Infographics
Indian Economy
India’s Fisheries Sector
For Prelims: Sagar Parikrama, Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana, Kisan Credit Card, Indian Blue Revolution, GPS Navigation systems, Palk Bay Scheme, Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund (FIDF), Aquaponics
For Mains: Status of the Fisheries Sector in India.
Why in News?
Government’s Sagar Parikrama is an evolutionary journey envisaged in the sea across the coastal belt aiming to resolve the issues of the fishermen and other stakeholders and facilitate their economic upliftment through various government schemes and programs, including PMMSY (Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana) and KCC (Kisan Credit Card).
What is the Sagar Parikrama Initiative?
- About:
- Sagar Parikrama’ program envisages to cover the maritime States/UTs in a phased manner. The journey began on March 5th, 2022, from Mandvi, Gujarat.
- The journey focuses on bridging the gaps in the expectations of fisher communities, developing fishing villages, and upgrading infrastructure such as fishing harbors and fish landing centers.
- Phases of Sagar Parikrama:
- Phase I: The journey covered three locations in Gujarat - Mandavi, Okha-Dwarka, and Porbandar.
- Phase II: Seven locations were covered in Mangrol, Veraval, Diu, Jafrabad, Surat, Daman, and Valsad.
- Phase III: Coastal areas of northern Maharashtra, including Satpati, Vasai, Versova, New Ferry Wharf (Bhaucha Dhakka), and Sasson Dock in Mumbai, were part of this phase.
- Phase IV: Udupi and Dakshina Kannada districts in Karnataka were covered during this phase.
- Upcoming Phase V: Phase V of Sagar Parikrama will cover six locations: Raigad, Ratnagiri, and Sindhudurg Districts in Maharashtra, and Vasco, Maorugoa, and Canacona in Goa.
- Maharashtra, with its extensive coastline of 720 km, has immense untapped potential in the fisheries sector.
- The state ranks 7th in fish production in the country, with marine fisheries contributing 82% and inland fisheries 18%.
- Goa, with a coastline of 104 km, also plays a vital role in the marine fishery sector, providing livelihoods to many.
What is the Status of the Fisheries Sector in India?
- About:
- As the third-largest fish producer and the second-largest aquaculture producer globally, India recognizes the significance of the fisheries and aquaculture industry.
- The Indian Blue Revolution has led to a major improvement in the fishing and aquaculture industries. The industries are regarded as sunrise sectors and are anticipated to have a big impact on the Indian economy.
- In the recent past, Indian fisheries has witnessed a paradigm shift from marine dominated fisheries to inland fisheries, with the latter emerging as a major contributor of fish production from 36% in the mid-1980 to 70% in the recent past.
- The fish production reached an all-time high of 16.25 MMT during FY 2021-22 with marine exports touching Rs. 57,586 Crores.
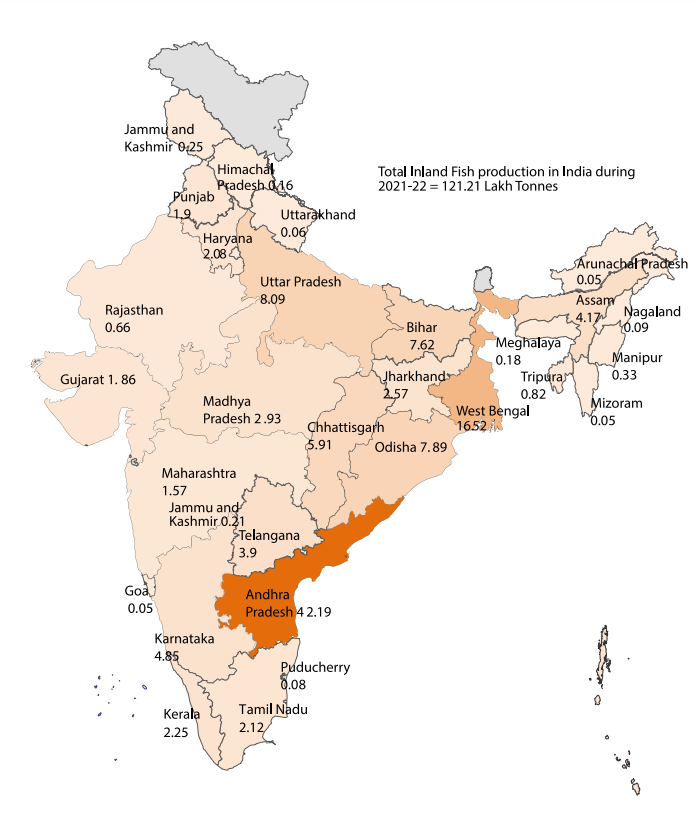
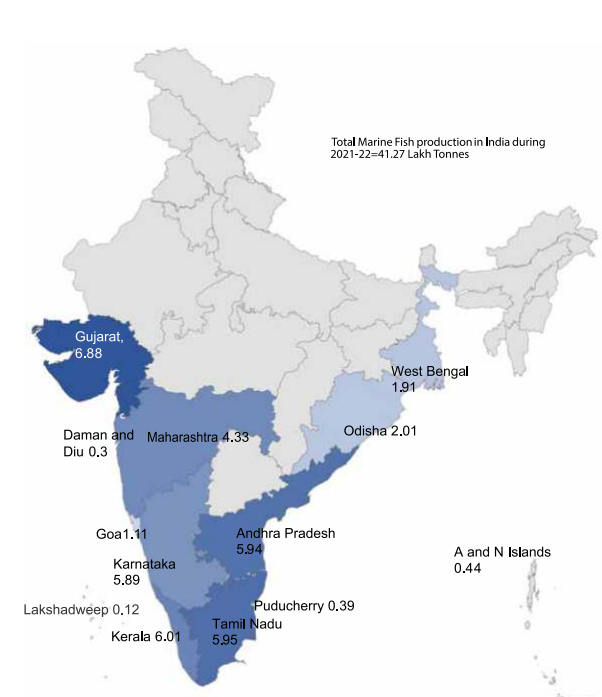
- Top Producing States:
- Andhra Pradesh is the largest producer of fish in India followed by West Bengal.
 |
 |
- Current Challenges:
- Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) fishing: IUU fishing exacerbates overfishing and undermines the sustainability of the sector.
- IUU fishing involves activities such as fishing without proper licenses, using banned gear, and disregarding catch limits. Weak monitoring and surveillance systems make it difficult to combat this problem effectively.
- Inadequate Infrastructure and Technology: Outdated fishing vessels, gear, and processing facilities hinder the efficiency and productivity of the sector. Insufficient cold storage and transportation infrastructure result in post-harvest losses.
- Limited access to modern fishing technology, such as fish finders and GPS navigation systems, restricts the ability to locate fish stocks accurately.
- Climate Change and Environmental Degradation: Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and changing currents have a profound impact on marine ecosystems and fish populations.
- Climate change leads to shifts in fish distribution, reduced productivity, and increased vulnerability to diseases. Pollution, habitat destruction, and coastal development further degrade marine ecosystems.
- Socio-Economic Issues: The fisheries sector in India is characterized by a large number of small-scale and artisanal fishers who face multiple socio-economic challenges.
- Low incomes, lack of access to credit and insurance, and inadequate social security measures contribute to the vulnerability of fishing communities.
- Gender disparities and the marginalization of women in fisheries also pose challenges.
- Market Access and Value Chain Inefficiencies: Despite India's significant fish production, there are challenges in accessing domestic and international markets.
- Poor post-harvest handling, limited value addition, and inadequate market linkages result in reduced profitability for fishers.
- Illegal, Unreported, and Unregulated (IUU) fishing: IUU fishing exacerbates overfishing and undermines the sustainability of the sector.
- Initiatives related to Fisheries Sector:
Way Forward
- Embrace Aquaponics: India can promote the adoption of aquaponics, a sustainable farming technique that combines fish farming with hydroponics.
- This system allows for the simultaneous cultivation of fish and plants, utilizing fish waste as a nutrient source for plant growth.
- Aquaponics reduces water usage, maximizes land productivity, and provides an additional source of income for fish farmers.
- Enhance Cold Chain Infrastructure: There is a need to improve the cold chain infrastructure to minimize post-harvest losses and maintain the quality of fish products.
- Also, there is a need to establish well-equipped fish collection centers near coastal areas and integrate them with modern storage facilities, transportation systems, and processing units.
- This will enable the efficient preservation and distribution of fish, reducing spoilage and increasing market value.
- Support Value Addition and Diversification: Encourage fish farmers to engage in value addition activities to increase their income. Provide training and financial assistance for fish processing, packaging, and branding.
- Promote the development of innovative fish-based products such as ready-to-eat snacks, fish oil supplements, fish leather, and collagen products. This will expand market opportunities and enhance the value chain.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Defining blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)


Social Justice
Global Report on Internal Displacement 2023
For Prelims: Global Report on Internal Displacement 2023, Internal Displacement, Conflict and Violence, Russia-Ukraine, Disaster, Flood, Monsoon.
For Mains: Internal Displacement and Issues, Global Report on Internal Displacement 2023.
Why in News?
Recently, the Internal Displacement Monitoring Centre has released a report titled- The Global Report on Internal Displacement 2023 (GRID-2023), which cites that the number of people displaced by disasters rose by 40% in 2022 rather than 2021.
- The IDMC is the world's leading source of data and analysis on internal displacement. It provides high-quality data, analysis and expertise on Internal Displacement with the aim of informing policy and operational decisions that can reduce the risk of future displacement.
What are the Key Findings of the GRID-2023?
- Total Number Of Displacements:
- The number of people living in internal displacement reached a record high of 71.1 million people across 110 countries and territories.
- 62.5 million as a result of conflict and violence, and 8.7 million as a result of disasters.
- Disasters displaced 8.7 million people internally in 88 countries and territories as of December 2022.
- This led to record levels of flood displacement in countries including Pakistan, Nigeria and Brazil.
- By 2021, 30.7 million new displacements were due to disasters. In 2022 some 150 countries/territories reported such displacement.
- Country wise Picture:
- Pakistan had the highest number of disaster displacements in the world in 2022, at 8.16 million.
- In Pakistan, floods displaced millions, accounting for a quarter of the global disaster displacements.
- The Philippines was at second rank and reported 5.44 million displacements and China at third rank with 3.63 million.
- India recorded the fourth largest disaster displacement, with 2.5 million displacements and Nigeria at fifth rank with 2.4 million.
- Pakistan had the highest number of disaster displacements in the world in 2022, at 8.16 million.
- Factors for Displacement:
- Disaster: The increase in disasters, particularly weather-related, is largely the result of the effects of La Niña which continued for a third consecutive year.
- The “triple-dip” La Niña caused widespread disasters across the world.
- Russia-Ukraine Induced Displacement: In 2022, the number of people displaced by the Russia-Ukraine war increased.
- The conflict caused a displacement of 16.9 million — “the highest figure ever recorded for any country.”
- The number of displacements associated with conflict and violence nearly doubled to 28.3 million.
- Disaster: The increase in disasters, particularly weather-related, is largely the result of the effects of La Niña which continued for a third consecutive year.
- Implications:
- Entrenched conflict, disasters and displacement aggravated Global Food Security in 2022, which was already a concern as a result of the slow and uneven recovery from the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Low-income countries, many of which are dealing with internal displacement, were most affected, in part given their reliance on food and fertilizer imports and international humanitarian aid.
- 75% of the countries assessed as facing crisis levels of food security have IDPs.
What is the Scenario of India?
- India recorded thousand numbers of internal displacement and 631,000 internally displaced people due to conflict and violence and 2.5 million due to disaster in 2022.
- India and Bangladesh started to experience flooding even before the official start of the monsoon season, which normally runs between mid-July and September.
- India’s north-eastern state of Assam was affected by early floods in May 2022 and the same areas were once again flooded in June. Nearly five million people were affected across the state.
- Some parts of India reported their lowest July 2022 rainfall in 122 years.
- By the end of the monsoon, 2.1 million displacements had been recorded across India, a significant decrease from the five million that occurred during the 2021 season.
What is Internal Displacement?
- About: Internal displacement describes the situation of people who have been forced to leave their homes but have not left their country.
- Factors of Displacement: Millions of people are uprooted from their homes or places of habitual residence each year in the context of conflict, violence, development projects, disasters and climate change and remain displaced within their countries’ borders.
- Components: Internal displacement is based on two components:
- The person’s movement is coerced or involuntary (to distinguish them from economic and other voluntary migrants);
- The person stays within internationally recognised state borders (to distinguish them from refugees).
- Difference from Refugee: According to the 1951 Refugee Convention, a “refugee” is a person who has been persecuted and forced to leave his native country.
- A precondition of being considered a refugee is that a person crosses an international border.
- Unlike refugees, internally displaced people are not the subject of any international convention.
- At the international level, no single agency or organisation has been designated as the global lead on protection and assistance of internally displaced persons.
- However, there are United Nations Guiding Principles on Internal Displacement.
What are the Recommendations?
- Conflict resolution, peacebuilding, disaster risk reduction, climate resilience, food security and poverty reduction must all be strengthened.
- There is an increasing need for durable solutions to meet the scale of the challenges facing displaced people. This spans the expansion of cash assistance and livelihood programmes that improve IDPs’ (Internally Displaced People) economic security, through investments in risk reduction measures that strengthen their communities’ resilience.
- Beyond immediate humanitarian assistance, investments are needed in anticipatory action and risk reduction measures that strengthen displaced communites' resilience.
- Developing IDP's livelihoods and skills would help to facilitate durable solutions by increasing their food security and their communities’ and countries’ self-reliance at the same time.


Social Justice
National Workshop on Empowering PwD in Education
For Prelims: Article 41 of the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP), National Education Policy: 2020, Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016, Accessible India Campaign, DeenDayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme, National Fellowship for Students with Disabilities
For Mains: Constitutional and Legislative Framework for Persons with Disability in India, Issues Associated with Persons with Disability in India.
Why in News?
The National Workshop on "Capacity building of training institutes and HRD in the disability field in the context of National Education Policy (NEP): 2020" was recently inaugurated in Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh.
- Organized by the Rehabilitation Council of India (RCI), the workshop aimed to empower individuals with disabilities and implement the goals of the NEP 2020.
- Also, the Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities, the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, is observing Global Accessibility Awareness Day (GAAD) on May 18th, 2023.
What is Global Accessibility Awareness Day?
- GAAD is an annual event celebrated on the third Thursday of May, dedicated to promoting awareness and understanding of digital accessibility for individuals with disabilities.
- It emphasizes the importance of designing and developing digital technologies with accessibility in mind, ensuring that everyone can access information, engage in online activities, and participate in the digital world without barriers.
What is the Constitutional and Legislative Framework for Persons with Disability (PwD) in India?
- The Constitution of India ensures equality, freedom, justice and dignity of all individuals and implicitly mandates an inclusive society for all including the persons with disabilities.
- Article 41 of the Directive Principles of State Policy (DPSP) states that the State shall make effective provision for securing the right to work, to education and to public assistance in cases of unemployment, old age, sickness and disablement, within the limits of its economic capacity and development.
- The main legislation on disability rights is the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
- The Act covers a wide range of specified disabilities and provides additional benefits for persons with benchmark disabilities and those with high support needs.
- The Act also provides for grant of guardianship by District Court or any authority designated by the State Government under which there will be joint decision-making between the guardian and the persons with disabilities.
What are the Issues Associated with Person with Disability in India?
- Accessibility Concern: One of the primary challenges is the lack of accessibility in public spaces, transportation, buildings, and infrastructure. Many places do not have ramps, elevators, or accessible toilets, making it difficult for people with disabilities to move around independently.
- Lack of Access to Education: Access to quality education is limited for people with disabilities.
- Special education facilities and trained teachers are scarce, and inclusive education practices are not widely implemented. This lack of educational opportunities hinders their personal and professional development.
- Lack of Proper Healthcare: A large number of disabilities are preventable, including those arising from medical issues during birth, maternal conditions, malnutrition, as well as accidents and injuries.
- However, there is a lack of awareness, lack of care, and lack of good and accessible medical facilities.
- Social Stigma and Discrimination: Negative attitudes and social stigma surrounding disabilities are prevalent in Indian society.
- People with disabilities often face discrimination, exclusion, and marginalization, which affects their self-esteem and social interactions.
What are the Recent Initiatives to Empowerment of PwD?
- India:
- Global Conventions to Which India is Signatory:
- Declaration on the Full Participation and Equality of People with Disabilities in the Asia-Pacific Region.
- Biwako Millennium Framework
- UN Convention on Protection and Promotion of the Rights and Dignity of Persons with Disabilities.
Note: Rehabilitation Council of India, established as a Statutory Body by an Act of Parliament, has the mandate to standardize, regulate, and monitor training programs, maintain the central rehabilitation register (CRR), and promote research in the field of special education and disability.
Way Forward
- Building Pathways to Inclusion: There is a need to design and construct accessible buildings, public spaces, transportation systems, and communication technologies should be prioritized. This includes features like ramps, elevators, tactile paths, audio announcements, and braille signage.
- Empowering Abilities with Cutting-Edge Solutions: There is a need to promote the development and adoption of affordable and locally sourced assistive technologies such as prosthetics, mobility devices, hearing aids, and communication tools. Embrace emerging technologies like 3D printing and AI to customize solutions for individuals.
- Unlocking Doors to Knowledge and Equality: Implementing inclusive education policies that ensure students with disabilities have equal access to quality education. This involves providing assistive devices, specialized training for teachers, accessible learning materials, and inclusive curriculum development.
- Shattering Stigmas through Awareness and Sensitization: There is a need to Conduct awareness campaigns to promote inclusivity and reduce societal stigmas around disability.
- This includes sensitizing communities, employers, educators, and healthcare providers about the rights, abilities, and potential of individuals with disabilities.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. India is home to lakhs of persons with disabilities. What are the benefits available to them under the law? (2011)
- Free schooling till the age of 18 years in government run schools.
- Preferential allotment of land for setting up business.
- Ramps in public buildings.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)


Biodiversity & Environment
Sea Butterflies
For Prelims: Sea Butterflies, Ocean acidification
For Mains: Impact of climate change on marine ecosystems, Ocean acidification
Why in News?
The population of the sea butterflies in the Southern Ocean is shrinking due to climate change, making them extremely vulnerable.
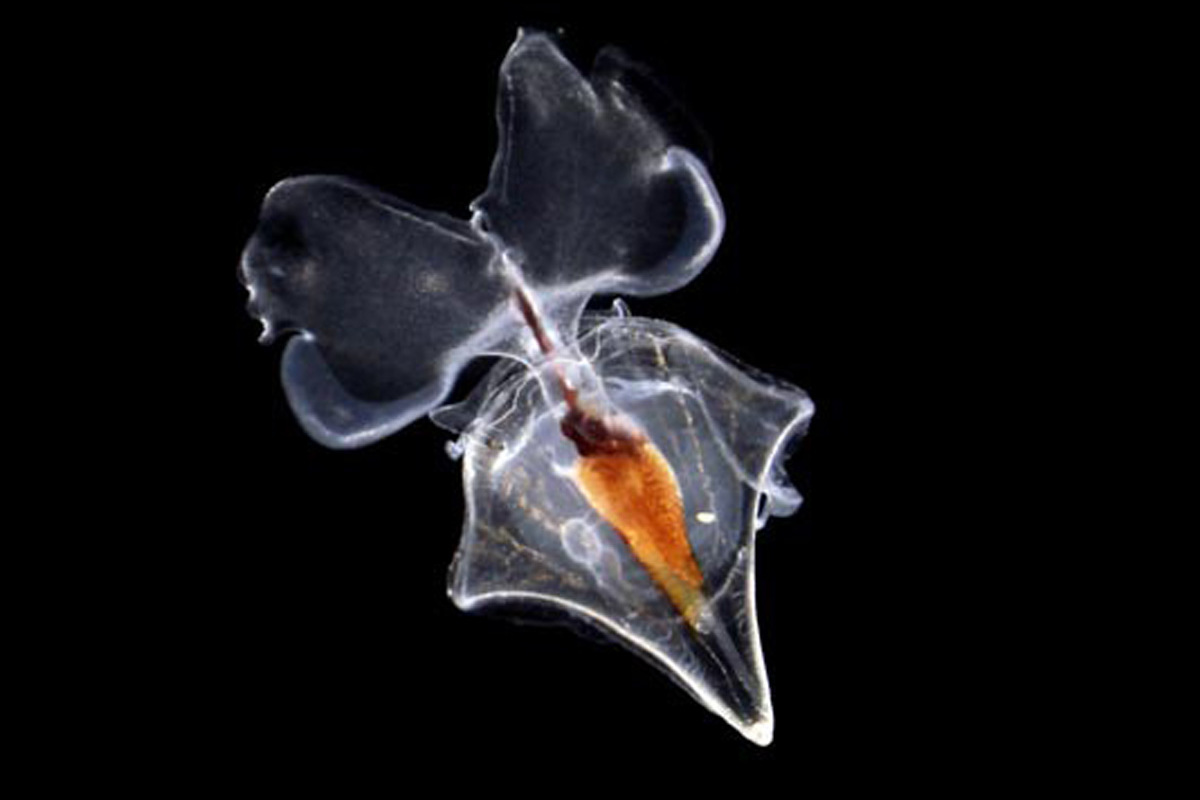
What are Sea Butterflies?
- About:
- Sea butterflies, scientific name Thecosomata, are a suborder of sea snails known as shelled pteropods.
- They have muscular feet that allow them to swim in water instead of gliding on solid surfaces.
- Sea butterflies are holoplanktonic (organisms that pass their whole life floating, drifting, or swimming weakly in the water) and spend their entire life cycle in the water column.
- They are found in all oceans but are more diverse and abundant in colder waters.
- Sea butterflies have bilateral symmetry and a coiled or uncoiled shell of various shapes and sizes.
- Their shell is mostly transparent and very fragile and can be easily dissolved by ocean acidification.
- They have a pair of wing-like lobes or parapodia for propulsion and a head with eyes, tentacles, and a mouth with a long proboscis to capture prey.
- They have a reduced or absent gill and rely on their body surface for gas exchange.
- Importance:
- They are a major food source for many fish, seabirds, whales, and other marine animals.
- They also play a key role in transporting carbon from the surface to the deep ocean through their shells and fecal pellets.
How does Climate Change Impact the Population of Sea Butterflies?
- Ocean Acidification:
- Increased carbon dioxide absorption by the ocean leads to higher acidity.
- Reduced availability of carbonate ions necessary for shell formation and maintenance.
- The ocean is the most acidic in winter because cooler water absorbs more CO2. This means, the winter months are the most dangerous for the shelled sea butterflies.
- Sea butterflies' shells can dissolve, weaken, or deform.
- Increased vulnerability to predators, infections, and stress.
- Affects metabolism, growth, reproduction, and survival.
- Ocean Warming:
- Rising ocean temperatures due to climate change.
- Changes in distribution and abundance of sea butterflies.
- Seek optimal thermal conditions for development and survival.
- Alters food availability and quality.
- Impacts ocean currents and mixing affecting sea butterfly transport.
- Ocean Deoxygenation:
- Warmer and stratified ocean leads to decreased oxygen levels.
- Affects sea butterflies' respiration and energy balance.
- Alters vertical migration patterns.
- Exacerbates effects of ocean acidification by increasing dissolved carbon dioxide concentrations.
How can this Reduced Population Impact Antarctic Marine Ecosystems?
- Reducing the Food Availability for Higher Trophic Levels:
- Sea butterflies serve as a major food source for fish, seabirds, whales, and other marine animals.
- Population decline of sea butterflies can lead to starvation, malnutrition, or reduced reproduction in their predators and prey.
- Sea butterflies serve as a major food source for fish, seabirds, whales, and other marine animals.
- Disrupting the Balance of the Marine Food Web:
- Sea butterflies play a crucial role in linking primary producers (phytoplankton) with secondary consumers (zooplankton) and higher trophic levels.
- Decline in sea butterfly population can alter the structure and function of the marine food web.
- Biodiversity and productivity of the Antarctic marine ecosystem may be affected.
- Decreasing the Carbon Sequestration Capacity of the Ocean:
- Sea butterflies contribute to the "biological pump," transporting carbon from the surface to the deep ocean through their shells and fecal pellets.
- Population decline reduces the amount of carbon sequestered (process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide) in the ocean.
- This results in increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and further ocean acidification.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. The acidification of oceans is increasing. Why is this phenomenon a cause of concern? (2012)
- The growth and survival of calcareous phytoplankton will be adversely affected.
- The growth and survival of coral reefs will be adversely affected.
- The survival of some animals that have phytoplanktonic larvae will be adversely affected.
- The cloud seeding and formation of clouds will be adversely affected.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. Assess the impact of global warming on the coral life system with examples. (2019)


Science & Technology
Artificial Sweeteners
For Prelims: Artificial sweeteners, Hypertension , World Health Organization (WHO), type-2 diabetes
For Mains: Artificial sweeteners and their role as sugar substitutes, potential risks for health in relation artificial sweeteners
Why in News?
Artificial sweeteners have gained popularity among calorie-conscious individuals seeking low-calorie options. However, recent studies have raised concerns about their long-term effectiveness for weight loss and potential health risks.
- The World Health Organization (WHO) has released recommendations against the use of artificial sweeteners for weight control and prevention of lifestyle diseases.
What are Artificial Sweeteners?
- About:
- Artificial sweeteners are sugar substitutes that are used as alternatives to natural sugars.
- These sweeteners are chemically synthesized and provide a sweet taste without the high calorie content of regular sugar.
- They are commonly used in various food and beverage products, including diet sodas, sugar-free desserts, and low-calorie snacks.
- Some examples of artificial sweeteners are saccharin, aspartame, acesulfame potassium (Ace-K), sucralose, neotame, and advantame.
- Benefits:
- Artificial sweeteners offer benefits for weight management, diabetes control, tooth decay prevention, and provide safe options for individuals with phenylketonuria (PKU), a genetic disorder, due to their low or zero-calorie content, minimal impact on blood sugar levels, non-fermentable nature, and absence of phenylalanine.
- Negative Impacts:
- Controversial Health Effects:
- Some studies suggest potential negative health effects of artificial sweeteners, such as an increased risk of metabolic disorders, and disrupted gut microbiota. However, scientific evidence remains inconclusive.
- Digestive Issues:
- Some people may experience digestive discomfort, such as bloating, gas, or diarrhea, after consuming products containing artificial sweeteners.
- Controversial Health Effects:
What are the Key Findings from the WHO Report?
- Findings:
- WHO advises against using artificial sweeteners as a means of achieving weight control or reducing the risk of non-communicable diseases.
- While short-term use may result in weight loss and reduced body mass index (BMI), long-term consumption of artificial sweeteners has been associated with weight gain.
- Some studies suggest a potential connection between artificial sweeteners and bladder cancer and preterm birth in pregnant women.
- Higher intake of artificial sweeteners, particularly in beverages and added to foods, is associated with an increased risk of type-2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease (including stroke and hypertension), and preterm birth.
- WHO Recommendations:
- Instead of relying solely on non-sugar sweeteners, the WHO recommends considering other methods to reduce the intake of free sugars, such as consuming naturally occurring sugars from fruits or opting for unsweetened food and beverages.
Example - Diet Colas:
- Diet colas, marketed as zero-calorie alternatives to regular colas, use artificial sweeteners to achieve the zero-calorie claim.
- The intense sweetness of artificial sweeteners can alter taste perception, making normal sweets seem less sweet and potentially leading to cravings for more sugary foods.
- Special attention is given to erythritol, which should be avoided due to its potential health risks.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Aspartame is an artificial sweetener sold in the market. It consists of amino acids and provides calories like other amino acids. Yet, it is used as a low-calorie sweetening agent in food items. What is the basis of this use? (2011)
(a) Aspartame is as sweet as table sugar, but unlike table sugar, it is not readily oxidized in human body due to lack of requisite enzymes.
(b) When aspartame is used in food processing, the sweet taste remains, but it becomes resistant to oxidation.
(c) Aspartame is as sweet as sugar, but after ingestion into the body, it is converted into metabolites that yield no calories.
(d) Aspartame is several times sweeter than table sugar, hence food items made with small quantities of aspartame yield fewer calories on oxidation.
Ans: (d)


Important Facts For Prelims
Innovations for Defence Excellence
Why in News?
Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX), the flagship initiative of the Ministry of Defence, has signed its 250th contract – first under Mission DefSpace – and 100th SPRINT (Navy) contract.
What are Mission DefSpace and SPRINT Navy Contracts?
- Mission DefSPace Contract:
- Space startup InspeCity has been awarded the first iDEX contract of Mission DefSpace.
- InspeCity had emerged as the winner of a challenge conducted by the Defence Space Agency focused on developing a gas based Micropropulsion system for cubesats.
- Cubesats are a class of small satellites and are easy to manufacture, modular, modular, low cost, integrate and launch. The cubesats are critical for launch-on-demand capabilities and are good for Imagery, Reconnaissance/communication, and also Intelligence Surveillance.
- This technology will enable precise manoeuvring and orbit correction for satellites, including the cubesat swarm being developed under Mission DefSpace.
- SPRINT (Navy) Contract:
- Siliconia Technologies Pvt Ltd, has emerged as the winner of a SPRINT (Supporting Pole-Vaulting in R&D through iDEX, NIIO and TDAC) Challenge focused on developing a lightweight Application-Specific Integrated Circuit (ASIC) based communication system for phased-array radars.
- The system provides multiple independent receiver/transmitter sources crucial for satellite tracking.
- It utilizes software-defined antennas for communication with Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit, and Geostationary Satellites.
What is iDEX?
- About:
- iDEX, launched in 2018, is an ecosystem to foster innovation & technology development in Defence and Aerospace by engaging innovators & entrepreneurs to deliver technologically advanced solutions for modernizing the Indian Military.
- It provides funding/grants to Micro Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), start-ups, individual innovators, R&D (Research and Developments) institutes and academia to carry out research and development.
- The iDEX-Prime aims to support projects requiring support beyond Rs 1.5 crore up to Rs 10 crore, to help ever-growing start-ups in the defence sector.
- iDEX portal was launched to provide wider publicity and better visibility of iDEX activities and enable more efficient running of future challenges through better information management.
- Objectives:
- Indigenization: Rapid development of new, indigenized and innovative technology.
- Innovation: Creates a culture of engagement with innovative startups to encourage co-creation.
- Funding:
- iDEX is funded and managed by “Defence Innovation Organisation (DIO)”.
- iDEX will function as the executive arm of DIO, carrying out all the required activities while DIO will provide high level policy guidance to iDEX.
- Achievement:
- iDEX has been awarded the prestigious Prime Minister Award for Public Policy in Innovation Category for the year 2021.
What is Mision DefSpace?
- It was inaugurated by Prime Minister of India during the October 2022 edition of India’s DefExpo.
- It aims to nurture the Indian Private Space industry through challenges addressing every stage of a space mission – from mission planning to satellite data analytics.
- This mission encompasses 75 Defense Space Challenges that directly suit the needs of end users.
- These challenges have been categorised into the existing DDP initiatives of iDEX, Make-I, and Make-2, allowing participation from private industries, including startups, MSMEs, and individual innovators.
- The challenges are categorized into five different domains:
- Launch System
- Satellite System
- Communication & Payload System
- Ground System, and Software System.
- Together, they offer an in-depth and complete understanding of space from a 360-degree perspective.
What are Government Initiatives Regarding Defense?


Important Facts For Prelims
Greenwashing TechSprint
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) will be among 13 international regulators taking part in the Global Financial Innovation Network's (GFIN) first-ever Greenwashing TechSprint.
- The RBI has invited Indian companies to participate in the Greenwashing TechSprint, an international initiative aimed at tackling greenwashing in the financial services industry.
What is Greenwashing TechSprint?
- The Greenwashing TechSprint is organized by the Global Financial Innovation Network (GFIN), a consortium of over 80 international organizations committed to supporting financial innovation for the benefit of consumers.
- The GFIN is currently chaired by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), a leading regulatory body in the United Kingdom.
- TechSprint aims to develop a tool or solution that can effectively help regulators and the market tackle the risks of greenwashing in financial services.
- The TechSprint will launch on 5th June and will run for 3 months, ending with a showcase day in September 2023.
What is the Global Financial Innovation Network?
- The GFIN was formally launched in January 2019 by an international group of financial regulators and related organizations.
- It is a network of over 70 organizations committed to supporting financial innovation in the interests of consumers.
- It seeks to provide a more efficient way for innovative firms to interact with regulators, helping them navigate between countries as they look to scale new ideas.
- The GFIN is overseen by the Coordination Group. The Coordination Group is made up of GFIN Members and sets the overall direction, strategy and annual work programme of the GFIN.
- The Coordination Group is currently being chaired by the Financial Conduct Authority (UK). Membership in the Coordination Group lasts for two years, and members meet twice a year to provide ongoing input and engagement into the work-streams.
- Members from India:
What is Greenwashing?
- About:
- Greenwashing refers to the practice of making false or exaggerated claims about the environmental benefits of a product, service, or company in order to present a misleading image of sustainability or eco-friendliness.
- It is a form of deceptive marketing that aims to capitalize on the growing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products and practices.
- The RBI recognizes the increasing number of investment products marketed as "green" or making wider sustainability claims.
- Exaggerated, misleading or unsubstantiated claims about Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) credentials damage confidence of the public in the product
- Greenwashing refers to the practice of making false or exaggerated claims about the environmental benefits of a product, service, or company in order to present a misleading image of sustainability or eco-friendliness.
- Major Forms of Greenwashing:
- Vague or Misleading Labels: Companies may use terms like "eco-friendly," "green," or "natural" without providing specific information or clear standards for what those terms mean.
- Irrelevant Claims: Companies may highlight a minor environmental improvement while ignoring more significant environmental issues related to their products or operations.
- For example, a car manufacturer might promote a fuel-efficient model while downplaying the environmental impact of its manufacturing processes.
- Hidden Trade-offs: This occurs when a product is marketed as environmentally friendly in one aspect but neglects to mention other negative environmental impacts.
- For instance, a disposable product might be labeled as biodegradable, but the production process still has a significant carbon footprint.
- Impacts of Greenwashing:
- Dilution of Genuine Efforts: Companies genuinely committed to sustainability and implementing eco-friendly practices can suffer because greenwashing makes it harder for consumers to differentiate between genuinely sustainable products and those that are falsely marketed.
- Legitimate sustainability initiatives may be overshadowed and undermined by companies engaging in greenwashing.
- Stifling Innovation: Greenwashing can discourage genuine innovation in sustainability.
- When companies can deceive consumers with superficial or misleading green claims, there may be less motivation to invest in developing truly sustainable solutions. This hinders the overall progress in creating environmentally friendly products and practices.
- Dilution of Genuine Efforts: Companies genuinely committed to sustainability and implementing eco-friendly practices can suffer because greenwashing makes it harder for consumers to differentiate between genuinely sustainable products and those that are falsely marketed.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following best describes the term “greenwashing:”?(2022)
(a) Conveying a false impression that a company’s products are eco-friendly and environmentally sound
(b) Non-Inclusion of ecological/ environmental costs in the Annual Financial Statements of a country
(c) Ignoring the disastrous ecological consequences while undertaking infrastructure development
(d) Making mandatory provisions for environmental costs in a government project/programme
Ans: (a)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
2023 SAFF Championship
The 2023 SAFF Championship is a biennial international men's football tournament for South Asian countries, organized by the South Asian Football Federation (SAFF). The 14th edition of the tournament will be hosted by India in Bengaluru from June 21 to July 3, 2023. India is the defending champion, having won its eighth title in 2021 by defeating Nepal in the final. The tournament will feature eight teams, including two guest teams from outside the region: Kuwait and Lebanon. Sri Lanka was unable to participate due to its suspension by FIFA (Fédération internationale de Football Association), while Afghanistan withdrew from SAFF and joined the Central Asian Football Federation. The eight teams are divided into two groups of four each, with the top two teams from each group advancing to the semi-finals. India is drawn in Group A with Kuwait, Nepal, and Pakistan, while Lebanon is in Group B with Maldives, Bhutan, and Bangladesh.
SAFF was formed in 1997 by founding Member Associations from Bangladesh, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and SriLanka. The SAFF motto ‘Unity in Strength’ depicts the power and bond of these seven Member Associations which is currently epitomized by the leader and President of SAFF. The SAFF Secretariat currently operates from Dhaka, Bangladesh. The SAFF is a part of the larger Asian Football Confederation (AFC).
Read more: Indian Football’s Vision 2047
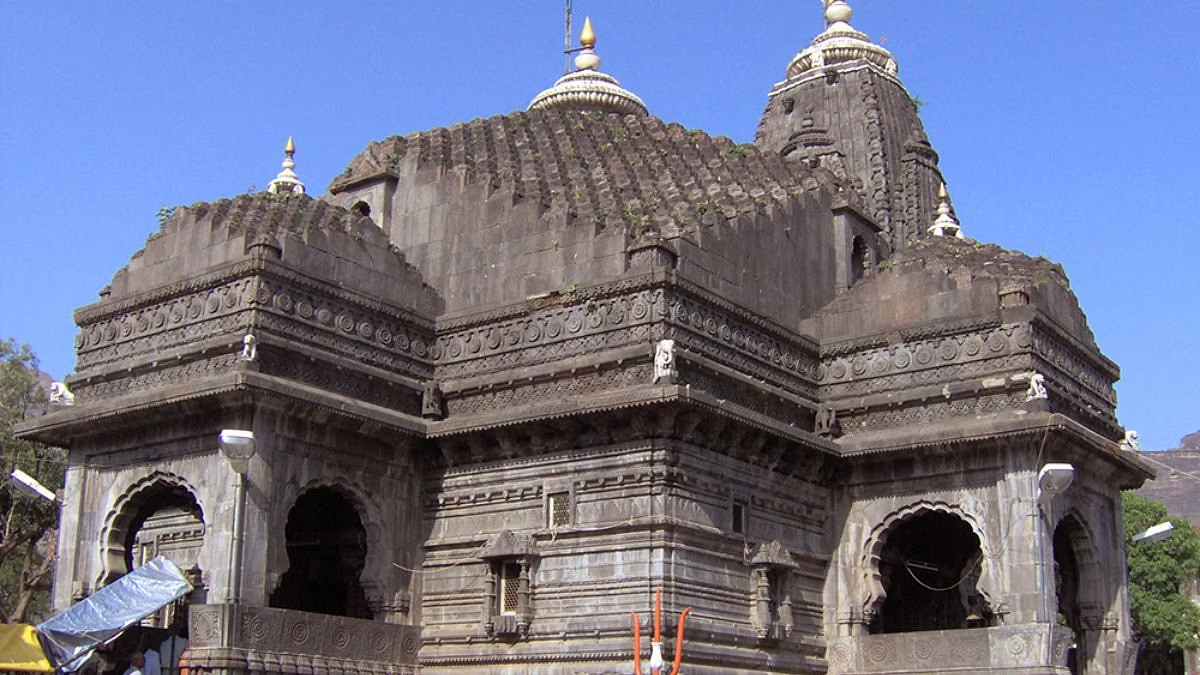
Trimbakeshwar Temple
Maharashtra has set up a special investigation team (SIT) to investigate an incident in which members of the minority community were accused of trying to enter the Trimbakeshwar temple in Nashik. As per the temple management, only Hindus are allowed to enter the temple, non-Hindus are not allowed to enter the temple.
Trimbakeshwar temple is an ancient and sacred Hindu temple dedicated to Lord Shiva, located in the town of Trimbak in the Nashik district of Maharashtra. It is one of the twelve Jyotirlingas, the holiest shrines of Shiva, where he is worshipped as Trimbakeshwar, the lord of three worlds. The temple was built by the third Peshwa Balaji Bajirao in the 18th century on the site of an old temple, near the mountain of Brahmagiri, from where the river Godavari originates. The temple is built of black stone in the Nagara style of architecture and is enclosed in a spacious courtyard.
Read more: Temple Architecture
World Hypertension Day
The Union Health Ministry of India has unveiled a groundbreaking initiative, the "75/25" program, on the occasion of World Hypertension Day (WHD) on 17th May 2023. This ambitious undertaking aims to screen and provide standard care to a staggering 75 million individuals with hypertension and diabetes by the year 2025.
WHD is an annual event that aims to raise awareness and promote education about hypertension or high blood pressure, which affects millions of people worldwide and can lead to serious complications such as heart failure, stroke, kidney damage, and liver damage. The theme for 2023 is “Measure Your Blood Pressure Accurately, Control It, Live Longer”, which focuses on combatting low awareness rates, especially in low to middle-income areas, and accurate blood pressure measurement methods. The event was inaugurated in May 2005 by the World Hypertension League (WHL), a non-governmental organization that works with the World Health Organization (WHO) and other partners to prevent and control hypertension. World Hypertension Day encourages people to know their numbers, check their blood pressure regularly, adopt a healthy lifestyle and seek medical advice if needed.
Read more: Hypertension
Kiru Hydro-electric Power Project
An investigation into alleged corruption in the Kiru hydro-electric power project in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K) has led the Central Investigation Bureau (CBI) to search Delhi and Rajasthan locations.
The Kiru Hydro Electric Project is proposed on River Chenab, located in Kishtwar district of J&K. The project is envisaged as a Run of River Scheme.
Run-of-river hydro projects use the natural downward flow of rivers and micro turbine generators to capture the kinetic energy carried by water.
Chenab River rises in the upper Himalayas in the Lahaul and Spiti districts of Himachal Pradesh state. The river is formed by the confluence of two rivers, Chandra and Bhaga, at Tandi, Himachal Pradesh. It flows through the Jammu region of J&K into the plains of Punjab, Pakistan, before flowing into the Indus River. Some of the important projects/dams on Chenab are Ratle Hydro Electric Project, Salal Dam- the hydroelectric power project, Dul Hasti Hydroelectric Plant, and Pakal Dul Dam (under construction).
Read More: Chenab River
Project Collaboration Agreement on Assistive Technology
The Department of Health Research (DHR), Ministry of Health and Family Welfare and World Health Organization (WHO) signed a Project Collaboration Agreement to foster research, innovation, and capacity building aimed at increasing access to high-quality affordable assistive technology.
This collaboration aims to work towards drawing global attention toward access to assistive technology, fostering research and innovation and developing and disseminating appropriate training programmes.
Assistive technology is an umbrella term covering the systems and services related to the delivery of assistive products and services. Assistive products maintain or improve an individual's functioning and independence, thereby promoting their well-being. For Example, technologies and devices such as prosthetics, braces, walkers, special switches, special-purpose computers, screen readers and specialised curricular software.
Read More: Assistive Technology