India-Oman Bilateral Meet
For Prelims: India-Oman Bilateral Meet, Indian Council of Cultural Relations (ICCR), India Oman Joint Vision Partnership For the Future, Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA).
For Mains: India-Oman Bilateral Meet, Bilateral, regional and global groupings and agreements involving India and/or affecting India’s interests.
Why in News?
Recently, India and Oman have adopted the India Oman Joint Vision Partnership For the Future, setting the stage for bilateral cooperation and charting pathways for future collaboration between the two countries.
- This Vision Document focuses on building partnerships in broadly 8 to 10 areas. These include maritime cooperation and connectivity, energy security, space, digital payments, health, tourism, hospitality, agriculture and food security.
What are the Key Highlights of the Bilateral Meet?
- Bilateral Agreements:
- Both countries have signed agreements on cooperation in the field of information technology, combating financial crimes, culture, and the establishment of a Hindi chair of the Indian Council of Cultural Relations (ICCR) in Oman.
- Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA):
- Both nations are engaged in discussions to finalize a CEPA. Substantial progress has been made, and leaders from both sides emphasized concluding this agreement at the earliest to boost economic ties.
- Oman-India investment Fund:
- The two sides announced the third tranche of Oman-India investment fund worth USD 300 million that would be used for channelising investment into the fastest growing sectors of the Indian economy.
- The fund was started as a 50:50 joint venture between the SBI and the Oman investment authority, with the first tranche of USD 100 million followed by USD 200 million.
- Digital Payments and Trade:
- Discussions revolved around the possibility of using India's digital payment system, UPI (Unified Payments Interface), in collaboration with an Omani platform.
- Additionally, exploring the potential of conducting trade in Rupees was considered, although it's still in the exploratory stage.
- Regional and International Issues:
- Leaders exchanged perspectives on regional and global matters, including the ongoing conflict between Hamas and Israel.
- They discussed the challenge of terrorism and advocated for a two-state solution to address the Palestine issue.
How have Been India-Oman Relationships so Far?
- Background:
- The two countries across the Arabian Sea are linked by geography, history and culture and enjoy warm and cordial relations, which are attributed to historical maritime trade linkages.
- The Sultanate of Oman is a strategic partner of India in the Gulf and an important interlocutor at the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC), Arab League and Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) fora.
- Gandhi Peace Prize 2019 was conferred on Late HM Sultan Qaboos in recognition of his leadership in strengthening the ties between India & Oman and his efforts to promote peace in the Gulf region.
- Defense Relations:
- Joint Military Cooperation Committee (JMCC):
- The JMCC is the highest forum of engagement between India and Oman in the field of defence.
- The JMCC is expected to meet annually, but could not be organised since 2018 when the meeting of the 9th JMCC was held in Oman.
- Military Exercises:
- Army exercise: Al Najah
- Air Force exercise: Eastern Bridge
- Naval Exercise: Naseem Al Bahr
- Joint Military Cooperation Committee (JMCC):
- Economic & Commercial Relations:
- Institutional mechanisms like Joint Commission Meeting (JCM) and Joint Business Council (JBC) oversee economic cooperation between India and Oman.
- India is among Oman’s top trading partners.
- India is the 2nd largest market for Oman’s crude oil exports for the year 2022 after China.
- India is also the 4th largest market for Oman’s non-oil exports for the year 2022 after UAE, US and Saudi Arabia and 2nd largest source of its import after UAE.
- Indian companies have invested in Oman in sectors like iron and steel, cement, fertilisers, textile etc.
- India-Oman Joint Investment Fund (OIJIF), a JV between State Bank of India and State General Reserve Fund (SGRF) of Oman, a special purpose vehicle to invest in India, has been operational.
- Indian Community in Oman:
- There are about 6.2 lakh Indians in Oman, of which about 4.8 lakh are workers and professionals. There are Indian families living in Oman for more than 150-200 years.
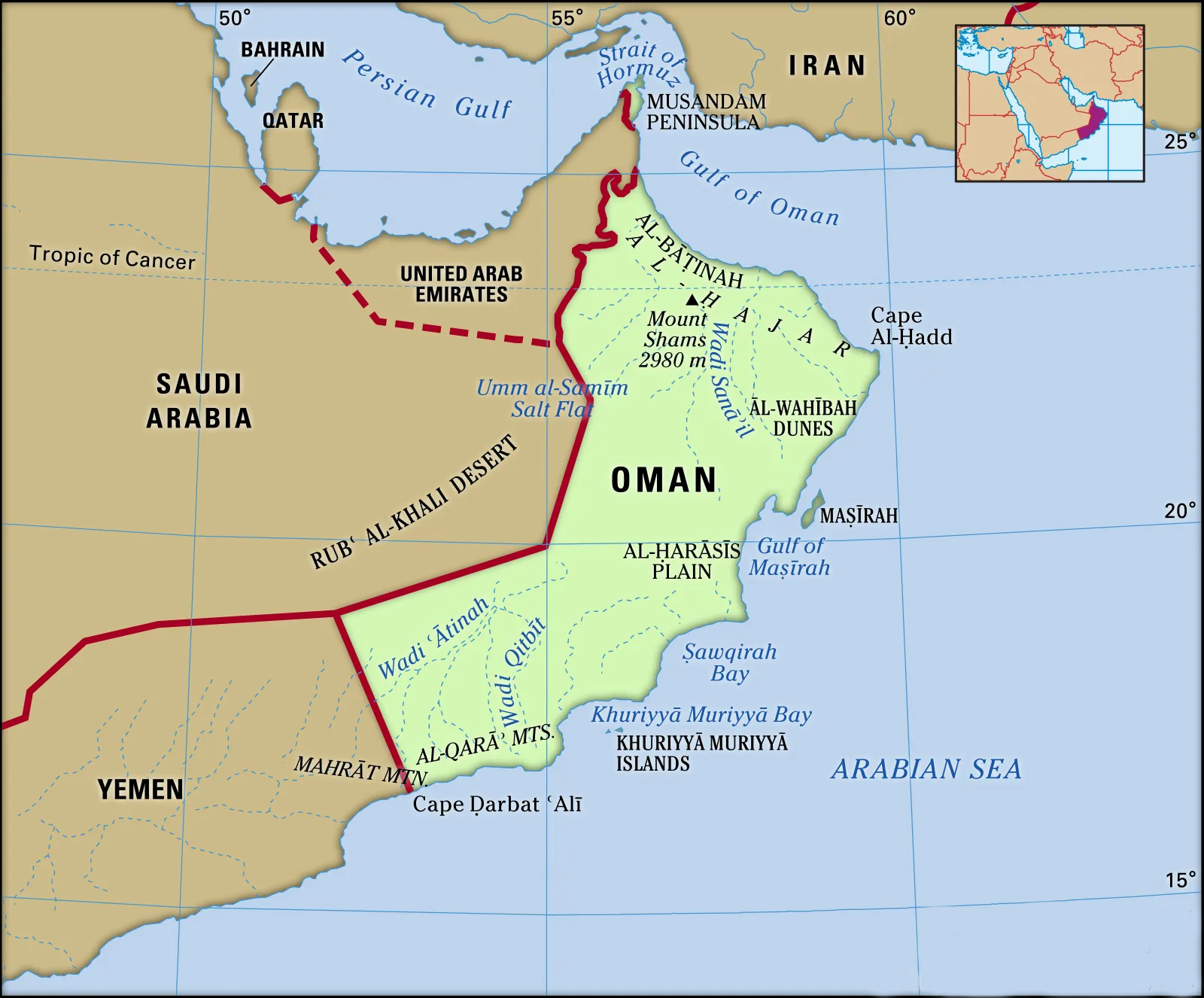
What is Oman’s Strategic Significance for India?
- Oman is at the gateway of Strait of Hormuz through which India imports one-fifth of its oil imports.
- Defence cooperation has emerged as a key pillar for the robust India-Oman strategic partnership. Defence exchanges are guided by a Framework MOU which was recently renewed in 2021.
- Oman is the only country in the Gulf region with which all three services of the Indian armed forces conduct regular bilateral exercises and staff talks, enabling close cooperation and trust at the professional level.
- Oman also actively participates in the Indian Ocean Naval Symposium (IONS).
- In a strategic move to expand its footprint in the Indian Ocean region, India has secured access to the key Port of Duqm in Oman for military use and logistical support. This is part of India’s maritime strategy to counter Chinese influence and activities in the region.
- The Port of Duqm is situated on the southeastern seaboard of Oman, overlooking the Arabian Sea and the Indian Ocean.
- It is strategically located, in close proximity to the Chabahar port in Iran. With the Assumption Island being developed in Seychelles and Agalega in Mauritius, Duqm fits into India’s proactive maritime security roadmap.
Key Facts About Oman
- Border Countries:
- United Arab Emirates (UAE) to the northwest.
- Saudi Arabia to the west and southwest.
- Yemen to the southwest.
- Deserts:
- The largest desert in Oman is the Rub' al Khali or the "Empty Quarter," one of the largest continuous sand deserts in the world.
- River:
- Oman doesn’t have perennial rivers; however, during seasonal rains, wadis (seasonal riverbeds) flow with water.
- The most notable is Wadi Bani Khalid, known for its natural pools and stunning scenery.
- Highest Mountain:
- Jebel Shams, situated within the Al Hajar mountain range, is the highest mountain in Oman.
- Geography:
- Oman is located on the southeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula, bordering the Arabian Sea, the Gulf of Oman, and the Persian Gulf.
Way Forward
- India does not have enough energy resources to serve its current or future energy requirements. The rapidly growing energy demand has contributed to the need for long term energy partnerships with countries like Oman.
- Oman’s Duqm Port is situated in the middle of international shipping lanes connecting East with West Asia.
- India needs to engage with Oman and take initiatives to utilise opportunities arising out of the Duqm Port industrial city.
- India should also work closely with Oman to enhance strategic depth in the region and add heft to its Indo-Pacific vision in the Western and Southern Part of Indian Ocean.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following is not a member of ‘Gulf Cooperation Council’? (2016)
(a) Iran
(b) Saudi Arabia
(c) Oman
(d) Kuwait
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is an alliance of 6 countries in the Arabian Peninsula – Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. Iran is not a member of the GCC.
- It was established in 1981 to promote economic, security, cultural and social cooperation between the members and holds a summit every year to discuss cooperation and regional affairs.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. A number of outside powers have entrenched themselves in Central Asia, which is a zone of interest to India. Discuss the implications, in this context, of India’s joining the Ashgabat Agreement, 2018. (2018)
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)
Logistics Ease Across Different State 2023
For Prelims: Logistics Ease Across Different States 2023, Logistics Performance Index, World Bank, Ease of Doing Business.
For Mains: Logistics Ease Across Different State 2023, Indian Economy and issues relating to planning, mobilization of resources, growth, development and employment.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Commerce & Industry has released the 5th edition of “Logistics Ease Across Different State (LEADS) 2023” report, which serves as a guide for stakeholders in the Logistics Sector by providing strategic insights.
What is Logistics Ease Across Different States (LEADS)?
- About:
- The LEADS is an indigenous data-driven index to assess logistics infrastructure, services, and human resources across all 36 States and UTs.
- LEADS continues to act as a guiding & bridging mechanism for the identification of interventions enhancing logistics efficiency at State/UTs. It reflects positively on international indices, like the Logistics Performance Index.
- LEADS aims to guide stakeholders in the logistics sector by offering strategic insights and fostering healthy competition among states and union territories to improve their logistics performance.
- LEADS was conceived on the lines of the Logistics Performance Index of World Bank in 2018 and has evolved over time.
- Evaluation Criteria:
- The report evaluates logistics performance based on three key pillars,
- Logistics Infrastructure
- Logistics Services
- Operating and Regulatory Environment
- The report evaluates logistics performance based on three key pillars,
- Methodology:
- The report is based on a pan-India primary survey conducted between May and July 2023, incorporating over 7,300 responses across 36 states/UTs. Additionally, it includes insights from over 750 stakeholder consultations facilitated by various associations.
What are the Key Highlights of the LEADS 2023?
- Achievers:
- Thirteen states and Union Territories, including Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Chandigarh, and Gujarat, are categorized as achievers in the logistics index chart 2023.
- These regions have shown efficient logistical services that contribute to export promotion and economic growth.
- Fast Movers:
- Kerala, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland are recognized as fast movers in the logistics index.
- These areas have shown significant progress and improvements in their logistical services.
- Aspirers:
- States and UTs in the aspirers category, such as Goa, Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh, and Jharkhand, are identified as regions with potential for growth in their logistics ecosystem. These areas are striving to enhance their logistical capabilities.
- Policy Reforms:
- The report emphasizes the significance of policy reforms such as industry status for logistics, digital initiatives (PM GatiShakti, Logistics Data Bank, Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP), GST), and the alignment of State Logistics Policies with the National Logistics Policy.
What is the Logistics Performance Index?
- The Logistics Performance Index (LPI), developed by the World Bank Group, is an interactive benchmarking tool created to help countries identify the challenges and opportunities they face in their performance on trade logistics and what they can do to improve their performance.
- LPI is the weighted average of the country's scores on the six key dimensions:
- Customs performance
- Infrastructure quality
- Ease of arranging shipments
- Logistics services quality
- Consignment tracking and tracing
- Timeliness of shipments
- India ranked 38th out of 139 countries in LPI 2023.
What are the Initiatives Related to Logistics?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. The Gati-Shakti Yojana needs meticulous coordination between the government and the private sector to achieve the goal of connectivity. Discuss. (2022)
Surat Diamond Bourse
For Prelims: Surat Diamond Bourse, Major Diamond Producing Countries, Lab-Grown Diamonds, Chemical vapor deposition method, Customs duty on imported seeds for Lab Grown Diamonds.
For Mains: Diamond Industry in India, Production Methods of Lab Grown Diamonds.
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Prime Minister inaugurated the Surat Diamond Bourse (SDB) in Gujarat, marking a significant development in the diamond and jewelry industry.
- The SDB stands as the world’s largest office complex. It aims to relocate the diamond trading hub from Mumbai to Surat, leveraging Surat's diamond cutting and polishing expertise.
What is the Status of the Diamond Industry in India?
- About Diamond: A diamond is a rare, naturally occurring mineral made up of pure carbon. The word diamond comes from the Greek word Adamas, which means indestructible.
- Diamond occurs in two types of deposits, primarily in igneous rocks of basic or ultrabasic composition and in alluvial deposits derived from the primary sources.
- Major Diamond Producing Countries: Russia, Botswana, Canada, South Africa, Democratic Republic of the Congo.
- Russia is the world's largest producer of rough diamonds, mining nearly 42 million carats in 2022.
Note
Recently, the G7 group of countries have announced direct import restrictions on Russian-origin diamonds from January 2024 and diamonds processed by third countries like India from March 2024, which has raised major concerns for the Indian gems and jewelry trade and diamond processing industry.
- However, Lab grown diamonds are gaining traction for their eco-friendly nature.
- Diamond Industry in India: India is the world's largest cutting and polishing center for diamonds, accounting for over 90% of polished diamond manufacturing globally.
- According to Indian Minerals Yearbook 2019, diamond fields of India are grouped into four regions:
- Central Indian tract of Madhya Pradesh, comprising Panna belt.
- South Indian tract of Andhra Pradesh, comprising parts of Anantapur, Kadapa, Guntur, Krishna, Mahabubnagar and Kurnool districts.
- Behradin-Kodavali area in Raipur district and Tokapal, Dugapal, etc. areas in Bastar district of Chhattisgarh.
- Eastern Indian tract mostly of Odisha, lying between Mahanadi and Godavari valleys.
- In 2022, India ranks first among the top exporters in cut & polished diamonds.
- According to Indian Minerals Yearbook 2019, diamond fields of India are grouped into four regions:
What are Lab-Grown Diamonds?
- About:
- Lab-grown diamonds (LGDs) are diamonds that are grown in a laboratory using advanced technology.
- They are also known as cultured, synthetic, man-made, or artisan-created diamonds.
- Natural diamonds form deep within the Earth over an extensive period, often up to three billion years, under extreme pressure and high temperatures.
- LGDs have essentially the same chemical, optical and physical properties and crystal structure as natural diamonds.
- Unlike mined diamonds, lab-grown diamonds do not involve the social and environmental ramifications associated with mining activities.
- Consequently, all LGDs are considered eco-friendly and contribute positively to environmental preservation.
- Lab-grown diamonds (LGDs) are diamonds that are grown in a laboratory using advanced technology.
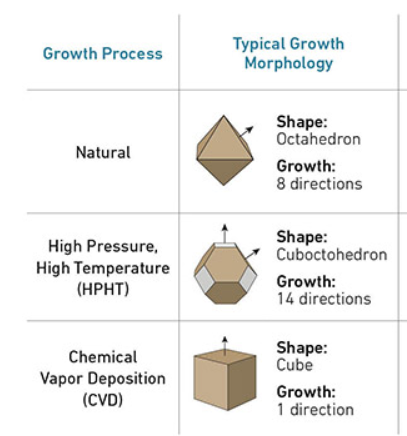
- Production Methods: LGDs are synthesized in laboratories via two primary methods: chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or high pressure, high temperature (HPHT).
- Both HPHT and CVD methods of growing diamonds artificially begin with a seed, a slice of another diamond.
- Market Share in India: India, known as a significant hub for diamond cutting and polishing, has experienced a notable surge in export earnings due to the increasing global demand for LGDs.
- However, their current share in the overall diamond industry stands at 2-3%.
- To improve the share, In Budget 2023-24, the Union Finance Minister announced elimination of Customs duty on imported seeds used in the manufacturing process of rough LGDs.
Arbitration Agreements In Unstamped Contracts Valid
For Prelims: Arbitration Agreements, Curative Petition, Supreme Court, Chief Justice of India, Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996, Article 51, Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Act, 2019
For Mains: Impact of Arbitration on Efficiency of Function of Judiciary.
Why in News?
Recently, a seven-judge Constitution Bench of the Supreme Court (SC) held that arbitration agreements embedded in unstamped or insufficiently-stamped substantive commercial contracts or instruments are not invalid, unenforceable or even non-existent.
- “Arbitration aims to provide speedy, efficient, and binding resolution of disputes that have arisen between the parties.
What are the Key Highlights of the SC Decision?
- Delivering the lead opinion in a curative petition overruling an earlier five-judge Bench verdict of the Supreme Court in the N.N. Global case, Chief Justice of India held that “non-stamping or inadequate stamping is a curable defect”.
- Non-payment or insufficient stamping of contracts under the Indian Stamp Act, 1899. would not affect arbitration proceedings under the Arbitration And Conciliation Act, 1996.
- The Arbitration Act is a self-contained code. Matters governed by the Arbitration Act such as the arbitration agreement, appointment of arbitrators and competence of the arbitral tribunal to rule on its jurisdiction have to be assessed in the manner specified under the law.
- Therefore, provisions of other statutes cannot interfere with the working of the Arbitration Act.
- The judgment gives a significant shot in the arm for India’s ambition to become an international arbitration hub to quickly resolve commercial disputes.
- Earlier, arbitrations on such disputes had struck a roadblock owing to non-payment of the required stamp duty for or insufficient stamping of contracts by the parties.
What is Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) Mechanism in India?
- Arbitration:
- The dispute is submitted to an arbitral tribunal which makes a decision (an "award") on the dispute that is mostly binding on the parties.
- It is less formal than a trial, and the rules of evidence are often relaxed.
- Generally, there is no right to appeal an arbitrator's decision.
- Except for some interim measures, there is very little scope for judicial intervention in the arbitration process.
- The Indian arbitration is governed and regulated by the Arbitration and Conciliation Act 1996 (which is amended in 2015, 2019 and 2021),
- The Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Act, 2019 seeks to establish an independent body called the Arbitration Council of India (ACI).
- Conciliation:
- A non-binding procedure in which an impartial third party, the conciliator, assists the parties to a dispute in reaching a mutually satisfactory agreed settlement of the dispute.
- Conciliation is a less formal form of arbitration.
- The parties are free to accept or reject the recommendations of the conciliator.
- However, if both parties accept the settlement document drawn by the conciliator, it shall be final and binding on both.
- Mediation:
- In mediation, an impartial person called a "mediator" helps the parties try to reach a mutually acceptable resolution of the dispute.
- The mediator does not decide the dispute but helps the parties communicate so they can try to settle the dispute themselves.
- Any person who undergoes the required 40 hours training stipulated by the Mediation and Conciliation Project Committee of the Supreme Court (SC) can be a mediator.
- He also needs to have at least 10 mediations resulting in a settlement and at least 20 mediations in all to be eligible to be accredited as a qualified mediator.
- Mediation leaves control of the outcome with the parties.
- Mediation Act, 2023 seeks to promote mediation, particularly institutional mediation, and provide a mechanism for enforcing mediated settlement agreements.
- Negotiation:
- A non-binding procedure in which discussions between the parties are initiated without the intervention of any third party with the object of arriving at a negotiated settlement to the dispute.
- It is the most common method of alternative dispute resolution.
- Negotiation occurs in business, non-profit organizations, government branches, legal proceedings, among nations and in personal situations such as marriage, divorce, parenting, and everyday life.
What is the Arbitration Council of India (ACI)?
- Constitutional Background: The Constitution of India, Article 51, India is obliged to endeavor to:
- Foster respect for international law and treaty obligations in the dealings of organized peoples with one country.
- Encourage settlement of international disputes by arbitration. ACI is a step in realization of this constitutional obligation.
- Objective:
- ACI aims to promote arbitration, mediation, conciliation and other alternative dispute redressal mechanisms.
- Composition of the ACI:
- The ACI will consist of a Chairperson who is either:
- A Judge of the Supreme Court/ A Judge of a High Court/ Chief Justice of a High Court.
- An eminent person with expert knowledge in conduct of arbitration.
- Other members will include an eminent arbitration practitioner, an academician with experience in arbitration, and government appointees.
- The ACI will consist of a Chairperson who is either:
Legal Insights: Supreme Judgment on Unstamped Arbitration Agreement
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to Lok Adalats, which of the following statements is correct? (2010)
(a) Lok Adalats have the jurisdiction to settle the matters at pre-litigative stage and not those matters pending before any court
(b) Lok Adalats can deal with matters which are civil and not criminal in nature
(c) Every Lok Adalat consists of either serving or retired judicial officers only and not any other person
(d) None of the statements given above is correct
Ans: (d)
Q2. With reference to Lok Adalats, consider the following statements: (2009)
- An award made by a Lok Adalat is deemed to be a decree of a civil court and no appeal lies against thereto before any court.
- Matrimonial/Family disputes are not covered under Lok Adalat.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. What are the major changes brought in the Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 through the recent Ordinance promulgated by the President? How far will it improve India’s dispute resolution mechanism? Discuss. (2015)
Initial Yak Domestication 2,500 Years Ago
Why in News?
A recent study has unveiled the earliest evidence of human domestication of yaks, discovered in Bangga, a settlement situated within the Shannan prefecture of the Tibetan Autonomous Region in China.
- Shannan, which shares borders with Bhutan and Arunachal Pradesh, is traversed by the Brahmaputra River.
What are the Major Highlights of the Study?
- Coexistence of Domesticated Yaks and Taurine Cattle: The study highlights the coexistence of domesticated yaks and taurine cattle within Bangga, indicating a sophisticated level of animal husbandry and agricultural practices from 2,500 years ago.
- The researchers also expressed surprise at the presence of taurine cattle in an area so near to the Indian subcontinent, where Zebus are predominant.
- It asserted that taurine cattle probably reached central and eastern Tibet from Anatolia (modern-day Turkiye) via the Silk Route and northern Tibet.
- Most modern cattle breeds of Europe as well as the temperate regions of Asia are taurine. They are distinct from the Zebu or humped breeds native to the Indian subcontinent and tropical Asia.
- Evidence of Hybridization and Advanced Breeding: Intriguingly, researchers unearthed evidence of hybrids, a result of intentional crossings between yaks and cattle, further underscoring the nuanced understanding ancient inhabitants possessed about animal breeding.
Note
There are an estimated 14 million to 15 million domestic yaks in the highlands of Asia alone. They are also found in the Indian Himalayan Border States and Union territories, such as Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh. However, wild yaks, never domesticated by humans, are on the brink.
What are the Major Points Related to Wild Yaks?
- About:
- The wild yak, known as Bos grunniens or Bos mutus, thrives in remote areas within the Tibetan plateau, specifically inhabiting high-elevation alpine tundra, grasslands, and cold deserts.
- The Convention on Migratory Species (CMS) reports that native wild yak population, while previously also found in Bhutan and Nepal, is now presumed extinct in those regions, limiting their current habitat to China and India.
- Major Threats to Wild Yaks:
- Habitat loss, genetic hybridization with domestic yaks, and poaching pose significant threats.
- Communities across the Himalayas and Tibetan Plateau use Dzo (Male hybrid) and Dzomo (Female hybrid), bred by crossing cattle and yaks.
- Disturbance from human activities and their livestock forces wild yaks to relocate to less favorable habitats, impacting their populations.
- Habitat loss, genetic hybridization with domestic yaks, and poaching pose significant threats.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Red list status: Vulnerable
- CITES: Appendix I of CITES
- The Wild Life (Protection) Amendment Act 2022: Schedule I
United Nations Convention against Corruption
Why in News?
The year 2023 marks the 20th anniversary of the United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC).
- The G20 also addresses anti-corruption efforts globally through its Anti-Corruption Working Group and includes related topics in the B20 and SAI20 discussions within the G20 Social track.
What is United Nations Convention against Corruption (UNCAC)?
- The UNCAC was signed on December 9, 2003 in Mexico and entered into force on 14th December 2005.
- The International Anti-Corruption Day was established on 9th December as a result of proposals by the Brazilian delegation to the Convention.
- It is the only legally binding multilateral international anti-corruption treaty.
- The Convention covers five main areas:
- Preventive Measures, Criminalization and Law Enforcement, International Cooperation, Asset Recovery, and Technical Assistance and Information Exchange.
- The Convention covers many different forms of corruption, such as bribery, trading in influence, abuse of functions, and various acts of corruption in the private sector.
What is the G-20 Anti-Corruption Working Group?
- The G-20 Anti-Corruption Working Group (ACWG) was set up in June 2010 at the Toronto Summit of G-20.
- It concentrates on sharing effective strategies to combat corruption. It also addresses emerging challenges, including the use of new technologies in countering corrupt practices.
- The ACWG is chaired by the Presidency of the G20 and a co-chair.
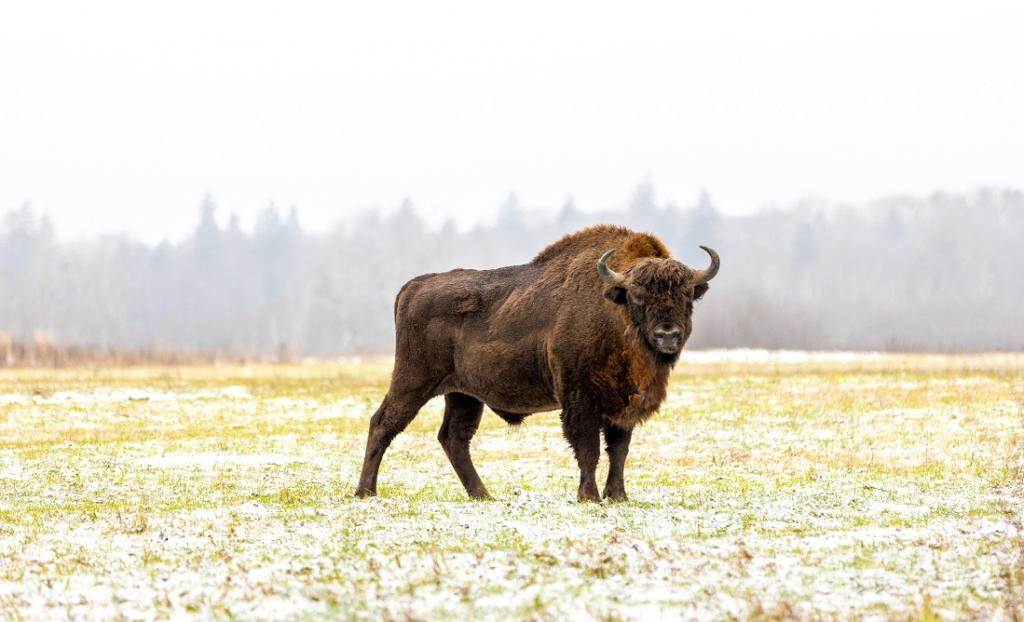
The Wisent: European Bison
Why in News?
Recently, the ongoing war in Ukraine has cast a shadow over conservation efforts aimed at preserving the wisent, also known as the European wood bison.
- This majestic creature, once abundant across the European continent, faced near-extinction by 1927.
- Despite successful conservation endeavors in Ukraine and Russia, the Russian invasion of Ukraine in February 2022 poses a significant threat to the revival and restoration of the wisent.
What is the Wisent (European Wood Bison)?
- About: The European wood bison (Bison bonasus) stands as the largest and heaviest terrestrial mammal in Europe.
- Once comprising three subspecies, only one, Bison bonasus bonasus, remains extant, with the other two having succumbed to extinction.
- Habitat: Thriving in grasslands, deciduous, and mixed forests,
- Noteworthy for its role as an ecosystem engineer, the wisent plays a crucial part in restoring grassland habitats.
- Distribution: Belarus; Lithuania; Poland; Russian Federation; Slovakia; Ukraine
- IUCN Red list Status: Near Threatened
- Threats: Rapid environmental change and hunting by humans were the main drivers of the wisent’s extirpation across Europe.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. ‘Invasive Species Specialist Group’ (that develops Global Invasive Species Database) belongs to which one of the following organizations?(2023)
(a) The International Union for Conservation of Nature
(b) The United Nations Environment Programme
(c) The United Nations World Commission for Environment and Development
(d) The World Wide Fund for Nature
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) is a global network of scientific and policy experts on invasive species, organized under the auspices of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). Hence, option (a) is correct.
- It was established in 1994.
- The ISSG manages the Global Invasive Species Database (GISD), which provides information on invasive alien species worldwide. The ISSG also maintains other online resources such as the Aliens-L listserv, the Invasive Species Compendium, the Global Register of Introduced and Invasive Species, and the Environmental Impact Classification for Alien Taxa.
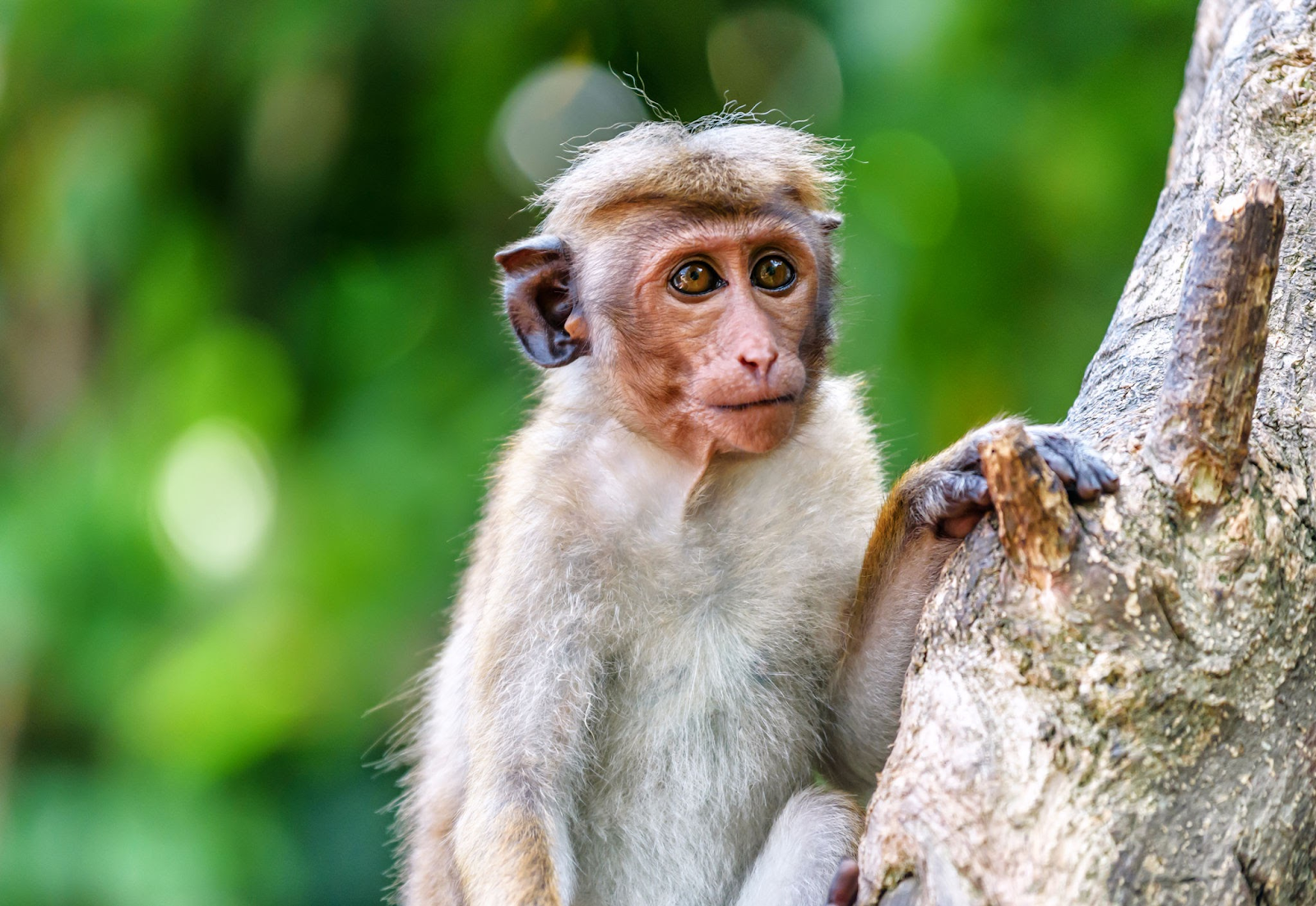
Bonnet Macaque Monkey
The discovery of 27 bonnet macaque monkey carcasses in a Karnataka village spotlights the escalating human-monkey conflict driven by habitat encroachment and diminishing wildlife spaces.
- Instances of monkey incursions for food in human territories have led to distressing events, like the suspected poisoning of macaques in Guthigaru village.
- The encroachment of farming into forest fringes, particularly coconut plantations and fruit orchards, draws monkeys when natural food sources diminish.
- The bonnet macaque (Macaca radiata) is a species of Old World monkey. They are gray-brown in color, have large ears, wrinkly faces, and a mop of hair on their heads that is parted in the middle.
- The bonnet macaque gets its name from the whorls of hair on the crown of its head that resemble a cap or bonnet.
- Bonnet macaques are endemic commensals: they are found only in peninsular India and live in close proximity with humans.
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable
Value Investing
Value investing entails purchasing assets below their intrinsic value, anticipating future appreciation. It was pioneered by Benjamin Graham and popularized by Warren Buffet on the belief that an asset's price will eventually match its intrinsic value.
- It focuses on exploiting the gap between an asset's price and intrinsic value for profitable returns, taking advantage of market fluctuations by buying during crises and selling during booms.
- For example, if a company's stock has an intrinsic value of 100 rupees per share, but the market price is only 60 rupees. A value investor seizes the opportunity, buying the undervalued stock.
- As the stock price rises toward its intrinsic value. The value investor then sells the stock at a profit, having taken advantage of the initial undervaluation.
- This contrasts with efficient market theory, as value investors capitalize on disparities between market prices and intrinsic worth, leveraging undervalued assets.
India, ADB Ink USD 250M Deal for Industrial Corridor Development
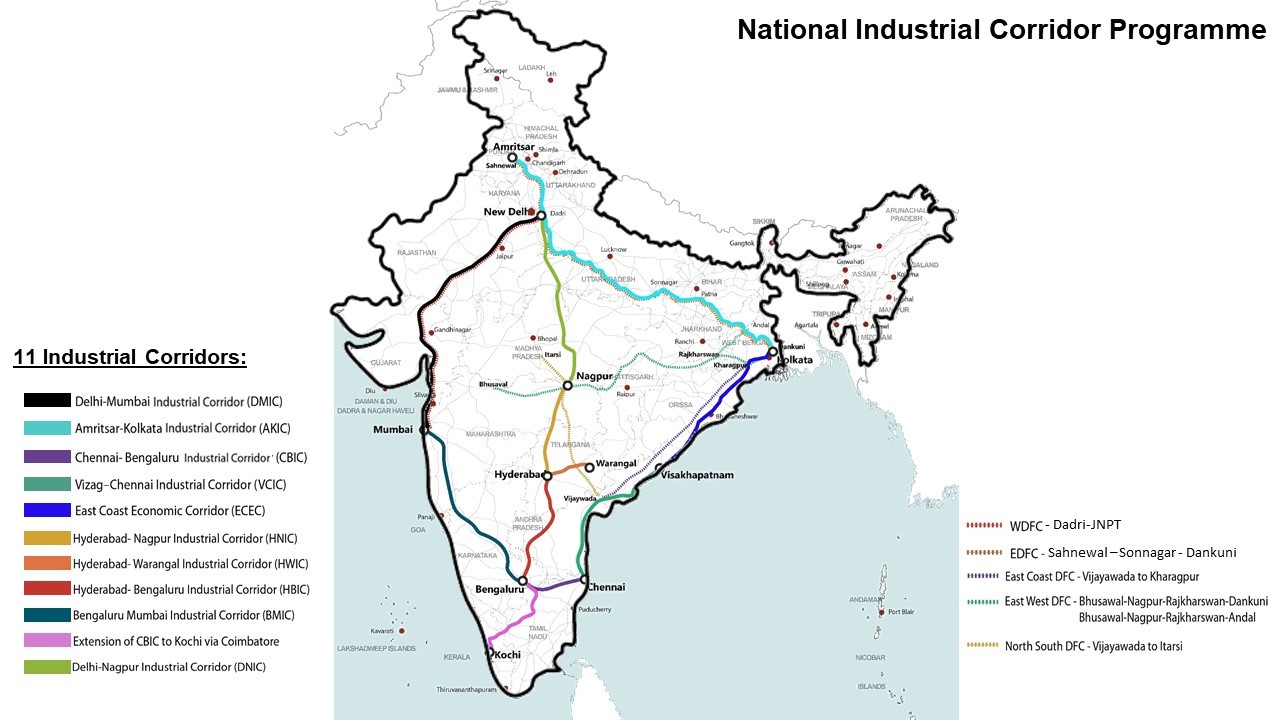
Recently, The Government of India and Asian Development Bank (ADB) signed a USD 250 million policy-based loan that will continue support to industrial corridor development to make manufacturing more competitive, strengthen national supply chains and links with regional and global value chains.
- This will help to strengthen policy frameworks for the Government of India’s National Industrial Corridor Development Programme (NICDP) and develop 11 industrial corridors.
- NICDP is India's most ambitious infrastructure programme aiming to develop new industrial cities as "Smart Cities" and converging next generation technologies across infrastructure sectors.
- National Industrial Corridor Development and Implementation Trust (NICDIT) is the implementing agency under the administrative control of Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT), Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
SATHEE Portal
Recently, the Minister of State for Education, in a written response in the Lok Sabha, announced that the Department of Higher Education,Ministry of Education in collaboration with IIT Kanpur, has initiated the SATHEE (Self-Assessment, Test, and Help for Entrance Examination) portal.
- The objective of the portal is to provide quality education to every student who intends to participate in competitive education such as JEE, NEET and various State level Engineering and other Examinations.
- To support students preparing for JEE and other engineering examinations, a 45 days crash course of JEE has been launched.
- Course is curated by IIT toppers, academicians and subject experts. This crash course is available in 5 languages including English.
- All India Council of Technical Education (AICTE) has developed an AI based translation tool. This tool supports 22 Indian languages.