Governance
17th ASER 2022
For Prelims: Annual Status of Education Report (ASER),2022, Nipun Bharat Mission
For Mains: Education Status in India
Why in News?
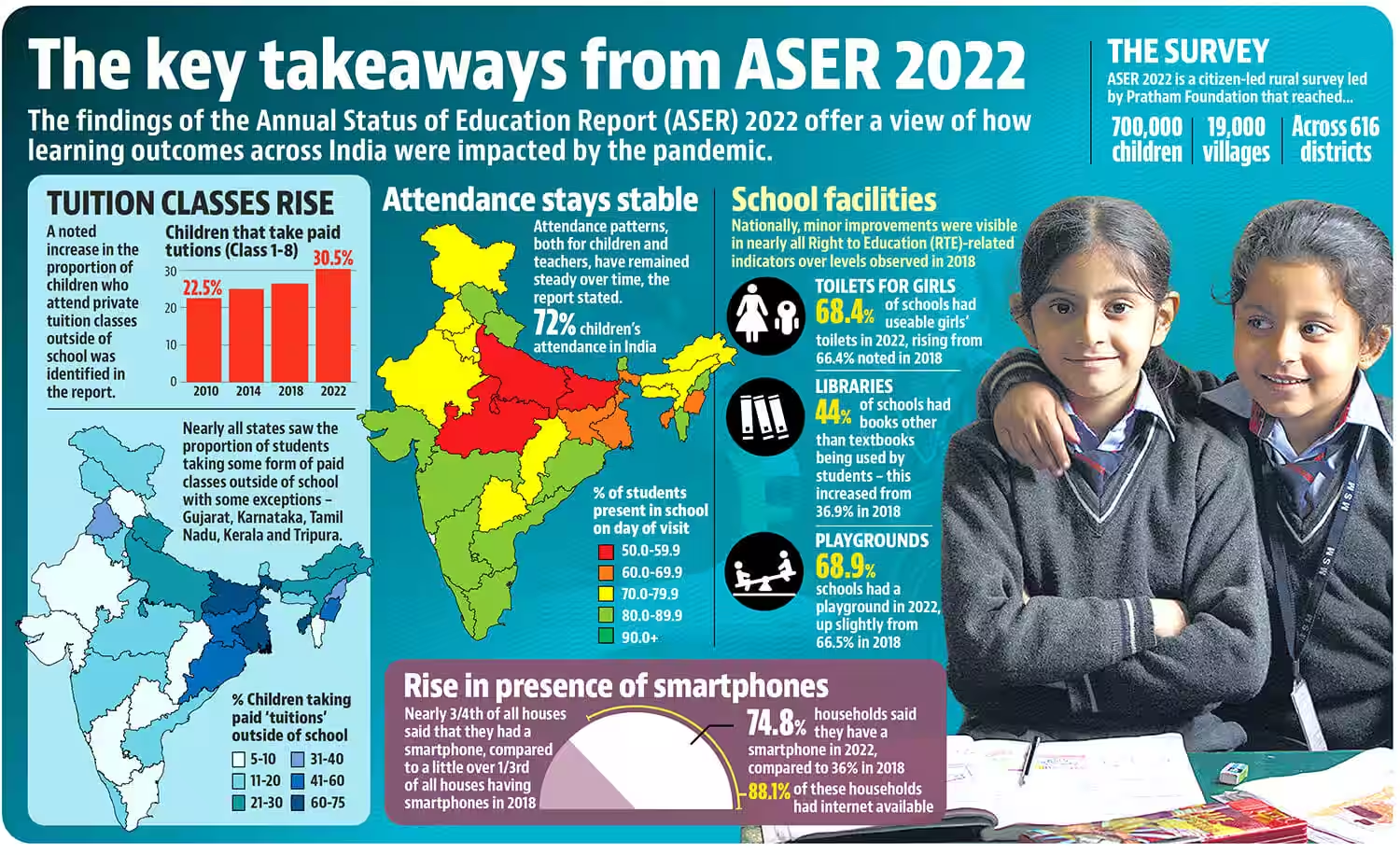
Recently, the 17th Annual Status of Education Report (ASER) 2022 was released by NGO Pratham, which highlights the impact of the pandemic on education.
- The report unveils high enrolment of children in schools which is a good performance indicator for government programmes like Nipun Bharat Mission.
What is ASER?
- The ASER, is an annual, citizen-led household survey that aims to understand whether children in rural India are enrolled in school and whether they are learning.
- ASER has been conducted every year since 2005 in all rural districts of India. It is the largest citizen-led survey in India.
- ASER surveys provided representative estimates of the enrolment status of children aged 3-16 and the basic reading and arithmetic levels of children aged 5-16 at the national, state and district level.
What are the Findings of the Report?
- Enrollment in Government Schools:
- According to the ASER, 2022 the country has seen an increase in the enrollment of children in government schools.
- Basic Reading and Arithmetic Skills:
- There has been a decline in the basic reading and arithmetic skills of young children in Class 3 and Class 5 in India.
- Proportion of Girls not Enrolled:
- The decrease in the proportion of girls not enrolled in schools for the age group 11-14 from 4.1% in 2018 to 2% in 2022 is a significant improvement and a positive development.
- This indicates that efforts to promote gender equality in education have been effective and have helped to increase the enrollment of girls in schools.
| Parameters | 2018 | 2022 | Trend |
| Overall Enrollment (Age Group 6-14) | 97.2% | 98.4% | Positive |
| Enrolled in Government School (Age Group 6-14) | 65.6% | 72.9% | Positive |
| Girls not Enrolled in School (Age Group 11-14) | 4.1% | 2% | Positive |
| Children in Std I-VIII Taking Paid Private Tuition Classes | 26.4% | 30.5% | Positive |
| Children in Std III (Government or Private Schools) Able to read at Std II level | 27.3% | 20.5% | Negative |
| Children in Std III who are able to at least do subtraction | 28.2% | 25.9% | Negative |
| Children in Std V across India who can do division | 27.9% | 25.6% | Negative |
| Government Schools with Less than 60 Students Enrolled | 29.4% | 29.9% | Negative |
| Average Teacher Attendance | 85.4% | 87.1% | Positive |
| Fraction of Schools with Useable Girls’ Toilets | 66.4% | 68.4% | Positive |
| Schools with Drinking Water Availability | 74.8% | 76% | Positive |


International Relations
India and Maldives
Prelims: SAGAR, Neighborhood First, Community Development Project (HICDP) scheme, India’s neighborhood policy, String of Pearls.
Mains: India- Maldives Relations and Way Forward.
Why in News?
Recently, India and Maldives have signed pacts on development projects in Maldives.
- Both the Maldives and Sri Lanka are India’s key maritime neighbours in the Indian Ocean Region and occupy a special place in the Prime Minister’s vision of ‘SAGAR’ (Security and Growth for All in the Region) and ‘Neighbourhood First’.
What is the Pact?
- Grant Assistance:
- It includes grant assistance of 100 million Rufiyaa (currency of Maldives) for the High Impact Community Development Project (HICDP) scheme.
- A number of socio-economic development projects are planned to be implemented throughout the country under this funding.
- Sports Complex and Academic Collaboration:
- It also included the development of a sports complex in Gahdhoo, and academic collaboration between Maldives National University and Cochin University of Science and Technology.
How has India’s Relations with Maldives been?
- Security Partnership:
- Defence cooperation extends to the areas of Joint Exercises - “Ekuverin”, “Dosti”, “Ekatha” and “Operation Shield” (begun in 2021).
- India provides the largest number of training opportunities for Maldivian National Defence Force (MNDF), meeting around 70% of their defence training requirements.
- Rehabilitation Centre:
- Signing of an USD 80-million contract for the Addu reclamation and shore protection project.
- A drug detoxification and rehabilitation centre in Addu built with Indian assistance.
- The centre is one of 20 high impact community development projects being implemented by India in areas such as healthcare, education, fisheries, tourism, sports and culture.
- Economic Cooperation:
- Tourism is the mainstay of Maldivian economy. The country is now a major tourist destination for some Indians and a job destination for others.
- In August 2021, Afcons, an Indian company, signed a contract for the largest-ever infrastructure project in Maldives which is the Greater Male Connectivity Project (GMCP).
- India is Maldives 2nd largest trading partner – rising up from its 4th position in 2018. In 2021, bilateral trade registered a growth of 31% over the previous year – overcoming the pandemic-related challenges.
- A Bilateral USD Currency Swap Agreement between RBI and Maldives Monetary Authority was signed on 22 July 2019.
- Infrastructure Projects:
- Hanimaadhoo International Airport Development project under an Indian credit line will add a brand-new terminal to cater to 1.3 million passengers a year.
- In 2022, the National College for Policing and Law Enforcement (NCPLE) was inaugurated by India’s External Affairs Minister.
- NCPLE is the largest grant project executed by India in Maldives.
What are the Challenges in India Maldives Relations?
- Political Instability:
- India’s major concern has been the impact of political instability in the neighbourhood on its security and development.
- The February 2015 arrest of Maldives’ opposition leader Mohamed Nasheed on terrorism charges and the consequent political crisis have posed a real diplomatic test for India’s neighbourhood policy.
- Radicalisation:
- In the past decade or so, the number of Maldivians drawn towards terrorist groups like the Islamic State (IS) and Pakistan-based jihadist groups has been increasing.
- This gives rise to the possibility of Pakistan based terror groups using remote Maldivian islands as a launch pad for terror attacks against India and Indian interests.
- In the past decade or so, the number of Maldivians drawn towards terrorist groups like the Islamic State (IS) and Pakistan-based jihadist groups has been increasing.
- China Angle:
- China’s strategic footprint in India’s neighbourhood has increased. The Maldives has emerged as an important 'pearl' in China’s “String of Pearls” construct in South Asia.
- Given the uncertain dynamics of Sino-Indian relations, China’s strategic presence in the Maldives remains a concern.
Way Forward
- India must play a key role within Indo-Pacific security space to ensure regional security in South Asia and surrounding maritime boundaries.
- The Indo-Pacific security space has been developed as a response to the growth of extra-regional powers (particularly China’s) in India’s maritime sphere of influence.
- At present, the ‘India Out’ campaign has support from a limited population but this cannot be taken for granted by the Indian government.
- If the issues raised by the supporters of the ‘India Out’ are not handled carefully and India does not effectively convince the Maldivians about its intentions behind the projects on the island nation, the campaign may change the domestic political situation in the Maldives and may set ripples in India’s currently favourable relationship with the country.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What do you understand by ‘The String of Pearls’? How does it impact India? Briefly outline the steps taken by India to counter this. (2013)
Q. Discuss the political developments in the Maldives in the last two years. Should they be of any cause for concern to India? (2013)


International Relations
India-Oman Strategic Dialogue
Prelims: India-Oman Strategic Dialogue, India-Oman Relations, Indo-Pacific, Maritime Safety and Security, Terrorism, Arabian Sea, IORA.
Mains: India-Oman Relations and its Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, the 8th India-Oman strategic dialogue was held in India, where both countries have underlined the need to work collectively to fight the challenge of terrorism, terrorist propaganda, abuse of cyberspace and misuse of new and emerging technologies.
- They agreed to hold the next round of the strategic dialogue in Oman in 2024.
What are the Highlights of the Dialogue?
- Both sides highlighted the high priority accorded by the leadership of both countries to further enhance their strategic ties based on trust and mutual respect.
- Discussions were held on a wide range of issues of mutual interest, including bilateral strategic and security cooperation, defence and regional security.
- Both sides reiterated the importance of preserving Maritime Safety and Security in the region.
- Both sides reiterated the importance of the strategic dialogue as an important mechanism of bilateral cooperation between India and Oman.
What are the Key Points of India-Oman Relationship?
- Background:
- The two countries across the Arabian Sea are linked by geography, history and culture and enjoy warm and cordial relations, which are attributed to historical maritime trade linkages.
- The Sultanate of Oman is a strategic partner of India in the Gulf and an important interlocutor at the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League and Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) fora.
- Gandhi Peace Prize 2019 was conferred on Late HM Sultan Qaboos in recognition of his leadership in strengthening the ties between India & Oman and his efforts to promote peace in the Gulf region.
- Defence Relations:
- Joint Military Cooperation Committee (JMCC):
- The JMCC is the highest forum of engagement between India and Oman in the field of defence.
- The JMCC is expected to meet annually, but could not be organised since 2018 when the meeting of the 9th JMCC was held in Oman.
- Military Exercises:
- Army exercise: Al Najah
- Air Force exercise: Eastern Bridge
- Naval Exercise: Naseem Al Bahr
- Joint Military Cooperation Committee (JMCC):
- Economic & Commercial Relations:
- Institutional mechanisms like Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) and Joint Business Council (JBC) oversee economic cooperation between India and Oman.
- India is among Oman’s top trading partners.
- India is the 2nd largest market for Oman’s crude oil exports for the year 2022 after China.
- India is also the 4th largest market for Oman’s non-oil exports for the year 2022 after UAE, US and Saudi Arabia and 2nd largest source of its import after UAE.
- Indian companies have invested in Oman in sectors like iron and steel, cement, fertilisers, textile etc.
- India-Oman Joint Investment Fund (OIJIF), a JV between State Bank of India and State General Reserve Fund (SGRF) of Oman, a special purpose vehicle to invest in India, has been operational.
- Indian Community in Oman:
- There are about 6.2 lakh Indians in Oman, of which about 4.8 lakh are workers and professionals. There are Indian families living in Oman for more than 150-200 years.
What is Oman’s Strategic Significance for India?
- Oman is at the gateway of Strait of Hormuz through which India imports one-fifth of its oil imports.
- Defence cooperation has emerged as a key pillar for the robust India-Oman strategic partnership. Defence exchanges are guided by a Framework MOU which was recently renewed in 2021.
- Oman is the only country in the Gulf region with which all three services of the Indian armed forces conduct regular bilateral exercises and staff talks, enabling close cooperation and trust at the professional level.
- Oman also actively participates in the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- In a strategic move to expand its footprint in the Indian Ocean region, India has secured access to the key Port of Duqm in Oman for military use and logistical support. This is part of India’s maritime strategy to counter Chinese influence and activities in the region.
- The Port of Duqm is situated on the southeastern seaboard of Oman, overlooking the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is strategically located, in close proximity to the Chabahar port in Iran. With the Assumption Island being developed in Seychelles and Agalega in Mauritius, Duqm fits into India’s proactive maritime security roadmap.
Way Forward
- India does not have enough energy resources to serve its current or future energy requirements. The rapidly growing energy demand has contributed to the need for long term energy partnerships with countries like Oman.
- Oman’s Duqm Port is situated in the middle of international shipping lanes connecting East with West Asia.
- India needs to engage with Oman and take initiatives to utilise opportunities arising out of the Duqm Port industrial city.
- India should also work closely with Oman to enhance strategic depth in the region and add heft to its Indo-Pacific vision in the Western and Southern Part of Indian Ocean.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(b) Saudi Arabia
(c) Oman
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is an alliance of 6 countries in the Arabian Peninsula – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Iran is not a member of the GCC.
- It was established in 1981 to promote economic, security, cultural and social cooperation between the members and holds a summit every year to discuss cooperation and regional affairs.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. A number of outside powers have entrenched themselves in Central Asia, which is a zone of interest to India. Discuss the implications, in this context, of India’s joining the Ashgabat Agreement, 2018. (2018)
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)


Important Facts For Prelims
Superconductivity
Why in News?
Recently, physicists at the University of L'Aquila in Italy have recently made a breakthrough by achieving a full microscopic understanding of the superconductivity of Mercury for the first time.
- Superconductivity was first discovered in mercury, yet scientists required 111 years to explain how it becomes superconducting.
What is Superconductivity?
- Superconductivity:
- Superconductivity refers to a state when a material can conduct electricity without any resistance. It is observed in many materials when they are cooled below a critical temperature.
- Superconductivity of Mercury:
- About:
- In 1911, Heike Kamerlingh Onnes discover superconductivity in mercury.
- Onnes had invented a way to cool materials to absolute zero – the lowest temperature possible.
- Using his technique, he found that at a very low temperature, called the threshold temperature, solid mercury offers no resistance to the flow of electric current. It was a watershed moment in the history of physics.
- Various Methodologies: Superconductivity of mercury is explained by various methodologies:
- The BCS Theory:
- In BCS (Bardeen-Cooper-Schrieffer) superconductors, vibrational energy released by the grid of atoms encourages electrons to pair up, forming so-called Cooper pairs.
- These Copper pairs can move like water in a stream, facing no resistance to their flow, below a threshold temperature.
- These could explain why mercury has such a low threshold temperature (around –270°C).
- Spin-Orbit Coupling:
- Spin-orbit coupling (SOC) is the way an electron’s energy is affected by the relationship between its spin and its momentum.
- SOC gave a better view of the phonons’ energies and explain why mercury has such a low threshold temperature (approx. –270º C).
- Coulomb Repulsion:
- Another factor was the Coulomb repulsion (a.k.a. ‘like charges repel’) between two electrons in each pair.
- The superconducting state is determined by a balance between an attractive interaction between electrons, mediated by phonons, and the repulsive Coulomb interaction (electrostatic repulsion between negative charges).
- The BCS Theory:
- About:
What is Mercury?
- Mercury is a naturally occurring element that is found in air, water and soil.
- Released into the atmosphere through natural processes such as weathering of rocks, volcanic eruptions, geothermal activities, forest fires, etc.
- Mercury is also released through human activities.
- It is the only metal which remains liquid at room temperature.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Due to improper/indiscriminate disposal of old and used computers or their parts, which of the following are released into the environment as e-waste? (2013)
- Beryllium
- Cadmium
- Chromium
- Heptachlor
- Mercury
- Lead
- Plutonium
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1, 3, 4, 6 and 7 only
(b) 1, 2, 3, 5 and 6 only
(c) 2, 4, 5 and 7 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
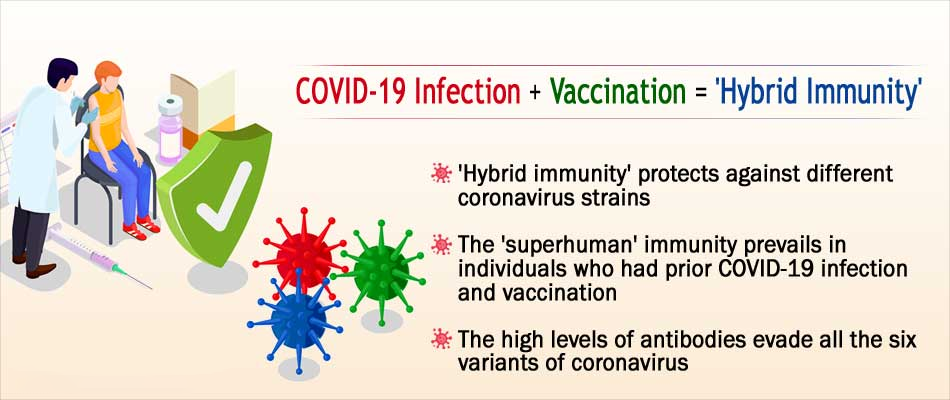
Hybrid Immunity
Why in News?
A recent study in the journal The Lancet Infectious Diseases held that “hybrid immunity” provides better protection against severe Covid-19, while all immunity against a re-infection wane within a few months.
- The study is based on a meta-analysis of 11 other studies on the protective effectiveness of previous SARS-CoV-2 (Covid) infection and 15 studies on the protective effectiveness of hybrid immunity.
What is Hybrid Immunity?
- Hybrid immunity from an infection is a combination of natural protection along with the immunity provided by the vaccine.
- It appears to result in stronger protection than just infection or vaccination alone.
- In the case of Covid-19, hybrid immunity is when someone recovers from a Covid infection before getting vaccinated.
What are the Highlights of the Study?
- Better Protection:
- A hybrid immunity offers a “higher magnitude and durability” of protection as compared to infection alone, emphasizing the need for vaccination.
- However, with the faster-spreading omicron variants leading to more infections and consequently more people developing this hybrid immunity.
- Efficacy of Hybrid Immunity:
- Protection against severe disease and hospitalisations from a Sars-CoV-2 infection alone was found to be 82.5% at three months after the last shot or infection.
- This protection stood at 74.6% at 12 months and 71.6% at 15 months.
- Protection against reinfection declined faster, standing at 65.2% at three months and dropping to 24.7% at 12 months and 15.5% at 15 months.
- In comparison, hybrid immunity with just the primary vaccine doses was found to be 96% at three months and 97.4% at 12 months.
- The same can offer 69% protection against reinfection at three months, dropping to 41.8% at 12 months.
- The effectiveness of hybrid immunity gained from infection coupled with the primary as well as a booster dose stood at 97.2% at three months and 95.3% at six months.
- Protection against severe disease and hospitalisations from a Sars-CoV-2 infection alone was found to be 82.5% at three months after the last shot or infection.
- Implications:
- It can be used to tailor guidance on the number and timing of SARS-CoV-2 vaccinations.
- It said that in regions with high Sars-CoV-2 sero-prevalence, the primary vaccination – focused mainly on those at the highest risk of severe disease such as the old or co-morbid – can offer high protection against severe disease and hospitalisation for at least one year.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Question (PYQ)
Q. In the context of vaccines manufactured to prevent COVID-19 pandemic, consider the following statements: (2022)
- The Serum Institute of India produced COVID-19 vaccine named Covishield using mRNA platform.
- Sputnik V vaccine is manufactured using vector-based platform.
- COVAXIN is an inactivated pathogen-based vaccine.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- COVISHIELD vaccine is based on the platform which uses a recombinant, replication-deficient chimpanzee adenovirus vector encoding the SARS-CoV-2 Spike (S) glycoprotein. Following administration, the genetic material of part of coronavirus is expressed which stimulates an immune response. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Sputnik V is the world's first registered vaccine based on a well-studied human adenovirus vector platform. It has been approved for use in 71 countries with a total population of 4 billion people. The vaccine is named after the first Soviet space satellite. The vaccine’s efficacy is 97.6%, based on the analysis of data on the incidence of coronavirus among Russians vaccinated with both vaccine components between December 5, 2020 and March 31, 2021. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Covaxin is an inactivated viral vaccine. This vaccine is developed with Whole-Virion Inactivated Vero Cell-derived technology. They contain inactivated viruses, which cannot infect a person but still can teach the immune system to prepare a defence mechanism against the active virus. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- Hence, option (b) is correct.


Important Facts For Prelims
New Plateau in the Western Ghats
Why in News?
Recently, a rare low-altitude basalt plateau discovered in Maharashtra in the Western Ghats can help study the effects of climate change on species survival and increase awareness of the conservation needs of rock outcrops and their immense biodiversity value in the global context.
What are the Important Findings About the Plateau?
- Low-Altitude Basalt Plateau: This is the fourth type of plateau to be identified in the region; the previous three are laterites at high and low altitudes and basalt at high altitudes.
- Diverse Biodiversity: During the survey of the plateau, 76 species of plants and shrubs from 24 different families were reported. This is considered an important discovery, as the plateau shares the vegetation with the three other rock outcrops, simultaneously holding a few unique species.
- This gives a unique model system to study the species' interactions in varying environmental conditions.
Note: Rock outcrops have seasonal water availability, limited soil and nutrients, making them ideal laboratories to study the effects of climate change on species survival. Plateaus are thus a valuable source of insight into how species can survive in extreme conditions.
Western Ghats: What's Important to Know?
- About:
- Western Ghats consists of a chain of mountains running parallel to India’s Western Coast and passing from the states of Kerala, Maharashtra, Goa, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
- The Western Ghats is one of four global biodiversity hotspots in India.
- The other three are the Himalayas, the Indo-Burma region and the Sundaland (includes the Nicobar Islands).
- It is recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Significance:
- The Ghats influence the Indian monsoon weather patterns that mediate the warm tropical climate of the region.
- They act as a barrier to rain-laden monsoon winds that sweep in from the south-west.
- Western Ghats are home to tropical evergreen forests, as well as to 325 globally threatened species.
- Plateaus are the dominant landscapes in the Western Ghats, significant because of the predominance of endemic species.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- In India, the Himalayas are spread over five States only.
- Western Ghats are spread over five States only.
- Pulicat Lake is spread over two States only.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (b)
Q2. ‘Gadgil Committee Report’ and ‘Kasturirangan Committee Report’, sometimes seen in the news, are related to (2016)
(a) constitutional reforms
(b) Ganga Action Plan
(c) linking of rivers
(d) protection of Western Ghats
Ans: (d)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
National Disaster Response Force (NDRF)
The Union Minister of Home Affairs recently greeted the National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) on its 18th Raising Day (January 19). NDRF is the world’s largest rapid reaction force dedicated to disaster response.
NDRF was formed in 2006 under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 with the purpose of a specialised response to natural and man-made disasters. The Kosi Floods in 2008 were NDRF’s first such mission.
Read More - Disaster Management Act, 2005
SC Refuses to Entertain Plea on Google-CCI Issue
The Supreme Court of India has refused to entertain a plea by Google against NCLAT’s order refusing the interim stay on ₹1,337 crore penalty on Google. The SC has granted Google 7 days to deposit 10% of the penalty imposed by the Competition Commission of India (CCI). The Indian companies have welcomed the SC’s stance against Google.
Earlier, CCI imposed a penalty on Google for “abusing its dominant position” in markets related to the Android mobile device ecosystem. Google filed an appeal with the NCLAT against the CCI order which was declined by NCLAT.
Read More - CCI Penalty on Google, National Company Law Appellate Tribunal (NCLAT), Competition Commission of India (CCI)
Sansad Khel Mahakumbh 2022-23
The Prime Minister of India recently inaugurated the 2nd phase of Saansad Khel Mahakumbh 2022-23 (18-28 Jan), organised in Basti (UP). The first phase was organised from 10-16 Dec 2022.
The Khel Mahakumbh is a novel initiative that provides an opportunity and a platform to showcase sporting talent, and motivates people to take sport as a career option.
Various types of competitions (indoor and outdoor) are organised by Khel Mahakumbh such as - wrestling, kabaddi, kho kho, basketball, football, hockey, volleyball, etc.
Through these games, performing athletes are being selected for further training under the Sports Authority of India.
Read More - Role of Sports in Aspirational India, Sports Governance in India
Pankaj Kumar Singh appointed as Deputy NSA
Recently, the retired Director General of the Border Security Force (BSF) Pankaj Kumar Singh was appointed as the Deputy National Security Advisor (D-NSA) in the National Security Council Secretariat for a period of 2 years.
As a D-NSA, he will assist the NSA - Ajit Doval, in creating and implementing India's national security strategies - assessing threats posed by terrorism, data security, cyber threats, readiness of concerned agencies and cooperation between different organisations dealing with security issues.
Read More - National Security Advisor, National Security Council