SC and Plea over Probe Agencies
For Prelims: SC, CBI, ED, Custodial violence, Human rights.
For Mains: Issues of political or Government interference on the Working of Probe Agencies and Associated Implications.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) has refused to entertain a plea by some political parties alleging "selective and targeted" use of Central probe agencies such as the CBI (Central Bureau of Investigation) and ED (Directorate of Enforcement) by the Central government against their leaders.
- The Enforcement Directorate (ED) frequently summons politicians, celebrities, and NGOs, leading to accusations that it is being used as a tool by the central government to control political opponents.
What is the SC’s Observation?
- The plea sought laying down guidelines for arrest, remand and bail for politicians.
- However, the SC, stated that politicians stand on the same footing as the citizens of the country and cannot have a different set of procedures. The court can intervene only in individual cases when the facts are before it, but it cannot lay down separate general guidelines only for politicians.
- The petitioners alleged a skewed application of the law leading to an "uneven playing field" and shrinking space for dialogue.
- Petitioner argued that there has been a huge increase in CBI and ED cases between 2014 and 2021, but there have been only 23 convictions. Of the 121 political leaders probed by ED and 124 probed by CBI, he said 95 % were from the opposition.
- However, the bench pointed out that the conviction rate in the country was dismal, and a politician is basically a citizen and, as citizens, all are amenable to the same law.
What makes Probe Agencies Vulnerable to Political Interferences?
- The ED and CBI in India are not statutory bodies and are instead governed by executive orders. This makes them more susceptible to political interference by the government of the day.
- As a result, these agencies have often been accused of carrying out politically motivated investigations or turning a blind eye to certain crimes based on political considerations.
- These agencies lack the necessary autonomy and independence to carry out their mandate of investigation and prosecution of crimes in a fair and transparent manner. Additionally, they are also susceptible to budgetary cuts or other forms of pressure that could impact their ability to function effectively.
What are the Concerns Related to Misuse of Central agencies?
- Political Influence: The agencies may be used by the ruling political party to target political opponents and dissenters, leading to the misuse of these agencies for political gains.
- In 2017 when the CBI had registered a case against Karti Chidambaram and a few others for allegedly receiving kickbacks in exchange for facilitating Foreign Investment Promotion Board (FIPB) which was said to be political motive.
- Lack of Transparency and Accountability: The agencies often work behind closed doors, and there is a lack of transparency in their functioning. This opacity can lead to suspicion and mistrust in their actions.
- There is a lack of accountability and oversight in the functioning of these agencies, which can lead to misuse and abuse of power.
- Abuse of Power: There have been instances where the agencies have been accused of overstepping their authority and misusing their power to intimidate or harass individuals.
- Violation of Human Rights: The agencies may use coercive tactics, such as illegal detentions, torture, and custodial violence, which violate human rights.
- In 2020, a father and son in Tamil Nadu were allegedly tortured to death in police custody. The incident sparked widespread outrage and calls for justice.
- Delayed Justice: The cases investigated by these agencies often take years to resolve, leading to a delay in justice and causing harm to the reputation and livelihood of individuals who may be innocent.
Way Forward
- There needs to be greater transparency and accountability in the functioning of these agencies. The agencies should operate independently of political influence and their actions should be guided solely by law and evidence.
- It is also important to ensure that the agencies are adequately staffed and resourced to carry out their duties effectively. This includes providing training and support to the staff, as well as ensuring that they have the necessary tools and equipment to carry out their work.
- There is a need to strengthen the legal and institutional frameworks that govern the functioning of these agencies. This will help to build public trust and confidence in the agencies and ensure that they are able to carry out their duties effectively and impartially.
- Giving probe agencies greater autonomy and a constitutional position could go a long way in addressing the issues of political influence and human rights violations in India.
- This would require political will and consensus-building among various stakeholders, but it is a necessary step to ensure that probe agencies are able to carry out their mandate of investigation and prosecution of crimes in a fair and transparent manner.
National Investigation Agency
For Prelims: Human Trafficking, Counterfeit currency or banknotes, Cyber-terrorism, NIA, Scheduled Offence, Terrorism, LWE, Insurgency, Radicalization, NIA Act 2008.
For Mains: National Investigation Agency, its function and scope of Jurisdiction, Radicalization - Issue, challenges, solution.
Why in News?
Recently, the National Investigation Agency (NIA) has registered an FIR (First Information Report) against two men who were previously arrested for allegedly Radicalizing youth.
- The NIA has charged the two men under various sections of the Indian Penal Code and the Unlawful Activities Prevention Act (UAPA), 1967.
Note: Radicalization is the process by which an individual or group adopts extreme beliefs and ideologies that reject or oppose the values, norms, and laws of mainstream society. It often involves exposure to propaganda, persuasive rhetoric, and persuasive individuals or groups who promote extremist views and ideologies.
What is the National Investigation Agency (NIA)?
- About:
- The NIA is a federal agency of the Indian government responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes related to Terrorism, Insurgency, and other national security matters.
- Federal agencies in a country typically have jurisdiction over matters that affect the country as a whole, rather than just individual states or provinces.
- It was established in 2009 following the Mumbai terrorist attacks in 2008, under the National Investigation Agency (NIA) Act, 2008, operates under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The National Investigation Agency (Amendment) Act, 2019 was passed in July 2019, amending the NIA Act, 2008.
- The NIA has the power to take over investigations of terrorism-related cases from state police forces and other agencies. It also has the authority to investigate cases across state boundaries without obtaining prior permission from state governments.
- The NIA is a federal agency of the Indian government responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes related to Terrorism, Insurgency, and other national security matters.
- Functions:
- Collecting, analyzing, and disseminating intelligence related to terrorism and other national security matters.
- Coordinating with other law enforcement agencies, both within India and internationally, in matters related to terrorism and national security.
- Conducting capacity building programs for law enforcement agencies and other stakeholders.
- Probe:
- The NIA can take up a probe in different ways. The State government can refer cases related to scheduled offences to the Central government for NIA investigation under Section 6 of the NIA Act 2008.
- The Central government can also direct the NIA to investigate a scheduled offence, either within or outside India, on its own accord.
- For prosecuting the accused under the UAPA and certain other scheduled offences, the NIA seeks the sanction of the Central government.
- There is a special cell to deal with LWE (Left Wing Extremism) cases related to terror financing. During the investigation of a scheduled offence, the NIA can also investigate any other offence connected to it. Finally, after investigation, the cases are presented before the NIA Special Court.
What are the Changes Made under NIA (Amendment) Act 2019?
- Offenses Outside India:
- The NIA originally had the power to investigate crimes within India, but the amended Act now allows it to investigate crimes committed outside of India, as long as it follows international treaties and the laws of the countries involved.
- If the Central Government believes a crime has been committed outside of India but falls under the jurisdiction of the Act, it can instruct the NIA to investigate the case as if it was committed in India.
- Widened Scope of the Law:
- The NIA can investigate crimes listed in the Schedule of the NIA Act.
- The Schedule originally included Acts like The Atomic Energy Act, 1962, The Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act, 1967, and The Anti-Hijacking Act, 1982, among others.
- With the amendment, the NIA can now also investigate cases related to,
- Human Trafficking,
- Counterfeit currency or banknotes,
- Prohibited arms,
- Cyber-terrorism,
- Crimes under the Explosive Substances Act, 1908.
- The NIA can investigate crimes listed in the Schedule of the NIA Act.
- Special Courts:
- The 2008 Act created Special Courts to try cases under the Act.
- The 2019 amendment allows the central government to designate Sessions Courts as Special Courts to try Scheduled Offences under the Act.
- Before doing so, the central government must consult with the Chief Justice of the relevant High Court. If multiple Special Courts exist in an area, the most senior judge will assign cases.
- State governments can also designate Sessions Courts as Special Courts for trying scheduled offences.
What are Scheduled Offences?
- The schedule for the Act specifies a list of offences which are to be investigated and prosecuted by the NIA.
- The list includes
- Explosive Substances Act
- Atomic Energy Act
- Unlawful Activities (Prevention) Act
- Anti-Hijacking Act
- Suppression of Unlawful Acts against Safety of Civil Aviation Act
- SAARC Convention (Suppression of Terrorism) Act
- Suppression of Unlawful Acts Against Safety of Maritime Navigation and Fixed Platforms on Continental Shelf Act
- Weapons of Mass Destruction and their Delivery Systems (Prohibition of Unlawful Activities) Act
- Any other relevant offences under the Indian Penal Code, Arms Act and the Information Technology Act.
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act
Buy Now
Voice Samples in Criminal Investigations
For Prelims: Voice Samples in crime investigations, Central Bureau of Investigation, Right to privacy.
For Mains: The reliability and accuracy of voice recognition technology in criminal investigations, Legal and ethical considerations surrounding the use of voice samples as evidence in court.
Why in News?
Recently, a political leader appeared before the Central Bureau of Investigation to submit his voice samples for corroboration with a particular speech concerning his alleged involvement in in the 1984 anti-sikh riots case.
- Voice samples have become an important tool in criminal investigations, allowing investigators to corroborate evidence and identify suspects.
How are Voice Samples Taken?
- Procedure:
- Investigating agencies move to the court to seek permission to collect a person’s voice sample. Samples are taken in an echo-proof room for a controlled and noise-free environment.
- A voice recorder is used to record the sample where the subject is asked to speak a specific clue word from a statement already part of the evidence.
- Methods of Comparison:
- An anonymous voice sample is compared with a suspect list of five persons; however, when the speaker is known, both the voice samples are corroborated.
- International phonetic alphabets are used for recording voice where the subject pronounces only a small part of the original statement (for ease of analysis).
- Voice Sampling in India:
- Semi-automatic spectrographic method of voice sampling is used in Indian forensic labs.
- The forensic lab submits the final report to the investigating agency, indicating whether the results of the voice sample analysis are positive or negative.
- However, in some countries, the automatic method is used, where a likelihood ratio of the voice samples is developed. This increases efficiency.
- Drawbacks:
- Inaccuracies may arise if the person’s voice is altered due to the effect of medicines or if the person is suffering from a cold.
- The credibility of the sample depends on the technique used by the expert and how the court analyzes it.
What is the Legality behind Collecting Voice Samples?
- In 2013, the Indian Supreme Court considered whether collecting voice samples would be violative of the fundamental right against self-incrimination or the right to privacy.
- Section 53 (1) of the Code of Criminal Procedure allows examination of accused by a medical practitioner at the request of a police officer to collect samples for DNA analysis or taking general body measurements and "such other tests necessary"
- The phrase "such other tests" in Section 53 (1) is read to include a collection of voice samples. However, there is no specific provision for testing voice samples under criminal procedure laws as it is a relatively new technological tool.
- In a split verdict in the 2013 case, the SC also acknowledged the absence of a specific law for this purpose.
- In a subsequent 3-judge bench hearing, the Supreme Court held that the fundamental rights of the accused will not be violated by collecting a voice sample for investigation.
- It held that the right to privacy cannot be construed as absolute and must bow down to compelling public interest.
- Recently, in 2022, a ruling by the Punjab and Haryana High Court also observed that voice samples resemble fingerprints and handwriting and are collected with permission in accordance with the law and are used for comparing evidence already collected.
What is the Right to Privacy?
- The right to privacy is protected as an intrinsic part of the right to life and personal liberty under Article 21 and as a part of the freedoms guaranteed by Part III of the Constitution.
- The Supreme Court described privacy and its importance in the landmark decision of K.S. Puttaswamy v. Union of India in 2017 that - Right to Privacy is a fundamental and inalienable right and attaches to the person covering all information about that person and the choices that he/ she makes.
What are the Past Cases where Voice Samples were Collected?
- India:
- A Special Courts under Essential Commodities and Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS) had allowed a plea moved by the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB) in February 2021, seeking the collection of voice samples among 33 accused in a drugs case it was investigating after the death of actor Sushant Singh Rajput.
- Other Countries:
- The US Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) first used the technique of voice identification analysis in the 1950s.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In addition to fingerprint scanning, which of the following can be used in the biometric identification of a person? (2014)
- Iris scanning
- Retinal scanning
- Voice recognition
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- Biometric verification is any means by which a person can be uniquely identified by evaluating one or more distinguishing biological traits.
- Unique identifiers include fingerprints, hand geometry, earlobe geometry, retina and iris patterns, voice waves, DNA, and signatures. The oldest form of biometric verification is fingerprinting.
- All the given processes, namely, Iris scans, Voice recognition, and Retinal scanning can be used for biometric identification. Hence, 1, 2 and 3 are correct. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer
Digital Health Summit 2023
For Prelims: Digital Health Summit 2023, 3D Printing, Fourth Industrial Revolution, Ayushman Bharat-Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY), CoWIN App, Ransomware Attack, Blockchain Technology.
For Mains: Issues Related to Digital Healthcare in India, Key Government Initiatives Related to Digital Health.
Why in News?
Recently, Digital Health Summit 2023 was organized by the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) in Goa.
- CII is a non-government, not-for-profit, industry-led and industry-managed organization.
What are the Major Highlights of Digital Health Summit 2023?
- It highlighted the importance of digital health innovations and how they can empower exponential medicine, including 3D printing, point-of-care diagnostics, robots, bioinformatics, and genomics.
- It aims to create a digital public goods framework to promote standards for interoperability, data privacy, and data security.
- It emphasised the need for "citizen-centric" digital health systems with equitable access to high-quality treatments.
- It also highlighted that health-tech is the most significant aspect of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and taking pre-emptive steps remains the key.
What is Digital Healthcare?
- About:
- Digital healthcare is a system of medical care delivery that uses an array of digital technologies to make quality medical care services accessible, affordable, and sustainable.
- The broad scope of digital health includes categories such as mobile health (mHealth), health information technology (IT), wearable devices, telehealth and telemedicine, and personalized medicine.
- The WHO Global Strategy on Digital Health, adopted in 2020 by the World Health Assembly, presents a roadmap to link the latest developments in innovation and digital health, and put these tools to action in order to improve health outcomes.
- Major Applications:
- Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Point-of-care Diagnostics (“POCD”) is an emerging trend in the medical device industry and encompasses a broad range of products which enables accurate diagnostics in resource limited setting by patients themselves or healthcare practitioners.
- In the recent past multiple applications such as biosensors, portable x rays, handheld ultrasounds and smartphone based POCD have been developed.
- Medical Virtual Assistants: Virtual health assistants and chatbots bridge the gap between patients and physicians and tend to the needs of the patients in between physical appointments through services such as appointment scheduling, maintain health records and other administrative tasks.
- Self-Monitoring Healthcare Devices: Monitors and sensors are now being integrated into wearables, which allow it to detect various physiological changes in the body.
- These smart devices are capable of tracking weight, sleep patterns, posture, diet and exercise.
- e-Pharmacies: An e-pharmacy is a pharmacy that operates over the internet and fulfils the orders through mail, courier or delivery persons
- Point-of-Care Diagnostics: Point-of-care Diagnostics (“POCD”) is an emerging trend in the medical device industry and encompasses a broad range of products which enables accurate diagnostics in resource limited setting by patients themselves or healthcare practitioners.
- Benefits of Digital Healthcare:
- Telemedicine has played a pivotal role in the decentralisation of healthcare and ensuring access to remote and advanced care.
- Patients in rural and remote areas can now access affordable and quality healthcare through online consultation and home delivery of medicines.
- Digital tools can provide healthcare providers with an extensive view of patient health by increasing access to health data.
What are the Challenges Related to Digital Healthcare in India?
- About:
- Driven by the Covid-19 pandemic, India has adopted digital health at a breathtaking pace. The unprecedented health crisis paved the way for the adoption of telemedicine and thus proved to be a dawn of remote and patient-centric care in India.
- Challenges:
- Absence of Clear Regulation: The absence of clear regulations and guidelines may lead to fraudulent practices, misuse of digital prescriptions, data theft, and misuse of electronic health records.
- Also, the lack of digital infrastructure and skilled professionals is another roadblock to the digitalization of the healthcare system in India.
- Data Privacy and Cybersecurity: Ensuring data privacy and cybersecurity is crucial to maintain patient trust in digital healthcare. Lack of security measures can lead to data breaches and compromise patient data.
- For example: An instance of ransomware attack occurred at AIIMS Delhi recently.
- No Statutory Backing to E-pharmacy: The Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 regulates the import, manufacturing and distribution of drugs in India.
- However, there is no statutory definition of “e-pharmacy” either under the Drugs and Cosmetics Act, 1940 or the Pharmacy Act, 1948.
- Absence of Clear Regulation: The absence of clear regulations and guidelines may lead to fraudulent practices, misuse of digital prescriptions, data theft, and misuse of electronic health records.
- Government Initiatives Related to Digital Health:
What are the WHO's Objectives for Promoting Digital Health and Innovation?
- Translating data, research, and evidence into action through standards for interoperability and data sharing and supporting implementation of digital solutions for informed decision making.
- Enhancing knowledge through scientific communities of practice facilitated by new technologies, enabling expert voices to come together around clinical and public health topics.
- Systematically assessing and linking country needs with supply of innovations, taking a proactive approach to identify, promote, co-develop, and scale innovations based on country needs.
Way Forward
- AI Powered Healthcare: Artificial intelligence (AI) is being increasingly used in healthcare to analyze large amounts of data, make diagnoses, and predict health outcomes.
- This technology has the potential to improve the accuracy and speed of healthcare delivery, while also reducing costs.
- Blockchain in Healthcare: Blockchain technology can help improve the security and privacy of health data, as well as streamline healthcare processes.
- By providing a secure and transparent way to store and share information, blockchain can help reduce errors, fraud, and administrative costs.
- Mobile Health (mHealth): mHealth involves the use of mobile devices and apps to deliver healthcare services remotely.
- This can be especially useful in rural areas, where access to healthcare is limited. mHealth can also help patients manage chronic conditions and communicate with healthcare providers more easily.
Buy Now
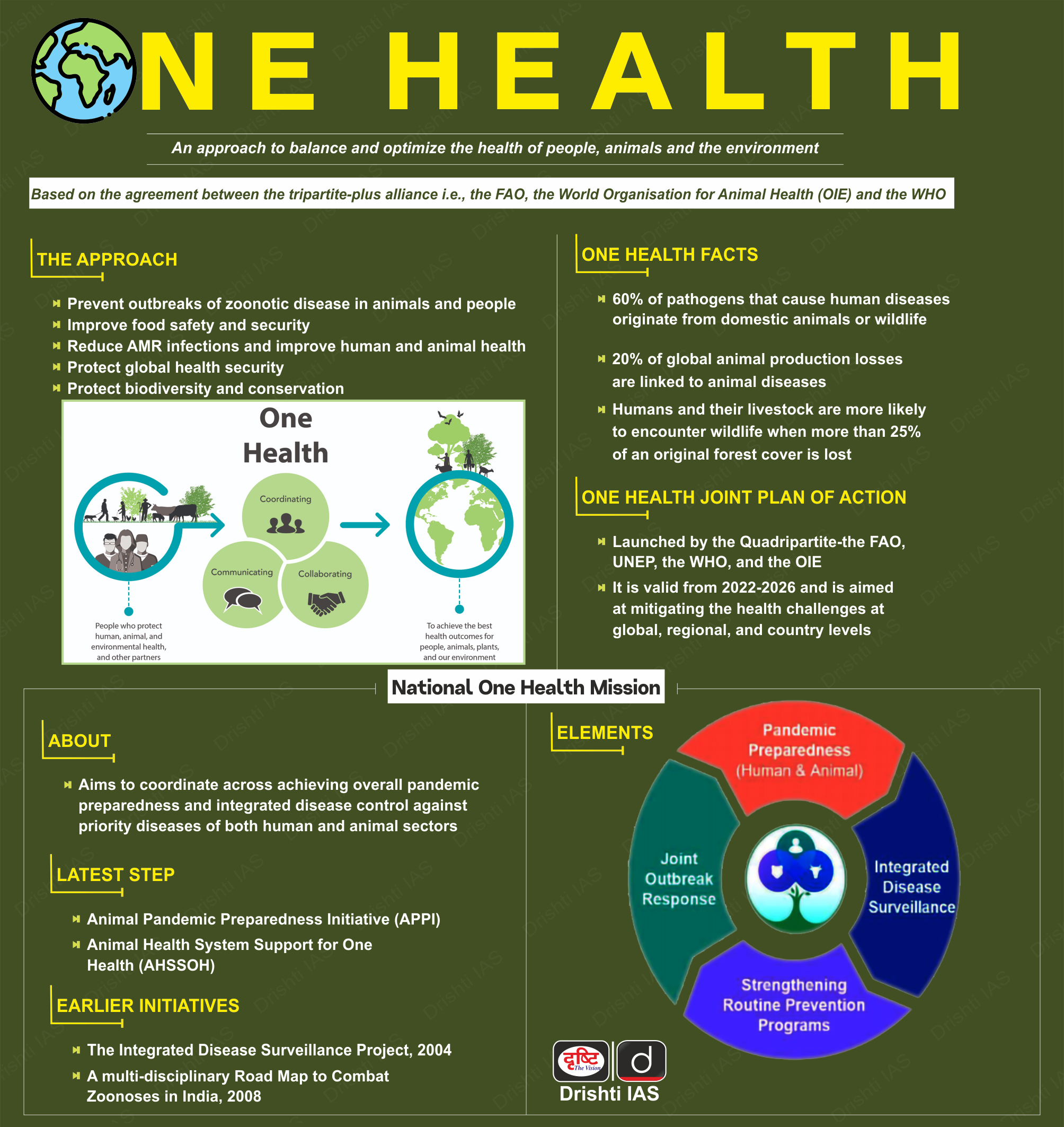
Animal Pandemic Preparedness Initiative and Animal Health System Support for One Health
For Prelims: One Health Approach, WHO, World Bank, Zoonotic Diseases.
For Mains: Animal Pandemic Preparedness Initiative, Animal Health System Support for One Health, One Health.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying has launched an Animal Pandemic Preparedness Initiative (APPI) under One Health Approach to address the threat of diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans.
- One Health approach recognizes the interconnectedness of human, animal, and environmental health.
- The Ministry has also launched Animal Health System Support for One Health (AHSSOH) project, funded by the World Bank.
What is the Animal Pandemic Preparedness Initiative (APPI)?
- About:
- The initiative is in line with the World Health Organization's (WHO) Global One Health strategy, which emphasizes the importance of multisectoral collaboration in addressing the threat of zoonotic diseases.
- It will help to improve veterinary services and infrastructure, disease surveillance capabilities, early detection and response, build the capacity of animal health professionals, and awareness among farmers through community outreach.
- Pillars of APPI:
- Disease Surveillance and Monitoring.
- Disease Model Algorithms and Early Warning System.
- Outbreak Investigation and Response.
- Ecosystem Coordination.
- Vaccine Development and Research and Development.
- Building Disaster Resilience.
- Funding.
- Regulatory Framework.
- Aim:
- The initiative aims to enhance India's preparedness and response capabilities to prevent and control zoonotic diseases, thereby safeguarding the health of both animals and humans.
What is Animal Health System Support for One Health (AHSSOH)?
- It aims to create an ecosystem for a better animal health management system using the One Health approach.
- The project will be implemented over a five-year period as Central sector scheme.
- It has set a goal to cover 151 districts in five participating states, focusing on upgrading 75 district/regional laboratories, as well as strengthening 300 veterinary hospitals/dispensaries.
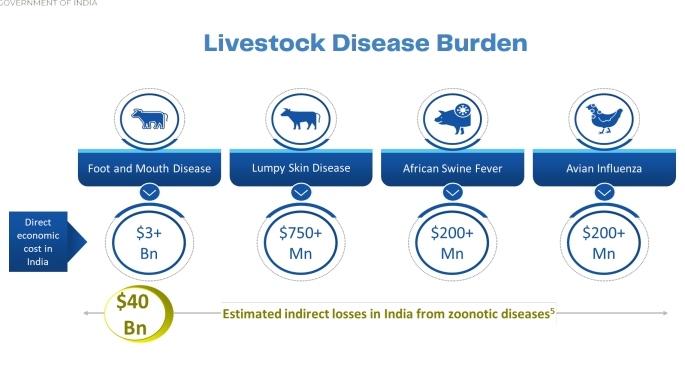
What is the Scenario of Livestock Diseases Burden and Livestock Sector?
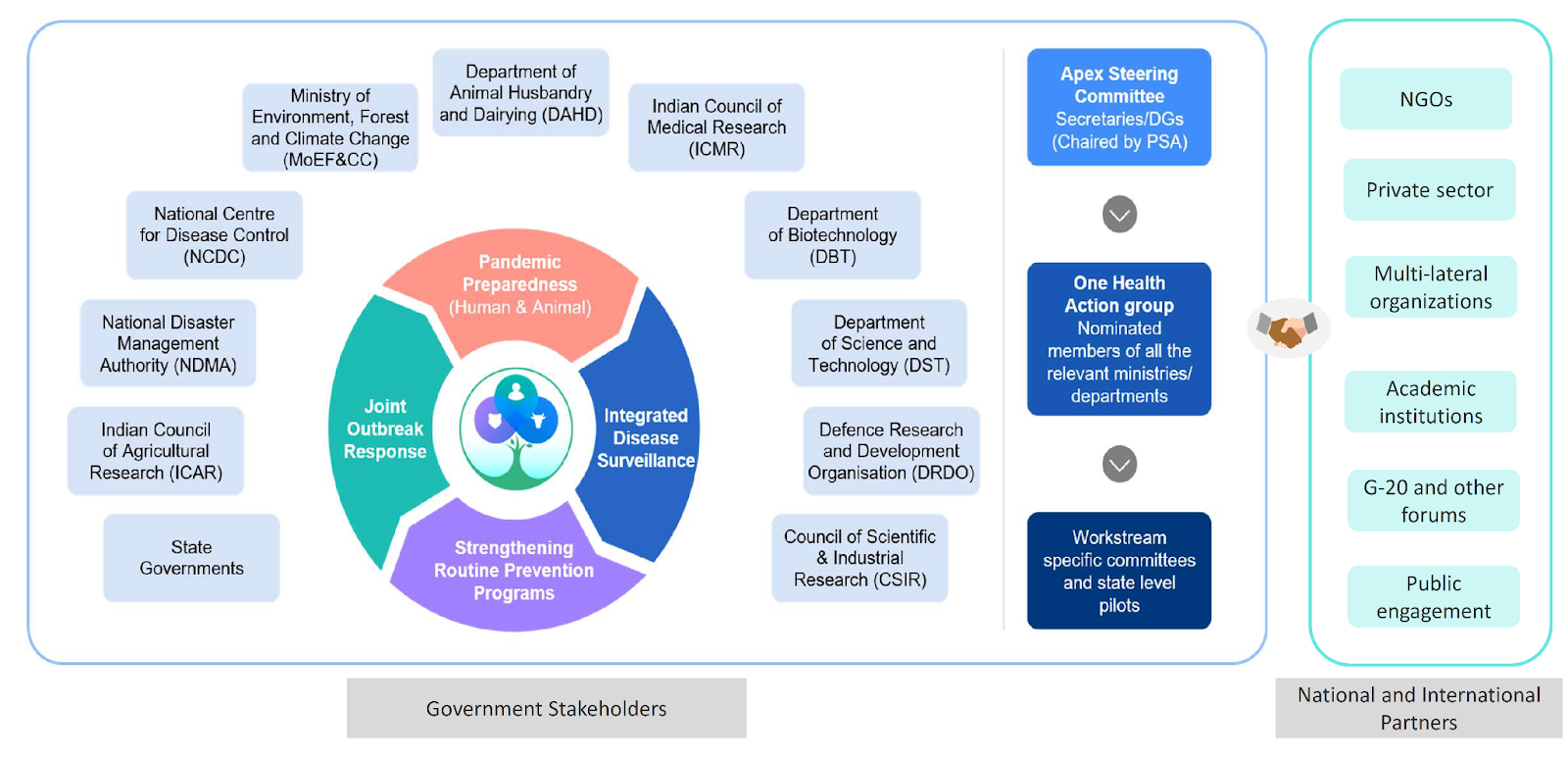
What is the National One Health Mission (NOHM)?
- One Health:
- One Health brings together different sectors to solve health, productivity, and conservation challenges, which is important for India with its diverse wildlife, large livestock population, and high human density.
- Recent disease outbreaks, like Covid-19, Lumpy Skin Disease, and Avian Influenza, show that addressing disease from just a human perspective isn't enough. We need to consider livestock and wildlife too.
- About:
- The NOHM is a cross-ministerial effort approved by the Prime Minister's Science, Technology, and Innovation Advisory Council (PM-STIAC) in its 21st meeting.
- The NOHM will be implemented by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare in collaboration with other ministries.
- Objective:
- The NOHM will focus on addressing the interdependence of human, animal, and environmental health to promote holistic and integrated approaches to disease control and prevention.
- It aims to promote a coordinated and integrated approach to disease control and prevention in India, addressing the interdependence of human, animal, and environmental health.
- Components:
- Strengthening surveillance and Early Warning Systems for zoonotic diseases and antimicrobial resistance
- Promoting research and development in One Health areas
- Improving capacity building for health professionals, veterinarians, and researchers
- Enhancing public awareness and community engagement on One Health issues
- Developing guidelines and policies for One Health interventions and strategies
- Establishing a One Health data repository and information system
- Facilitating national and international collaborations and partnerships to address One Health challenges.
G7's Commitment Towards Carbon-free Electricity Production
For Prelims: G7 Summit Hiroshima, Global Energy Crisis, Net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, IPCC, Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana, Green Energy Corridor, National Smart Grid Mission (NSGM)
For Mains: G7, Indian Initiatives Related to Carbon-Free Electricity.
Why in News?
The Group of Seven (G7) countries' Climate and Energy Ministers and envoys have committed to ensuring carbon-free electricity production by 2035 and accelerating the phase-out of coal. The agreement was made at Sapporo, Japan, ahead of the G7 summit in Hiroshima in May 2023.
- India was also invited in the summit as a ‘guest’, in the context of its G20 presidency.
What are the Major Highlights of the Agreement?
- Recognising the current global energy crisis and economic disruptions, the agreement calls for accelerating the clean energy transition to net-zero greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by 2050.
- The G7 states cited the urgent need to reduce GHG emissions by around 43% by 2030 and 60% by 2035.
- The participants agreed to accelerate solar and wind energy investments to produce 1,000 gigawatts of solar power and 150 gigawatts of wind power from off-shore platforms by 2030 in line with IPCC's AR6 Report that repeats the need to ensure that global temperatures do not increase by more than 1.5°C of pre-industrial levels by the end of the century.
- They reaffirmed that fossil fuel subsidies are inconsistent with the goals of the Paris Agreement and committed to eliminating inefficient fossil fuel subsidies by 2025.
- Key Issues that Lacked any Concrete Action:
- Increasing efforts to assist other countries scale up their energy transition and energy efficiency.
- The funding provided by developed countries continues to fall short of the commitment of USD100 billion per year made in UNFCCC COP27.
- UK and Canada's proposal to phase-out coal by 2030
- Increasing efforts to assist other countries scale up their energy transition and energy efficiency.
What is G7?
- About:
- The Group of Seven (G7) is an intergovernmental organisation consisting of seven major advanced economies: Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- The G7, originally G8 (before Russia was uninvited), was set up in 1975 as an informal forum of leaders from the world’s most advanced economies.
- Objectives:
- The G7's primary objective is to foster economic growth and stability among its member countries.
- It serves as a forum for leaders to discuss issues of mutual concern, including trade, economic policy, and international security.
- The G7 also works to promote cooperation and coordination on issues such as climate change, poverty reduction, and global health.
- Meetings:
- The G7 holds an annual summit where the leaders of its member countries meet to discuss and address issues of mutual concern.
- The summit rotates among member countries, with each country hosting the event in turn.
- The G7 holds an annual summit where the leaders of its member countries meet to discuss and address issues of mutual concern.
- Significance:
- Economic Powerhouses: The G7 countries are some of the world's largest and most powerful economies, representing 40% of the world’s economic activity.
- They are also among the world's leading trading nations, with significant influence over global trade policies and regulations.
- Global Governance: The G7 is an important institution of global governance, with significant influence over international institutions such as the United Nations and the World Trade Organization.
- Its policies and decisions can have significant implications for global economic and political stability.
- Economic Powerhouses: The G7 countries are some of the world's largest and most powerful economies, representing 40% of the world’s economic activity.
- Criticisms:
- The G7, which consists of some of the world's most developed economies, is responsible for around a quarter of global carbon emissions.
- It's a staggering figure that underscores the significant role that these countries play in driving climate change
- The G7 has faced criticism for being exclusive and unrepresentative of the world's population, as it represents only a small fraction of the global population and excludes countries such as India and China, which are major economic powers.
- Critics have also argued that the G7's influence has declined in recent years as emerging economies have become more important in the global economy.
- The G7, which consists of some of the world's most developed economies, is responsible for around a quarter of global carbon emissions.
What are India’s Initiatives Regarding Carbon-Free Electricity?
- Pradhan Mantri Sahaj Bijli Har Ghar Yojana (SAUBHAGYA): Empowering rural and urban households through access to reliable and affordable electricity
- Green Energy Corridor (GEC): Synchronising grid-connected renewable energy with India’s national transmission network
- National Smart Grid Mission (NSGM) and Smart Meter National Programme (SMNP): Modernising India’s power sector into a secure, adaptive, sustainable, and digitally enabled ecosystem
- Perform, Achieve and Trade (PAT): Enhancing energy efficiency and curtailing emissions of hard-to-abate industrial sectors.
- National Determined Contributions (NDCs): As per the updated NDC, India now stands committed to reduce Emissions Intensity of its GDP by 45% by 2030, from 2005 level and achieve about 50% cumulative electric power installed capacity from non-fossil fuel-based energy resources by 2030.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20?
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”.Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)
Q. Write a note on India’s green energy corridor to alleviate the problem of conventional energy. (2013)
Buy Now
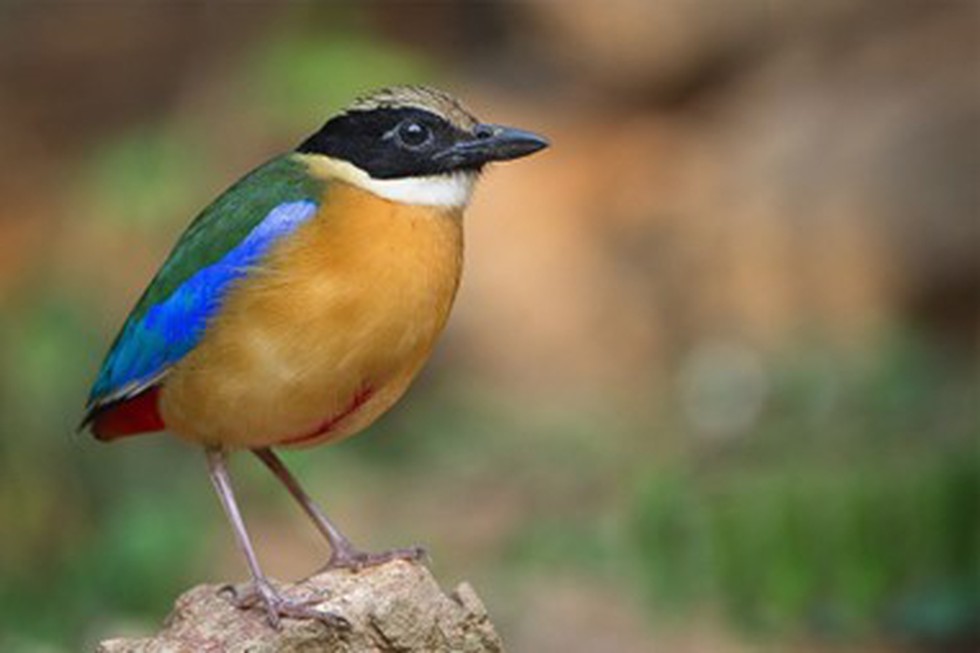
Mangrove Pitta Bird
Why in News?
Recently, the first mangrove pitta bird census was conducted in two coastal districts of Odisha (Kendrapara and Jagatsingpur).
What is the Mangrove Pitta?
- About:
- The Mangrove Pitta bird (Pitta megarhyncha) is a species of bird that can be found in a few pockets of eastern India, including Odisha's Bhitarkanika and West Bengal's Sundarbans.
- The Mangrove Pitta bird is a ground forager (an animal that searches widely for food) and tree rester that primarily inhabits coastal mangrove forests in India.
- IUCN Status:
- The IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) has categorized and evaluated the species and has listed it as "Near Threatened".
- Distribution:
- India, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Indonesia.
- Importance:
- This species is important because it is a bio-indicator of the health of mangrove forests, which are crucial to maintaining ecological balance in coastal areas.
What Was the First-Ever Census of Mangrove Pitta Birds?
- This census was conducted using a point count method, where direct sightings and chirping sounds were used to count the birds.
- The census of Mangrove Pitta birds found that a total of 179 individual birds were counted.
- The highest concentration of these birds was found in the mangroves near the Mahipura river mouth inside the Bhitarkanika National Park.
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Blastomycosis
Blastomycosis is a rare fungal infection caused by the Blastomyces fungus that is found in the midwestern, south-central, and southeastern states of the US. The fungus is typically present in moist soil and decomposing wood and leaves. The fungus is endemic to Michigan state, US.
The disease is contracted by inhaling the spores of the fungus, which can be dispersed in the air if the soil is disturbed. Symptoms of blastomycosis include fever, cough, breathing difficulty, and muscle aches, with severe infections potentially spreading to other organs such as the skin, bones, and brain. While antifungal medications are available for treating the disease, the course of treatment can be long-lasting, lasting between six months and a year.
Read more: Fungal Infection - Mucormycosis
Declining Tiger Population in Sundarbans
The Sundarbans, home to the largest mangrove forest in the world and one of the last strongholds of the Bengal tiger, has slipped in its ranking among India's tiger reserves.
Despite a rise in its tiger population, the Sundarbans has been ranked 31st among the 51 tiger reserves in the country for forest management, according to the recently released Management Effectiveness Evaluation (MEE) report. Lack of adequate manpower and the vulnerability of the location to climate change and submergence from sea level rise has been identified as the major challenges. However, the Sundarbans have been doing well in containing major problems like poaching and tiger-human conflict.
Periyar in Kerala was the top-ranked tiger reserve with a score of 94.38%, followed by Satpura in Madhya Pradesh with 93.16% in the MEE report. The MEE report suggested that area development committees need to become functional under divisional commissioners to monitor illegal tourism, and more management coordination is required between India and Bangladesh Sundarbans forest areas.
Sundarbans, including the forest covering both the present tiger reserve and South 24 Parganas district, have been under increasing climate change impacts, and it is important to carry out the related assessment.
Read more: Sundarbans, Tiger Census 2022
Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)
The Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has released a Consultation Paper on "Issues Related to Low Power Small Range FM Radio Broadcasting". It seeks to gather feedback and comments from stakeholders on the need and timing for the introduction of a new service provider for the drive-in theatre application, as well as on issues related to low-power short-range FM radio broadcasting.
Such broadcasting is considered an effective method of sound broadcasting for services intended for limited locations and reception areas, such as hospital radio services, amusement parks, business premises, closed communities, small habitations, and local events.
TRAI regulates telecom services including fixation/revision of tariffs for telecom services which were earlier vested in the Central Government.
Read more: Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)
Global Conference on Compressed Biogas (CBG)
Recently, the Indian Federation of Green Energy (IFGE) organized a Global Conference on Compressed Biogas (CBG), in which the Union Minister of Petroleum & Natural Gas and Housing & Urban Affairs highlighted the importance of domestic production of biofuels.
This is seen as a key strategy in reducing the import of fossil fuels and ultimately achieving the goal of net zero emissions. CBG production offers several benefits, including the reduction of natural gas imports, GHG emissions, agricultural residue burning, providing remunerative income to farmers, employment generation, and effective waste management. Additionally, the byproduct of CBG manufacturing, Fermented Organic Manure (FOM), may be applied in the agricultural sector to encourage organic farming and lower the usage of artificial fertilizers.
India has set a target to increase the share of gas in the energy mix to 15% in 2030, and the speedy expansion of CBG will help in meeting the additional requirement from domestic resources. The Sustainable Alternative Towards Affordable Transportation (SATAT) Scheme, which explores various waste streams as feedstock for CBG production, was highlighted in the conference. India aims to set up 5,000 commercial CBG plants by 2024-25 and produce 15 MMT of CBG.
The government is focused on developing a conducive ecosystem to promote sustainability for all actors of the Triple Bottom Line (environment, society, and economy), and the recently announced Amrit Kaal Budget 2023 provides a significant boost to India's Biogas and clean energy revolution.
Read more: Compressed Biogas (CBG)