International Relations
Changing Dynamics of Global South
For Prelims: Global South, Group of 77 (G-77), Global North, Green Energy Fund, G20 summit, UN Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC), European Union (EU), Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), Quad, Indo-Pacific Economic Forum, BRICS summit, G7 summit, Brandt Line.
For Mains: History of the Global South, Scenario of Global South's Increasing Influence, Influence of the Global South in Global Politics
Why in News?
Earlier in 2023, the Prime Minister of India organised a virtual summit on the "Voice of the Global South", involving approximately 125 countries. The objective of this summit was to solicit the opinions and input of countries from the Global South in order to determine the priorities for the region.
What is the History of the Global South?
- Historical Context: The term "Global South" is often used to highlight the historical legacy of colonialism and the economic disparities between the formerly colonised nations and the developed Western nations.
- It underscores the challenges faced by these countries in achieving economic growth and development.
- Formation of the G-77: In 1964, the Group of 77 (G-77) countries came into existence when they signed a Joint Declaration during the first session of the UN Conference on Trade and Development (UNCTAD) in Geneva.
- The G-77 became the largest intergovernmental organisation of developing countries at the time.
- Purpose of G-77: It was created to promote the economic interests of developing countries and improve their ability to negotiate on international economic issues within the UN system.
- It now includes 134 countries across Asia, Africa, South America, the Caribbean and Oceania. China is not technically part of the group, hence, the grouping is often referred to as "G-77+China" in multilateral forums.
- UNOSSC: The UN Office for South-South Cooperation (UNOSSC) was established in 1974. Its role is to coordinate cooperation between countries in the Global South and with developed countries or multilateral agencies, in collaboration with the G-77.
What led to the Revival of Global South?
- In the early decades of the 21st century, there was a noticeable decline in interest and attention towards the Global South.
- This trend was particularly evident in countries like India and Indonesia, which were perceived as moving away from their ‘Third World’ origins and seeking a more prominent role on the global stage as they reformed and expanded their economies.
- However, in recent times, the Global South has regained its importance and relevance, signifying a growing recognition of the region's significance in shaping the emerging global order. Several key factors are cited as contributing to this resurgence:
- Impact of Covid-19 Pandemic: The Covid-19 pandemic had a severe impact on many countries in the Global South, both in terms of public health and economic challenges. This crisis refocused attention on the vulnerabilities and needs of these nations.
- Economic Downturn: The economic downturn resulting from the pandemic disproportionately affected countries in the Global South, highlighting the need for international cooperation and support.
- Repercussions of Russia-Ukraine Conflict: The Russia-Ukraine conflict had a global economic impact. This had ripple effects on the developing world, further underscoring the interconnectedness of global affairs and the importance of the Global South in international diplomacy.
Why is the Term Global South Criticised?
- Inaccuracy of the Term: The term "Global South" is criticised for its inaccuracy in representing the countries it was intended to describe.
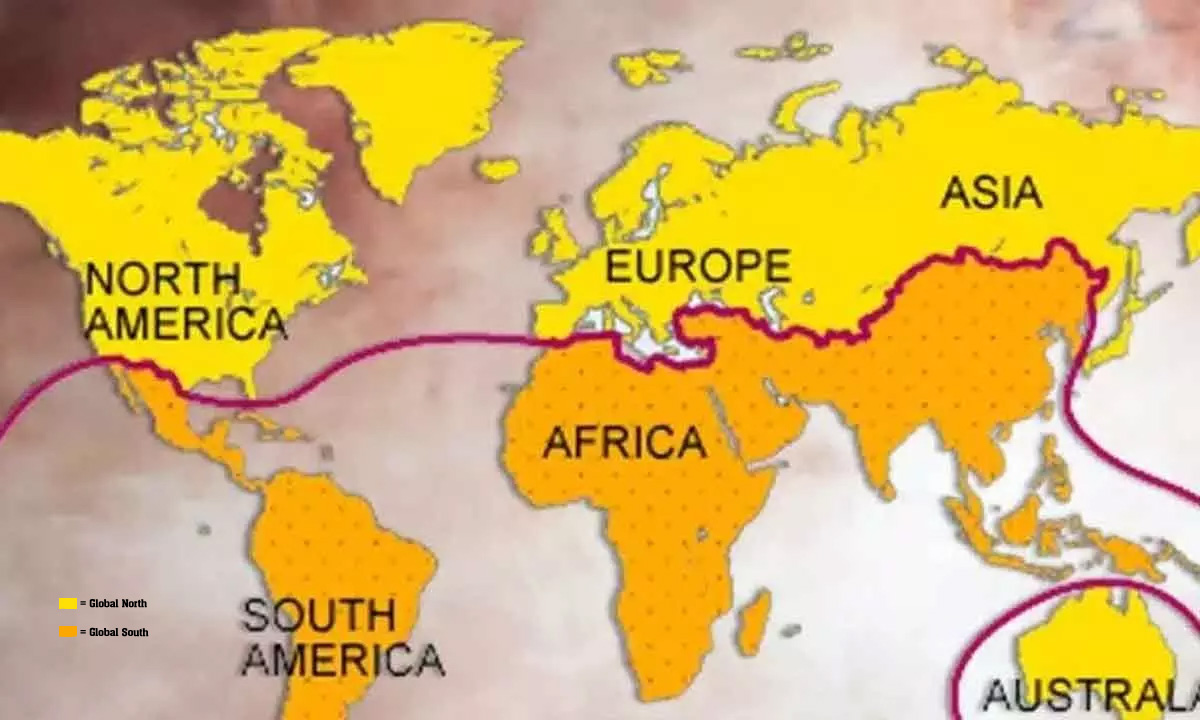
- It is pointed out that some countries typically considered part of the Global South, like India, are actually located in the Northern Hemisphere, while others, such as Australia, are in the Southern Hemisphere but often categorised as part of the Global North.
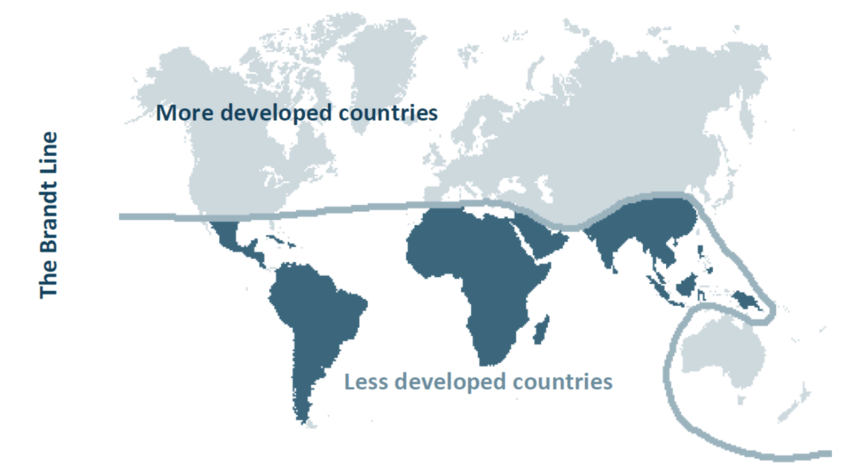
- Need for a More Precise Classification: In the 1980s, the recognition of this inaccuracy led to the development of the "Brandt Line" - a curve that more accurately divided the world into the economic North and South based on factors like economic development and wealth distribution, rather than simply by geographical location.
What are the Demands of the Global South?
- Proportionate Voice at Global Level: The Global South, comprising countries with significant populations, recognises that they have the most at stake in shaping the future of the world.
- With three-fourths of the global population residing in these countries, they argue that they should have a proportionate and meaningful voice in global decision-making processes.
- Equitable Representation: Global South demands an equitable representation in global governance. The current model of global governance may not adequately reflect the demographic and economic realities of the world, and there is a call for change to ensure that the voices of the Global South are heard and considered.
What Signifies the Influence of the Global South in Global Politics?
- Prioritising Global South: India's Presidency of the G20 was driven by the priorities of the Global South. This suggests a growing awareness of the need to address issues and concerns that are particularly relevant to developing countries in the Global South.
- Global South Leadership: The fact that developing countries like Indonesia, India, Brazil, and South Africa are consecutively hosting the G20 summit indicates a desire for greater leadership and influence from the Global South in global decision-making processes.
- These countries represent a significant portion of the world's population and economies.
- Inclusivity: The "Voice of the Global South" summit demonstrates a commitment to inclusivity and consultation with a wide range of nations from the Global South.
- This indicates a shift away from traditional power structures dominated by Western countries.
- Multilateralism: The emphasis on the Global South's priorities and the involvement of these countries in hosting and shaping the G20 agenda reflects a commitment to multilateralism, where decisions are made collectively by a diverse group of nations.
- Rising Influence of Developing World: This is evident through the participation of various organisations such as G20, BRICS, Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO), Quad, the Indo-Pacific Economic Forum, and other global players who are actively seeking involvement from countries in the Global South in decision-making processes.
What is the Evidence of the Global South's Increasing Influence?
- Establishment of the 'Loss and Damage Fund': At the COP27 Climate Change conference in Egypt, the establishment of the 'Loss and Damage fund' was celebrated as a significant win for the Global South.
- It signifies a recognition of the disproportionate burden borne by countries in the Global South.
- Global South in COP28: In the upcoming UNFCCC COP 28 in the UAE, it is anticipated that countries from the Global South will take a leading role in driving discussions on mitigating climate change.
- G7 Inclusivity: Japan, as the host of the G7 summit, made a notable effort to involve developing countries such as India, Brazil, Vietnam, Indonesia, Comoros, and the Cook Islands in the discussions.
- This was seen as an outreach to the Global South, indicating a desire for a more inclusive dialogue among the world's wealthiest nations.
- BRICS Summit Expansion: The BRICS summit, held in South Africa, expanded its membership from five to 11 members. This expansion was attributed to a concerted effort to engage with and incorporate more countries from the Global South into the BRICS grouping, underscoring its growing importance.
- G-77 Summit in Cuba: The G-77 summit held recently in Havana, Cuba showcased the significance of the Global South on the global stage, as it brought together a substantial number of developing countries to discuss key issues.
- African Union's Inclusion into G20: The inclusion of the 55-nation African Union into the G20 is seen as a significant outcome of the conference indicating a growing recognition of the African nations in global affairs and the need to include their perspectives and contributions in shaping the emerging global order.
Conclusion
As the world navigates through complex challenges and opportunities, the Global South's influence continues to evolve, and its demands for equitable representation and a meaningful voice in global governance remain at the forefront. The global community is witnessing a rebalancing of power dynamics, with the Global South playing an increasingly vital role in shaping the future of international politics and cooperation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. ‘The long-sustained image of India as a leader of the oppressed and marginalised nations has disappeared on account of its new found role in the emerging global order.’ Elaborate. (2019)


Indian Heritage & Culture
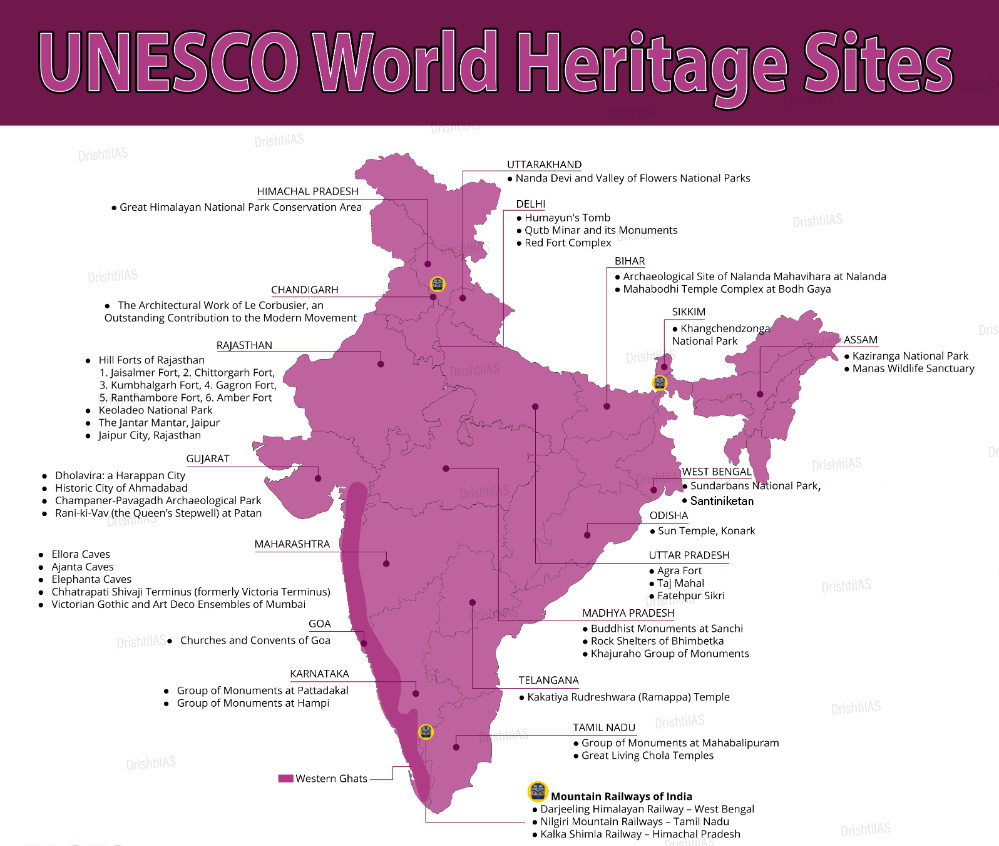
Santiniketan Becomes India's 41st World Heritage Site
For Prelims: Santiniketan, UNESCO’s World Heritage List,Rabindranath Tagore, Debendranath Tagore, Visva Bharati University, Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
For Mains: Importance of declaration of Santiniketan as UNESCO world heritage sites.
Why In News?
Recently, Santiniketan, which is a town located in Birbhum district of West Bengal, was included in the UNESCO’s World Heritage List.
- The efforts to have Santiniketan recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site have been ongoing since 2010. Santiniketan has been recognized by UNESCO as India's 41st World Heritage Site.
Why is Santiniketan Well Known?
- Historical Significance: In 1862, Rabindranath Tagore's father, Debendranath Tagore, spotted this scenic landscape and decided to establish an ashram, building a house called Santiniketan, meaning "abode of peace".
- Name Change: The area, originally called Bhubadanga, was renamed Santiniketan by Debendranath Tagore due to its conducive environment for meditation.
- Educational Legacy: In 1901, Rabindranath Tagore chose a significant portion of land and established a school based on the Brahmachary Ashram model. This school later evolved into Visva Bharati University.
- UNESCO World Heritage Site: The Ministry of Culture proposed Santiniketan for inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List, emphasising its importance in human values, architecture, arts, town planning, and landscape design.
- Archaeological Preservation: The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has been involved in the restoration of several structures in Santiniketan, preserving its historical and cultural heritage.
Who was Rabindranath Tagore?
- Early Life:
- Rabindranath Tagore was born on May 7, 1861, in Calcutta, India, into a prominent Bengali family. He was the youngest of thirteen children.
- Tagore was a polymath and excelled in various fields. He was not only a poet but also a philosopher, musician, playwright, painter, educator, and social reformer.
- Nobel Laureate:
- In 1913, Rabindranath Tagore became the first Asian to be awarded the Nobel Prize in Literature for his collection of poems titled "Gitanjali" (Song Offerings).
- Knighthood:
- Rabindranath Tagore was awarded with Knighthood for Services to Literature by King George V in 1915.
- Tagore renounced his title of Knighthood after the 1919 Jallianwala Bagh Massacre.
- Composer of National Anthems:
- He wrote the national anthems of two countries, "Jana Gana Mana" (the Indian national anthem) and "Amar Shonar Bangla" (the Bangladesh national anthem).
- Literary Works:
- His literary works include poems, short stories, novels, essays, and plays. Some of his notable works include "The Home and the World," "Gora," Gitanjali, Ghare-Baire, Gora, Manasi, Balaka, Sonar Tori, and "Kabuliwala."
- He is also remembered for his song ‘Ekla Chalo Re’.
- Social Reformer:
- He was an advocate for social reform, promoting ideas of unity, harmony, and tolerance. He criticised British colonial rule and worked for Indian independence.
- Tagore's Philosophy:
- His philosophy emphasised the importance of humanism, spirituality, and the connection between nature and humanity.
- Literary Style:
- Tagore's writing style was marked by its lyrical and philosophical qualities, often exploring themes of love, nature, and spirituality.
- Death:
- He passed away on August 7, 1941, leaving behind a rich legacy of literature and a lasting impact on Indian and world culture.
What are UNESCO’s World Heritage Sites?
- A World Heritage Site is a place that is listed by UNESCO for its special cultural or physical significance.
- The list of World Heritage Sites is maintained by the international 'World Heritage Programme', administered by the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
- This is embodied in an international treaty called the Convention concerning the Protection of the World Cultural and Natural Heritage, adopted by UNESCO in 1972.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Which one of the following National Parks has a climate that varies from tropical to subtropical, temperate and arctic? (2015)
(a) Khangchendzonga National Park
(b) Nandadevi National Park
(c) Neora Valley National Park
(d) Namdapha National Park
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. What was the difference between Mahatma Gandhi and Rabindranath Tagore in their approach towards education and nationalism?(2023)


Social Issues
Suicidal Patterns in India
For Prelims: World Suicide Prevention Day, International Association for Suicide Prevention, National Crime Records Bureau, Mental Healthcare Act (MHA), 2017, KIRAN Helpline, Manodarpan Initiative, National Suicide Prevention Strategy 2022
For Mains: Factors Contributing to the Problem of Suicide in India
Why in News?
Recently, World Suicide Prevention Day was observed serving a sobering reminder of the persistent problem of female suicide in India, especially among housewives.
- Despite being an often-overlooked issue, housewives consistently rank among the top categories for suicide, with alarming numbers reported in recent years.
World Suicide Prevention Day
- World Suicide Prevention Day (WSPD) is observed on 10th September every year. It was established in 2003 by the International Association for Suicide Prevention (IASP) in conjunction with the WHO.
- It focuses attention on the issue, reduces stigma and raises awareness among organizations, government, and the public, giving a singular message that suicide can be prevented.
- “Creating hope through action” is the triennial theme for the WSPD from 2021 - 2023. This theme is a reminder that there is an alternative to suicide and aims to inspire confidence and light in all of us.
What are the Challenges Faced by Housewives in India?
- Recent Statistics: The National Crime Records Bureau reported that housewives accounted for 51.5% of female suicides in 2021.
- Among the major states, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, and Karnataka featured at the top of this list.
- Housewives also account for around 15% of all suicides, highlighting the magnitude of this issue.
- Challenging Circumstances:
- Limited Mobility: Many women in India face restrictions on their mobility, particularly in rural areas.
- Societal norms and safety concerns often discourage them from traveling alone or venturing far from their homes.
- This limited mobility can lead to feelings of isolation and helplessness.
- Restricted Financial Autonomy: Economic dependence on their spouses or families can make women vulnerable to various forms of abuse. Lack of financial independence limits their ability to make choices and escape abusive situations.
- Marital Control: Traditional gender roles and patriarchal norms in Indian society often result in women having little control over their lives, especially in the context of marriage.
- Expectation that women should conform to the wishes of their husbands and in-laws can lead to feelings of powerlessness.
- Physical, Sexual, and Emotional Abuse: Domestic violence, including physical, sexual, and emotional abuse, is a significant problem in India. Many women endure these forms of abuse in silence due to stigma, fear of reprisal, or lack of support systems.
- Reluctance to Seek Help: Societal stigma around discussing mental health issues and seeking help for them is widespread in India. Many women hesitate to seek external assistance or confide in others about their struggles, leading to a lack of access to mental health support.
- Limited Mobility: Many women in India face restrictions on their mobility, particularly in rural areas.
What are the Other Factors Contributing to the Problem of Suicide in India?
- Agricultural Distress and Farmer Suicides: India's agrarian economy faces numerous challenges, including erratic weather patterns, land degradation, and high input costs.
- This has led to a significant number of farmer suicides due to debt burdens and crop failures.
- In rural areas of India, access to lethal means like pesticides is relatively easy, and this contributes to a higher rate of impulsive suicides.
- Educational Pressure: India's competitive education system places immense pressure on students to perform well academically.
- The fear of failure and the high expectations of parents lead to mental health issues and suicides, with students feeling they have no way out.
- Lack of Mental Health Services: Despite recent efforts to improve mental health services, there is still a shortage of mental health professionals and limited access to affordable mental healthcare, especially in rural areas.
- It amplifies the mental health crisis in India and emerges as a paramount concern linked to the rise in suicides.
- Family Pressure on LGBTQ+ Individuals: Many LGBTQIA+ individuals in India face severe discrimination and rejection from their families, leading to feelings of isolation and depression.
- The lack of acceptance and support within families is a significant factor contributing to suicides in this community.
- Cyberbullying: With the rise of technology and social media, cyberbullying has become a significant issue, particularly among young people. Online harassment and bullying can have severe consequences on mental health and lead to suicides.
What are the Recent Government Initiatives Related to Suicide Prevention?
Way Forward
- Levering AI and Innovation to Empower Housewives: There is a need to introduce AI-powered skill development and job placement programs specifically designed for housewives who wish to enter or reenter the workforce.
- AI can help identify skills and job opportunities that align with their interests and abilities.
- These programs can provide training in various fields, such as remote work, freelancing, or part-time employment, allowing housewives to gain financial independence and a sense of purpose.
- Improve Access to Mental Health Care: There is a need to increase the availability of mental health services, especially in rural and underserved areas, by building more mental health clinics and training more mental health professionals.
- There is a need to integrate mental health services into primary healthcare to ensure early detection and intervention for mental health disorders.
- Legislation and Regulation: There is a need to implement stricter regulations on the sale of pesticides, which are a common method of suicide in rural areas.
- Also, enforcing laws against cyberbullying and online harassment can contribute to reduction in mental distress among young people.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:
Mains
Q. Why suicide among young women is increasing in Indian society? (2023)

Indian Economy
India’s Outward and Inward Investment Trends
For Prelims: Outward Direct Investment (ODI), Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), Tax Havens.
For Mains: India’s Outward and Inward Investment Trends, and Implications on Indian Economy.
Why in News?
In the fiscal year 2023, India saw a significant increase in Outward Direct Investment (ODI) by Indian firms, as well as a surge in inward Foreign Direct Investment (FDI), according to a census conducted by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI).
What is Foreign Direct Investment (FDI)?
- FDI is a type of cross-border investment in which an investor from one country establishes a lasting interest in an enterprise in another country.
- FDI can take various forms, such as acquiring shares, establishing a subsidiary or a joint venture, or providing loans or technology transfers.
- FDI is considered to be a key driver of economic growth, as it can bring in capital, technology, skills, market access and employment opportunities to the host country.
What is Outward Direct Investment (ODI)?
- An ODI is a business strategy in which a domestic firm expands its operations to a foreign country.
- Employing ODI is a natural progression for firms if their domestic markets become saturated and better business opportunities are available abroad.
- American, European, and Japanese firms have long made extensive investments outside their domestic markets.
- China has emerged as a large ODI player in recent years.
What are the Key Highlights of the Outward Direct Investment Trends?
- Singapore Leads in ODI:
- Singapore emerged as the largest beneficiary of Indian ODI in FY2023, receiving Rs 2.03 lakh crore, representing 22.3% of the total ODI, indicating the growing interest of Indian firms in the Singaporean market.
- Singapore serves as a crucial hub for Indian businesses expanding internationally.
- Singapore, the US, the UK, and the Netherlands were among the top destinations, receiving 60% of the total Rs 9.1 lakh crore invested during FY23.
- Singapore emerged as the largest beneficiary of Indian ODI in FY2023, receiving Rs 2.03 lakh crore, representing 22.3% of the total ODI, indicating the growing interest of Indian firms in the Singaporean market.
- Overall ODI Growth:
- Indian firms' total ODI rose by an impressive 19.46%, reaching Rs 9.11 lakh crore in FY2023, compared to Rs 7.62 lakh crore in 2022.
- Tax Havens in the Mix:
- Bermuda, Jersey and Cyprus are three jurisdictions known for tax benefits and are in the top ten countries that received Indian ODI.
- Bermuda, in particular, is renowned for its favourable tax policies, including no taxes on profits, income, dividends, or capital gains.
- Bermuda, Jersey and Cyprus are three jurisdictions known for tax benefits and are in the top ten countries that received Indian ODI.
What are the Key Highlights of Inward Foreign Direct Investment Trends?
- Total FDI Growth:
- India witnessed a notable increase in FDI flows, with the total FDI inflow in FY2023 reaching Rs 49.93 lakh crore, compared to Rs 46.72 lakh crore in 2022.
- US Tops Inward FDI:
- The United States was the largest source of inward FDI in India in FY2023, bringing in Rs 8.58 lakh crore, accounting for 17.2% of the total share.
- Other Major FDI Contributors:
- Mauritius, the UK, and Singapore followed the US in contributing to India's FDI. The top ten countries were responsible for over 90% of the total FDI inflows.
What are the Implications of the Growing ODI and FDI on Indian Economy?
- The growth in ODI and FDI indicates the increasing global footprint of Indian firms and a willingness to invest in and expand operations overseas, contributing to economic growth and diversification.
- Investing in a variety of countries and sectors allows Indian firms to diversify risks, gain access to new markets, technology, and resources, and improve competitiveness.
- If India continues to attract significant FDI from various countries, its appeal as an investment destination and potential for economic development and job creation will increase.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Justify the need for FDI for the development of the Indian economy. Why there is gap between MoUs signed and actual FDIs? Suggest remedial steps to be taken for increasing actual FDIs in India. (2016)


Economy
India Authorised to Issue OIML Certificates
For Prelims: International Organization of Legal Metrology, Legal Metrology, Metric Convention, International System of Units (SI), Foreign Exchange.
For Mains: Significance of OIML Certification Authority for India.
Why in News?
Recently, India has become the 13th country that can issue OIML (International Organization of Legal Metrology) Certificates.
- The Legal Metrology Division, Department of Consumer Affairs, is now authorised to issue OIML certificates.
What is Legal Metrology?
- Legal Metrology refers to a branch of metrology that focuses on the regulation and legislation concerning measurements and measuring instruments to ensure accuracy, consistency, and fairness in commercial transactions and other areas where measurements play a critical role.
- Metrology is the science of measurement and its application.
- The primary objective of legal metrology is to protect the interests of both consumers and producers by establishing clear and uniform standards for measurements.
Note:
- The CSIR-National Physical Laboratory (NPL-India) is India’s National Metrology Institute' (NMI) that maintains standards of SI units in India and calibrates the national standards of weights and measures.
What is the International Organization of Legal Metrology (OIML)?
- About:
- The OIML was established in 1955 and headquartered in Paris.
- It is an international standard-setting body that develops model regulations, standards and related documents for use by legal metrology authorities and industry.
- It plays a crucial role in harmonising national laws and regulations on the performance of measuring instruments like clinical thermometers, alcohol breath analysers, radar speed measuring instruments, ship tanks found at ports, and petrol dispensing units.
- India’s Membership:
- India became a member of the OIML in 1956. In the same year, India signed the Metric Convention.
- The Metric Convention of 1875, more formally known as the Metre Convention or Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed on 20th May, 1875, in Paris, France.
- World Metrology Day is celebrated on this day.
- It established the International System of Units (SI), which is the modern form of the metric system.
- The Metric Convention of 1875, more formally known as the Metre Convention or Treaty of the Metre, is an international treaty that was signed on 20th May, 1875, in Paris, France.
- India became a member of the OIML in 1956. In the same year, India signed the Metric Convention.
- OIML Certificate:
- The OIML-CS is a system for issuing, registering and using OIML certificates, and their associated OIML type evaluation/test reports, for instruments like digital balance, clinical thermometers, etc.
- To sell a weight or measure in the international market an OIML Pattern Approval certificate is mandatory. It is a single certificate accepted worldwide.
- With the addition of India, the number of countries authorised to issue OIML certificates has increased to 13.
- Countries that can Issue OIML Certificates:
- Australia, Switzerland, China, Czech Republic, Germany, Denmark, France, the UK, Japan, Netherlands, Sweden, and Slovakia (and now India too).
What is the Significance of India’s Becoming OIML Certificate Authority?
- Ease in Exports: For instance, suppose there is an equipment-manufacturer making digital balances in Noida who wants to export to the US or to any other country. Earlier, he would be required to go to one of the other 12 (eligible) countries for certification.
- Now, the certificates can be issued in India and the equipment will be exportable (without incurring additional testing fees), and acceptable to the entire world.
- Better Forex: The move is expected to help the Indian economy in several ways, including an increase in exports, earning of Foreign Exchange, and generation of employment.
- Since only 13 countries are authorised, neighbouring countries and manufacturers can come to India to get their certification done. So it will be a revenue earner for India in terms of foreign exchange.


Indian Economy
Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting Framework
For Prelims: Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs, Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting, United Nations Children's Fund, National Stock Exchange, Planning Commission, SEBI .
For Mains: Measures to Improve Corporate Governance in India.
Why in News?
Recently, Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs (IICA), organised a workshop on Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting in collaboration with United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) and National Stock Exchange(NSE) at the NSE premises in MumbaI.
What is Business Responsibility and Sustainability Reporting Framework?
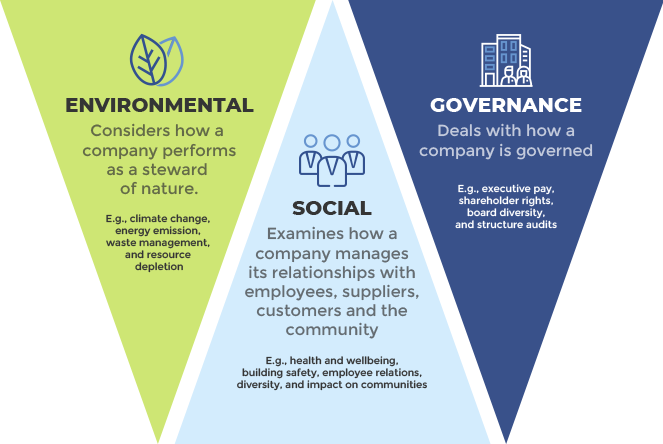
- BRSR is a mandatory disclosure mechanism for top 1000 listed companies or businesses to report their performance on Environmental, social, and corporate governance (ESG) parameters and demonstrate their commitment to responsible business practices.
- SEBI in 2021 replaced Business Responsibility Reports (BRR) with BRSR.
- BRSR is rooted in the nine principles outlined in the National Guidelines for Responsible Business Conduct (NGRBC). The nine principles are:
- Businesses should conduct and govern themselves with integrity, and in a manner that is ethical, transparent and accountable.
- Businesses should provide goods and services in a manner that is sustainable and safe.
- Businesses should respect and promote the well-being of all employees, including those in their value chains.
- Businesses should respect the interests of and be responsive to all their stakeholders.
- Businesses should respect and promote human rights.
- Businesses should respect and make efforts to protect and restore the environment.
- Businesses, when engaging in influencing public and regulatory policy, should do so in a manner that is responsible and transparent.
- Businesses should promote inclusive growth and equitable development.
- Businesses should engage with and provide value to their consumers in a responsible manner.
What is Environmental, Social, and Corporate Governance?
- ESG represents a set of guidelines that compel companies to adhere to improved standards in their operations, encompassing better governance, ethical conduct, environmentally sustainable practices, and social responsibility.
- Since the introduction of the United Nations Principles for Responsible Investing (UNPRI) in 2006, the ESG framework has become an integral aspect of contemporary businesses, recognized as an inseparable component of modern corporate practices.
What is the Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs?
- The Indian Institute of Corporate Affairs (IICA) was registered as a society on September 12, 2008 under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- The proposal to establish the IICA was approved by the Planning Commission in February 2007.
- It is an autonomous institute and works under the aegis of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs to deliver opportunities for research, education, and advocacy.
- It is also a think tank that curates a repository of data and knowledge for policy makers, regulators as well as other stakeholders working in the domain of corporate affairs.
What is the United Nations Children's Fund?
- The United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF), originally known as the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund, was created by the United Nations General Assembly on 11 December 1946, to provide emergency food and healthcare to children and mothers in countries that had been devastated by World War II.
- In 1950, UNICEF's mandate was extended to address the long-term needs of children and women in developing countries everywhere.
- In 1953, it became a permanent part of the United Nations System.
What is the National Stock Exchange?
- National Stock Exchange (NSE) is a leading stock exchange market in India which provides fully automated screen based trading in India.
- NSE was incorporated in 1992. It was recognised as a stock exchange by SEBI in April 1993 and commenced operations in 1994 with the launch of the wholesale debt market.
- One of its more popular offerings is the NIFTY 50 Index, which tracks the largest assets in the Indian equity market.


Important Facts For Prelims
Skill India Digital
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister for Skill Development and Entrepreneurship, launched Skill India Digital (SID).
- This comprehensive digital platform aspires to provide every Indian with access to quality skill development, relevant opportunities, and entrepreneurial support.
What is Skill India Digital?
- About:
- Skill India Digital (SID) is envisioned as the Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for skilling, education, employment, and entrepreneurship in India.
- It aims to bring together various skilling initiatives and create a seamless ecosystem for skill development, aligning with the principles of the G20 framework for building DPIs.
Note: Digital public infrastructure refers to blocks or platforms such as digital identification, payment infrastructure and data exchange solutions that help countries deliver essential services to their people, empowering citizens and improving lives by enabling digital inclusion.
- Core Features of SID:
- Comprehensive Skill Development: SID extends industry-relevant skill courses, job opportunities, and entrepreneurship support, ensuring comprehensive skill development.
- Digital Transformation: With a focus on digital technology and Industry 4.0 skills, SID seeks to make skill development more innovative, accessible, and personalised.
- Information Gateway: SID serves as a central information hub for all government skilling and entrepreneurship initiatives, facilitating easy access for citizens seeking career advancement and lifelong learning.
- Intersection of Skill India and Digital India: SID intersects with the government's vision of Skill India and Digital India, creating opportunities for the youth.
- Key Elements Enhancing SID:
- Aadhaar/AI-based Facial Authentication: Ensuring secure access and verification.
- Digital Verifiable Credentials (DVC): Providing a tamper-proof, verifiable record of qualifications.
- AI and ML Recommendations: Offering personalised learning paths and career guidance.
- Citizen-Centric Approach: Ensuring inclusivity by supporting multiple Indian languages.
- Interoperability: Promoting the integration of government training programs.
Note:
- SID has introduced Digitally Verified Credentials, revolutionising how qualifications are exhibited and recognized.
- These tamper-proof credentials empower users to present their qualifications confidently in a digital format.
- Moreover, the platform integrates Digital CVs with personalised QR Codes, simplifying the sharing of skills and qualifications with potential employers and partners.
What are the Other Government Initiatives Related to Skill Development?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, and financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Yashobhoomi
The Indian Prime Minister recently inaugurated the first phase of the India International Convention and Expo Centre (IICC) called ‘Yashobhoomi’, at Dwarka, New Delhi.
- With a total project area of over 8.9 lakh square metres and total built up area of more than 1.8 lakh square metres, ‘Yashobhoomi’ will find its place among the world’s largest MICE (Meetings, Incentives, Conferences, and Exhibitions) facilities.
- It also demonstrates a strong commitment to sustainability as it is equipped with a state-of-the-art wastewater treatment system with 100% wastewater reuse, provisions of rainwater harvesting, and its campus has received Platinum certification from Confederation of Indian Industry’s Indian Green Building Council (IGBC).
Read more: Indian Green Building Council (IGBC)
CJI Unveils Transparent Approach for SC Judge Appointments
Recently, the Chief Justice of India (CJI) disclosed an initiative to enhance transparency in the appointment of judges to the Supreme Court.
- In addressing the imperative for objective assessments of potential judicial appointees, the CJI, has introduced a team comprising scholars, interns, and law researchers.
- Their core responsibility revolves around conducting a comprehensive evaluation of the top 50 judges in India who are being considered for appointments to the SC.
- This initiative, under the auspices of the Centre for Research and Planning, has been devised to establish transparent selection criteria while safeguarding the confidentiality of the process.
- Although the specific criteria for identifying the top 50 judges have not been explicitly elucidated yet.
- As of now, the appointments are made on the basis of several criteria, which include seniority, regional representation and merit while following a Memorandum of Procedure moulded through the Three Judges Cases.
Read more: Appointment of Judges in Supreme Court
Hyderabad Liberation Day
In 2022, 17th September was declared to be celebrated annually as the Hyderabad Liberation Day. The day signifies the merger of the erstwhile Hyderabad State under Nizam rule with the Indian Union.
- Hyderabad, a significant princely state ruled by the Nizams, acknowledged British sovereignty.
- Like Junagadh and Kashmir, Hyderabad did not join India before or even after gaining independence on August 15, 1947; its Nizam aimed to remain independent and bolster his military.
- However, internal turmoil led to the Indian Army's entry into Hyderabad on September 13, 1948, under Operation Polo to prevent regional instability and integrate Hyderabad into India.
- After integration, the Nizam retained his position as head of state, similar to other princely rulers who joined India.
- He withdrew complaints to the UN, despite protests from Pakistan and international criticism, resulting in Hyderabad becoming part of India without further UN involvement.
Read More: Hyderabad Liberation Day
International Coastal Clean-up (ICC) Day, 2023
On 16 September 2023, the Indian Coast Guard (ICG) conducted International Coastal Clean-up (ICC) Day, 2023 across all Coastal States and UTs.
- Since 2006, the day has been held worldwide on the 3rd Saturday of September, annually, under the aegis of the UNEP and South Asia Co-operative Environment Programme (SACEP) (in South Asian Region).
- This year, Maharashtra witnessed the highest participation of volunteers followed by Tamil Nadu.
- The ICG was established in August 1978 by the Coast Guard Act, 1978 as an independent Armed force of India.
- The concept of forming ICG came into being after the 1971 war and the blueprint for a multidimensional Coast Guard was conceived by the visionary Rustamji Committee (1974).
- It is the 4th largest Coast Guard in the world and is headquartered in New Delhi. It functions under the Ministry of Defence.
Read More: Indian Coast Guard