian action.
What are the Recommendations for Comprehensive Policy Action?
- Health Policies: Governments should support and promote universal access to sexual and reproductive health, aiming for long and healthy lives for all.
- Equality in Education: Addressing gaps in skills and the quality of education, particularly in fields like STEM, will empower women and girls in the digital age.
- Work-life Balance and Support for Families: Policies and services addressing work-life balance, including affordable quality childcare, parental leave schemes, and flexible working arrangements, should be invested in.
- Women's Equal Participation: Targets and action plans should be established to achieve gender parity in all spheres of public life, while discriminatory laws and regulations holding women back must be eliminated.
- Violence Against Women: Implementing comprehensive measures focused on prevention, changing social norms, and eliminating discriminatory laws and policies is crucial.
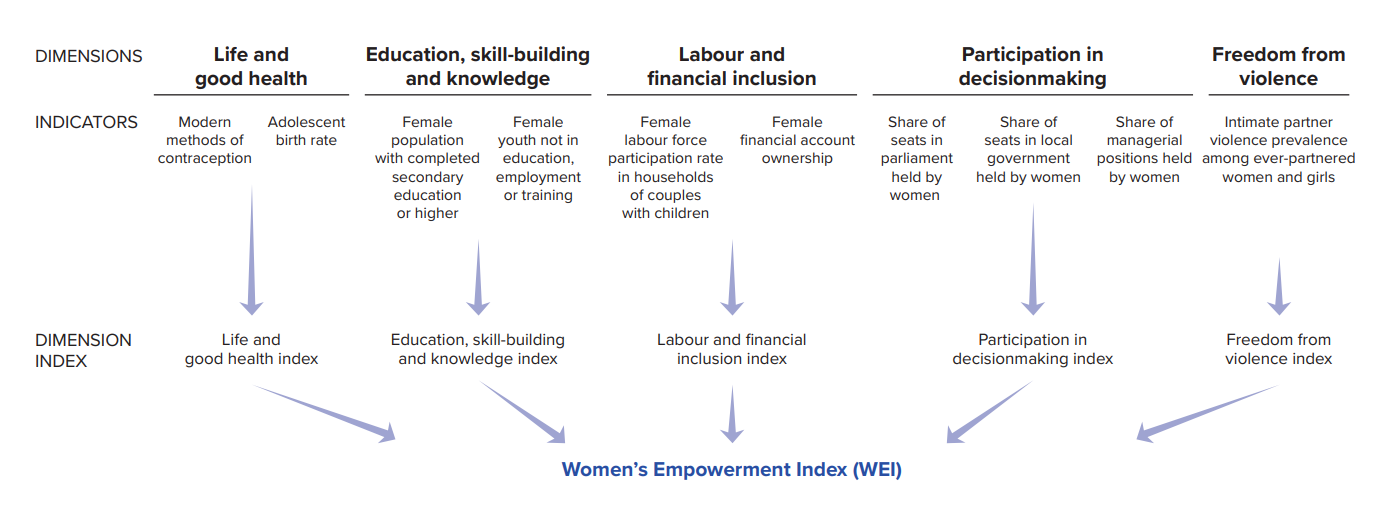
What is the Women's Empowerment Index (WEI)?
- The WEI is a composite index developed by UN Women and UNDP.
- It measures women's empowerment across five dimensions: life and good health, education, skill-building and knowledge, labor and financial inclusion, participation in decision-making, and freedom from violence.
- The WEI captures women's power and freedom to make choices and seize life opportunities.
- The development of the WEI marks a significant milestone in evidence-based policymaking and serves as a baseline for monitoring the government's progress towards Sustainable Development Goal 5 (SDG5) on gender equality and empowerment of women and girls.
What is the Global Gender Parity Index (GGPI)?
- The GGPI is a composite index that assesses gender disparities in key dimensions of human development, including health, education, inclusion, and decision-making.
- The GGPI is developed by UN Women and UNDP as part of a new global report titled ‘The Path to Equality: Women’s Empowerment and Gender Parity in Human Development’, which was launched in July 2023.
- The GGPI aims to capture the status of women relative to men across different contexts and dimensions. It also reflects the multidimensional and interrelated nature of gender equality.
What are the Indian Initiatives to reduce Gender Gap in Social, Economic and Political Life?
- Economic Participation and Health and Survival:
- Beti Bachao Beti Padhao: It ensures the protection, survival and education of the girl child.
- Mahila Shakti Kendra: Aims to empower rural women with opportunities for skill development and employment.
- Rashtriya Mahila Kosh: It is an apex micro-finance organization that provides micro-credit at concessional terms to poor women for various livelihood and income generating activities.
- Sukanya Samriddhi Yojna: Under this scheme girls have been economically empowered by opening their bank accounts.
- Female Entrepreneurship: To promote female entrepreneurship, the Government has initiated Programmes like Stand-Up India and Mahila e-Haat (online marketing platform to support women entrepreneurs/ SHGs/NGOs), Entrepreneurship and Skill Development Programme (ESSDP).
- Kasturba Gandhi Balika Vidyalaya: They have been opened in Educationally Backward Blocks (EBBs).
- Political Reservation: Government has reserved 33% of the seats in Panchayati Raj Institutions for women.
- Capacity Building of Elected Women Representatives: It is conducted with a view to empowering women to participate effectively in the governance processes.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following gives ‘Global Gender Gap Index’ ranking to the countries of the world? (2017)
(a) World Economic Forum
(b) UN Human Rights Council
(c) UN Women
(d) World Health Organization
Ans: (a)
Amended Rules Relating to Retirement Benefits of IAS, IPS, IFOS Pensioners
For Prelims: All India Services (AIS), Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), Government Policies & Interventions, Civil services rules, Death Cum Retirement Benefits Amendments Rules 2023.
For Mains: Indian Administrative Service (Cadre) Rules 1954, All India Services (AIS), Deputation of AIS Officer, Federal Nature of AIS Officers, Centre State Relations, Role of Civil Services in a Democracy
Why in News?
The Central government has amended All India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules 1958 relating to retirement benefits of IAS, IPS (Indian Police Service) and IFos (Indian Forest Service) pensioners.
- The Rules 1958 were amended by the Department of Personnel and Training (DoPT), to Rules 2023.
- It mainly focuses on retired intelligence or security related organizations.
What are the Changes Made by the 2023 Rule?
- The central government empowers itself to act against IAS, IPS and IFos and withhold or withdraw their pension even without a reference from the state government if they are found guilty of grave misconduct or are convicted of a serious crime.
- The amended rules reiterate that the decision of the Central Government on withholding or withdrawing the pension “shall be final”.
- Rules added ‘grave misconduct’ includes communication or disclosure of any document or information mentioned in the Official Secrets Act and a ‘serious crime’ includes any crime involving an offence under the Official Secrets Act.
- Earlier rule 3(3) in the All-India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958, which stated that the Central government may withhold or withdraw pension or any part of it “on a reference from the State Government concerned.
- Rules added ‘grave misconduct’ includes communication or disclosure of any document or information mentioned in the Official Secrets Act and a ‘serious crime’ includes any crime involving an offence under the Official Secrets Act.
- Members of intelligence or security-related organizations who have served in such capacities shall not write or publish any writings without obtaining prior clearance from the head of their respective organization.
What will be the Effect of Changed Rules?
- The Centre may not have to wait for a reference from the state government to act against a pensioner found guilty of grave misconduct or convicted of a serious crime by a Court.
- If the state government concerned does not send such references in such cases, the central government may initiate a process of action.
- Expressing and writing in the media and writing books which disclose sensitive information by the officials of security and intelligence organisations will result in action against officials of security and intelligence organisations concerned.
- The proposed amendment would weaken the State’s political control over the bureaucracy.
- It would hobble effective governance and create avoidable legal and administrative disputes. Because amended rules will provide unrestricted power to central govt to act against retired officers.
What is All India Services (Death-cum-Retirement Benefits) Rules, 1958?
- Section 3 of the All-India Services Act. 1951(61 of 1951) empowers the Central Government, after consultation with the Governments of the States concerned, to make such rules.
- They shall apply to all people who retired from the Service on or after the 29th of October 1951.
- They do not apply to those members of the Service who were promoted to the Service from the State Services or were appointed to the Service under the Indian Administrative Service (Extension to States) Scheme or the Indian Police Service
- Nothing contained in these rules shall apply to the people appointed to the service on or after the 1st day of January 2004.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Q. “Institutional quality is a crucial driver of economic performance”. In this context suggests reforms in the Civil Service for strengthening democracy. (2020)
India-UK Free Trade Agreement Negotiations
For Prelims: India-UK Free Trade Agreement Negotiations, India-UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA), European Free Trade Association (EFTA), Intellectual Property Rights (IPR).
For Mains: India-UK Free Trade Agreement Negotiations.
Why in the News?
India and the UK are currently engaged in negotiations to resolve contentious issues in the ongoing talks for the India-UK Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- This comprehensive trade deal holds significant importance for India as it will serve as a template for upcoming trade pacts, including those with the EU (European Union) and the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) countries (viz., Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland).
What are the Contentious Issues under the Negotiations?
- Intellectual Property Rights: In Intellectual Property Rights (IPR), India does not want to compromise on the production of life-saving generics.
- Global Value Chains (GVC): Discussions are underway to address the complexities associated with global value chains and ensure favorable outcomes for India.
- Digital Trade: In the area of digital trade and data protection, India is yet to firm up its own domestic laws and hence doesn’t want to take on commitments.
- Rules of Origin (ROO): ROO, which determines the national source of a product, has been a contentious issue in the FTA talks.
- These are important in trade negotiations since countries levy duties or impose restrictions on products based on the source of imports.
- India wants to have strict rules of origin in place to ensure that third countries do not take unfair advantage of the FTA.
- These are important in trade negotiations since countries levy duties or impose restrictions on products based on the source of imports.
- Labour and Environment: Labour and environmental commitments are being taken for the first time and they have to be done in a manner which is not unfavorable to India.
- India has unilaterally made tremendous progress and does not want additional conditions.
- The UK, on the other hand, wants more stringent IPRs, free cross-border data flow and rules against data localisation, liberal ROOs and commitments in the areas of labour and environment,
What is the Background of India-UK Free Trade Agreement?
- In 2022, India and the UK had launched the formal Free Trade Agreement (FTA) negotiations. Until then, both countries are contemplating an interim free trade area, which will result in reducing tariffs on most of the items.
- Both countries agreed to an early harvest scheme or a limited trade agreement to lower tariffs on a small set of goods apart from easing rules for select services.
- Further, they agreed to avoid “sensitive issues” and focus on areas where there is more complementarity.
- The agriculture and dairy sectors are considered sensitive sectors for India in trade talks.
- Also, a target of doubling the trade between India and the United Kingdom (UK) by 2030 was also set.
What is a Free Trade Agreement?
- It is a pact between two or more nations to reduce barriers to imports and exports among them.
- Under a free trade policy, goods and services can be bought and sold across international borders with little or no government tariffs, quotas, subsidies, or prohibitions to inhibit their exchange.
- The concept of free trade is the opposite of trade protectionism or economic isolationism.
- FTAs can be categorized as Preferential Trade Agreement, Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
How has Been India-UK Trade Relations?
- The trade between India and the UK had “more than doubled” between 2007 and 2019.
- By the end of 2022, India was the UK’s twelfth largest trading partner. This accounted for 2.0% of the UK’s total trade.
- For goods, India was the UK’s thirteenth largest trading partner and for services it was the tenth largest.
- In 2022-23, India-UK bilateral trade had increased 16% to USD 20.36 billion
What can be the Significance of FTA between India & the UK?
- Increasing Exports of Goods: Trade deals with the UK can boost exports for large job-creating sectors such as textiles, leather goods, and footwear.
- India is also expected to register a quantum jump in the export of Marine Products through the recognition of 56 marine units of India.
- Clarity on Services Trade: The FTA is expected to provide certainty, predictability and transparency and will create a more liberal, facilitative and competitive services regime.
- There is also great potential for increasing exports in service sectors like IT/ITES, Nursing, education, healthcare, including AYUSH and audio-visual services.
- Exit from RCEP: India opted out of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership deal in November 2019.
- Therefore, there is a renewed focus on trade deals with the US, the European Union and the UK, which are key markets for Indian exporters and are keen to diversify their sourcing.
- Strategic Advantage: The UK is a permanent member of the UN Security Council, and one of the strategic partners of India.
- Strengthening bonds with the trade would seek UKs support at global issues like standoff with China in the Ladakh sector of the Line of Actual Control (LAC) and claim for permanent seat at UNSC.
Way Forward
- The ongoing negotiations for the India-UK Free Trade Agreement hold significant importance for India's trade relations.
- The focus is on addressing contentious issues such as intellectual property rights, global value chains, digital trade, and rules of origin.
- The cautious approach and slow pace of negotiations reflect India's commitment to securing a comprehensive deal while protecting its interests.
- The outcome of these negotiations will shape India's future trade agreements, making it a matter of careful consideration and strategic decision-making.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2018)
- Australia
- Canada
- China
- India
- Japan
- USA
Which of the above are among the ‘free-trade partners’ of ASEAN?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 3, 4, 5 and 6
(c) 1, 3, 4 and 5
(d) 2, 3, 4 and 6
Ans: (c)
Bhoomi Samman 2023
For Prelims: Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme, Aadhaar Card, Unique Land Parcel Identification Number , Blockchain-based system, Geographic Information System.
For Mains: Challenges Associated with Digitisation of Land Records
Why in News?
Recently, the President of India presented the “Bhoomi Samman” 2023 at a function organised by the Union Ministry of Rural Development.
What is “Bhoomi Samman”?
- The “Bhoomi Samman” is a prestigious award scheme launched by the Union Ministry of Rural Development to recognize and incentivize the achievements of states and districts in the implementation of the Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP).
- The award is presented by the President of India to the state secretaries and district collectors along with their teams who have excelled in achieving saturation of the core components of DILRMP, such as:
- Computerization of land records
- Digitization of cadastral maps
- Integration of textual and spatial data
- Survey/re-survey using modern technology
- Computerization of registration
- Interoperability between registration and land records
Note: Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (erstwhile National Land Record Modernization Programme) under the Ministry of Rural Development was revamped and converted as a Central Sector Scheme with effect from 1st April, 2016 with 100% funding by the Centre.
What are the Advantages of Digitalisation of Land Records?
- Transparency and Accountability: Digitization increases transparency in land transactions, reducing the scope for unethical and illegal activities related to land.
- Disaster Management: Digital records are more resilient to natural calamities like floods and fires, safeguarding essential land-related documents from loss.
- Land Parcel Identification Number: Similar to Aadhaar Card, the Unique Land Parcel Identification Number provided under the Digital India Land Information Management System allows efficient land utilization and enables the formulation and implementation of new welfare schemes.
- Resolution of Land Disputes: Access to land-related information in a free and convenient manner aids in resolving ownership and land-use disputes, reducing the burden on the administration and judiciary.
What are the Challenges Associated with Digitisation of Land Records?
- Fragmented Land Records: India's land records are maintained by multiple authorities at different levels - village, district, and state.
- The lack of uniformity and integration between these records can create difficulties when attempting to centralize and digitize them.
- Technological Infrastructure and Connectivity: Digitization requires adequate technological infrastructure, including hardware, software, and internet connectivity.
- In rural areas, where most land is located, the availability of such infrastructure can be limited, hindering the digitization process.
- Data Security and Privacy: Land records contain sensitive personal and property-related information.
- Ensuring the security and privacy of this data during digitization and beyond is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and misuse.
Way Forward
- Blockchain-based Land Records: Implement a blockchain-based system to store and manage land records.
- Blockchain's decentralized and immutable nature ensures transparency, reduces the possibility of fraud, and fosters trust in land transactions.
- Drone Surveys and GIS Mapping: Use drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and Lidar technology to conduct accurate surveys of land parcels.
- Integrate the data with Geographic Information System (GIS) mapping to create a dynamic and real-time representation of land records.
- Standardization and Interoperability: Establish uniform data standards and formats to ensure compatibility and seamless integration of land records across different departments and systems.
- This will enable efficient data sharing and retrieval.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to land reforms in independent India, which one of the following statements is correct? (2019)
(a) The ceiling laws were aimed at family holdings and not individual holdings.
(b) The major aim of land reforms was providing agricultural land to all the landless.
(c) It resulted in cultivation of cash crops as a predominant form of cultivation.
(d) Land reforms permitted no exemptions to the ceiling limits.
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Discuss the role of land reforms in agricultural development Identify the factors that were responsible for the success of land reforms in India. (2016)
Link Between Bacterial Infection and Endometriosis
Why in News?
Despite the prevalence of Endometriosis, the underlying causes and mechanisms of endometriosis remain unclear. However, a recent study has shed light on a potential link between a specific bacteria and the development and aggravation of endometriosis.
What is Endometriosis?
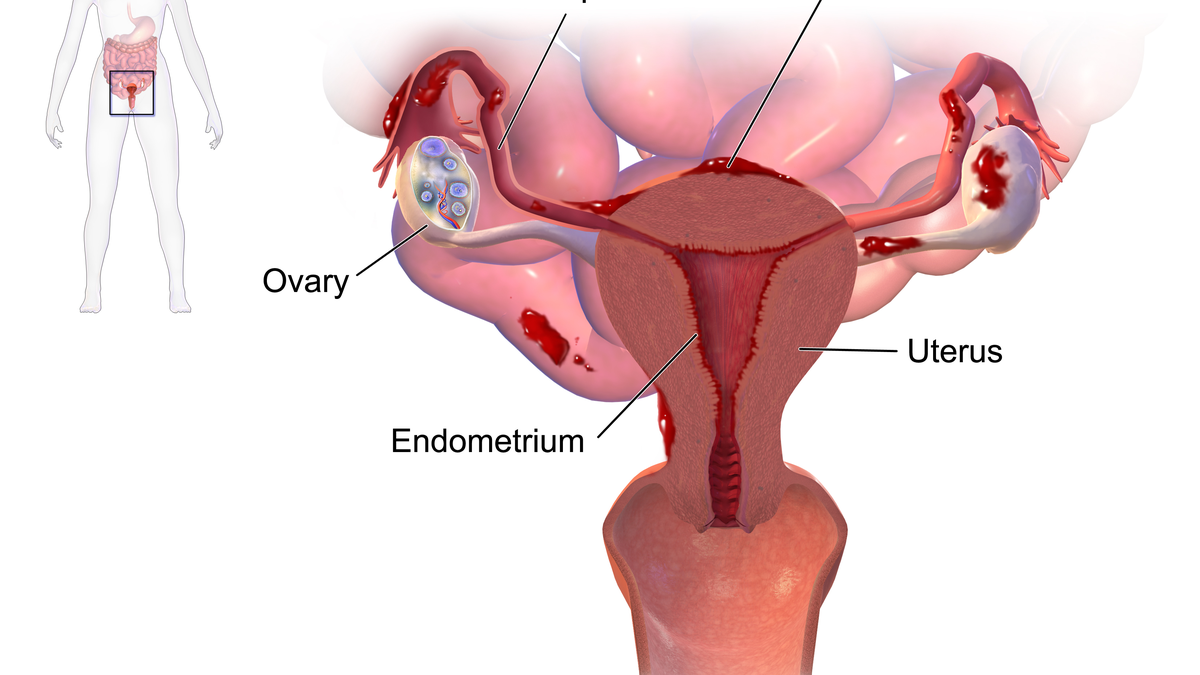
- About:
- It is a chronic condition that affects that affects approximately one in 10 women worldwide. It occurs when the tissue that normally lines the uterus (endometrium) grows outside of it, forming lesions on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, bladder, bowel or other pelvic organs.
- The exact cause of endometriosis is still unknown.
- Impacts:
- Women with endometriosis often experience infertility, chronic pain during periods, pelvic pain, bloating, nausea, fatigue, and may also be at a higher risk of depression and anxiety.
- Current Available Treatments:
- Hormonal Therapy: Certain hormone-based treatments, like birth control pills or hormone-containing intrauterine devices, can help control the growth of endometrial tissue.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic surgery can be performed to remove or destroy the endometrial tissue growths.
- Fertility Treatment: For women facing fertility issues, assisted reproductive technologies like in vitro fertilization (IVF) can be considered.
What is the Bacterial Infection Linked to Endometriosis?
- The bacterial infection linked to endometriosis is caused by a species of bacteria called Fusobacterium.
- Fusobacterium is normally found in the mouth and the gut, where it can cause dental plaque, gum disease, appendicitis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- However, it can also spread to other parts of the body through the bloodstream or sexual contact, causing infections in the lungs, brain, liver or reproductive organs.
- The link between Fusobacterium and endometriosis was discovered by a team of researchers from Japan, who conducted a study involving 155 women, 79 of whom had endometriosis and 76 of whom did not.
- The researchers analyzed the DNA of the bacteria present in the blood, saliva and vaginal fluid of the women, and found that Fusobacterium was detected in 64% of the women with endometriosis, compared to only 7% of the women without endometriosis.
- This finding could help expand the range of treatment options for endometriosis. For example, antibiotics or probiotics could be used to target Fusobacterium or restore a healthy balance of bacteria in the body.
- However, more research is needed to confirm the causal relationship between Fusobacterium and endometriosis, and to understand how it affects different women with different symptoms and severity of the condition.
Henley Passport Index 2023
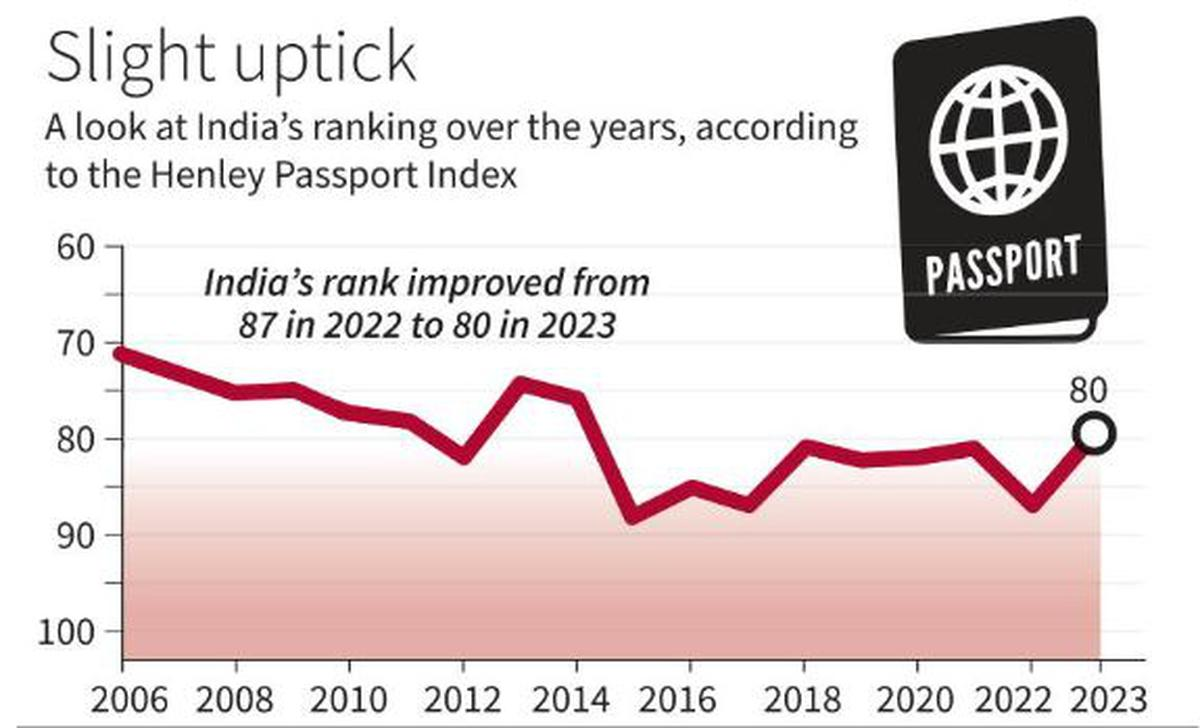
Why in News?
In the latest Henley Passport Index 2023, Indian passport has climbed seven places to secure the 80th rank, up from 87th in 2022, giving its holders visa free access to 57 countries.
What is Henley Passport Index?
- About:
- The Henley Passport Index is a ranking system that evaluates all the world's passports based on the number of travel destinations their holders can access without the need for a prior visa.
- This index encompasses 199 different passports and covers 227 travel destinations.
- It is compiled and published by Henley & Partners, a global citizenship and residence advisory firm.
- The Henley Passport Index is a ranking system that evaluates all the world's passports based on the number of travel destinations their holders can access without the need for a prior visa.
- India's Passport Performance Over the Years:
- Global Rankings and Shifts:
- Top Position: Singapore now holds the most powerful passport in the world, granting its citizens visa-free access to an impressive 192 travel destinations out of 227 worldwide.
- Japan previously held the top spot on the Henley Passport Index for five years.
- Runners-up: Germany, Italy, and Spain share the second position on the index.
- Japan, along with Austria, Finland, France, Luxembourg, South Korea, and Sweden, shares the third spot.
- Decline of the United States: Over the past decade, the United States has experienced a steady decline on the index, falling two places to the eighth spot.
- Top Position: Singapore now holds the most powerful passport in the world, granting its citizens visa-free access to an impressive 192 travel destinations out of 227 worldwide.
- Henley Openness Index:
- About:
- Henley & Partners also introduced the Henley Openness Index, which measures the number of nations a country allows visa-free access to.
- In this ranking, India was placed 94th out of 97 countries, offering visa-free access to only four nations.
- Most Open Countries: The top 20 'most open' countries predominantly comprise small island nations and African states, with the exception of Cambodia.
- 12 countries offer exceptional openness, providing visa-free or visa-on-arrival entry to all 198 passports in the world (excluding their own).
- These countries are Burundi, Comoro Islands, Djibouti, Guinea-Bissau, Maldives, Micronesia, Mozambique, Rwanda, Samoa, Seychelles, Timor-Leste, and Tuvalu.
- Least Open Countries: Afghanistan, North Korea, Papua New Guinea, and Turkmenistan were ranked at the bottom of the Henley Openness Index, as they do not permit visa-free access for any passport holders.
- About:
Visa-Free Access V/s Visa on Arrival
- Visa-Free Access: Visa-free access means that citizens of certain countries can enter another country without the need to obtain a visa in advance.
- They are allowed to stay for a specified period, usually determined by bilateral agreements or international treaties, without the requirement of obtaining a visa.
- Visa on Arrival: Visa on arrival means that travelers from specific countries can obtain a visa upon arriving at their destination country's airport or border checkpoint.
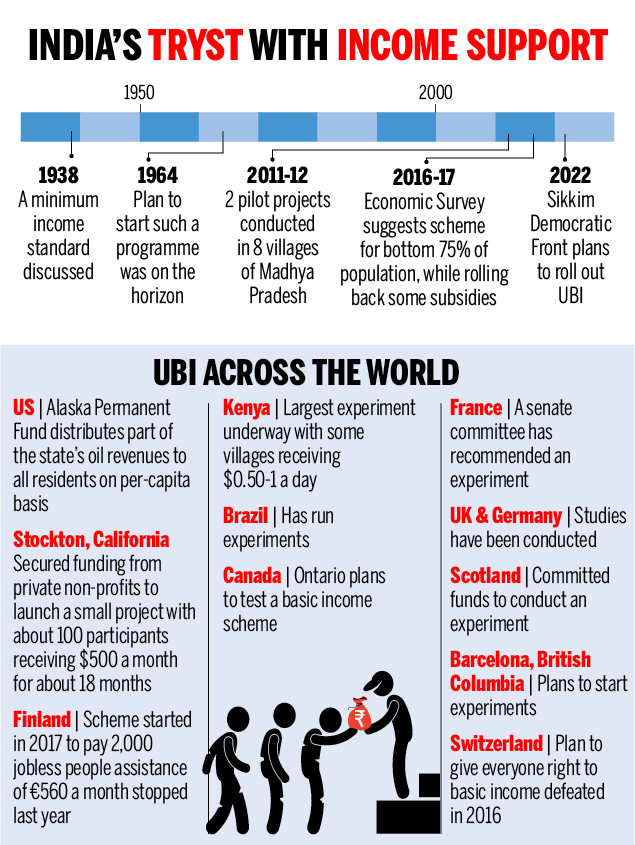
Rajasthan Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill, 2023
Why in News?
The Rajasthan Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill, 2023, introduced by the Rajasthan government, aims to provide additional income support to people in the state. The Bill seeks to help citizens cope with inflation and improve their financial stability.
- The Bill has three broad categories: right to minimum guaranteed income, right to guaranteed employment, and right to guaranteed social security pension.
What is the Rajasthan Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill, 2023?
- Key Components of the Bill:
- Right to Minimum Guaranteed Income:
- The Bill guarantees a minimum income for every adult citizen for 125 days a year.
- Each adult citizen will receive minimum income through the Indira Gandhi Shahri Rozgar Guarantee Yojana in urban areas and the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) in rural areas.
- The state will add 25 days of employment to MGNREGA's 100 days for rural areas.
- Right to Guaranteed Employment:
- The government will pay minimum wages weekly or fortnightly after the completion of work in urban and rural employment schemes.
- A designated officer will ensure job sites are within five kilometers of the registered job card address.
- If employment is not provided within 15 days of application, the applicant will receive a weekly unemployment allowance “and in any case not later than a fortnight.”
- Right to Guaranteed Social Security Pension:
- The Bill ensures that people falling under categories like old age, specially abled, widows, and single women receive a pension.
- The pension will see an annual increase of 15% in two installments, starting from the financial year 2024-2025.
- The Bill ensures that people falling under categories like old age, specially abled, widows, and single women receive a pension.
- Right to Minimum Guaranteed Income:
- Distinguishing from Cash Transfer Schemes:
- The Rajasthan Minimum Guaranteed Income Bill is unique as it legally guarantees both minimum income support and guaranteed employment and pensions, setting it apart from regular cash transfer schemes. It reflects Mahatma Gandhi's vision of comprehensive welfare measures.
- The Bill covers all families in the state, offering employment and pension support to various vulnerable groups. Cash transfer schemes may have limited coverage.
- The Bill includes annual increment in pensions, ensuring they keep pace with inflation. Cash transfer schemes may not have such provisions.
- The Bill takes a comprehensive approach towards social security, aiming to benefit vulnerable sections of society.
- Criticism against the Bill:
- While the Bill has received praise for its efforts to address economic disparities, some critics argue that the additional expenditure of Rs 2,500 crore per year may strain the state's finances.
- They express concerns about the long-term sustainability of the scheme and the potential burden it may place on taxpayers.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Advancing Aviation Sector in India
Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) investing Rs. 98,000 crore (2019-2024) in airport infrastructure to meet growing air traffic demands.
- Safety oversight is ensured through regular surveillance and audits by the Directorate General of Civil Aviation (DGCA).
- Emphasis on sustainable aviation, encouraging carbon neutrality and adoption of green energy at airports.
- The MoCA is committed to achieving Sustainable Aviation in collaboration with the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), following the principles and provisions of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC).
- MoCA strives to achieve the same under the National Civil Aviation Policy 2016, which aims to limit CO2 emissions in Indian aviation.
Positive Impact of Centre's Mandated Health Spending
The Study in Public Health for All journal reveals the positive impact of the Centre's mandated spending on health through the National Health Mission (NHM) over 15 years.
- NHM linked funding to compliance with the Central government's schemes, encouraging States to invest more in primary health care.
- Increased allocation in States' health budgets due to NHM's conditional allocation.
- Target of 8% of the total State budget for health remains unachieved.
- NHM's efforts contributed to a decline in infant mortality rate and reduced disparities in per capita public spending across States.
- Study recommends States develop concrete plans for primary health care delivery.
- Urges Centre to establish a National Database of Health System Cost to estimate comprehensive primary health care expenses.
- Realistic cost estimates for delivering healthcare and assessing cost-per-year of quality-adjusted life year (QALY) gained through primary healthcare interventions are crucial for progress.
Read more: National Health Mission (NHM)
India Bans Non-Basmati White Rice Exports to Stabilize Domestic Market
The Indian government has imposed an immediate ban on the export of non-basmati white rice, except for certain ongoing shipments.
- This variety of rice had accounted for 25% of the total rice exports from the country.
- This step was taken in response to the 11.5% increase in domestic rice prices in 2022 and a subsequent 35% surge in exports of this rice variety during 2022-23.
- The Ministry attributed this surge in exports to various factors, including high international prices driven by geopolitical scenarios, El Nino influences, and extreme climatic conditions in other rice-producing countries.
- The ban aims to stabilize the domestic market and ensure adequate availability of non-basmati white rice for Indian consumers, while export policies for basmati rice and non-basmati parboiled rice remain unchanged.
Read more: Basmat Rice, El Nino, Extreme climatic conditions
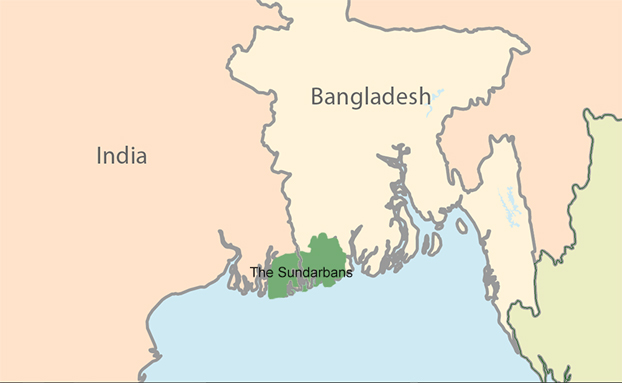
Barges Navigating Sundarbans Allegedly Trigger Erosion and Disrupt Siltation
The Sundarbans, a fragile ecosystem comprising around 100 islands shared by humans and wildlife, is facing threats as allegations arise that barges transporting fly ash from Indian power plants to Bangladesh are causing erosion along river banks.
- While the Inland Waterways Authority of India refutes the claims, locals report increased erosion near inhabited islands.
- Balancing economic interests and conservation becomes crucial, prompting authorities to assess the impact of barge traffic on the Sundarbans' unique environment and protect it for the future.
Read more: Sundarbans, Inland Waterways Authority of India, Fly ash